有中心集中荷载作用的任意变厚度的旋转扁薄壳的非线性弯曲
侯朝胜
(天津大学建筑工程学院,天津 300072)
有中心集中荷载作用的任意变厚度的旋转扁薄壳的非线性弯曲
侯朝胜
(天津大学建筑工程学院,天津 300072)
中心集中荷载作用的变厚度圆板或旋转扁壳的轴对称非线性弯曲,迄今鲜见研究成果.取三次B样条函数和对数函数为试函数,用配点法计算任意变厚度圆板的大挠度和旋转扁壳的非线性稳定.计算了中心集中荷载作用的圆板及它和反向均布荷载同时作用圆板且其中心挠度为零的特殊情形.给出了中心集中荷载作用下,线性或多项式型变厚度的圆锥壳、球壳或四次多项式型旋转壳的上、下临界荷载.等厚度圆板和球壳的计算结果同其他方法的结果做了比较.结果表明样条配点法有更高的精度和更大的荷载收敛范围.
旋转扁壳;任意变厚度;非线性稳定;中心集中荷载;复合荷载;样条配点法
中心集中荷载作用的变厚度薄板壳的轴对称大挠度计算,由于中心力的边界条件处理困难,迄今鲜见研究成果.但在小挠度假定、线性或二次方变厚度的条件下,已有圆板的三次近似解答[1].中心集中荷载作用的等厚度圆板的大挠度及球壳上临界荷载的计算,已有一些解答及实验结果[2-7].当荷载较大,因非线性较强使收敛性恶化,这些方法得不出解答或得不出可靠解答.笔者附加对数函数,把文献[8]的公式和方法推广,满意地解决了中心集中荷载的问题.
1 基本方程及边界条件
采用同文献[8]一样的模型,但壳顶还有中心集中荷载P作用.引入同文献[8]一样的符号和无量纲量,再引入

式中:µ 为泊松比;c为壳底面圆半径;E为弹性模量;h0为壳中心厚度.设文献[8]中的分布荷载为均布荷载 q,则变厚度旋转扁薄壳的大挠度方程式的无量纲形式为[2-3,7-9]

2 问题的求解
因板壳中心有集中荷载,中心点的大挠度方程式不成立,中心是奇点,根据板壳理论,从中心竖向力的平衡可导出边界条件式(7),故必须寻求满足边界条件式(7)的试函数.选对数函数和三次 B样条函数为试函数,分划x定义域为 n等分,分点号依次为 0,1,…,n,虚设2个结点-1,n+1,取 1/s n= ,ix is= ,设


对 i=0结点,忽略变厚度产生的奇异性,按等厚度考虑,并且忽略中心集中荷载产生的径向力,对式(1)和式(2)可得[8]
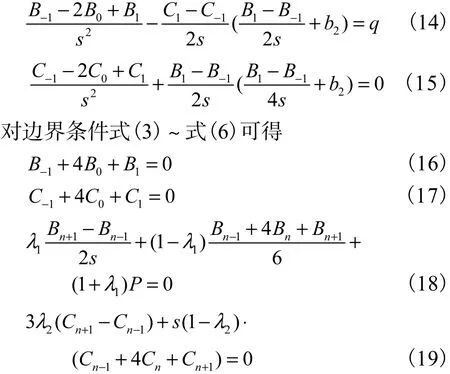
式(12)~式(19)共 2n+6 个非线性方程,用牛顿迭代法求解可以确定2n+6个待定系数Bi、Ci(i=-1,0,1,…,n,n+1),进一步可得内力及挠度.挠度表达式为

式中积分常数1c由边界条件式(8)确定.
程序中使用双精度数(有 16位有效数字),用牛顿迭代法解非线性方程组,满足以下两条件之一,认为收敛而结束迭代:①每个方程残数的绝对值小于10-10;②每个方程残数的绝对值小于0.01,并且相邻两次迭代Bi、Ci的最大相对误差的绝对值小于10-10.临界荷载计算方法见文献[8].
3 算例及说明


例1在中心集中荷载作用下圆板的线性解见表 1.
Lo等[1]用参数法得到了线性解.不考虑薄膜应力的影响,可得线性解.即令 Ci=0(i=-1,0,1,…,n+1),解线性方程组式(12)、式(14)、式(16) 和式(18),得到 n+3 个待定系数 Bi(i=-1,0,1,…,n+1).文献[1] 中 d1、d2的最大值为 0.3.
例 2受中心集中荷载的固定夹紧等厚度圆板见表2.
文献[2]的最大值为 P=3.使用摄动法,收敛范围[4]为中心挠度 wc=2.7(对应 P=5.53).

