基于高效液相色谱指纹图谱的玛咖及其制品真实性识别
刘兴勇,邵金良,陈兴连,王 丽,黎其万,刘宏程
(云南省农业科学院质量标准与检测技术研究所,昆明 650223;农业部农产品质量监督检验测试中心,昆明 650223)
基于高效液相色谱指纹图谱的玛咖及其制品真实性识别
刘兴勇,邵金良,陈兴连,王 丽,黎其万,刘宏程※
(云南省农业科学院质量标准与检测技术研究所,昆明 650223;农业部农产品质量监督检验测试中心,昆明 650223)
玛咖及其制品的真实性是保障品质的关键。为了研究玛咖及其制品的差异,对玛咖制品进行真实性鉴别,分别以不同产地、色型的玛咖及玛咖制品为供试材料,对其进行高效液相色谱(high performance liquid chromatography,HPLC)指纹图谱不同识别方法的研究。采用Waters Symmetry ShieldTMC18(250 mm×4.6 mm,5 μm)色谱柱,乙腈-水为流动相梯度洗脱,检测波长210 nm,体积流量0.80 mL/min,各成分得到较好分离。经方法学验证,方法具有较好的精密度、重复性和稳定性。对19个玛咖样品和6个玛咖制品HPLC指纹图谱进行分析,确定了15个色谱峰为玛咖和其制品的特征指纹峰,建立了玛咖及其制品的指纹图谱。以数字化指纹图谱为基础,分别进行主成分分析、判别分析和相似度分析。结果表明,3种方法均能使玛咖与玛咖制品得到较为一致的模式识别结果。主成分二维平面图和判别分析能够区分玛咖和玛咖制品,具有简便、直观的特点,玛咖与玛咖制品相似度分析差异显著(P<0.05),分别为0.916和0.668,不同来源和色型的玛咖、玛咖制品间相似度均无显著差异(P>0.05)。结果显示玛咖制品具有玛咖的特征峰,但含量存在差异。3种方法均能准确地体现指纹图谱的一致性和特征性,为玛咖和玛咖制品的区分及玛咖制品真实性保障提供了参考。利用HPLC指纹图谱可对玛咖及其制品的真实性进行鉴别。
加工;模式识别;玛咖;高效液相色谱;指纹图谱
刘兴勇,邵金良,陈兴连,王 丽,黎其万,刘宏程.基于高效液相色谱指纹图谱的玛咖及其制品真实性识别 [J].农业工程学报,2016,32(6):302-307.doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.06.042 http://www.tcsae.org
Liu Xingyong,Shao Jinliang,Chen Xinglian,Wang Li,Li Qiwan,Liu Hongcheng.Authenticity identification of Maca and its product based on high performance liquid chromatography fingerprint[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE),2016,32(6):302-307.(in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.06.042 http://www.tcsae.org
