状态依赖的随机干扰对一类流行病模型的影响
赵延辉,魏凤英
(福州大学数学与计算机科学学院,福建 福州 350116)
状态依赖的随机干扰对一类流行病模型的影响
赵延辉,魏凤英
(福州大学数学与计算机科学学院,福建 福州 350116)
研究了一类状态依赖的随机干扰对流行病模型的影响,讨论了具有饱和发生率的流行病模型的绝灭性及平稳分布.根据伊藤公式及构造的李雅普诺夫函数,证明了解的存在唯一性.主要研究结果说明:在适当的充分条件下疾病会灭绝;该模型存在一个遍历的平稳分布;利用傅里叶变换,得到了解在地方病平衡点渐近服从三维正态分布.数值模拟验证了所得结论的有效性.
随机扰动;流行病模型;饱和发生率;平稳分布;正态分布
0 引言
1992年,Mena-Lorca等[1]在假设种群密度并非恒定不变,且易感者具有常数输入率,部分感染者在恢复后具备免疫能力情形下,讨论了双线性传染率的流行病模型
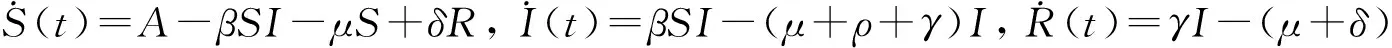
(1)
其中:S(t),I(t)与R(t)分别代表t时刻易感者、感染者与恢复者的数量;A表示易感者的常数恢复率;β是疾病的传染率,βS表示单位时间内被一位感染者所传染的人数,βSI是单位时间内被所有感染者所传染的人数;μ表示平均自然死亡率;ρ是感染者的因病平均死亡率;δ是免疫丧失率;γ为感染者的恢复率.
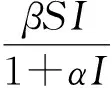
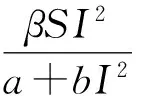
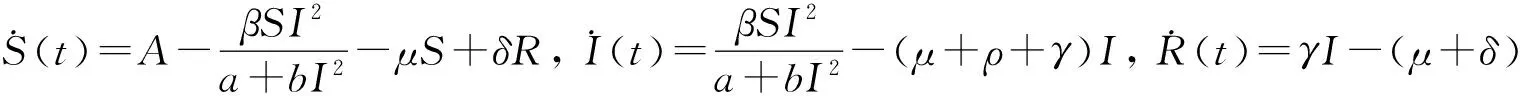
(2)
对模型(2)引入线性随机白噪声干扰项,即随机干扰是状态变量S,I,R的线性函数,得到干扰后的随机SIRS流行病模型
(3)
其中:B1,B2,B3为相互独立的一维标准的布朗运动;σ1,σ2与σ3分别是易感者、感染者与恢复者的随机噪声强度.
