Sacrococcygeal Teratoma
Key Facts
Synonyms:Sacrococcygeal teratoma(SGT),germ cell tumor of coccyx
Definition:Tumors containing hair,teeth,cartilage,and fat extending from the coccyx and potentially growing both internally and externally.
Classic imaging appearance:Calcifications,mixed solid and cystic components,fat-fluid-debris levels,bone,hair,and cartilage.
Most common tumor of the newborn,most are diagnosed in-utero or within first few days of life.
Only 17% of sacrococcygeal teratoma have malignant features.Malignant characteristics increase with age at diagnosis,surgical subtype(typeⅣ,entirely internal,is worst),male gender,and presence of necrosis or hemorrhage.More common in females,but more likely to be malignant in males.
Imaging Findings
B est imaging clue:Presence of multiple tissue types,including hair,calcium,bone,fat,fluid levels and involvement of tissues around coccyx.
CT Findings:Demonstrates the fatty components,calcium,and fluid levels well.
MR findings:Similar to CT,mixed signal intensity components,chemical shift artifact at fat interfaces.
Heterogeneous enhancement
Other modality findings:Ultrasound may be limited due to large size and presence of shadowing calcium and bone elements
Imaging Recommendations:CT or MR to determine full extension of mass and aid surgical planning.
Imaging Findings
Best imaging clue:Transverse lucency at base of odontoid on lateral view or sagittal or coronal reformations
Anatomy:In children,a synchondrosis occurs between ossification centers of the dens and the body of C2;this rarely is injured and widened in trauma.The os terminale,a small separate ossification center,occurs at the tip of the dens in the midline.
医学词汇注释与简要讲解
Sacrococcygeal teratoma 骶尾部畸胎瘤
coccyx 尾骨
fat-fluid-debris levels 脂-液平
in-utero 宫(腔)内
骶尾部畸胎瘤的恶性特征包括:(1)诊断时的年 龄;(2)类 型(Ⅳ型,完全腹内型是最恶性的);(3)男性;(4)肿瘤内坏死或出血。
exophytic 外生性
Differential Diagnosis
(1)Exophytic Rhabdomyosarcoma:Presence of calcium,bone and hair suggest teratoma.(2)Myelomeningocele:More than just neural elements and CSF present on imaging continuity with thecal sac.
rhabdomyosarcoma 横纹肌肉瘤
myelomeningocele 脊髓脊髓膨出
thecal sac 硬膜囊
autosomal 常染色体
alpha-fetoprotein 甲胎蛋白
Currarino's triad
Currarino's 三联征:肛门直肠畸形-骶骨畸形-骶前肿物
分型
Ⅰ型 完全腹外型
Ⅱ型 腹内外型(哑铃状,各一半)
Ⅲ型 腹内为主型
Pathology
General path comments:Surgical resection must include the coccyx or risk of recurrence Increases.
Genetics:Sporadic,not inherited;reports of parent-child(autosomal dominant)or syndromic association.
Teratoma may be a component of Currarino's triad.