0 引言
玛咖(Maca)Lepidium meyenii Walp.为十字花科植物,原产于海拔4 000~4 500 m的秘鲁安第斯山脉地区[1],营养成分丰富,是一种食药兼用植物,其中的酰胺[2]、膳食纤维[3]、芥子油苷和多酚[4]等功效成分增加了玛咖的附加值,成为衡量其质量的指标。经研究表明玛咖根茎具有改善记忆、增强免疫、增强精子活力、抗疲劳、抗氧化等多种功效[5-8],中国于2011年经卫生部第13号公告批准玛咖为新资源食品,并大规模引种栽培成功。新鲜玛咖经过一定加工工艺制成干片、粉末和药剂等商品化产品,但由于产品失去玛咖原有的感官特性及加工过程中添加其它假冒成分,从外观上极难鉴别其真伪和确保质量。近年来中国玛咖产业的快速发展导致缺乏质量评价和真伪鉴别的方法和依据,市场较混乱。因此,如何保障玛咖及其制品的品质及真实性成为发展玛咖产业亟待解决的问题。
对玛咖的真伪鉴别技术正在进行探索性研究中。Jim[9-10]、Chen[11]等分别采用GC/MS(气相色谱-质谱联用仪,gas chromatography-mass spectrometer)、近红外光谱技术从挥发油的独特图谱特征和分子生物学技术对玛咖和易混淆品进行了鉴别和质量评价,该技术适用于玛咖原材料的鉴别。挥发性成分的含量相对较低,影响因素多,检测分析对仪器要求较高。市场中的玛咖制品往往是玛咖粉碎后添加其它易混品制成,同样含有玛咖的独特成分,如玛咖酰胺、芥子油苷等提取物含量被作为衡量玛咖及其产品质量的主要标准之一[12]。研究表明,游离脂肪酸和苄胺是生成玛咖酰胺的前体,玛咖干燥过程中组织软化破坏,释放游离脂肪酸,芥子油苷内源性代谢水解生成异硫氰酸酯的同时产生大量苄胺[2]。玛咖中芥子油苷含量受到样品色型、状态、干燥方式等影响[13],从而导致玛咖酰胺含量产生差异,且芥子油苷广泛存在于玛咖茎、叶和十字花科植物中[14]。因此,不能单独从玛咖酰胺和芥子油苷等含量来判别玛咖及其制品的真实性。针对玛咖及其制品真伪鉴别的报道较鲜见,需要建立广泛适用的方法。玛咖及其制品均为多组分复杂体系,因此鉴别其真实性应采用与之相适应的,且能提供丰富鉴别信息的检测方法。通过建立高效液相色谱指纹图谱能较为全面地反映玛咖及其制品中化学成分的种类与数量,进而对质量进行整体描述和评价。相关学者采用高效液相色谱法对玛咖中的酰胺类、玛咖烯和芥子油苷等组分进行了研究[15-16],为从HPLC(高效液相色谱,high performance liquid chromatography)指纹图谱来鉴别玛咖及其制品的真伪和保障质量提供了参考,并且高效液相色谱技术方便快捷,已广泛应用在茶叶[17-18]、中药[19]等鉴别和评价。
