大白菜中马拉硫磷农药的表面增强拉曼光谱快速检测
黄双根,吴 燕,胡建平,刘木华,吴瑞梅,范 苑,王晓彬
(1.江苏大学现代农业装备与技术教育部重点实验室,镇江212013;2.江西农业大学工学院生物光电及应用重点实验室,南昌330045)
大白菜中马拉硫磷农药的表面增强拉曼光谱快速检测
黄双根1,2,吴 燕2,胡建平1※,刘木华2,吴瑞梅2,范 苑2,王晓彬2
(1.江苏大学现代农业装备与技术教育部重点实验室,镇江212013;2.江西农业大学工学院生物光电及应用重点实验室,南昌330045)
为了检测大白菜中马拉硫磷农药残留,该文采用表面增强拉曼光谱技术结合化学计量学方法建立马拉硫磷残留的快速检测模型。采用硫酸镁、N-丙基乙二胺、石墨化炭黑和C18去除大白菜中蛋白质、脂肪、碳水化合物等物质的影响。利用不同预处理方法对原始光谱信号进行预处理,建立大白菜中马拉硫磷残留的偏最小二乘模型。研究发现,大白菜中马拉硫磷的检测浓度达到1.082 mg/L以下;归一化预处理后建立的模型预测性能最好。配制5个未知浓度样本验证模型的准确度,预测值与真实值相对误差的绝对值为0.70%~9.84%,预测回收率为99.30%~109.84%;配对t检验的结果表明样本的预测值与真实值之间无明显差异,说明模型是准确可靠的。结果表明,SERS(surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy)方法可以实现大白菜中马拉硫磷残留的快速检测。
光谱分析;农药;检测;表面增强拉曼光谱;大白菜;马拉硫磷;偏最小二乘;快速检测
黄双根,吴 燕,胡建平,刘木华,吴瑞梅,范 苑,王晓彬.大白菜中马拉硫磷农药的表面增强拉曼光谱快速检测[J].农业工程学报,2016,32(6):296-301.doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.06.041 http://www.tcsae.org
Huang Shuanggen,Wu Yan,Hu Jianping,Liu Muhua,Wu Ruimei,Fan Yuan,Wang Xiaobin.Rapid detection of malathion residues in Chinese cabbage by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE),2016,32(6):296-301.(in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.06.041 http://www.tcsae.org
0 引言
马拉硫磷(malathion),化学名称为O,O-二甲基-S-[1,2-二(乙氧基羰基)乙基]二硫代磷酸酯,属低等毒性有机磷杀虫剂,具有触杀、胃毒和一定的熏蒸作用[1],适用于烟草、茶和蔬菜上的刺吸式口器和咀嚼式口器害虫,如主要用于防治稻纵卷叶螟、稻飞虱、菜蚜、菜青虫等害虫。中毒症状为头晕、无力、呕吐、流涎、痉挛、昏迷等。目前,马拉硫磷农药的常规检测方法有液相色谱和液质联用的方法[2-3]、气相色谱和质谱联用的方法[4-5]等,这些方法具有准确、灵敏度高等特点,但前处理复杂、成本高、检测速度慢,不适合现场实时快速检测筛选[6-7]。
表面增强拉曼光谱(surface-enhanced Raman spec troscopy,SERS)技术是指分子吸附到某些粗糙金属(如金、银、铜)的表面或溶胶中,在激发区域内,金属表面或近表面电磁场增强,使吸附分子的拉曼信号强度增强104~106倍[8-10]。SERS技术能实现对微量样品的快速检测,可以实现单分子检测[11-12]。SERS技术具有样品制备简单[13]、操作简便、灵敏度高等优点,已逐步应用于食品和农产品中农药残留的快速检测[14-16]。Shende等[17]采用固相萃取技术对橙汁进行前处理,结合SERS技术,检测最低浓度为50 μg/L。Li等[18]以银纳米粒子作为增强基底,应用SERS技术检测了苹果表皮的甲拌磷和倍硫磷农药残留,最低检测浓度分别为0.05和0.4 mg/L。张萍等[19]采用表面增强拉曼光谱检测技术结合快速溶剂提取前处理方法建立了豆芽中6-BA残留物质的快速检测方法。Kim等[20]以苯并咪唑类为研究对象,采集不同pH值下待测溶液的表面增强拉曼光谱,对拉曼谱峰进行了归属。He等[21]利用SERS技术结合一个快速简单的方法实现了苹果表面噻菌灵农药的检测,检测时间大约10 min。目前利用表面增强拉曼光谱技术结合化学计量学方法检测大白菜中农药残留还没有报道。
