Effect of steam explosion treatment on phenolic acid composition of wheat bran and its antioxidant capacity
Liu Chong,Zhang Ruiting,Liu Benguo,Zheng Xueling※
(1.College of Grain and Food,Henan University of Technology,Zhengzhou 450001,China;2.School of Food Science, Henan Institute of Science and Technology,Xinxiang 453003,China)
Effect of steam explosion treatment on phenolic acid composition of wheat bran and its antioxidant capacity
Liu Chong1,Zhang Ruiting1,Liu Benguo2,Zheng Xueling1※
(1.College of Grain and Food,Henan University of Technology,Zhengzhou 450001,China;2.School of Food Science, Henan Institute of Science and Technology,Xinxiang 453003,China)
The effects of steam explosion Steam explosion pretreatment is widely used at industrial scales.In this study,we mainly focused on the effects of steam explosion treatment(SET)on the phenolic acid composition and antioxidant activities of wheat bran, to provide theoretical support for the wheat industry development.The SET was performed at different pressures(0.5,1.5,2.5 MPa) and different residence times(30 s,90 s).It was prior to rapid decompression(explosion)brought about by opening the ball valve.The exploded materials were collected,dried under vacuum and powdered.The phenolic compounds in wheat bran were divided into 2 fractions by methanol extraction and alkaline hydrolysis,the free phenolic acids and the bound phenolic acids.Different fractions contained different phenolic acid profiles,so High-performance liquid chromatography(HPLC)was used for analysis of main phenolic acids(vanillic acid,syringic acid,4-coumaric acid,ferulic acid)in 280 nm and 320 nm.The total phenolic content of the sample was discussed before and after SET.Several authoritative methods of antioxidant capacity,like 2,2-Diphenyl-1-(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl) hydrazyl(DPPH)radical-scavenging capacity,reducing capacity and 2,2′-Azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) diammonium salt(ABTS)radical scavenging assay,antioxidant assay in a linoleic acid system were also determined in this paper.The results indicated that the contents of main phenolic acids increased with SET.In the free phenolic acids,the content of vanillic acid was increased about 50%after steam explosion.The significant increasing in the contents of syringic acid,4-coumaric acid and ferulic acids could be observed,at 2.5MPa 30s,the increasing of content was separately 10,36,11-fold higher than that of the untreated one.Also,when the wheat bran was treated at 2.5 MPa with 30 s,the highest contents of these free phenolic acids was obtained except vanillic acid,and the further increase of the treatment pressure or time could decrease the content of the phenolic acids in wheat bran.In the bound phenolic contents,it demonstrated that the contents of syringic acid,4-coumaric acid,ferulic acids increased with increasing SET to reach a peak at 2.5 MPa with 30 s,and then decreased.The highest contents were 36.561±0.544, 39.025±0.202,1 442.474±42.990 μg/g separately at 2.5 MPa with 30 s.The content of ferulic acids ranged from 59.060±4.310 to 1 442.474±42.990 μg/g,nearly increased 25 times higher than the untreated one,which indicated that the SET is an effect method to free the phenolic acids in wheat bran.We also found that the bound phenolic contents of vanilic acid and ferulic acid were significantly higher than the free phenolic contents,indicating that these two major phenolic acids in wheat bran were not extractable by aqueous methanol but released upon alkaline hydrolysis.Especially for ferulic acid,the content in bound part was nearly 4.4 times higher than that in free part.The total phenolic content of the sample was detected by the Folin-Ciocalteu method.There was no difference between the untreated sample and steam-exploded samples at 0.5 MPa.Then,with the increase of treatment time and pressure of steam explosion,the total phenolic contents increased with increasing SET to reach a peak at 2.5 MPa,30 s,and then decreased.The total phenolic content of the sample treated at 2.5 MPa,30 s was 28 mg/g,nearly 9 times higher than the untreated one.Several authoritative methods of antioxidant capacity gave the consistent conclusion,compared with the untreated sample,the steam-exploded wheat bran showed the higher DPPH and ABTS radical scavenging activities,antioxidant activity in a linoleic acid system and reducing power.SET is an efficient pretreatment method to release the insoluble bound phenolic acids and enhance the antioxidant capacity of wheat bran.The analysis indicates that when the wheat bran is treated by 2.5 MPa with 30 s,the release content of phenolic acids reach is the best and the antioxidant activity reach is the highest in the treatments.