本研究以玛咖及其制品为试验对象,旨在建立玛咖及其商品化产品HPLC指纹图谱,并通主成分分析、判别分析和相似度评价等识别方法和模式,对玛咖及其制品指纹图谱进行分析,为玛咖及其制品的区分及玛咖制品真伪鉴别提供参考。
1 材料与方法
1.1 仪器、试剂与材料
Waters Alliance 2695高效液相色谱仪(美国Waters公司),包括四元泵溶剂淋洗系统、自动进样系统,2487紫外检测器,Empower色谱工作站;Laborata 4000-efficient旋转蒸发仪(德国Heidolph公司);AE100型电子分析天平(梅特勒-托利多仪器有限公司);KQ500-E型超声清洗器(江苏昆山市超声仪器有限公司)。乙腈(德国Merck公司)色谱纯;哇哈哈矿泉水;石油醚(国药集团)分析纯。玛咖产地为云南丽江、香格里拉、会泽、寻甸、四川雅安、西藏曲水、林周县,并经鉴定确认为玛咖的地下根茎部分,玛咖制品为玛咖干片、片剂,购自市场,具体来源见表1。
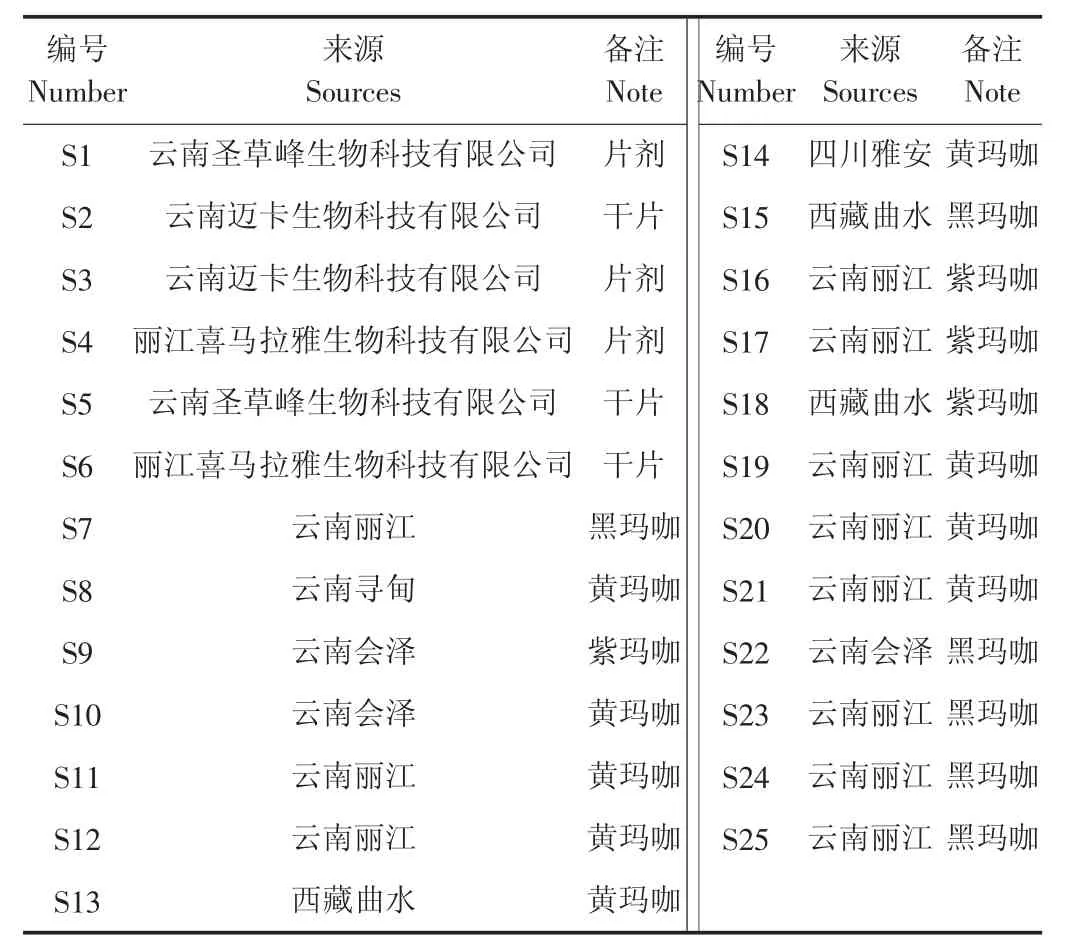
表1 玛咖来源信息Table 1 Information about sources of Maca
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 液相色谱条件
色谱柱Waters Symmetry ShieldTM(C18,5 μm,4.6×250 mm);进样量10.0 μL;柱温30.0℃;检测波长210 nm;流速为0.80 mL/min;流动相A为水,流动相B为乙腈;玛咖石油醚提取成分复杂,经条件优化处理,将梯度洗脱程序设计为:0~10 min,80%A→10~35 min,80%~60%A→35.0~40.0 min,60%~40%A→40~45 min,40%~35%A→45~50 min,35%~20%A→50~55 min,20%~60%A→55~65 min,60%~80%A。
1.2.2 供试液的制备
晒干样品和制品用粉碎机粉碎过60目筛,依据玛咖热风干燥特性[20]于电热鼓风干燥箱中70℃干燥至恒质量,自封袋密封保存于干燥器皿中。供试液制备参照文献[15],精确称取烘干的粉末约1.000 g,置于100 mL锥形瓶中,加入石油醚10 mL,200 MHz超声30 min,放置至室温后过滤,旋转蒸发仪浓缩至干,加入5 mL乙腈溶解,经0.45 μm微孔滤膜过滤备用。
1.2.3 数据处理