1 解的存在唯一性
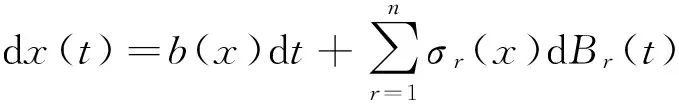
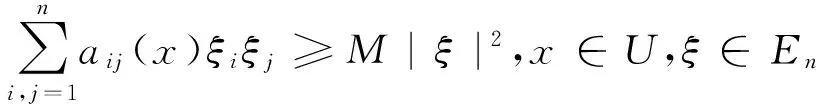

引理3[9]假设存在有界开集U⊂En且满足以下性质:
(1) 在开集U及其邻域中,扩散阵A(x)的最小特征值是非零的;

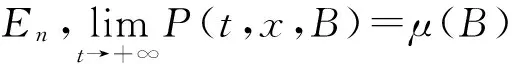
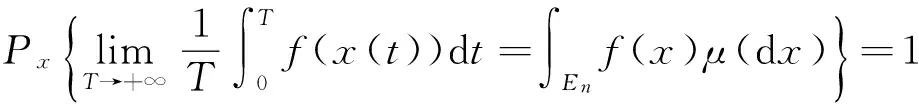
(4)
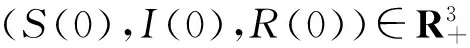
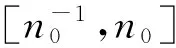
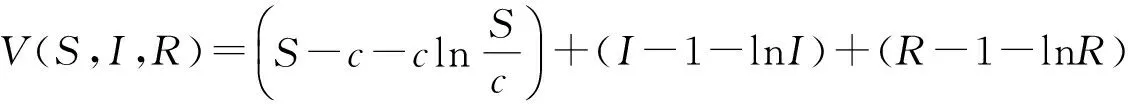
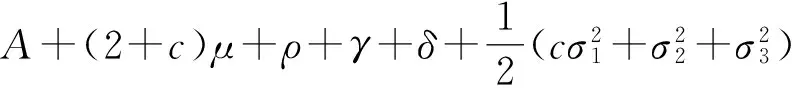
(5)
于是
dV(S,I,R)≤Mdt+σ1(S-c)dB1(t)+σ2(I-1)dB2(t)+σ3(R-1)dB3(t).
(6)
将上式两端从0到τn∧T积分后,再取数学期望得
EV(S(τn∧T),I(τn∧T),R(τn∧T))≤V(S(0),I(0),R(0))+MT<+∞.
对每一个ω∈Φn={τn≤T},S(τn,ω),I(τn,ω),R(τn,ω)中至少有一个等于n-1或n,则
+∞>V(S(0),I(0),R(0))+MT≥E[IΦn(ω)V(S(τn∧T),I(τn∧T),R(τn∧T))]≥