steam;crops;wheat bran;steam explosion;phenolic acid;antioxidant activity
Liu Chong,Zhang Ruiting,Liu Benguo,Zheng Xueling.Effect of steam explosion treatment on phenolic acid composition of wheat bran and its antioxidant capacity[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering(Transactions of the CSAE), 2016,32(6):308-314.(in English)doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.06.043 http://www.tcsae.org
刘 翀,张瑞婷,刘本国,郑学玲.蒸汽爆破处理对麦麸的酚酸组成及其抗氧化活性的影响[J].农业工程学报,2016,32(6):308-314. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.06.043 http://www.tcsae.org
0 Introduction
Wheat bran is one of the main by-products of wheatmilling industry. Wheat bran mainly contains two physiological active substances,namely polysaccharides and phenolic compounds.The wheat phenolic compounds are mainly phenolic acids,flavonoids and lignans.Ferulic acid is the most important phenolic acid[1],so it is an excellent free radical scavenger and possesses the strong antioxidant capacity,which plays an important role in the prevention of cancer[2].
Chinese wheat production is the highest in the world. According to statistics,currently the mean effective utilization rate of world's food resources is less than 60%,especially for the processing by-products,such as oat bran and wheat germ. The wheat bran production in China is as high as more than 30 million tons every year.While,most was used in feed,wine, vinegar and soy sauce,only a small amount was used for deep processing,which causes the waste of wheat resource.
Steam explosion was invented by W.H.M Ason as early as 1928.First applications of the steam-explosion technology to pretreat the biomass were conducted in the early 1980s[3].It is an economical and promising process which has been widely used for the pretreatment of plant raw materials[4],such as hardwood lignin[5],raw garlic[6],bamboo stem[7].Nowadays,steam explosion pretreatment is widely used at industrial scales.The essence of the SET is that,it will suddenly release the compressed steam seeping into plant organization in a short time to produce low molecular weight substance[4].After steam explosion,cellulose and hemicellulose have different degree of degradation,cellulose and lignin are separated because of the structural fracture,thus increases the contact area with water and air,which makes them easier to achieve hydrolysis saccharification.Additionally,it has been reported that insoluble bound phenolics are abundant in cell walls and linked by hydrogen bonding,hydrophobic interactions,and covalent bonds such as ester bonds between phenolic acids and polysaccharides[4].The degradation of lignin and cellulose by steam explosion allows the release of phenolic acids which is bounded to it.It is reported that SET could effectively release bound phenolic compounds and enhance the antioxidant capacity of barley bran[4].Meanwhile,the environmental impact of steam explosion is alsomore limited because this technology does not use any(or very little)chemical agent[3-4].
The comprehensive utilization of wheat bran is the development trend of grain and oil food industry.One possible strategy for improving the bioavailability of wheat bran phenolics is to release the insoluble bound phenolic acids. This could be achieved using aqueous phase chemical[8], enzymatic[9],and/or fermentation methods[10].Whether SET could also be an effect method?To our knowledge,there is no comprehensive report on the utilization of steam explosion pretreatment for the generation of antioxidant from wheat bran biomass.In this study,we mainly focused on the effects of SET on the phenolic acid composition and antioxidant activities of wheat bran,to provide theoretical support for the development of wheat industry.
1 Experimental section
1.1 Chemicals
The wheat bran was form Xinliang Flour Company. Anhydrous ethanol,methanol,vanillic acid,syringic acid,4-coumaric acid,ferulic acid,trichloroacetic acid(TCA),ferric chloride,ammonium thiocyanate,ferrous chloride,hydrochloric acid,potassium persulfate,gallic acid,the forint phenol, disodium hydrogen phosphate,sodium dihydrogen phosphate, iron hydride potassium,sodium carbonate,2,2-Dipheny-lpicrylhydrazyl(DPPH),ABTS,linoleic acid were purchased from Sigma.
1.2 Steam explosion treatment
The relationship could be established between the temperature(pressure)of the process and the retention time, resulting in an improvement of the hydrolysis yields[3].In this study,steam explosion was performed using a QBS-80 batch steam explosion apparatus(Hebi Gentle Bioenergy Ltd., China).The materials were steamed for different pressures (0.5,1.5,2.5 MPa)and times(30 s and 90 s),prior to rapid decompression(explosion)brought about by opening the ball valve.The exploded materials were collected,dried under vacuum and powdered.