将样品按给定的色谱条件进行操作,记录色谱图如图1,横坐标表示色谱峰的出峰时间,纵坐标表示色谱峰的响应值大小,建立指纹图谱,指纹图谱的评价采用相似度进行。相似度反映了不同样品间在某种恒定分析情况下特定成分在含量及组成上的相似程度,常用来对中药进行质量及真伪的鉴别。相似度计算常用夹角余旋法,夹角余弦是将指纹图谱数据视为多维空间向量,使指纹图谱的相似性问题转化为多维空间中向量间的相似问题,计算按公式(1)进行。
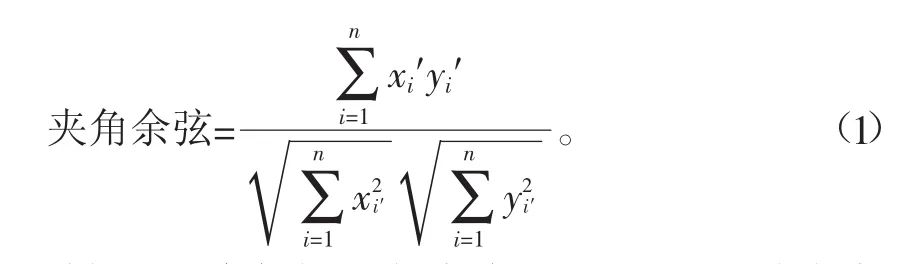
式中xi′为样品图谱中各共有峰峰面积;yi′为对应的标准图谱中每个组分峰面积。以所有样品中都出现的峰为共有峰,采用均值法产生标准图谱R,以样品中每个共有峰峰面积平均值为对应标准图谱峰面积。采用“中药色谱指纹图谱相似度评价系统A版”软件绘制图谱叠加图。用SPSS17.0软件进行主成分分析和判别分析来评价指纹图谱对玛咖及其制品质量评价及真伪鉴别的可靠性。
2 结果与分析
2.1 方法学试验
通过对同一批样品进行精密度试验、稳定性试验、重复性试验,以色谱峰9为参照峰,各主要色谱峰相对保留时间RSD(relative standard deviation)值均分别小于3.5%,相对峰面积RSD值小于5%,表明仪器精密度良好,重复性好,供试液在24 h内稳定。
2.2 指纹图谱的建立
将样品供试液按上述HPLC指纹图谱方法测定,将19份玛咖样品粉末及6份玛咖制品按给定的方法条件进行操作,记录HPLC色谱图如图1。图1为共有峰图谱,横坐标表示色谱峰出峰时间,纵坐标表示色谱峰响应值大小,共标定15个色谱峰作为HPLC指纹图谱的共有峰,15个共有峰的面积占总峰面积在92.5%~97.8%之间,其中9号峰分离完全,出峰时间适中,峰面积较大,在各样品中均存在,设为参照峰。
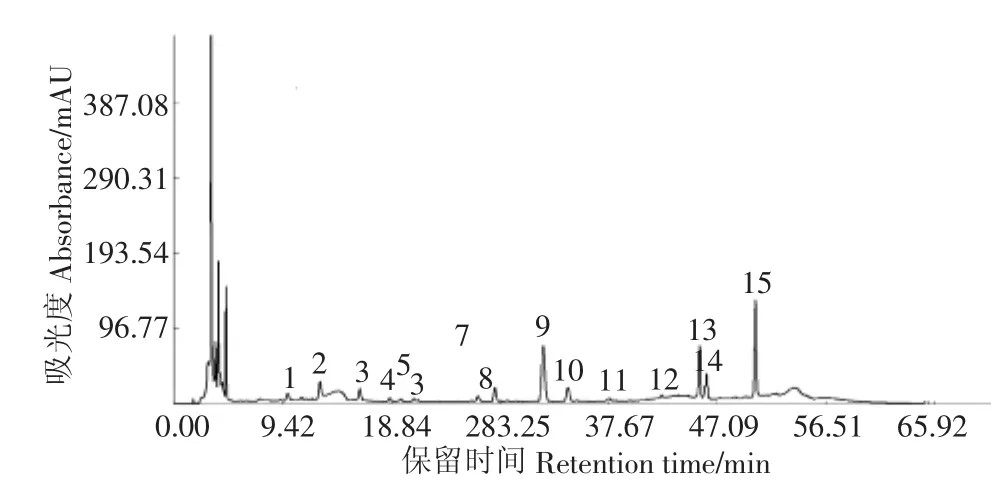
图1 玛咖共有峰HPLC图谱Fig.1 HPLC of common peak of Maca
2.3 玛咖及其制品指纹图谱的模式识别
2.3.1 主成分分析
主成分分析(principal component analysis,PCA)是对多变量数据进行降维处理的一种方法,可用较少的变量去解释原来样品中的大部分变量,选出比原始变量个数少又能解释大部分样品变量的几个新变量,并用以解释样品的综合性和差异性。为验证所建指纹图谱对玛咖与玛咖制品区别的可靠性,以HPLG指纹图谱中标定的15个共有峰峰面积原始数据为变量,用SPSS 17.0统计分析软件对数据进行主成分分析,依据主成分个数提取原则提取特征根大于1的主成分,得到成分载荷矩阵结果见表2。成分载荷矩阵中每一列数值表示相关变量与提取主成分间的相关系数,其绝对值越大,则主成分对该变量的代表性也越大。15个共有峰中共提取5个主成分,累计贡献率为100%。