Etiology-Pathogenesis(theories):Probably results from rests of pluripotential cells at the caudal end of notochord/spine(Hensen's node)or“twinning accident”with incomplete separation during embryogenesis.
Epidemiology:Prevalence is about 1 in 35,000 to 40,000 births.Much more common in females(M:F ratio=1 to 3 or 4).
Gross pathologic,surgical features:typical of all teratomas-multiple tissue types in varying stages of maturation and differentiation
Surgical Subtypes
TypeⅠprimarily external in location(47%)
TypeⅡdumbbell shaped,equal internal/external components(34%)
TypeⅢprimarily located within the abdomen/pelvis(9%)
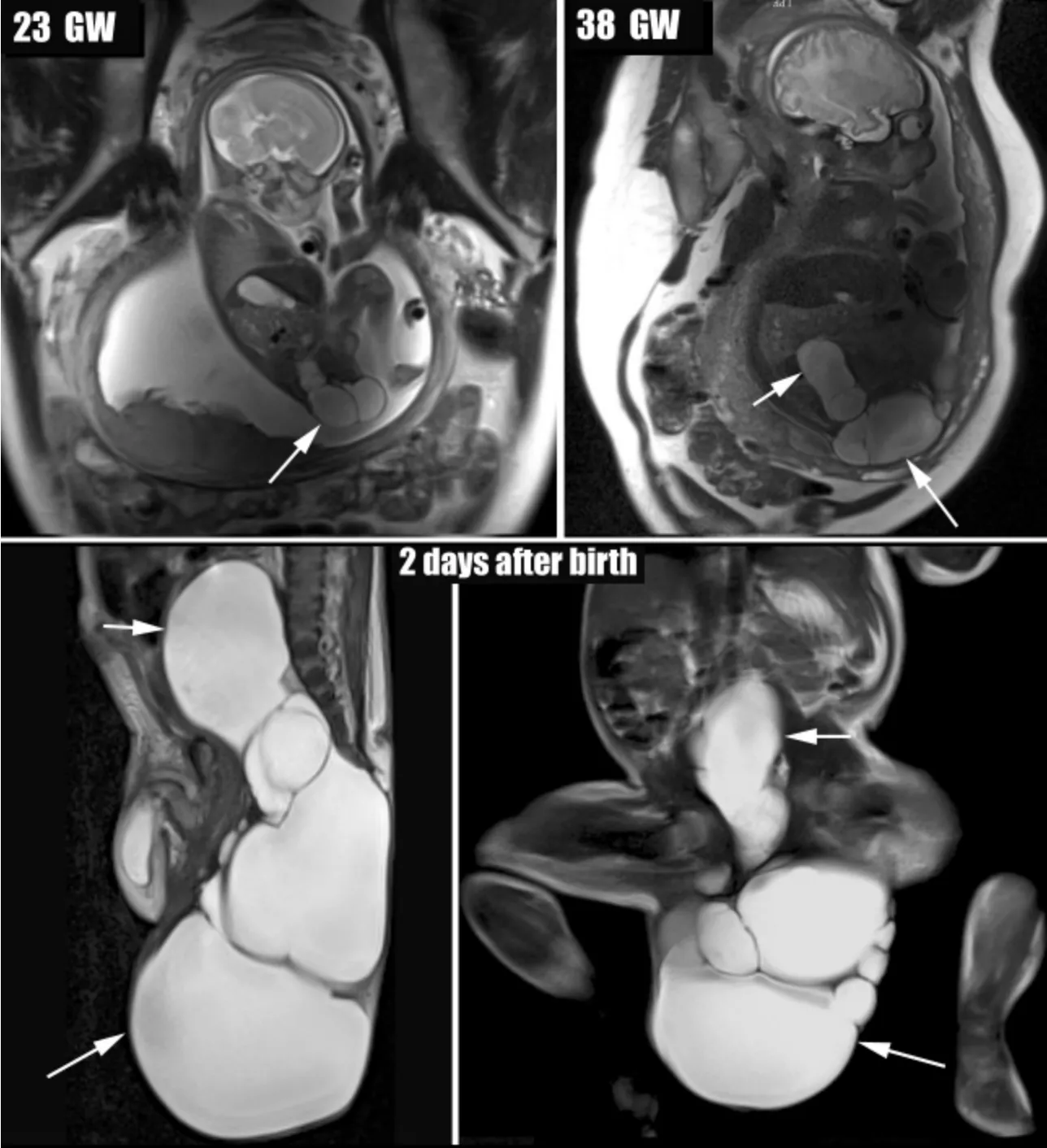
Fig 1 a)Sacrococcygeal teratoma(arrows)with intradural and extramedullary extension was seen in a fetus on sagittal T2WI at 23 gestational weeks.b)The predominantly cystic tumor (arrows)became greater on sagittal T2WI at 38 gestational weeks.c)Teratoma(arrow)was shown on sagittal and coronal T2WI after birth.
TypeⅣentirely internal,no external component visible(10%)
Clinical Issues
Polyhydramnios is frequent.High output failure(result of tumor hemorrhage and/or arteriovenous shunting)leads to hepatomegaly,placentomegaly and hydrops fetalis.Development of hydrops grave,signals imminent fetal demise.
Intrauterine fetal demise is about 20%(cystic)-65%(solid),and premature labor up to 50%.
Exophytic masses are easily diagnosed.Masses that are entirely internal may have delayed diagnosis,presenting with urinary symptoms,urinary retention,or constipation.Masses diagnosed after the first birthday and located only internally have a worse prognosis.
Serum alpha-fetoprotein is useful tumor marker postoperatively
Treatment
Polyhydramnios,mild placentomegaly or early featl nonimmune hydrops are indications for resection of sacrococcygeal teratoma or in-utero radiofrequency ablation(offered at some centers).
Thick placentomegaly,severe hydrops,or pre-eclampsia no longer candidate for fetal surgery.
Complete(postnatal)surgical resection to include the coccyx.
Partial(prenatal)resection may induce SCT maturation.
Benign tumors do not require additional therapy.
Malignant tumors are treated with chemotherapy and radiation.
Prognosis
Excellent in benign tumors(esp.cystic),variable in malignant(esp.solid)tumors with late diagnosis.
Risk for malignancy 10%.at term,65%-90% if diagnosed after 2 months
Mortality rate in fetus is 20%~65%,but 5% in full-term perinatal deaths are attributable to tumor rupture.
Recur if coccyx not resected.
Ⅳ型 完全腹内型
【prefix】poly- 多的、聚合的
polyhydramnios 羊水过多
polygon 多边形
【suffix】-magaly 肿大
hepatomegaly 肝(肿)大
placentomegaly 胎盘肿大
hydrops fetalis 胎儿水肿
urinary retention 尿潴留
constipation 便秘
alpha-fetoprotein 甲胎蛋白
eclampsia 子痫