1.3 Determination of phenolic acid composition
Phenolic acids were extracted and analyzed using HPLC[2,11-12].Briefly,the powder(5 g)was extracted three times with 200 mL of 80%methanol for 1h at 70℃ .After centrifugation, the supernatants were combined, then concentrated by rotary evaporation at 50℃,filtered,adjusted to pH 1-2 using 6 M HCl.The clear supernatant was extracted with diethyl ether/ethyl acetate(1∶1,v/v)for five times at 1∶1(v/v)solvent to supernatant ratio.The ether/ethyl acetate extracts were rotary evaporated to dryness by vacuumevaporator at 50℃.The dried extract was dissolved into 10 mL by methanol to obtain the free phenolic acid fraction.Then, the water phase was treated by 20 mL 4 M NaOH for 4 h under a nitrogen atmosphere at 40℃,adjusted to pH 1-2 using 6 M HCl,then rotary evaporated to dryness by vacuum-evaporator at 50℃.And the dried extract was dissolved into 10 mL by methanol to obtain the bound phenolic acids.
The analysis of phenolic compounds in wheat bran was determined according to the method described by Kim.et al[2], with modifications.A sample of 10 μL was analyzed using Agilent Technologies 1260 infinity equipped with C18(2) column(250 mm×4.6 mm).The mobile phase consisted ofacetonitrile(solvent A)and purified water with 1%acetic acid (solvent B).The flow rate was set at 1 mL/min and the column temperature was at 30℃.Gradient elution was performed as follows:0~30 min,100~88%solvent B;30~60 min,88~50% solvent B;60~70 min 50~0%solvent B;70~80 min,0~100% solvent B.
1.4 Preparation of the extract for antioxidant assays
The powder(2 g)was ultrasonic extracted five times with 30 mL of80% methonalsolution for20 min.After centrifugation at 3 000 r/min for 10 min,the supernatant was diluted to 250 mL by 80% methanol for the following antioxidant assays.
1.5 Measurement of total phenolic content
Folin-Ciocalteu method was used to determine the total phenolic content.Briefly,0.3 mL of the extract solution was diluted to 10 mL with distilled water,mixed with 0.5 mL of Folin-Ciocalteu phenol reagent.The reaction mixture was shaken vigorously.After 5 min,5 mL of 5%Na2CO3solution was added to mixture.H2O was added immediately to make a final volume of 25 mL.The solution was allowed to stand for 90 min.Then,the absorbance was read at 750 nm.The total phenolic content of extract solution was measured as gallic acid equivalents[12].
1.6 DPPH radical scavenging assay
The DPPH radical scavenging assay was determined according to the published method[13].Two mL 0.2 mM of DPPH solution(dissolved in ethanol)was mixed with 2 mL of the extract solution.The solution mixture was shaken vigorously and incubated for 30 min in the dark at room temperature.After that,the absorbance was measured at 517 nm against the blank.Control was ethanol instead of the antioxidant solution,and reagent blank was ethanol instead of DPPH solution.The inhibition of the DPPH radical was calculated as follows:
DPPH scavenging activity(%):

1.7 Reducing power
Briefly,0.5 mL of the untreated and steam-exploded sample solution was mixed with 2.5 mL of phosphate buffer (0.2 M,pH 6.6)and 2.5 mL of 1%K3Fe(CN)6(dissolved in distilled water).The mixture solution was incubated at 50℃and rapidly cooled after 20 min.2.5 mL of 10%TCA was added to the mixture,which was then centrifuged at 3 000 rpm for 10 min.2.5 mL of supernatant was mixed with 2.5 mL of distilled water and 0.5 mL of 0.1%FeCl3,and the absorbance was read at 700 nm after 10 min.The reagent blank was 80% of methanol instead of sample solution.Increased absorbance of mixture solution indicated reducing power[14].
1.8 ABTS radical scavenging assay
Briefly,5 mL of ABTS(7 mM)was mixed with 88 μL of potassium persulphate(2.45 mM)and then was allowed to stand for 12 h in the dark at room temperature.The solution was diluted with phosphate buffered saline(0.05 M,pH 7.4)until the absorbance was 0.70±0.02 at 734 nm.The solution was kept for 30 min in the dark before being used.0.15 mL of the extract solution was mixed with 2.85 mL of the solution described above,shaken vigorously,and then left to stand at room temperature for 10 min.The absorbance of the reaction mixture was measured at 734 nm.The control was 80%of methanol instead of the sample solution.The ABTS radical scavenging capacity of the sample was calculated as follows:

1.9 Antioxidant assay in a linoleic acid system
The 200 μL of the extract solution was added to a solution mixture of 4 mL of phosphate buffer(0.05 M,pH 7.0),2 mL of 2.5%linoleic acid dissolved in ethanol and 4 mL of distilled water,left to stand for 30 min in the dark at 40°C.The level of lipid peroxidation was measured every 12 h by the ferric thiocyanate method[15].Briefly,100 μL of the sample solution was mixed with 8 mL of 75%ethanol,100 μL of 30% ammonium thiocyanate and 100 μL of 20 mM FeCl2(dissolved in 3.5%hydrochloric acid).After 3min at room temperature, the absorbance of the mixture solution was measured at 500 nm.The controls were 80%of methanol instead of the sample. The peroxidation inhibition percent was calculated according to the following formula:

2 Results and discussion
We stop the treatment condition at 2.5 MPa 90 s,when increasing the treatment pressures and residence time,the material would become burnt and the structure were broken seriously.There would be no significance to go on the research.