本文采用SERS技术结合化学计量学方法对大白菜中马拉硫磷残留进行快速检测。以大白菜为载体,马拉硫磷农药为研究对象,模拟农药残留状态,利用快速溶剂提取前处理方法对大白菜中马拉硫磷农药进行提取,采用无水无水硫酸镁、N-丙基乙二胺(primary secondary amine,PSA)、石墨化炭黑和C18去除蛋白质、脂肪、碳水化合物等物质的影响,结合化学计量学方法,实现大白菜中马拉硫磷农药的快速检测,为实现农药残留检测提供快速、简便、准确的检测方案。
1 材料与方法
1.1 仪器与试剂
拉曼光谱仪(RamTracer-200-HS,欧普图斯光学纳米科技有限公司);天平(AR3202CN,精度为0.01 mg,奥豪斯电子天平);低速离心机(JW1024,安徽嘉文仪器设备有限公司);涡漩混合器(Vortex-Genie 2/2T,上海凌初环保仪器有限公司);气相色谱串联质谱仪(Agilent GC 700,美国安捷伦科技有限公司);色谱柱(HP-5MS,5%Phenyl Methyl Silox,30 m×250 μm×0.25 μm,美国安捷伦科技有限公司)。
马拉硫磷标准品(99.5%,中国标准物质网);乙腈,乙腈(色谱纯,国药集团化学试剂北京有限公司);PSA、无水硫酸镁、C18和石墨化炭黑(分析纯,国药集团化学试剂北京有限公司);氯化钠(分析纯,国家标准物质信息中心);表面增强试剂(OTR202、OTR103,欧普图斯光学纳米科技有限公司);有机滤膜(0.22 μm,安捷伦科技有限公司);大白菜(江西农业大学试验基地)。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 样品制备
马拉硫磷标准溶液配制:准确量取标准品马拉硫磷200 mg于200 mL容量瓶中,加入乙腈超声溶解后,定容至刻度,得到浓度为1 000 mg/L的马拉硫磷储备溶液,放置于4℃避光环境中存放。再用乙腈将1 000 mg/L的马拉硫磷储备溶液分别稀释为100、50、20、15、10、5、2、1和0.5 mg/L的标准工作液。
大白菜中马拉硫磷农药残留的模拟过程及提取:1)称取50g大白菜放置于保鲜膜中,使用喷壶按比例喷洒浓度为100mg/L的马拉硫磷标准储备液。配置76种不同浓度大白菜样本,每个浓度复制2份,编号1~76。晾干后,分别放入搅拌机将样品加工成浆状,备用。2)称取10 g大白菜样本于50 mL离心管中,依次加入10 mL乙腈、5 g氯化钠和1 g无水乙酸钠,摇匀后涡旋混合器上混合1 min,将离心管放入离心机以4200r/min的速度离心5min,上清液为黄色。3)取上述黄色上清液2 mL,放于装有适量硫酸镁、PSA、石墨化炭黑和C18的15mL离心管中,摇匀后在涡旋混合器上混合1 min,去除蛋白质、脂肪、碳水化合物等物质的影响,将此离心管放入离心机以4200r/min的速度离心5 min,得到无色上清液,上清液过0.22 μm有机滤膜,上机检测拉曼光谱。4)取步骤3)的过滤液1 mL,加入10 mL离心管,氮吹。5)氮吹后,在10mL离心管中加入1mL乙酸乙酯,涡旋振荡。6)取步骤5)的溶液100μL,和900μL乙腈混合,稀释10倍,涡旋振荡,过0.22μm有机滤膜,放置于进样瓶,上气相质谱仪检测大白菜样本中马拉硫磷的真实残留值。
1.2.2 拉曼光谱数据采集