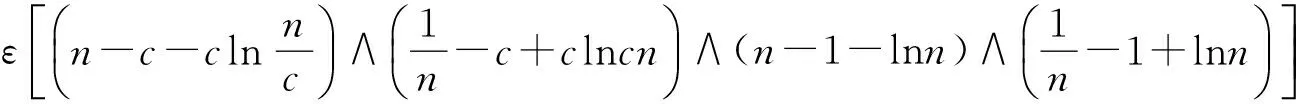
(7)
其中IΦn(ω)为Φn的示性函数.令n→+∞,有+∞>V(S(0),I(0),R(0))+MT≥+∞,矛盾.因此τ∞=+∞几乎处处成立,定理得证.
2 解的绝灭性及平稳分布
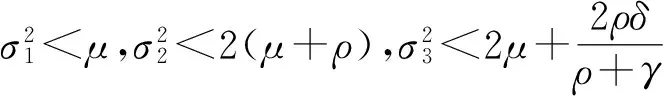
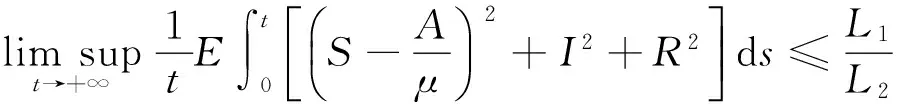
(8)
其中
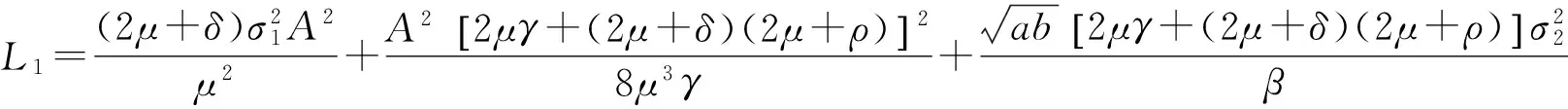
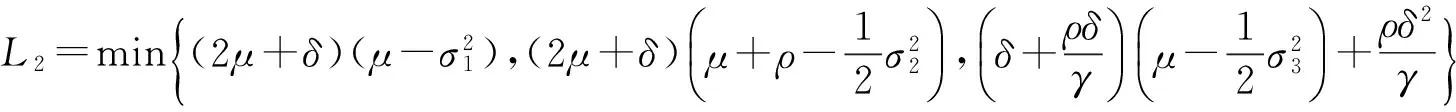
(9)
定义C2-函数
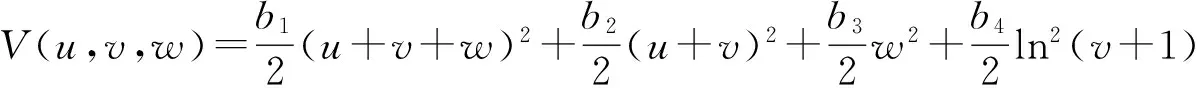
b1V1+b2V2+b3V3+b4V4,
(10)
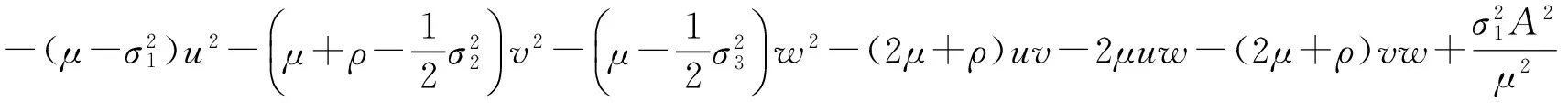
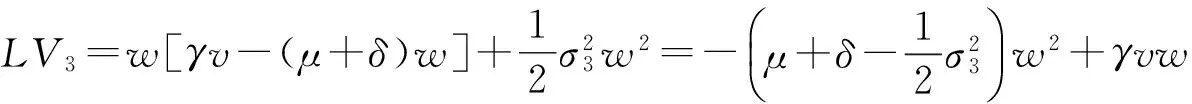
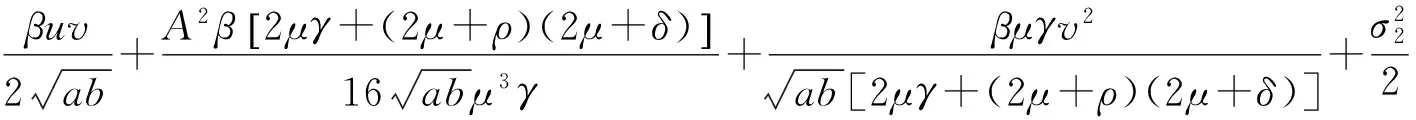
(11)
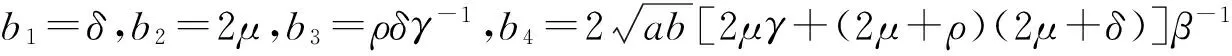
-L2(u2+v2+w2)+L1,
(12)
从而
dV≤[-L2(u2+v2+w2)+L1]dt+udB1(t)+vdB2(t)+wdB3(t).