2.1 Composition and content of phenolic acids
The HPLC chromatograms of 4 standard phenolic acids (vanillic acid,syringic acid,4-coumaric acid,ferulic acid)are shown in Fig.1.The phenolic compounds extracted in wheat bran were divided into two fractions by methanol extraction and alkaline hydrolysis,which were the free phenolic acids and the bound phenolic acids.Different fractions contained different phenolic acid profiles.It was separately detected in 280 and 320 nm(Fig.2).Clearly,the contents of phenolic acid had an obvious increase after steam explosion,especially for ferulic acid.
Phenolic acids in wheat predominately exist in the insoluble bound form,ester linked to cell wall materials (celluloses and hemicelluloses)in wheat bran[4,10].According toGong,L.[4],steam explosion led to the hydrolysis of glycosidic bonds in the hemicelluloses and celluloses.It was beneficial for morphological change of phenolic acids and the release of phenolic acids combined to the hemicelluloses and celluloses. Concentrations of individual phenolic acids in different fractions in wheat bran are shown in Table 1 and Table 2.
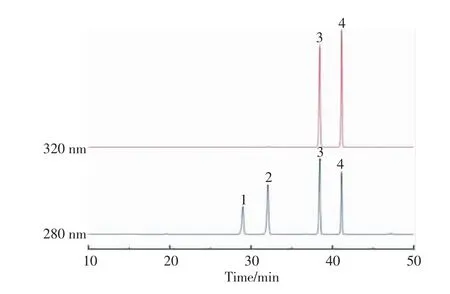
Fig.1 HPLC chromatograms of standard mixture of phenolic acids at 280 nm and 320 nm
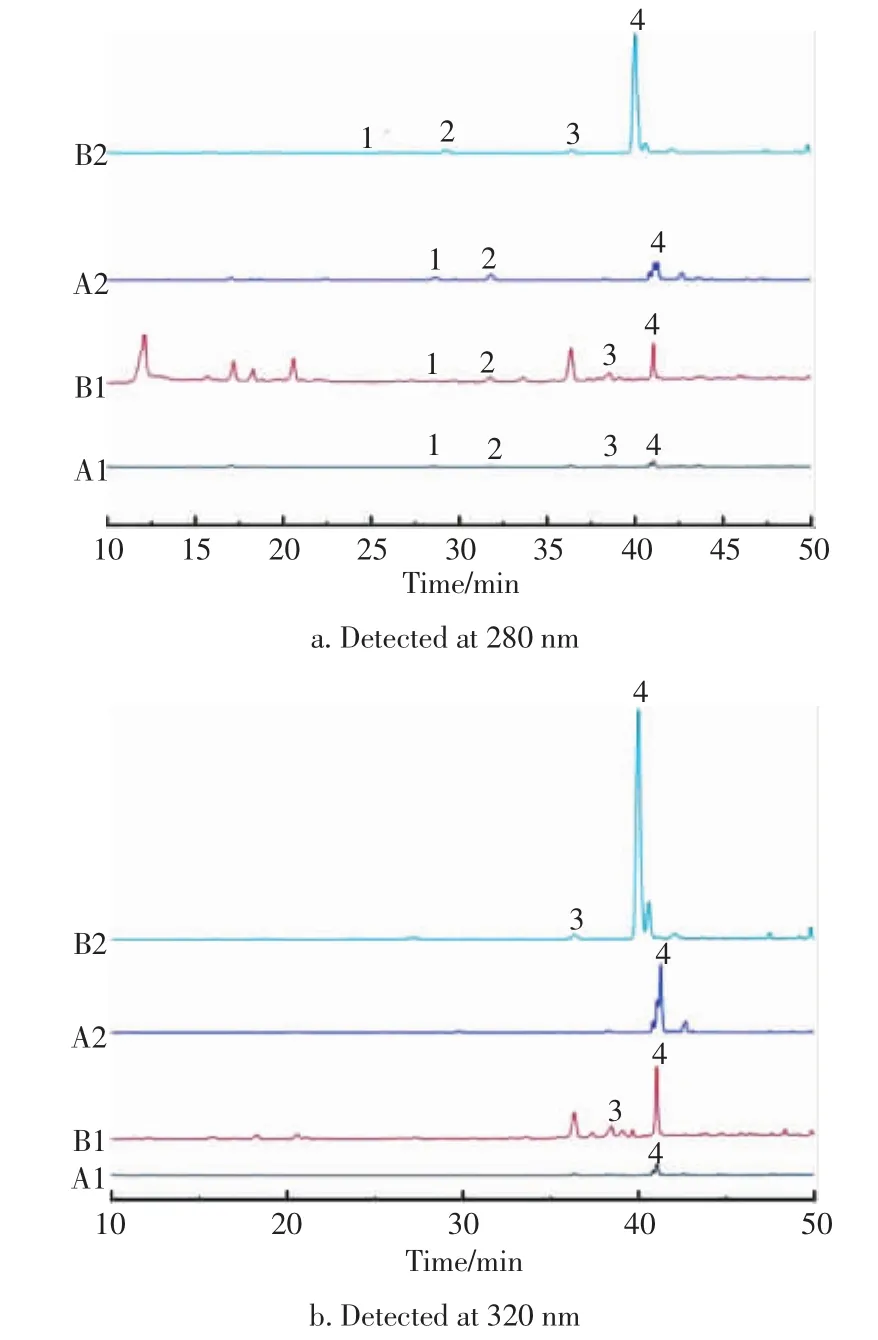
Fig.2 HPLC profiles of typical fractions of wheat bran extracts at 280 and 320 nm
