肺癌组织中Kras通路分子CylinD1、Caspase-3的表达差异及其临床意义的研究
娄永富 邱模昌 周晓东 章彦 江章贵 黄奕

[关键词] 非小细胞肺癌;CylinD1;Caspase-3;病理特征;预后
[中图分类号] R734.2 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-9701(2021)29-0013-04
Study on the expression difference and clinical significance of Kras pathway molecules CylinD1 and Caspase-3 in lung cancer tissues
LOU Yongfu1 QIU Mochang2 ZHOU Xiaodong1 ZHANG Yan1 JIANG Zhanggui1 HUANG Yi1
1.Department of Thoracic Surgery,the People's Hospital of Shangrao City in Jiangxi Province,Shangrao 334000,China; 2.Department of Teaching Affairs, Jiangxi Medical College, Shangrao 334000,China
[Abstract] Objective To study the expression difference and clinical significance of Kras pathway molecules CylinD1 and caspase-3 in non-small cell lung cancer(NSCLC) tissues. Methods Patients with stage Ⅰ-ⅢA NSCLC who underwent surgical resection in our hospital from March 2016 to December 2017 were selected. The mRNA expression levels and protein expression levels of CylinD1 and Caspase-3 in NSCLC tissues and adjacent non-cancerous tissues were detected. Patients were followed for progression-free survival(PFS). Results The mRNA and protein expression levels of CylinD1 in NSCLC tissues were higher than those in the paracancerous tissues(P<0.05). The mRNA and protein expression levels of Caspase-3 in NSCLC tissues were lower than those in the paracancerous tissues(P<0.05). The mRNA expression level and protein expression level of CylinD1 was higher in stage ⅢA,poorly differentiated NSCLC tissues than in stage Ⅰ-Ⅱ,moderately and well-differentiated NSCLC tissues(P<0.05). The mRNA expression level and protein expression level of Caspase-3 in stage ⅢA,poorly differentiated NSCLC tissues were lower than those of stage Ⅰ-Ⅱ,moderately well-differentiated NSCLC tissues (P<0.05). PFS was shorter in NSCLC patients with CyclinD1 expression levels ≥ median than in NSCLC patients with CyclinD1 expression levels < median(P<0.05). NSCLC patients with Caspase-3 expression levels≥median had longer PFS than NSCLC patients with Caspase-3 expression levels < median(P<0.05). Conclusion Increased expression of Kras pathway molecule CyclinD1 and decreased expression of Caspase-3 in NSCLC are related to pathological progress and deterioration of prognosis.