拉曼光谱检测参数如下:激发波长为785 nm,功率为200 mW,扫描范围400~1 800 cm-1,分辨率为4 cm-1,积分时间为10 s,积分2次求平均,向2 mL进样瓶中依次加入500 μL OTR202、20 μL待测液、100 μL OTR103,混合均匀后其采集表面增强拉曼光谱。
1.2.3 气相色谱串联质谱试验条件
色谱条件 色谱柱(HP-5MS,5%Phenyl Methyl Silox,30 m×250 μm×0.25 μm)进样口温度:250℃;升温程序:初始柱温为50℃,保持2 min,以50℃/min升至150℃,以5℃/min升至200℃,以16℃/min升至280℃;升至300℃,保持2 min(后运行);载气为高纯氦气(纯度≥99.999%),恒压64.469 6 kPa;载气流速为1.2 mL/min;进样量1 μL;进样方式:不分流进样[22]。
质谱条件 EI源;接口温度:230℃;四极杆温度:150℃;传输线温度:280℃;溶剂延迟0 min;碰撞气为高纯氮气(纯度≥99.999%);采集模式:多反应监测模式(multireactions monitoring,MRM)。
1.2.4 数据处理
采用标准正态变量变换(standardnormalvariate,SNV)、多元散射校正(multiplicative scatter correction,MSC)、归一化(normalization)3种预处理方法对原始光谱数据进行预处理,消除基线偏移、随机噪声和背景的干扰,利用偏最小二乘回归(partial least squares,PLS)方法建立大白菜中马拉硫磷农药残留的预测模型,以RMSECV、Rc、RMSEP、Rp对模型进行综合评价。采用5个未知浓度样本评价模型准确度,对模型的真实值与预测值进行配对t检验,以验证模型的准确度。所有数据分析基于MATAB R2010a和SPASS V17.0平台完成。
2 结果与分析
2.1 马拉硫磷的表面增强拉曼光谱
图1为马拉硫磷农药的表面增强拉曼光谱图和背景信号拉曼光谱。从图1可看出,马拉硫磷农药分子结构包含了P=S、C-C、P-S、C-H、C-O-C、P-O、C=O和C-O等基团。图1(a)为马拉硫磷表面增强拉曼光谱图(浓度为20mg/L),764、816、862、1 096、1 152、1 448和1 724 cm-1处强度较高,对这7处拉曼特征峰进行归属[23-25]:764 cm-1处拉曼特征峰为有机磷化物中P=S和P-O键伸缩振动引起的,816 cm-1归属于C-H面外弯曲振动,862 cm-1归属于CO-C对称伸缩振动,1 096 cm-1归属于C-C伸缩振动,并伴有CH2面内变形振动,1 152 cm-1归属于P-S伸缩振动,1 448 cm-1归属于C-O基团对称伸缩振动,1 724 cm-1归属于C=O伸缩振动。这些特征峰可作为马拉硫磷农药分子的定性判别依据。

图1 马拉硫磷标准溶液和背景信号的拉曼光谱Fig.1 Raman spectra of malathion solution and background signals
从图1(a)和(b)可看出,马拉硫磷标准溶液的普通拉曼光谱只出现了乙腈的拉曼峰,而未出现马拉硫磷农药的拉曼特征峰。背景信号(c)和(d)比较微弱,而且出峰位置和马拉硫磷的拉曼特征峰不一致。另外,对这4类数据进行主成分分析(n=5)得到的结果见图2。从图2中看出,马拉硫磷的表面增强拉曼光谱信号和背景信号(金胶和乙腈)有很好的分离。由此说明,SERS技术能够用来检测马拉硫磷农药。

图2 主成分分析结果Fig.2 Results of principal component analysis
2.2 马拉硫磷标准溶液的表面增强拉曼光谱分析