The contents of free phenolic acids in the untreated and steam-exploded wheat bran are shown in Table 1.The content of vanillic acid was increased about 50%after steam explosion. The significant increasing in the contents of syringic acid,4-coumaric acid and ferulic acids could be observed,at 2.5 MPa 30 s,the increasing of content was separately 10,36,11-fold higher than that of the untreated one.Also,when the wheat bran was treated at 2.5 MPa with 30 s,the highest contents of these free phenolic acids was obtained except vanillic acid. And the further increase of the treatment pressure or time could decrease the content of the phenolic acids in wheat bran.
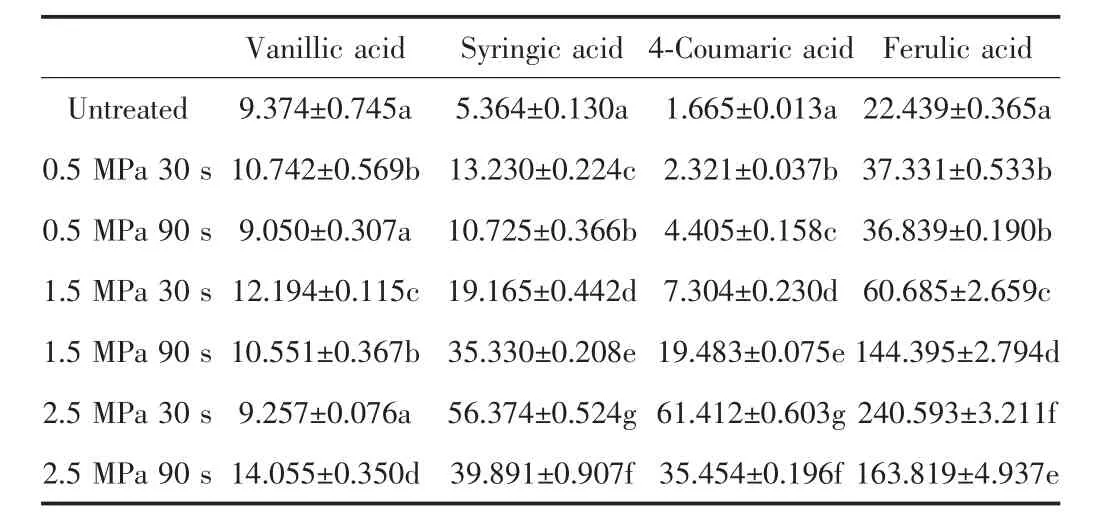
Table.1 Contents of main free phenolic acids of untreated and steam-exploded wheat bran(μg.g-1)
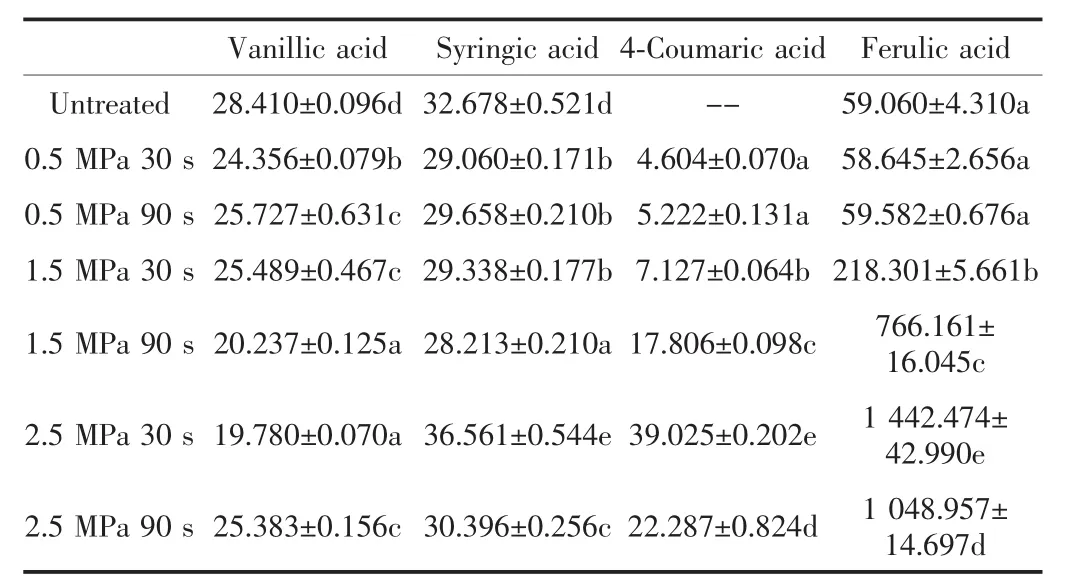
Table.2 Contents of main bound phenolic acids of untreated and steam-exploded wheat bran(μg.g-1)
Table 2 depicts the contents of bound phenolic acids of untreated and steam-exploded wheatbran.The bound phenolic contents of vanilic acid and ferulic acid were significantly higher than the free phenolic contents,indicating that these two major phenolic acids in wheat bran were not extractable by aqueous methanol but released upon alkaline hydrolysis.Especially for ferulic acid,the content in bound part reached 1 442.474±42.990 μg/g,which was nearly 4.4 times higher than that in free part.It demonstrates that the contents of syringic acid,4-coumaric acid,ferulic acids increased with increasing SET to reach a peak at 2.5MPa 30s, and then decreased.The highest contents were separately 36.561±0.544,39.025±0.202,1 442.474±42.990 μg/g at 