健康教育干预对社区中老年颈椎病患者自我管理能力干预效应分析*
岑 川 马海琴
健康教育干预对社区中老年颈椎病患者自我管理能力干预效应分析*
岑川马海琴
上海市宝山区张庙街道长江路社区卫生服务中心(上海 200431)
摘要:目的评价健康教育对社区中老年颈椎病患者自我管理能力干预的效果。方法选取本社区门诊经牵引治疗后的颈椎病患者90例,随机分为干预组和对照组各45例,对干预组进行系列有序系统的健康教育干预活动和随访督导,对照组只进行随访,评价两组干预前后颈椎病相关基础知识测试成绩(总均分)、防治保健知识知晓率、预防措施执行率。结果干预后,干预组较对照组颈椎病相关基础知识测试成绩(总均分)、防治保健知识知晓率、预防措施执行率都有明显提高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论社区综合健康教育干预可以提高患者对疾病的认知,以及患者疾病自我管理能力。
关键词:神经根型颈椎病;自我管理;社区;健康教育
颈椎病是目前严重危害中老年患者的骨关节退行性变的社区常见病,压迫周围组织、韧带、肌肉、神经而引起的相应的颈项部僵硬,上肢麻木,眩晕等临床症状。临床中分为颈型、神经根型、脊髓型、椎动脉型、食管压迫型及混合型,以神经根型居多。有调查表明51~60岁中老年的患病率为33.8%,明显高于其他年龄段[1],已严重影响病患的日常生活质量。我院开展社区中老年神经根型颈椎病患者系列有序健康教育,对疾病的认知及自我管理能力上取得较好效果,现报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1一般资料上海宝山区长江路社区服务中心门诊及其服务点自2011年4月-2011年8月门诊收治的居住张庙街道社区范围,并根据《2010版颈椎病诊治与康复指南》确诊神经根型颈椎病诊断标准及排除标准,经牵引治疗,疗程结束后以疗效评估临床治愈和显效者为入组患者共90例,按随机法把入选患者分为干预组和对照组。干预组45例,其中男5例,女40例,年龄(62.31±6.92)岁,病程(13.11±7.23)年;对照组45例,其中男7例,女38例,年龄(60.67±6.90)岁,病程(11.47±7.14)年。两组患者性别、年龄、病程、病情等一般资料差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),有可比性。
1.2方法
1.2.1问卷调查自行设计调查表,内容包括基本情况、个人生活习惯、颈椎病相关基础知识测试、颈椎病防治知识知晓、颈椎病预防措施执行情况等。
1.2.2干预方法对干预组进行颈椎病专题健康教育,以沙龙讲座形式每月组织患者集中进行, 1~2次颈椎病系列专题健康教育活动(责任医师亦参加),为期1年。每次都进行基础知识测试。健康教育内容包括颈椎病自我防治保健知识,防治保健操指导、健康生活方式指导等。责任医师每月定期1次上门督导(症情记录、防治保健措施执行等)。对照组不采取任何健康干预措施,每月集中组织1次进行一般健康教育,责任医师每月上门1次进行病情随访(症情记录),不进行任何督导。
1.3评估指标①颈椎病相关基础知识测试成绩(总均分):两组患者共10次相同健康教育知识测试,每组每次干预前、后各1次的测试(初、复测)成绩的总均分(满分100分)。②防治保健知识知晓率:两组进行防治保健知识知晓问卷调查,知晓率=实得分/满分×100%。每3月进行一次评估。③预防措施执行率:两组执行各项预防措施的人数占各组总人数的比率。每3月进行一次评估。

2 结果
2.1干预前后颈椎病相关基础知识测试成绩(总均分)两组比较显示:干预后,干预组相关基础知识测试(含生理病理基础知识、诱发因素及治疗知识、日常不良生活习惯知识、日常防治保健知识)成绩总均分高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。两组干预前比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),见表1。

表1 两组基础知识测试成绩(总均分)比较 ±s)
2.2干预前后防治保健知识知晓率(%)两组比较显示:干预前两组防治保健知识知晓率比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),干预后干预组较对照组提高幅度大,差异有统计学意义(χ2=12.359,P=0.000),见表2。