(13)
对上式两边从0到t积分再取数学期望有
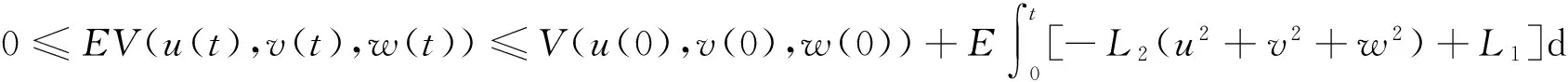
(14)
故

(15)
定理3 假设(S*,I*,R*)是模型(2)的地方病平衡点.若
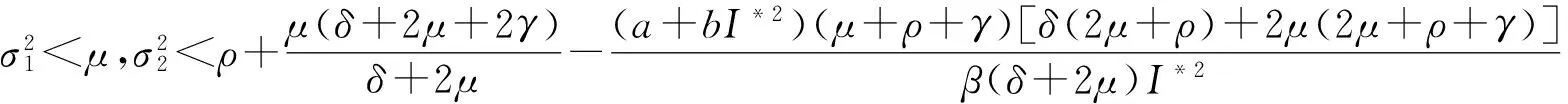
(16)
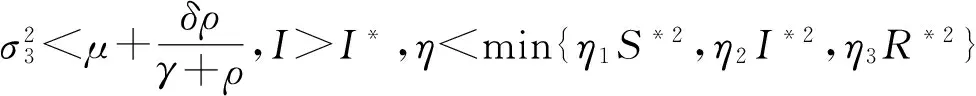
则模型(3)存在遍历的平稳分布.其中
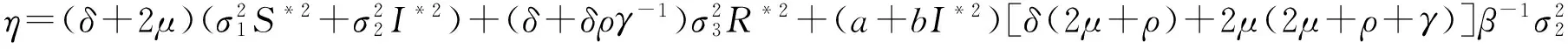
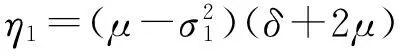
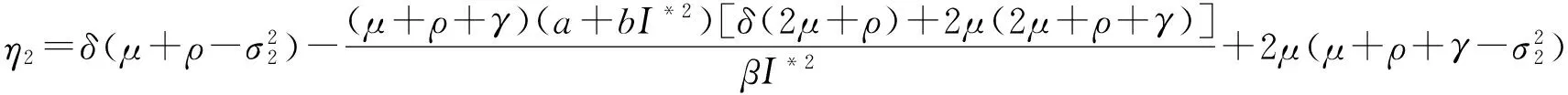

(17)
证明 由于(S*,I*,R*)是模型(2)的地方病平衡点,满足
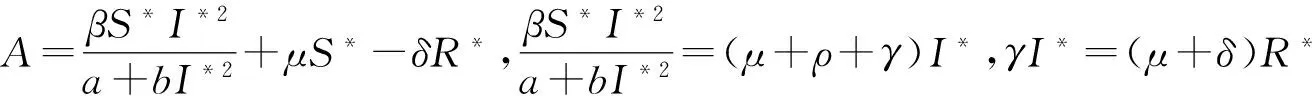
定义C2-函数
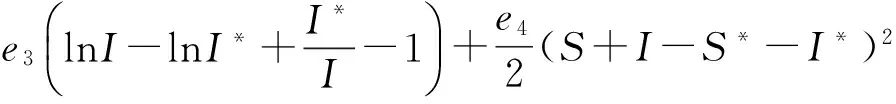
(18)
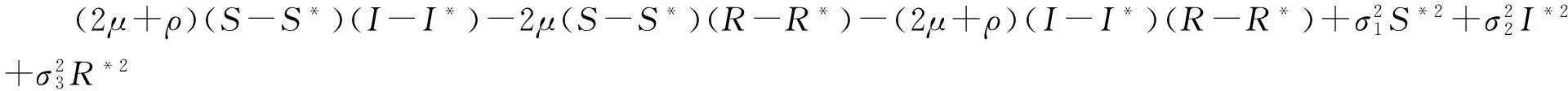
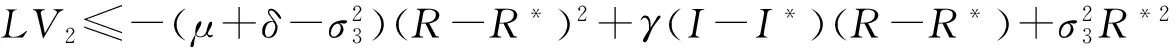
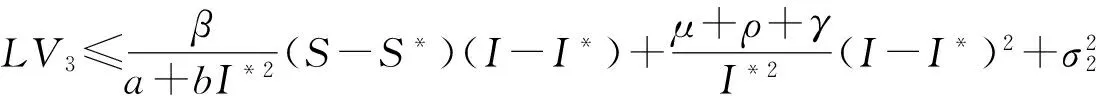
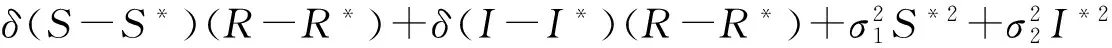
(19)
取e1=δ,e2=δργ-1,e3=β-1(a+bI*2)[δ(2μ+ρ)+2μ(2μ+ρ+γ)],e4=2μ,则由(17)式得
LV≤-η1(S-S*)2-η2(I-I*)2-η3(R-R*)2+η.