第1主成分特征值为6.384,方差贡献率为42.558%,包含了共有峰1、2、3、6、7、9、10、11和13的信息;第2主成分特征值为3.443,方差贡献率为22.956%,包含峰5、8和12的信息;第3主成分特征值为2.523,方差贡献率为16.818%,代表峰15的信息;第4主成分特征值为1.568,方差贡献率为10.450%,代表峰14的信息;第5主成分特征值为1.083,方差贡献率为7.218%,代表峰4的信息。从累计贡献率来看,取前4个主成分时,累计贡献率为92.78%。根据主成分分析原理,取前4个为主要成分足可以说明各指标的信息。以表2第1、2主成分载荷建立PCA因子分布平面图,见图2,除制品中的S2样品外,玛咖和玛咖制品可以区分开,说明二者差异主要集中在前2个主成分中。
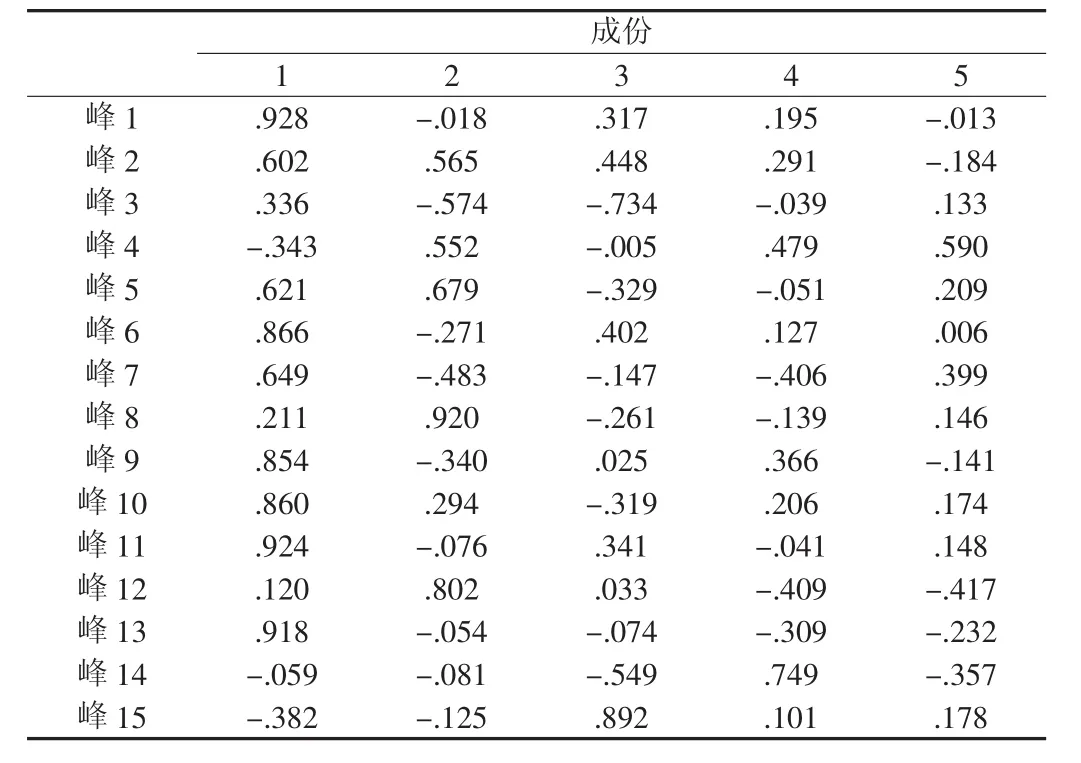
表2 成分载荷矩阵Table 2 Component loading matrix

图2 供试样品指纹图谱主成分分析Fig.2 Principal component analysis of fingerprints obtained from samples
2.3.2 玛咖及其制品判别分析
线性判别分析(linear discriminant analysis,LDA)是以部分样品数据信息建立判别模式,再用判别模式对另一部分样品进行验证,从而达到区分鉴别目的的一种数据分析方法,常与主成分分析相互补充应用。以指纹图谱中标定的共有峰原始峰面积为变量,用SPSS17.0软件进行判别分析,将分类样品设为玛咖和制品两类,共有峰峰面积为自变量,采用留一法交叉验证,将每一个样本作为测试样本,其它样本作为训练样本来衡量分类结果。输出预测分类结果见表3。玛咖和玛咖制品在初始判别中正确率均为100%,交叉验证中玛咖有一个样品(S7)误判为玛咖制品,正确率为94.7%,对玛咖制品的判别正确率为100%,整体正确率为97.4%。判别分析结果与主成分分析结果高度一致,进一步证明所建玛咖和玛咖制品指纹图谱具有较好代表性。
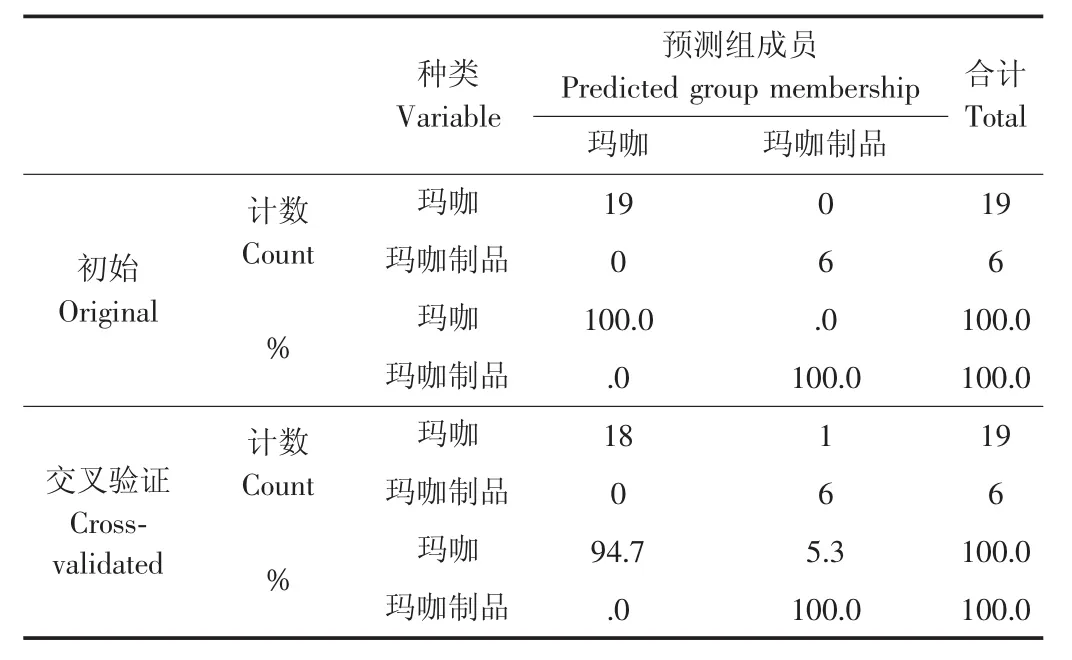
表3 判别分析结果Table 3 Result of discriminant analysis
2.3.3 相似度分析
为进一步验证主成分和判别分析的结果,对指纹图谱进行相似度分析。相似度可通过数字化形式直接反映出玛咖与玛咖制品的差异。相似度计算结果见表4。方差分析结果表明,玛咖和玛咖制品相似度差异较大(P< 0.05),玛咖相似度平均值为0.916,除S7外都在0.80以上,玛咖制品相似度平均值为0.668,除S2外相似度均在0.80以下。相似度分析结果在主成分分析和判别分析中均得以体现。不同玛咖制品间相似度差异不显著(P>0.05),玛咖干片平均相似度为0.737,片剂为0.598。