图3为不同浓度马拉硫磷标准溶液的表面增强拉曼光谱。由图3可看出,随着马拉硫磷标准溶液浓度的增加,其特征峰的强度不断增强,但各特征峰的峰强度变化速度不同:1 096、1 152、1 448和1 724 cm-1处随浓度变化较快,816和862 cm-1处随浓度变化较慢,764 cm-1处变化最慢,这可能是因为纳米增强粒子与马拉硫磷农药分子中各个基团表面吸附力的大小和方向不同导致的。从图3中可看出,随着马拉硫磷浓度的降低,拉曼特征峰的强度逐渐减弱,浓度为20、10、5 mg/L时,马拉硫磷的7处拉曼峰明显,易识别;浓度为0.5 mg/L时,764 cm-1处峰强十分微弱,但依然能识别出,其他的特征峰已不能识别。由此表明,利用SERS技术检测马拉硫磷标准溶液能够达到0.5 mg/L以下。

图3 不同浓度马拉硫磷标准溶液的表面增强拉曼光谱Fig.3 SERS spectra of malathion with different concentrations
2.3 大白菜中马拉硫磷农药残留检测结果分析
受蛋白质、脂肪、碳水化合物等物质的干扰,马拉硫磷农药分子的拉曼信号被削弱。本文采用无水无水硫酸镁、PSA、石墨化炭黑和C18对大白菜提取液进行净化处理,减弱大白菜提取液中蛋白质、脂肪、碳水化合物等物质的干扰,净化后含马拉硫磷农药的大白菜溶液的表面增强拉曼光谱如图4所示。图4(a)-(c)中,764、816、862和1724cm-1处特征峰明显,易识别;浓度为2.256 mg/L时,764、816和862 cm-1处的峰强度明显降低,依然能识别,1 724 cm-1处的拉曼特征峰已无法识别;浓度为1.082 mg/L时,764和816 cm-1处特征峰依然存在,峰强十分微弱,但依然能识别。因此,利用表面增强拉曼光谱方法检测大白菜中马拉硫磷农药的最低检测浓度在1.082 mg/L以下。从图4中看出,马拉硫磷溶液的拉曼特征峰强度随浓度的增大而增强。因此,可采用化学计量方法建立大白菜中马拉硫磷农药残留的预测模型,对马拉硫磷农药进行定量分析。

图4 不同浓度的大白菜马拉硫磷提取液的表面增强拉曼光谱Fig.4 SERS spectra of malathion solutions extracted from chinese cabbage with different concentrations
拉曼光谱采集时,会受到随机噪声、基线漂移、外界杂散光和电荷耦合器件(charge-coupled device,CCD)热稳定噪声等因素影响,直接影响模型的可靠性和稳健性。因此,需要对原始光谱进行预处理,增强特征信息,提高模型的预测能力。本文采用3种预处理方法,由各种预处理方法处理后所建偏最小二乘法模型的预测效果来优化最佳预处理方法。根据76个样本的测量值,采用2:1的分配方案,从每3个样品中选择2个作为校正集,剩余的1个作为预测集,所以校正集由51个样品组成,预测集由25个样品组成。表1为原始光谱经不同预处理方法后所建模型结果。

表1 不同预处理方法下模型校正和预测的结果Table 1 Results for each of pre-processing method for calibration and prediction model
由表可知,经3种预处理方法后所建模型的预测结果均优于原始光谱,原始光谱归一化预处理后,当主成分数为13时所建模型的性能最好。模型对校正集样本的相关系数(Rc)为0.983 2,交互验证均方根误差(RMSECV)为1.78 mg/L,模型对预测集样本的相关系数(Rp)为0.973 2,预测均方根误差(RMSEP)为2.37 mg/L,较高的Rc和较低的RMSECV说明采用表面增强拉曼光谱方法预测大白菜中马拉硫磷农药残留是可行的。图5为经归一化预处理后预测集样本的预测值与测量值之间的散点图。

图5 归一化预处理后预测集的散点图Fig.5 Scatter diagram of prediction set by normalization
2.4 模型准确度验证
2.4.1 预测相对误差和回收率
为了验证方法的准确度,对5个未知浓度大白菜样本进行前处理,用GC-MS方法测定5个未知浓度农药大白菜样本的真实值。对5个未知浓度农药大白菜样本分别采集SERS信号,用上述方法建立的预测模型对5个未知浓度农药大白菜样本进行预测,将真实值与预测值的进行比较,结果见表2。由表2可知,本方法的预测结果与GC-MS方法结果基本一致,真实值与预测值相对误差为0.38%~6.80%,回收率为96.1%~107.29%,表明利用表面增强拉曼光谱方法快速检测大白菜中马拉硫磷农药残留是可行的。