[Key words] Non-small cell lung cancer; CylinD1; Caspase-3; Pathological features; Prognosis
肺癌是我国发病率居首位的恶性肿瘤,非小细胞肺癌(Non-small cell lung carcinoma,NSCLC)是肺癌最主要的病理类型[1]。Kras基因是Ras基因家族中3种癌基因之一,发生突变后处于持续激活状态并介导促增殖、抗凋亡作用。已有研究报道,Kras基因突变与NSCLC的发病密切相关[2-3],但Kras通路参与NSCLC发病的机制尚不十分明确。细胞周期蛋白D1(CyclinD1)和含半胱氨酸的天冬氨酸蛋白水解酶-3(Cysteinyl aspartate specific proteinase-3,Caspase-3)是Kras通路中重要的兩种分子,前者促进细胞周期发展及细胞增殖,后者促进细胞凋亡[4-5]。为了阐明Kras通路在NSCLC发病中的作用,本研究分析NSCLC中CylinD1、Caspase-3的表达差异及其临床意义,现报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选择2016年3月至2017年12月在我院接受手术切除的Ⅰ~ⅢA期NSCLC患者作为研究对象,纳入标准:①经术后病理诊断为NSCLC,病理分期Ⅰ~ⅢA期;②临床病理资料完整;③术后留取NSCLC组织及癌旁组织;④术后随访资料完整。排除标准:①术前接受过放化疗或其他抗肿瘤治疗者;②既往有其他恶性肿瘤病史者。共纳入152例,其中男84例,女68例,年龄41~67岁、平均(59.58±10.93)岁。本研究获得医院医学伦理委员会批准,患者签署知情同意书。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 CylinD1、Caspase-3 mRNA表达的检测 取NSCLC组织和癌旁组织,采用RNA提取试剂盒提取组织中的RNA并反转录为cDNA,采用荧光定量PCR试剂盒对cDNA进行扩增,分别使用目的基因CylinD1、Caspase-3的特异性引物及内参基因β-actin的特异性引物,得到相应基因的PCR循环曲线及循环阈值,以β-actin为内参、计算CylinD1及Caspase-3的mRNA表达水平。
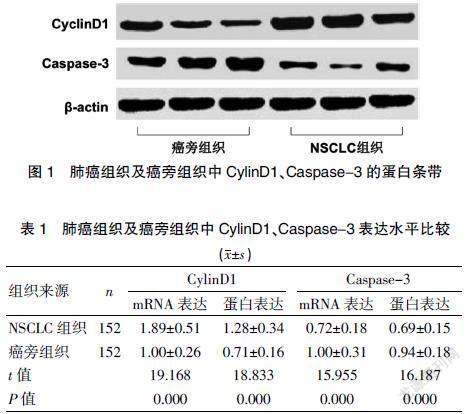
1.2.2 CylinD1、Caspase-3蛋白表达的检测 取NSCLC组织和癌旁组织,加入组织裂解液进行匀浆、提取组织蛋白,将蛋白样本煮沸变性后进行Western blot检测。首先在SDS-聚丙烯酰胺凝胶内进行电泳,而后电转移至PVDF膜,室温封闭1 h,4℃孵育CylinD1、Caspase-3及β-actin的一抗过夜,次日室温孵育二抗1 h,最后在凝胶成像系统内显影,得到CylinD1、Caspase-3及β-actin的蛋白条带,根据条带吸光值,以β-actin为内参计算CylinD1、Caspase-3的蛋白表达水平。
1.2.3 无进展生存期(Progression free survival,PFS)的随访 采用门诊复诊、电话回访等方式进行随访,随访内容为PFS,随访截止时间为2020年10月31日,从病理确诊日期至发生复发转移日期或随访截止日期为PFS。
1.3观察指标及评价标准
观察指标包括CylinD1、Caspase-3的mRNA表达水平及蛋白表达水平,以及患者的PFS。
1.4 统计学方法
采用SPSS 21.0统计学软件进行分析,经正态性检验符合正态分布的计量资料以均数±标准差(x±s)表示,组间比较采用t检验;预后采用生存曲线进行描述,组间比较采用Log-rank检验。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 肺癌组织及癌旁组织中CylinD1、Caspase-3表达水平的比较
与癌旁组织比较,NSCLC组织中CylinD1的mRNA表达水平及蛋白表达水平均明显升高,Caspase-3的mRNA表达水平和蛋白表达水平明显降低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见图1、表1。
2.2 不同病理特征NSCLC组织中CylinD1、Caspase-3表达水平的比较