表2 两组干预前后防治保健知识知晓率(%)比较 (例,%)
2.3干预前后预防措施执行率(%)两组比较显示:干预前,两组预防措施(纠正不良体位姿势、注意颈部肌肉休息、纠正睡眠体位、加强颈部受凉防护、颈椎保健操)执行率比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。干预后,干预组各项执行情况均优于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),见表3。
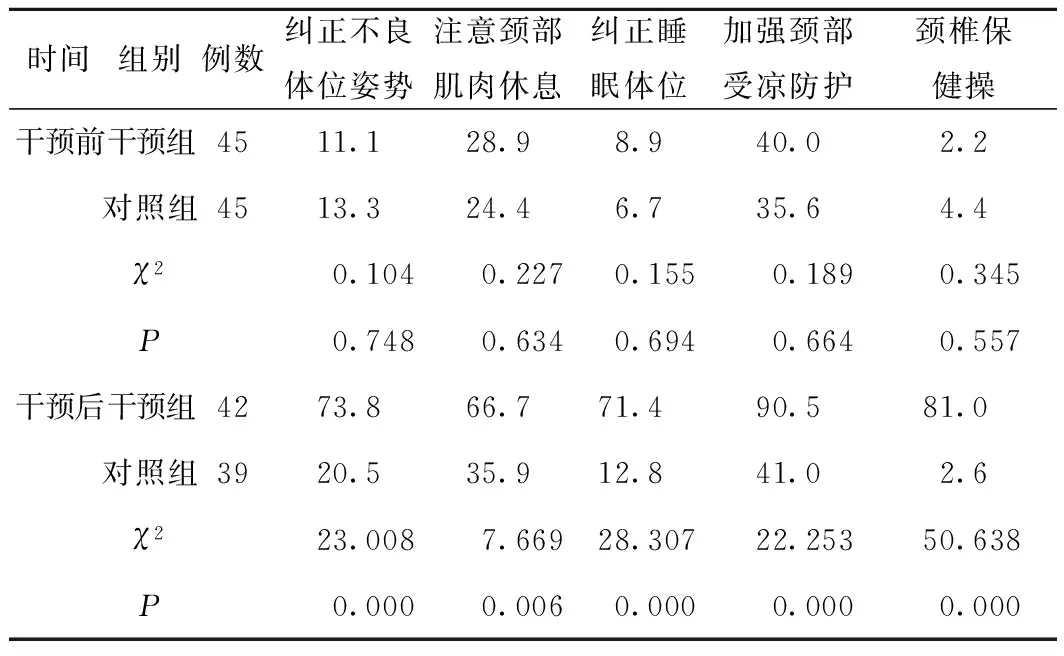
表3 两组干预前后预防措施执行率(%)比较 (例,%)
3 讨论
神经根型颈椎病是颈椎病临床中最常见的一种。牵引治疗是神经根型颈椎病的有效治疗手段,但牵引疗法治疗神经根型颈椎病远期疗效上尚不能令人满意[2]。我社区卫生服务中心通过历时一年的时间以团队形式开展系列有序的健康干预宣教活动,不仅让社区中老年颈椎病患者了解掌握了正确的颈椎病防治保健知识,而且也大大提高了患者疾病自我管理的能力,纠正不良生活方式和行为,让患者主动参与到颈椎病保健防护中。
事实表明,社区开展颈椎病健康教育干预活动是普及社区颈椎病防治知识、提高患者疾病自我管理主动性有效的方法。
参考文献
[1]杨新文,朱远熔,汪志良.上海市徐汇区颈椎病患者情况调查分析[J]. 中国康复,2011,26(2):101-102.
[2]董一谕,颜景芳.神经根型颈椎病的康复护理研究[J].护士进修杂志,2005,6(20):553-554.
*基金项目:上海宝山区区科委基金项目(No.10-E-43)
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1003-8914.2016.01.070
文章编号:1003-8914(2016)-01-0133-02
收稿日期:(本文校对:方宗君2014-12-25)
Analysis on the Intervention Effect of the Health Education on the Self Management Ability of Elderly Patients with Cervical Spondylosis in Community
CEN ChuanMA Haiqing
(Baoshan District Zhangmiao Subdistrict Changjiang Road Community Health Service Center, Shanghai 200431, China)
Abstract:ObjectiveTo evaluate the intervention effect of the health education on the self management ability of elderly patients with cervical spondylosis in community. MethodsNinety cases patients with cervical spondylosis treated by traction were selected in the Out-patient Department of the community health service center, and they were randomly divided into intervention group with 45 cases and control group with 45 cases. The intervention group was given a series of orderly systematic health education intervention activities and following-up supervision. The control group was only given following-up evaluation. Before and after the study, the basic knowledge of cervical spondylosis test score, the rate of the awareness of the prevention and health knowledge and the execution rate of the preventive measures were evaluated. ResultsAfter intervention, the basic knowledge of cervical spondylosis test score, the rate of the awareness of the prevention and health knowledge and the execution rate of the preventive measures of the intervention group were increased obviously, and the difference between two groups had the statistical significance (P<0.05). ConclusionThe community comprehensive health education intervention for cervical spondylosis can improve the patient’s awareness of the disease and the self management ability.
Key words:Cervical spondylosis of nerve root type; Self management; Community; Health education