定理4 若模型(2)的地方病平衡点(S*,I*,R*)是稳定的,则模型(3)的解(S,I,R)渐近服从三维正态分布N((S*,I*,R*),C(S,I,R)(0)).
证明 模型(3)简记为(dS,dI,dR)T=g(S,I,R)dt+σ(S,I,R)dB(t),在地方病平衡点(S*,I*,R*)泰勒展开,又由于偏差S-S*,I-I*,R-R*不大,且σ1,σ2,σ3是较小的噪声强度,所以σ1(S-S*),σ2(I-I*),σ3(R-R*)较小,忽略高阶项,得到近似模型
df=[g(S*,I*,R*)+g′(S*,I*,R*)f]dt+σ(S*,I*,R*)dB(t).
(20)
其中f=(S-S*,I-I*,R-R*)T,σ(S*,I*,R*)=diag(σ1S*,σ2I*,σ3R*),
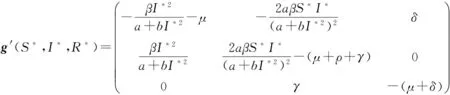
由于(S*,I*,R*)是稳定的,所以g(S*,I*,R*)=0,g′(S*,I*,R*)<0,从而方程(20)退化为三维Ornstein-Uhlenbeck过程
df-g′(S*,I*,R*)fdt=σ(S*,I*,R*)dB(t),
(21)
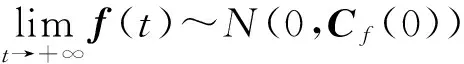
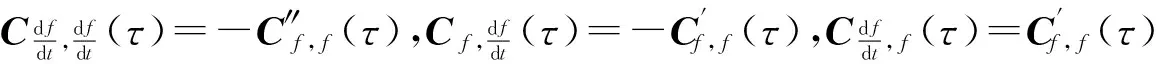
(22)
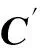
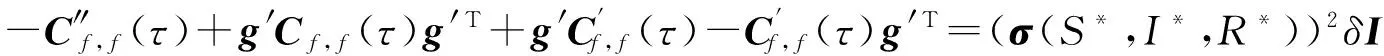
(23)
-(iω)2Sf(ω)+g′Sf(ω)g′T+iωg′Sf(ω)-iwSf(ω)g′T=(σ(S*,I*,R*))2.
(24)
由于g′的所有特征值都具有严格的负实部,所以g′±iωI是可逆矩阵,于是
Sf(ω)=(g′-iωI)-1(σ(S*,I*,R*))2[(g′+iωI)T]-1.
(25)
将上式作傅里叶逆变换,并取τ=0,得到方差矩阵
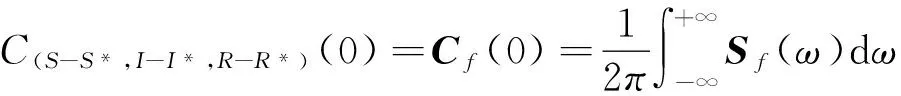
(26)
故Cf(0)=C(S,I,R)(0).
3 数值模拟
利用Milstein高阶方法[10],得到离散化方程组
(27)
其中ξi,k(i=1,2,3,k=1,2,3,…,n)为独立高斯随机变量N(0,1).
在模型(3)中,取初值(S(0),I(0),R(0))=(5,3.5,1.5),及参数
A=2,β=0.01,a=1.5,b=0.5,μ=0.03,δ=0.74,
ρ=0.45,γ=0.35,σ1=0.013,σ2=0.001,σ3=0.05.