表1 在中心集中荷载(P=3)作用下线性或二次方变厚度圆板线性解的中心挠度wcTab.1 Central deflections wc of linear solutions of circular plates with linearly or quadratically variable thickness subjected to central loading(P=3)

表2 受中心集中荷载作用的固定夹紧等厚度圆板Tab.2 Circular plate (uniform thickness) subjected to central loading with rigidly clamped edge
例 3受均布荷载和反向中心集中荷载作用且中心挠度为零的固定夹紧等厚度圆板见表3.
设均布荷载 q,中心集中荷载 Pi=-Kiq(i=1,2,…),K1=0.25 和 K2=0.24,复合荷载 q+P1或 q+P2作用在圆板上,计算得中心挠度分别为 w1、w2.利用线性插值计算使中心挠度为零的K3,然后在q+P3作用下,计算得出中心挠度 w3.设 Ki、wi、Ki+1、wi+1、Ki+2和wi+2为已知,根据拉格朗日二阶插值计算使中心挠度为零的Ki+3,在q+Pi+3作用下,计算其中心挠度 wi+3.此过程继续下去,直到中心挠度的绝对值小于允许误差 10-10.当荷载很大时允许误差应适当增加.在均布荷载q和中心集中荷载-Kmq共同作用下,圆板中心挠度为零.文献[3]的最大值为 q=23.文献[7]的最大值为 q=100.
例 4受中心集中荷载的简单支承等厚度球壳上临界荷载见表4.
有限元法(FEM)的解答是使用 ANSYS程序,剖分为 500个轴对称壳元(shell51),用弧长法得出的临界荷载.
例 5受中心集中荷载的线性变厚度球壳(b2=10)和圆锥壳(b1=10)的稳定见表5.



表3 受均布荷载和反向中心集中荷载且中心挠度为零的固定夹紧等厚度圆板Tab.3 Zero central deflection of circular plate (uniform thickness) subjected to uniformly distributed loads and reverse cen-Tab. 3 tral loading with rigidly clamped edge

表4 受中心集中荷载的简单支承等厚度球壳的上临界荷载Tab.4 Upper critical load of spherical shell subjected to central loading with an uniform thickness and simply supported edge

表5 受中心集中荷载的线性变厚度球壳(b2=10)和圆锥壳(b1=10)的临界荷载Tab.5 Upper and lower critical loads of spherical shells(b2=10)and conical shells(b1=10) subjected to central loading with Tab.5 linearly variable thickness