不同病理类型、原发部位NSCLC组织中CylinD1、Caspase-3的mRNA表达水平及蛋白表达水平比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);病理分期ⅢA期NSCLC组织中CylinD1的mRNA表达水平及蛋白表达水平高于Ⅰ~Ⅱ期NSCLC组织(P<0.05),Caspase-3的mRNA表达水平及蛋白表达水平低于Ⅰ~Ⅱ期NSCLC組织(P<0.05);低分化NSCLC组织中CylinD1的mRNA表达水平及蛋白表达水平高于中高分化NSCLC组织(P<0.05),Caspase-3的mRNA表达水平及蛋白表达水平低于中高分化NSCLC组织(P<0.05)。见表2。
2.3 不同CylinD1表达的NSCLC患者预后比较
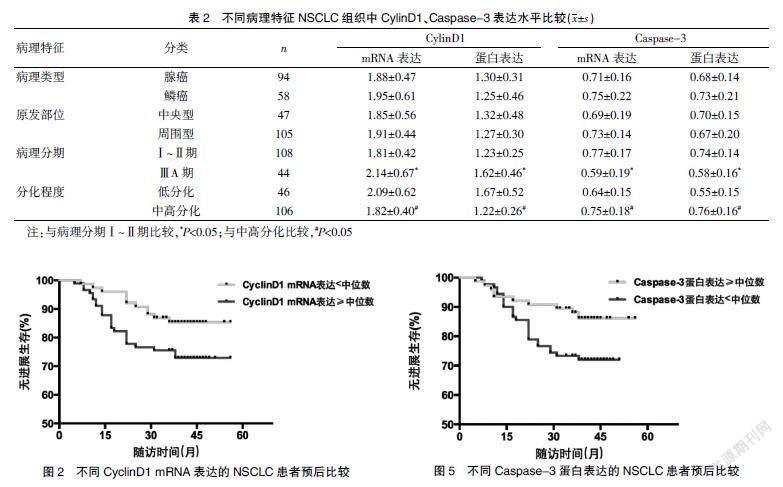
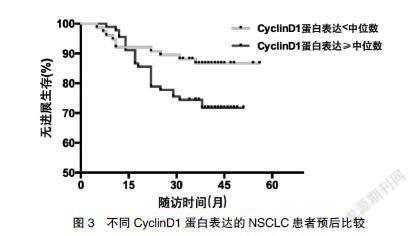
CylinD1 mRNA表达≥中位数、蛋白表达≥中位数的NSCLC患者PFS较CylinD1 mRNA表达<中位数、蛋白表达<中位数的NSCLC患者缩短(P<0.05)。见图2~3。
2.4 不同Caspase-3表达的NSCLC患者预后比较
Caspase-3 mRNA表达≥中位数、蛋白表达≥中位数的NSCLC患者PFS较Caspase-3 mRNA表达<中位数、蛋白表达<中位数的NSCLC患者延长(P<0.05)。见图4~5。
3 讨论
NSCLC是肺癌最主要的病理类型,发病机制复杂,涉及环境因素、遗传因素、基因突变等多环节、多因素。Kras基因是重要的癌基因,编码产物具有GTP酶活性、是表皮生长因子受体下游重要的通路之一,该基因发生突变会使p21蛋白GTP酶活性降低,进而造成Kras通路持续处于激活状态。在NSCLC发病过程中,普遍存在Kras基因突变,突变主要涉及12或13位密码子。相关的临床研究并未发现Kras基因突变与NSCLC病理特征的关系[6-7],在NSCLC发病过程中,Kras基因突变后下游信号通路的变化与病理进展及预后的关系尚缺乏临床证据。因此,本研究将以Kras通路分子为切入点,深入探讨Kras通路分子在NSCLC发病中的作用。
Kras通路激活具有广泛的生物学效应,在恶性肿瘤发病中的效应包括促增殖、抗凋亡。在Kras通路发挥促增殖作用的过程中,其下游分子CyclinD1的表达显著上调;在Kras通路发挥抗凋亡作用的过程中,其下游分子Caspase-3的表达显著下调。已有研究报道,在NSCLC、结直肠癌等多种恶性肿瘤的发病过程中,肿瘤病灶内CyclinD1的表达增加、Caspase-3的表达降低[8-10]。本研究选择152例接受手术切除治疗的NSCLC患者,对NSCLC组织及癌旁组织中CyclinD1、Caspase-3表达的差异进行分析,与癌旁组织比较,NSCLC组织CyclinD1的mRNA表达及蛋白表达均明显升高,Caspase-3的mRNA表达水平和蛋白表达水平明显降低,与既往文献关于NSCLC中CyclinD1表达升高、Caspase-3表达降低的结果一致。
CyclinD1具有促增殖作用,能够与细胞周期依赖蛋白激酶结合并加速细胞周期发展,进而促进细胞有丝分裂及增殖[11];Caspase-3具有促凋亡作用,线粒体凋亡途径、死亡受体凋亡途径等不同途径最终均作用于Caspase-3,该分子能够作用于多聚聚合酶PARP并影响DNA修复,进而启动细胞凋亡[12]。在恶性肿瘤的发展过程中,细胞增殖增强、凋亡减弱能够促进病灶生长和转移,同时也可能影响肿瘤分化。本研究结果显示,在证实NSCLC中CyclinD1表达升高、Caspase-3表达降低后,进一步分析了CyclinD1、Caspase-3表达与病理进展的关系,随着NSCLC分化程度降低、病理分期增加,病灶内CyclinD1表达升高、Caspase-3表达降低,提示NSCLC中CyclinD1表达升高、Caspase-3表达降低与病理进展有关。
NSCLC病理进展是影响预后的重要因素。有研究报道,病理分期增加是NSCLL患者预后的独立影响因素[13-14]。本研究已证实CyclinD1表达升高、Caspase-3表达降低与NSCLC的病理进展有关,在此基础上进一步分析CyclinD1、Caspase-3表达与NSCLC患者预后的关系。已有临床研究报道,CyclinD1表达升高、Caspase-3表达降低与乳腺癌、膀胱癌预后恶化有关[15-17]。本研究对NSCLC患者的预后进行随访,通过绘制PFS的KM曲线并分析证实,随着NSCLC中CyclinD1表达升高、Caspase-3表达降低、患者的PFS明显缩短,提示NSCLC中CyclinD1、Caspase-3的异常表达与患者预后恶化有关。
综上所述,NSCLC中Kras通路分子CyclinD1表达升高、Caspase-3表达降低;CyclinD1、Caspase-3的异常表达与病理进展、预后恶化有关。
[参考文献]
[1] 陈万青,李贺,孙可欣,等. 2014年中国恶性肿瘤发病和死亡分析[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志,2018,40(1):5-13.