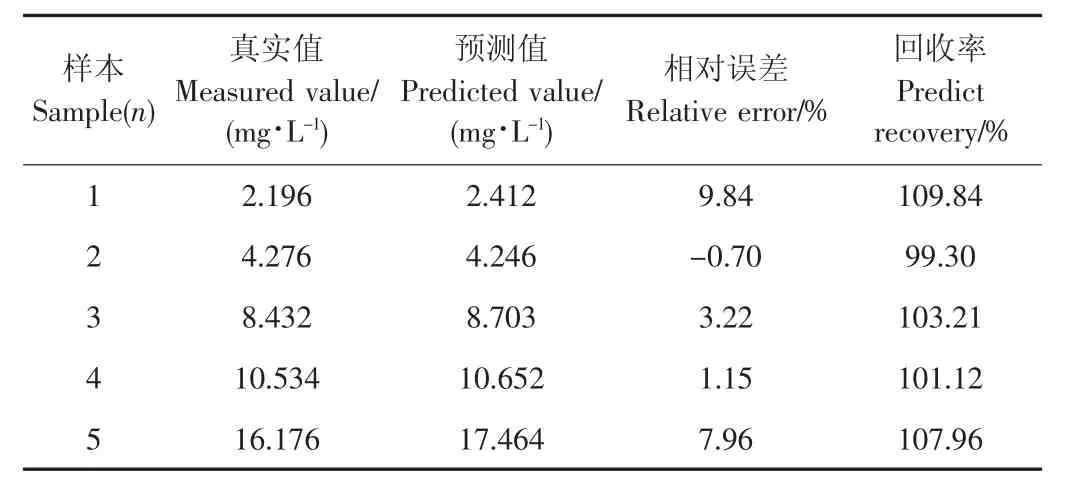
表2 大白菜中马拉硫磷农药的真实值与预测值对比Table 2 Predicted value and measured value of malathion in chinese cabbage
2.4.2 配对t检验
表3为5个未知农药大白菜样本的真实值与预测值配对t检验结果,t=-1.589,其绝对值小于t0.05,4=2.776,表明真实值与预测值之间无明显差异,说明利用表面增强拉曼光谱方法快速检测大白菜中马拉硫磷农药残留的预测结果是准确可靠的。

表3 真实值与预测值配对t检验结果Table 3 t-test result between reference values and prediction values
3 结论
1)采用表面增强拉曼光谱技术和快速溶剂提取前处理方法快速检测大白菜中马拉硫磷农药残留,找到了马拉硫磷农药分子的7个拉曼特征峰,这些特征峰可作为马拉硫磷农药的定性定量判别依据,该方法对大白菜中马拉硫磷农药的检测浓度达到1.082 mg/L以下。
2)采用标准正态变换、多元散射校正和归一化对大白菜马拉硫磷提取液的原始拉曼光谱进行预处理,结果表明,经归一化预处理后所建PLS模型预测性能最好。
3)用5个未知浓度的大白菜样本对模型的准确性进行验证,结果显示本方法的预测结果与经典化学法测量值基本一致;配对t检验结果显示样本的预测值与实际测量值之间无显著差异,说明采用该方法检测大白菜中的马拉硫磷农药残留是准确可靠的。研究结果表明SERS技术能够实现对大白菜中农药残留的检测,研究方法和思路能为农产品中其他农药的拉曼光谱快速检测提供参考。
[1]谢锋,孙海达,李占彬,等.QuEChERS-表面增强拉曼光谱联用快速测定豆类蔬菜中马拉硫磷残留[J].食品科技,2014,39 (8):286-290.Xie Feng,Sun Haida,Li Zhanbin,et al.QuEChERS sample preparation method for rapid screening of malathion in legume vegetables by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy[J].Food Science and Technology,2014,39(8):286-290.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[2]王岙,高茜,王晓丽,等.高效液相色谱法同时测定水体中马拉硫磷和阿特拉津[J].吉林大学学报(理学版),2008,46(1):157-161.Wang Ao,Gao Qian,Wang Xiaoli,et al.Simultaneous determination of malathion and atrazine in water by high performance liquid chromatography[J].Journal of Jilin University (Science Edition),2008,46(1):157-161.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[3]Xu Zhenlin,Deng Hao,Deng Xingfei,et al.Monitoring of organophosphorus pesticides in vegetables using monoclonal antibody-based direct competitive ELISA followed by HPLC-MS/ MS[J].Food Chemistry,2012,131(4):1569-1576.