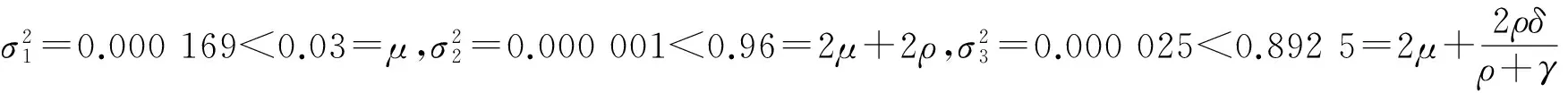
取模型(3)的初值(S(0),I(0),R(0))=(2.4,1.2,0.5),k=10 000,t=200,参数A=45,β=0.07,a=0.02,b=0.085,μ=0.3,δ=0.95,ρ=0.65,γ=0.24,σ1=0.025,σ2=0.008,σ3=0.024.则定理3的条件成立,因此模型(3)的解在地方病平衡点周围振荡,并渐近服从三维正态分布N((S*,I*,R*),C(S,I,R)(0)),这说明疾病将流行.
[1] MENA-LORCA J,HETHCOTE H W.Dynamic models of the infectious disease as regulator of population sizes[J].Journal of Mathematical Biology,1992,30:693-716.
[2] BROWN G C,HASIBUAN R.Conidial discharge and transmission efficiency of Neozygites floridana:an entomopathogenic fungus infecting two-spotted spider mites under laboratory conditions[J].Journal of Invertebrate Pathology,1995,65(1):10-16.
[3] RUAN S G,WANG W D.Dynamical behavior of an epidemic model with a nonlinear incidence rate[J].Journal of Differential Equations,2003,188(1):135-163.
[4] JIANG D Q,YU J J,JI C Y,et al.Asymptotic behavior of global positive solution to a stochastic SIR model[J].Mathematical and Computer Modelling,2011,54(12):221-232.
[5] 赵亚男,王宇,夏兰,张晓颖.随机SIQS传染病系统的灭绝性和遍历性[J].吉林大学学报(理学版),2013,51(6):1081-1084.
[6] LAHROUZ A,OMARI L.Extinction and stationary distribution of a stochastic SIRS epidemic model with non-linear incidence[J].Statistics & Probability Letters,2013,83(4):960-968.
[7] GARD T C.Introduction to stochastic differential equations[M].New York:Marcel Dekker,1988:35-55.
[8] ZHU C,YIN G.Asymptotic properties of hybrid diffusion systems[J].SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization,2007,46(4):1155-1179.
[9] KHASMINSKII R.Stochastic stability of differential equations[M].Alphen:Sijthoff and Noordhoff,1980:43-93.
[10] HIGHAM D J.An algorithmic introduction to numerical simulation of stochastic differential equations[J].Siam Review,2001,43(3):525-546.
(责任编辑:李亚军)
Impact of random perturbations with state-dependent on an epidemic model
ZHAO Yan-hui,WEI Feng-ying
(College of Mathematics and Computer Science,Fuzhou University,Fuzhou 350116,China)
This paper focuses on the impact of random perturbations with state-dependent on an epidemic model.The extinction and the stationary distribution of the epidemic model with a saturated incidence are discussed.By means of Ito’s formula and constructing Lyapunov functions,the existence and uniqueness of a global positive solution is investigated.The main results declare that the disease will die out under some sufficient conditions.And the model admits a stationary distribution with ergodic property and the solution asymptotically follows a three-dimensional normal distribution around the endemic equilibrium according to Fourier transform.Some numerical simulations are carried out to show the efficiency of our main results.
random perturbations;epidemic model;saturated incidence;stationary distribution;normal distribution
1000-1832(2017)01-0009-06
10.16163/j.cnki.22-1123/n.2017.01.002
2015-11-20
国家自然科学基金资助项目(11201075);福建省自然科学基金资助项目(2016J01015).
赵延辉(1990— ),女,硕士,主要从事随机微分方程研究;魏凤英(1976—),女,博士,教授,主要从事生物数学与随机微分方程研究.
O 211 [学科代码] 110·64
A