不同产地玛咖相似度差异不显著(P>0.05),会泽、丽江、曲水分别为0.882,0.928和0943。不同色型玛咖相似度差异不显著(P>0.05),黄、紫、黑玛咖分别为0.920、0.922和0.904。不同产地及色型的玛咖相似度均无显著差异,说明所建指纹图谱具有针对性和整体性。从图3a指纹图谱叠加图可看出玛咖制品共有色谱峰峰面积较小,说明玛咖在加工过程中可能损失了相关组分。规模化玛咖干燥多采用自然晾干,温度相对较低,细胞不易损伤,对玛咖中成分保存较好[20],而真空干燥由于细胞的破损,温度的波动及黑芥子酶对芥子油苷的水解作用使芥子油苷显著降解[13,22]。从图3b的不同色型玛咖与玛咖制品的对照图谱来看,不同色型玛咖共有峰一致,而制品色谱图中出现许多非共有峰,说明加工中可能添加了其他成分。因此,通过指纹图谱相似度分析可以用来鉴别玛咖及其制品真实性。
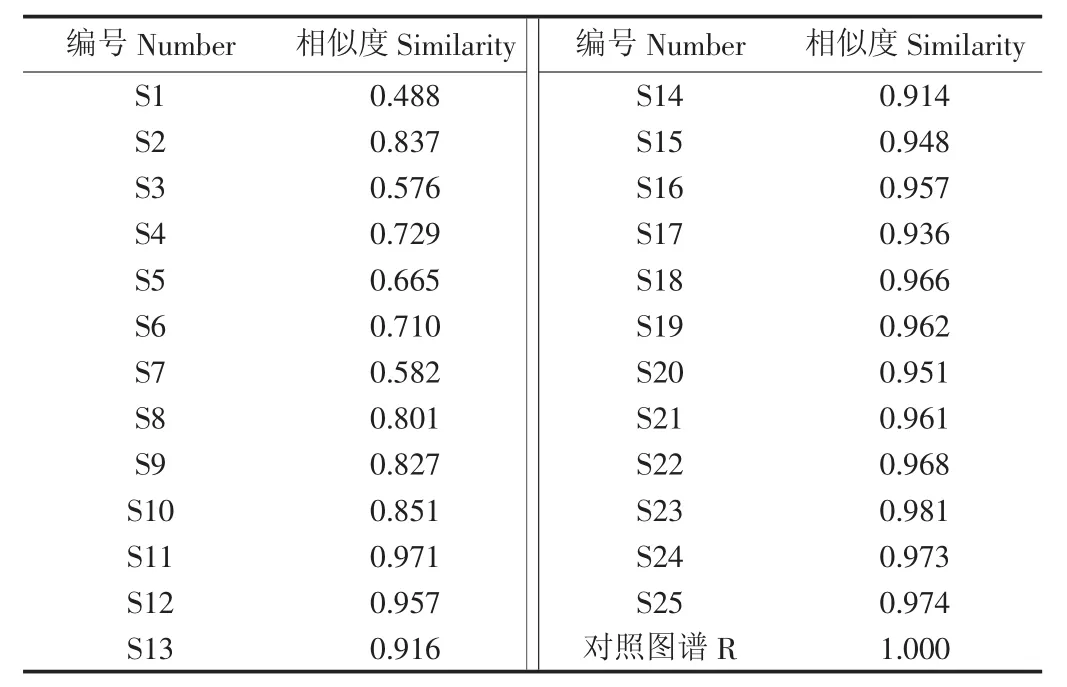
表4 玛咖指纹图谱相似度Table 4 Similarity evaluation on Maca
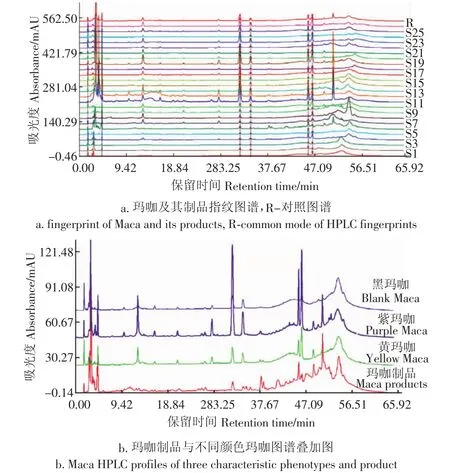
图3 玛咖及其制品HPLC指纹图谱Fig.3 HPLC fingerprint for Maca and products
通过玛咖HPLC指纹图谱中共有峰的存在可对玛咖制品真实性进行识别,但指纹图谱无法反映制品中玛咖的含量,且玛咖制品中有效成分的含量影响因素众多[12,20],制品在没有添加其他成分情况下,由于加工工艺等影响也可导致有效成分含量降低而存在差异。将来需要结合质谱等手段进一步研究玛咖中添加外来成分有效成分含量变化,确定制品中玛咖的比例等。
3 结论
玛咖制品与玛咖具有共同指纹峰,可以反映玛咖制品的真实性。通过玛咖和玛咖制品的HPLC指纹图谱,二者能够较好区分,说明二者在相关成分上具有差异。以主成分分析、判别分析和相似度分析三种模式进行识别,结果显示利用主成分分析和判别分析可以区分玛咖和玛咖制品。相似度分析表明玛咖和玛咖制品相似度差异较大(P<0.05),不同来源、色型玛咖之间、玛咖制品之间指纹图谱相似度无显著差异(P>0.05)。所建指纹图谱具有较好的稳定性和代表性,可用于玛咖及其制品的真实性识别。
[1]Gonzales G F,Cordova A,Vega K,et al.Effect of Lepidium meyenii(Maca),a root with aphrodisiac and fertility-enhancing properties,on serum reproductive hormone levels in adult healthy men[J].Journal Endocrinology,2003,176(1):163-168.