2.5MPa 30s.The content of ferulic acids ranged from 59.060± 4.310 to 1 442.474±42.990 μg/g,nearly increased 25 times higher than the untreated one,which indicated that the SETwas an effect method to free the phenolic acids in wheat bran.
HPLC analysis indicated that ferulic acid was the main phenolic acid in wheat bran.The SET could release more ferulic acid from the bound fraction.The optimal treatment could be set at 2.5 MPa with 30 s.
2.2 Total phenolic content analysis
Many studies[1,13,16-18]have been carried out to prove the significant correlations between the phenolic contents and antioxidant activity.The total phenolic contents of the extract were determined by the Folin-Ciocalteu method are shown in Fig.3(a).There was no difference between the untreated sample and steam-exploded samples at 0.5 MPa. Then,with the increase of treatment time and pressure of steam explosion,the total phenolic contents increased with increasing SET to reach a peak at 2.5 MPa,30 s,and then decreased.The total phenolic content of the sample treated at 2.5 MPa,30 s was nearly 9 times higher than the untreated one.
When the wheat bran was treated at 2.5 MPa with 30 s, the total phenolic content reached 28 mg/g,which is significantly higher than previous reports:3.967 mg/g by the hydrolysis treatment[2],1.2 mg/g by the flavourzyme 500 L treatments at a level of 221 U/g[19]and 2.2~2.9 mg/g by the extraction of 50%acetone[1].

Fig.3 Total phenolic content and antioxidant activities of untreated and steam-exploded wheat bran.