[4]王吉祥,向文娟,王亚琴,等.GPC-GC/MS测定火腿中多种有机磷农药的残留[J].食品研究与开发,2014,35(2):77-80.
[5]Alves A A R,Rodrigues A S,Barros E B P,et al.Determination of pesticides residues in brazilian grape juices using GC-MSSIM[J].Food Analytical Methods,2014,7(9):1834-1839.
[6]李晓舟,于壮,杨天月,等.SERS技术用于苹果表面有机磷农药残留的检测[J].光谱学与光谱分析,2013,33(10):2711-2714. Li Xiaozhou,Yu Zhuang,Yang Tianyue,et al.Detection of organophosphorus pesticide residue on the surface of apples using SERS[J].Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2013,33 (10):2711-2714.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[7]Müller C,David L,Chis V,et al.Detection of thiabendazole applied on citrus fruits and bananas using surface enhanced Raman scattering[J].Food Chemistry,2014,145:814-820.
[8] 欧阳雨.乐果涂膜表面增强拉曼光谱研究[J].分析测试学报,2012,31(8):996-1000. OuyangYu.Surface-enhanced raman scattering study of dimethoate coating[J].Journal of Instrumental Analysis,2012, 31(8):996-1000.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[9]Huang S G,Hu J P,Guo P,et al.Rapid detection of chorpyriphos residues in rice by surface-enhanced Raman scattering[J].Analytical Methods,2015(7):4334-4339.
[10]Nguyen T H D,Zhang Z,Mustapha A,et al.Use of graphene and gold nanorods as substrates for the detection of pesticides by surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2014,62(43):10445-10451.
[11]Guerrini L,Sanchez C S,Cruz V L,et al.Surface-enhanced Raman spectra of dimethoate and omethoate[J].Journal of Raman Spectroscopy,2011,42(5):980-985.
[12]Buyukgoz G G,Bozkurt A G,Akgul N B,et al.Spectroscopic detection of aspartame in soft drinks by surface-enhanced Ramanspectroscopy[J].EuropeanFoodResearchandTechnology, 2015,240(3):567-575.
[13]李水芳,张欣,李姣娟,等.拉曼光谱法无损检测蜂蜜中的果糖和葡萄糖含量[J].农业工程学报,2014,30(6):249-255. Li Shuifang,Zhang Xin,Li Jiaojuan,et al.Non-destructive detecting fructose and glucose content of honey with Raman spectroscopy[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2014,30(6):249-255.in Chinese with English abstract)
[14]Dhakal S,Li Y Y,Peng Y K,et al.Prototype instrument development for non-destructive detection of pesticide residue in apple surface using Raman technologyc Journal of Food Engineering,2014,123:94-103.
[15]Wijaya W,Pang S,Labuza T P,et al.Rapid detection of acetamiprid in foods using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy(SERS)[J].Journal of Food Science,2014,79(4): T743-T747.
[16]Craig A P,Franca A S,Irudayaraj J.Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy applied to food safety[J].Annual Review of Food Science and Technology,2013,4(1):369-380.
[17]Shende C,Inscore F,Sengupta A,et al.Rapid extraction and detection of trace chlorpyrifos-methyl in orange juice by surfaceenhanced Raman spectroscopy[J].Sensing and Instrumentation for Food Quality and Safety,2010,4(3-4):101-107.
[18]Li X Z,Zhang S,Yu Z,et al.Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopic analysis of phorate and fenthion pesticide in apple skin using silver nanoparticles[J].Applied Spectroscopy,2014, 68(4):483-487.
[19]张萍,郑大威,刘晶,等.基于表面增强拉曼光谱技术的豆芽6-BA残留快速检测方法[J].光谱学与光谱分析,2012,32(5):1266-1269. Zhang Ping,Zheng Dawei,Liu Jing,et al.Rapid detection of 6-benzylaminopurine residues in sprout beans by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy[J].Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2012,32(5):1266-1269.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[20]Kim M S,Kim M K,Lee C J,et al.Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy of benzimidazolic fungicides:benzimidazole and thiabendazole[J].Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society,2009, 30(12):2930-2934.
[21]He L L,Chen T,Labuza T P.Recovery and quantitative detection of thiabendazole on apples using a surface swab capture method followed by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy[J].Food Chemistry,2014,148:42-46.