[2]Eliana E,Antonella H,Kofer W,et al.Bioactive maca(Lepidium meyenii)alkamides are a resultoftraditionalAndean postharvest drying practices[J].Phytochemistry,2015,116(8): 138-148.
[3]Chen J J,Zhao Q S,Wang L W,et al.Physicochemical and functional properties of dietary fiber from maca(Lepidium meyenii Walp.)liquor residue[J].Carbohydrate Polymers,2015, 32(5):509-512.
将上述所得数据均带入SPSS23.0统计学软件中,将两组患者的并发症发生率作为计数资料,采用(%)表示,行χ2检验;将患者的血糖水平、生活质量评分作为计量资料采用(±s),行 t检验;P<0.05 为差异有统计学意义。
[4]David C,Rosana C,Omar B,et al.Optimized methodology for the simultaneous extraction of glucosinolates, phenolic compounds and antioxidant capacity from maca(Lepidium meyenii)[J].Industrial Crops and Products,2013,49:747-754.
[5]Rubio J,Caldas M,Davila S,et al.Effect of three different cultivars of Lepidium meyenii(Maca)on learning and depression in ovariectomized mice[J].BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine,2006,6(1):23-29.
[6]JunLee K,Dabrowski K,Rinchard J,et al.Supplementation of maca(Lepidium meyenii)tuber meal in diets improves growth rate and survival of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum)alevins and juveniles[J].Aquaculture Research, 2004,35(3):215-223.
[7]Gonzales C,Rubio J,Gasco M,et al.Effect of short-term and long-term treatments with three ecotypes of Lepidium meyenii (MACA)on spermatogenesis in rats[J].Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 2006,103(3):448-454.
[8] 何钊,冯颖,徐珑峰,等.云南种植玛咖乙醇提取物的体外抗氧化活性分析[J].食品科学,2010,31(15):39-43. He Zhao,Feng Ying,Xu Longfeng,et al.In vitro antioxidant activity of extract of maca(Lepidium meyenii walpers)cultivatedin Yunnan[J].Food Science,2010,31(15):39-43.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[9]Jin Wenwen,Xiong yue,Yu Longjiang.Identification and quality evaluation ofLepidium meyenii.(Maca)based on gas chromatographic analysis of its essential oils from roots[J]. Agricultural science&technology,2006,7(3):2-9.
[10]Jin W W,Zhang Y Z,Mei S,et al.Identification of Lepidium meyenii(Walp.)based on spectra and chromatographic characteristics of its principal functional ingredients[J].Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2007,87(12):2251-2258.
[12]Melnikovova I,Havlik J,Cusimamani E F,et al.Macamides and fatty acids content comparison in maca cultivated plant under field conditions and greenhouse[J].Bol Latinoam Caribe Plant Med Aromat,2012,11(5):420-427.
[13]甘瑾,冯颖,张弘,等.三种色型玛咖芥子油苷组分及含量分析[J].中国农业科学,2012,45(7):1365-1371. Gan jin,Feng ying,Zhang hong,et al.Analysis on composition and content of glucocinolate in three color types of maca (Lepidium meyenii)[J].Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2012,45(7): 1365-1371.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[14]Fahey J W,Zalemann A T,Talaley A T.The chemical diversity and distribution of glucosinolates and isothiocyanates among plants[J].Phytochemistry,2001,56(1):5-51.
[15]Ganzera M,Zhao J P,Muhammad I,et al.Chemical Profiling and Standardization of Lepidium meyenii(Maca)by Reversed Phase High Performance Liquid Chromatography[J].Chem.Pharm. Bull.2002,50(7):988-991.
[16]Li G,Ammermann U,Quirós C.Glucosinolate contents in maca (Lepidium peruvianum Chacón)seeds,sprouts,mature plants and several derived commercial products[J].Economic Botany, 2001,55(2):255-262.
[17]He X Y,Li J K,Zhao W,et al.Chemical fingerprint analysis for quality control and identification of Ziyang green tea by HPLC [J].Food Chemistry,2015,171(3):405-411.
[18]胡燕,齐桂年.南路边茶高效液相色谱指纹图谱的建立[J].现代食品科技,2013,29(9):2283-2287. HU Yan,QI Guinian.Establishment of high performance liquid chromatographicfingerprint of southern route tea[J].Modern Food Science and Technology,2013,29(9):2283-2287.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[19]陈东东,周萍,白钢钢,等.基于HPLC中药指纹图谱技术延胡索药材及其制剂的质量控制探讨[J].中国中药杂志,2015,40(12):2470-2473. Chen Dongdong,Zhou Ping,Bai Ganggang,et al.Discussion of HPLC fingerprint of traditional Chinese medicine of Corydalis yanhusuo and its preparation[J].China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2015,40(12):2470-2473.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[20]张弘,郑华,于连松,等.玛咖真空干燥特性及工艺参数优化[J].农业工程学报,2012,28(增刊1):267-272. Zhang Hong,Zheng Hua,Yu Liansong,et al.Vacuum drying characteristics and technological parameters optimization of maca[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering(Transactions of the CSAE),2012,28(Supp.1):267-272.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[21]涂行浩,张弘,郑华,等.贮藏温度对玛咖根块采后品质的影响[J].食品科学,2013,34(2):282-287. Tu Xinghao,Zhang Hong,Zheng Hua,et al.Effect of storage temperature on postharvest of maca tuber[J].Food Science, 2013,34(2):282-287.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[22]Yábar E,Pedreschi R,Chirinos R,et al.Glucosinolate content and myrosinase activity evolution in three maca(Lepidium meyeniiWalp.)ecotypesduring preharvest,harvestand postharvest drying[J].Food Chemistry,2011,127(4):1576-1583.