2.3 DPPH radical scavenging activity
The DPPH radical scavenging capacity assay is a decolorization assay.The DPPH radical is stable organic nitrogen centered free radical with a characteristic dark purple color.When reduced to its nonradical form by antioxidants, the characteristic dark purple becomes colorless[20].
DPPH radical scavenging activities of the samples are showen in Fig.3(b).The results showed that the DPPH radical scavenging activities of the steam-exploded sample were higher than that of the untreated sample.And with the increase of time and pressure of stream explosion,the DPPH radical scavenging activities increased until 1.5 MPa,90 s.Then the DPPH radical scavenging activities remained basically unchanged,which indicated that the function of SET on the release of phenolic acids ester linked to cell wall materials was limited.After steam explosion in a certain treatment condition range,cellulose and hemicellulose had different degree of degradation,was beneficial for the release of phenolics acids.
2.4 Reducing power assay
Reducing power assay is a simple and reliable method commonly used for measuring the total antioxidant capacity. It is believed that antioxidant activity and reducing power are correlated.The reducing power of the samples is shown in Fig.3(c).It could be found that the reducing power of the steam-exploded sample was higher than that of the untreated sample.The sample treated at 2.5 MPa,30 s, showed the highest reducing power.However,when the treatment was 2.5 MPa with 90 s,the reducing powerappeared a decrease of 7.3%.This result showed the same trend compared with total phenolic acids content,which indicated that reducing power and total phenolic acids content might be correlated.
2.5 ABTS Radical Scavenging Assay
ABTS.+is a nitrogen centered radical with a bluegreen color.When reduced by antioxidants to its nonradical (ABTS)form,it will become colorless and the maximum absorption at 734 nm also disappears.The ABTS radical scavenging assays are shown in Fig.3(d).All the samples showed the ABTS radical scavenging activities.With the increase of time and pressure of stream explosion,the activity increased until 1.5 MPa,90 s,which was nearly 5.3 times higher than the untreated one.Then the ABTS Radical Scavenging activities remained basically unchanged.The conclusion was similar with the result of DPPH radical scavenging assay.
2.6 Antioxidant Activity in a Linoleic Acid System
Linoleic acid emulsion system is commonly used to test the samples′antioxidant activities.The antioxidant activities of the samples in linoleic acid system are shown in Fig.4.The results showed that,the antioxidant activities of each of the samples had a trend of increasing with time. The control group had an obvious increase,which showed that the auto oxidation of linoleic acid was significant. Besides,the steam-exploded group had a slower increase compared to the untreated one.The results showed that the wheat bran extract solution in linoleic acid system had an ability to provide hydrogen protons to remove free radicals, block or inhibit chain reaction,inhibit linoleic acid autooxidation.Steam-exploded samples with the condition 2.5 MPa and 30 s showed better ability ofinhibiting peroxidation reaction.
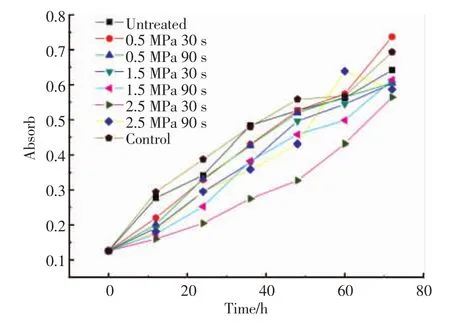
Fig.4 Antioxidant activities of untreated and steam-exploded wheat bran in linoleic acid system
3 Conclusions
SET was an efficient pretreatment method to release the bound phenolic acids and enhance the antioxidant capacity of wheat bran.
1)HPLC results in this paper gave us conspicuous dates to certify the increase of contents of phenolic acids after SET,especially for ferulic acid.The content of bound ferulic acids ranged from 57.232 to 1 454.092 μg/g,nearly increased 25 times higher than the untreated one.2.5 MPa with 30 s was the best treatment condition,after which the contents of phenolic acids decreased.
2)Total phenolic content of wheat bran increased after SET,when it was treated by 2.5 MPa with 30 s,the contentreached highestto 28 mg/g,afterwhich it decreased,while still higher than the untreated one.
3)Several authoritative methods of antioxidant capacity gave the consistent conclusion,when the treatment condition increased to 1.5 MPa 90 s or 2.5 MPa 30 s,the antioxidant activity reached the highest.
In conclusion,2.5 MPa 30 s was the optimum SET treatment condition,the release contents of phenolic acids reached the best and the antioxidant activity reached high.
[1]Zhou K,Su L,Yu L.Phytochemicals and antioxidant properties in wheat bran[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2004,52(20):6108-6114.