[2] Araujo LH,Souza BM,Leite LR,et al. Molecular profile of KRAS G12C-mutant colorectal and non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. BMC Cancer,2021,21(1):193.
[3] Griesinger F,Eberhardt W,Nusch A,et al. Biomarker testing in non-small cell lung cancer in routine care: Analysis of the first 3,717 patients in the German prospective,observational,nation-wide CRISP Registry (AIO-TRK-0315)[J]. Lung Cancer,2021,152:174-184.
[4] Stein CK,Pawlyn C,Chavan S,et al. The varied distribution and impact of RAS codon and other key DNA alterations across the translocation cyclin D subgroups in multiple myeloma[J]. Oncotarget,2017,8(17):27 854-27 867.
[5] Mahmoudi N,Delirezh N,Sam MR. Modulating pluripotency network genes with omega-3 DHA is followed by caspase-3 activation and apoptosis in DNA mismatch repair-deficient/KRAS-mutant colorectal cancer stem-like cells[J]. Anticancer Agents Med Chem,2020,20(10):1221-1232.
[6] 陳灵锋,陈小岩,俞训彬. 非小细胞肺癌驱动基因突变与临床病理特征的关系[J]. 中华病理学杂志,2016,45(4):221-225.
[7] 罗炜,王慧,徐韫健,等. 非小细胞肺癌患者KRAS基因突变情况分析[J]. 广东医学,2014,35(13):2025-2028.
[8] 黄虎,栗娜,杨柳,等. 非小细胞肺癌组织中NF-κB和CyclinD1及p27表达与患者化疗敏感性[J]. 贵州医科大学学报,2019,44(2):195-199.
[9] Kovtunenko OV,Bakaiev AA,Shponka IS. Analysis of expression of p63 and caspase-3 and their predictive value in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of maxillary sinus[J]. Wiad Lek,2019,72(12 cz 1):2305-2314.
[10] Yao Q,Wang W,Jin J,et al. Synergistic role of Caspase-8 and Caspase-3 expressions:Prognostic and predictive biomarkers in colorectal cancer[J]. Cancer Biomark,2018, 21(4):899-908.
[11] Chen Y,Huang Y,Gao X,et al. CCND1 amplification contributes to immunosuppression and is associated with a poor prognosis to immune checkpoint inhibitors in solid tumors[J]. Front Immunol,2020,10(11):1620.
[12] Do BH,Nguyen TPT,Ho NQC,et al. Mitochondria-mediated Caspase-dependent and Caspase-independent apoptosis induced by aqueous extract from Moringa oleifera leaves in human melanoma cells[J]. Mol Biol Rep,2020,47(5):3675-3689.
[13] 宋冠初,郭根燕,陸永涛,等. 110例局部非小细胞肺癌手术治疗的预后分析[J]. 现代肿瘤医学,2020,28(10):1659-1663.
[14] 周舟,侯炜. 非小细胞肺癌术后患者预后相关因素回顾性分析[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2019,34(10):4820-4823.
[15] Liu X,Jiang S,Tian X,et al. Expression of cleaved caspase-3 predicts good chemotherapy response but poor survival for patients with advanced primary triple-negative breast cancer[J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol,2018,11(9):4363-4373.
[16] Yang X,Zhong DN,Qin H,et al. Caspase-3 over-expression is associated with poor overall survival and clinicopathological parameters in breast cancer:A meta-analysis of 3091 cases[J]. Oncotarget,2017,9(9):8629-8641.
[17] March-Villalba JA,Ramos-Soler D,Soriano-Sarrió P,et al. Immunohistochemical expression of Ki-67,Cyclin D1,p16INK4a,and Survivin as a predictive tool for recurrence and progression-free survival in papillary urothelial bladder cancer pTa/pT1 G2(WHO 1973)[J]. Urol Oncol,2019,37(2):158-165.
(收稿日期:2021-05-06)