表6 受中心集中荷载的十次多项式变厚度、四次多项式旋转壳的临界荷载、挠度和内力Tab.6 Critical loads, deflection and internal forces of quartic polynomial shells subjected to central loading with variable thickness of ten-degree polynomial
表6中,当边界条件变为固定夹紧或可移夹紧时,临界荷载不存在(加载时没有明显的跳变荷载值).
4 结 论
(1)导出的任意变厚度旋转壳大挠度的计算式,当不计薄膜应力的影响,令壳的矢高为零,大挠度方程退化为圆板弯曲的线性方程.线性解同用参数法[1]得的解答非常一致.在等厚度的条件下,当荷载较小时所得的结果同其他方法包括有限元法所得的结果非常一致[2-7],这说明本文的方法是可靠的.
(2) 有中心集中荷载作用,本文首次计算了任意变厚度板壳轴对称非线性弯曲问题,并取得了满意的结果.本文方法比有限元法的计算时间少得多.
(3) 没有明显的跳变荷载值是指当荷载逐渐增加(每步增加 P=1或 5),中心挠度和内力也逐渐增加,加载曲线不会分支.例5和例6的结果说明由于边缘的支承条件、壳厚或曲面形状改变(尽管壳的矢高不变),壳的稳定性问题可不再存在.
(4) 一般,浮点数的有效数字足够长,只要点数增加,可得到更高精度的解答.用不同的点数计算同一问题,比较它们的结果可判断解答的精度和收敛范围.对比同文献[8]的结果,要得到同样的精度,中心集中荷载比分布荷载需要更多的点数.
(5) 笔者用附加函数处理奇点的方法,可为许多具有奇点的物理问题的解决提供借鉴和参考.
[1]Lo W K,Lee L T. Equivalent systems for variable thickness circular plates[J].Computers and Structures,1996,58(5):957-977.
[2]Yeh Kaiyuan,Zheng Xiaojing,Zhou Youhe. On some properties and calculation of the exact solution to Von Karman’s equations of circular plates under a concentrated load[J].Int J Non-linear Mech,1990,25(1):17-26.
[3]Zheng Xiaojing,Zhou Youhe.Exact solution to large deflection of circular plates under compound loads[J].Scientia Sinica,Series A,1987,39(4):391-404.
[4]Cao Jingjun. Computer-extended perturbation solution for the large deflection of a circular plate(Part 2):Central loading with clamped edge[J].Quarterly J Mech Appl Math,1997,50(3):333-347.
[5]Kaplan A.Buckling of Spherical Shells:Thin-Shell Structure Theory,Experiment and Design[M]. London:Prentice-Hall,1974.
[6]Bushnell D. Bifurcation phenomena in spherical shells under concentrated and ring loads[J].AIAA J,1967,32:2034-2040.
[7]Hou Chaosheng,Yue Yanlin. Axisymmetrical nonlinear bending and buckling of a circular plate under large load[J].Transactions of Tianjin University,2005,11(3):216-222.
[8]侯朝胜,李 磊. 任意变厚度的旋转扁薄壳非线性稳定的样条函数解法[J]. 天津大学学报,2006,39(12):1446-1450.
Hou Chaosheng,Li Lei. Spline solution of nonlinear stability of revolving shallow shell with arbitrarily variable thickness[J].Journal of Tianjin University,2006,39(12):1446-1450(in Chinese).
[9]侯朝胜,武法聘.任意变厚度的旋转扁薄壳非线性稳定的幂函数解法[J]. 计算力学学报,2005,22(5):633-638.
Hou Chaosheng,Wu Fapin.Power function solution of nonlinear stability of shallow revolutionary shell with arbitrarily variable thickness[J].Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics,2005,22(5):633-638(in Chinese).
Nonlinear Bending of Revolving Shallow Shells with Arbitrarily Variable Thickness Under Central Loading
HOU Chao-sheng
(School of Civil Engineering,Tianjin University,Tianjin 300072,China)
Heretofore few research on the axisymmetrical nonlinear bending of a circular plate or a revolving shallow shell with variable thickness under a central loading has been published. With cubic B-spline and logarithmic functions taken as trial functions,for the large deflection of a circular plate and nonlinear stability of a revolving shallow shell with arbitrarily variable thickness the solutions were computed bythe method of point collocation. A circular plate was studied when subjected to action of a central loading or the compound loadof it and reverse uniformly distributed loads, in which the central deflection of the circular plate was zero. Under a central loading,upper and lower critical loads of shells were calculated including conical shells,spherical shells and quartic polynomial shells with linearly or polynomial variable thickness. The results of the circular plate and spherical shell of an identical thickness were compared with those obtained by other methods. Results show higher precision and wider range of convergent loads can be reached by using the spline collocation method.
revolving shallow shell;arbitrarily variable thickness;nonlinear stability;central loading;compound load;spline collocation method
TU33
A
0493-2137(2011)03-0210-05
2009-06-30;
2009-10-16.
侯朝胜(1945— ),男,副教授.
侯朝胜,lghcs@yahoo.com.cn.