Authenticity identification of Maca and its product based on high performance liquid chromatography fingerprint
Liu Xingyong,Shao Jinliang,Chen Xinglian,Wang Li,Li Qiwan,Liu Hongcheng※
(Institute of Quality Standards and Testing Technology,Yunnan Academy of Agricultural Sciences,Kunming 650223,China;Supervision&Testing Center for Farm Products Quality,Ministry of Agriculture,Kunming 650223,China)
Maca has many health benefits and high price in China and the products may be adulterated,so authenticity is important to its quality.In order to identify the authenticity of maca products and analyze difference of maca and its products,chromatographic fingerprint peaks identification and difference analysis were used at Yunnan Academy of Agricultural Sciences(YAAS),Kunming city,Yunnan province,China,in 2015.Common maca products including tablets and dry film were purchased on Kunming markets and different ecotypes and regions maca collected from Lijiang,Tibet and Huize,which have big planting scale with representative.Fresh maca samples were by natural drying and smashed to powder less than 60 mesh,then dried to constant weight by drier at 70℃.About 1.000 g dried sample was ultrasonic extraction under 200 MHz with 10 mL petroleum ether for 30 min,then filtered with filter paper,rotary evaporator was usedto concentrate dry,added 5 mL acetonitrile to dissolve extract,and filtered by 0.45 μm filter membrane.Chromatographic peaks of maca were separated effectively by use A Waters Symmetry ShieldTMC18column with a detection wavelength of 210 nm and a gradient program with acetonitrile-water,and under 0.80 mL/min flow rate.According to the method validation,method has high precision,good repeatability and stability,and same batch maca samples chromatographic peaks relative retention time and relative peak area standard deviation relative values were less than 3.5%and 5%, respectively.19 batches of maca samples and 6 maca products fingerprint were analyzed,and the number 9 peak was set as reference peak to correct retention time because of separated complete,moderate appearance time,and larger peak area and all samples were existed.15 common characteristic peaks were determined of maca and its products basis retention time, their area accounted 92.5%-97.8%for total peak area,established the high performance liquid chromatography(HPLC) fingerprint of maca and its products,and digital fingerprint was also established based on relative retention time and corresponding peak area.Maca products common chromatographic peaks area were smaller compared with maca,and also contained some non-common peaks,this explained some components were lose in process and other components was added. Fingerprint for maca(Lepidium meyenii Walp.)and maca products was investigated based on three different recognition methods such as principal component analysis(PCA),discriminant analysis(LDA)and similarity analysis.PCA was performed based on digital fingerprint.PCA extracted characteristic root was greater than 1,then 5 principal components were extracted representing the information of sample,and cumulative contribution rate was 100%with component loading matrix.Two-dimensional scatter plot was drawn by use principal component 1 and 2 loading,so maca and its products can be distinguished by scatter plot.LDA divided samples into two categories,then chromatographic peaks area were as independent variable and one cross validation was used,and the classification result had 97.4%correct recognition rate for maca and its products.Maca samples could be distinguished obviously from maca product samples by using method of either two-dimensional map or LDA.Similarity were calculated by included angle,and similarity analysis indicated that maca and its products have difference(P≤0.05),and similarity value were 0.916 and 0.668,respectively,and not only no significant differences(P≥0.05)between different origins and ecotypes maca,but also between maca products.Maca from Huize,Lijiang,Tibet were 0.882,0.928 and 0943,respectively.Different ecotypes Maca of yellow,purple and blank were 0.920,0.922 and 0.904,respectively.Maca dry film and tablets were 0.737 and 0.598,respectively.The results showed that each of the three employed methods could reflect consistent pattern recognition results and characteristics of fingerprint. The results showed that maca products have characteristic components of maca,but their content had differences.This could provide an identification method and reference for guaranteeing the authenticity and quality of Maca products.
processing;pattern recognition;Maca;high performance liquid chromatography;fingerprint chromatography
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.06.042
TS207.7
A
1002-6819(2016)-06-0302-06
2015-07-18
2016-01-11
云南省科技惠民专项(农业)重点项目(2014RA054)
刘兴勇(1985—),男,主要从事农产品品质研究。昆明 云南省农业科学院质量标准与检测技术研究所,650223。
Emial:liuxingyong0993@163.com
※通信作者:刘宏程,博士,研究员,从事农产品质量与品质分析检测。昆明 云南省农业科学院质量标准与检测技术研究所,650223。
Emial:liuorg@163.com