[2]Kim K H,Tsao R,Yang R,et al.Phenolic acid profiles and antioxidant activities of wheat bran extracts and the effect of hydrolysis conditions[J].Food Chemistry,2006,95(3):466-473.
[3]Jacquet N,Maniet G,Vanderghem C,et al.Application of steam explosion as pretreatment on lignocellulosic material:a review [J].Industrial&Engineering Chemistry Research,2015,54(10): 2593-2598.
[4]Gong L,Huang L,Zhang Y.Effect of steam explosion treatment on barley bran phenolic compounds and antioxidant capacity[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2012,60(29): 7177-7184.
[5]Wu G,Heitz M,Chornet E.Improved alkaline oxidation process for the production of aldehydes(vanillin and syringaldehyde) from steam-explosion hardwood lignin[J].Industrial&Engineering Chemistry Research,1994,33(3):718-723.
[6]Noda Y,Asada C,Sasaki C,et al.Extraction method for increasing antioxidant activity of raw garlic using steam explosion[J].Biochemical Engineering Journal,2013,73:1-4.
[7]SunSL,WenJL,MaMG,etal.Structuralfeaturesand antioxidant activities of degraded lignins from steam exploded bamboo stem [J].Industrial Crops and Products,2014,56:128-136.
[8]Verma B,Hucl P,Chibbar R N.Phenolic acid composition and antioxidant capacity of acid and alkali hydrolysed wheat bran fractions[J].Food Chemistry,2009,116(4):947-954.
[9]Sancho A I,Bartolomé B,Gómez-Cordovés C,et al.Release of ferulic acid from cereal residues by barley enzymatic extracts[J]. Journal of Cereal Science,2001,34(2):173-179.
[10]Moore J,Cheng Z,Hao J,et al.Effects of solid-state yeast treatment on the antioxidant properties and protein and fiber compositions ofcommon hard wheatbran[J].Journalof Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2007,55(25):10173-10182.
[11]Onyeneho S N,Hettiarachchy N S.Antioxidant activity of durum wheat bran[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,1992, 40(9):1496-1500.
[12]Xu G,Ye X,Chen J,et al.Effect of heat treatment on the phenolic compounds and antioxidant capacity of citrus peel extract[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food chemistry,2007,55 (2):330-335.
[13]Sun T,Ho C T.Antioxidant activities of buckwheat extracts[J]. Food Chemistry,2005,90(4):743-749.
[14]Joseph G S,Jayaprakasha G K,Selvi A T,et al.Antiaflatoxigenic and antioxidant activities of Garcinia extracts[J].International Journal of Food Microbiology,2005,101(2):153-160.
[15]Zhu K X,Lian C X,Guo X N,et al.Antioxidant activities and total phenolic contents of various extracts from defatted wheat germ[J].Food Chemistry,2011,126(3):1122-1126.
[16]Liu Q,Yao H.Antioxidant activities of barley seeds extracts[J]. Food Chemistry,2007,102(3):732-737.
[17]Zhang W,Zhao X,Sun C,et al.Phenolic composition from different Loquat(Eriobotrya japonica Lindl.)cultivars grown in china and their antioxidant properties[J].Molecules,2015,20(1): 542-555.
[18]Zhou K,Yu L.Antioxidant properties of bran extracts from Trego wheat grown at different locations[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2004,52(5):1112-1117.
[19]Moore J,Cheng Z,Su L,et al.Effects of solid-state enzymatic treatments on the antioxidant properties of wheat bran[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2006,54(24):9032-9045.
[20]Yu L.Wheat Antioxidants(Z).United States of America:John Wiley&Sons,Inc.,Hoboken,New Jersey.2007,208-218.
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.06.043
S816.5
:A
:1002-6819(2016)-06-0308-07
Received date:2015-07-20 Revised date:2016-01-26
Foundation items:Special Fund for the Construction of Wheat Technology System in Henan Province(No.S2010-01-G06);Research Foundation of HAUT(No. 2013JCYJ01);Program for Innovative Research Team in University of Henan Province(No.13IRTSTHN008).
Biography:Liuchong(1978-),male,instructor,PhD,mainly engaged in research on cereal chemistry and quality.Henan University of Technology,Zhengzhou, 450001.Email:liuachong@126.com.
※Correspongding author:Zheng Xueling(1972-),female,PhD,doctoral supervisor,mainly engaged in cereal science.Henan University of Technology,Zhengzhou, 450001.Email:xlzhenghaut@126.com.