[22]莫李桂,马盛韬,李会茹,等.气相色谱/三重四极杆串联质谱法检测土壤中氯代多环芳烃和溴代多环芳烃[J].分析化学,2013,41(12):1825-1830. Mo Ligui,Ma Shengtao,Li Huiru,et al.Determination of chlorinated and brominated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil samples by gas chromatography coupled with triple quadrupole mass spectrometry[J].Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry,2013,41(12):1825-1830.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[23]孙旭东,郝勇,刘燕德.表面增强拉曼光谱法检测农药残留的研究进展[J].食品安全质量检测学报,2012,3(5):421-426.
[24]朱自莹,顾仁敖,陆天虹.拉曼光谱在化学中的应用[M].沈阳:东北大学出版社,1998.
[25]朱自莹,译.有机化合物的特征拉曼频率[M].北京:中国化学会),1980.
Rapid detection of malathion residues in Chinese cabbage by surfaceenhanced Raman spectroscopy
Huang Shuanggen1,2,Wu Yan2,Hu Jianping1※,Liu Muhua2,Wu Ruimei2,Fan Yuan2,Wang Xiaobin2
(1.Key Laboratory of Modern Agriculture Equipment and Technology,Ministry of Education,Jiangsu University,Zhenjiang 212013,China; 2.Optics-Electrics Application of Biomaterials Lab,College of Engineering,Jiangxi Agricultural University,Nanchang 330045,China)
The traditional pesticide residues detection methods had the disadvantages of complex sample preparation, expensive apparatus and high cost.For developing a rapid analysis detection method of pesticide residues,we investigated a surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS)method coupled with colloidal gold for detection and characterization malathion residues in Chinese cabbage.Chemometric method was used to establish a rapid detection model of malathion pesticide residues in Chinese cabbage.A 200 mg/L standard solution was prepared by dissolving malathion power in acetonitrile.The standard solution was serially diluted with ultrapure water to prepare working solutions of 100,50,20,15, 10,5,2,1 and 0.5 mg/L.Fresh Chinese cabbages were collected from the agronomy experimental base of Jiangxi Agricultural University in June 2015.The Chinese cabbages were used to prepare samples as follows.50 g Chinese cabbages were weighed and transferred on a plastic wrap.76 Chinese cabbage samples were manufactured by spraying different concentration standard solution with a sprinkling can,and each concentration has two parallel samples.Then the 76 samples were homogenized separately by pulverizer.After that,the sample preparation steps were implemented for both SERS collection and GC-MS measurement as follows.1)10 g homogenized chinese cabbage sample,1 g anhydrous sodium acetate,5 g sodium chloride and 10 mL acetonitrile were blended in a centrifuge tube of 50 mL,and the centrifuge tube was vibrated for 1 min with a vortex mixer.A homogeneous solution was obtained and then separated for 5 min at a speed of 4 200 rpm on the centrifuge,and a yellow supernatant was acquired.2)2 mL of the supernatant was injected to a centrifuge tube of 15 mL containing anhydrous Magnesium sulfate,PSA,graphitized carbon and C18for removing the effect of protein, fat,carbohydrates and other substances in Chinese cabbage.The centrifuge tube was blended for 1 min and then centrifuged for 5 min at a speed of 4 200 r/min.Then,the colourless supernatant was filtered.The filtrate was used directly for SERS measurement in the Optics-Electrics Application of Biomaterials Lab.3)1 mL of the filtrate was transferred into a 10 mL centrifuge tube and condensed with a termovap sample concentrator at 60℃until the solvent absolutely evaporated. 4)The concentrated pesticide was diluted with 1 mL ethyl acetate and shaken for a moment.Then the eluted solution was transferred into a vial and used to measure its actual value by GC-MS in Jiangxi Entry-Exit Inspection and Quarantine technology center.Then three methods as SNV,MSC and Normalization were used to optimize the original Raman spectra signals,and the PLS models of malathion pesticide residues in Chinese cabbage were established.The limit of detection (LOD)can reach the level of 1.082 mg/L by SERS method,and the concentration can meet the tolerance levels for malathion pesticide residues in chinese cabbage.The model predictive performance used normalization preprocessing method was optimal.The correlation coefficient of the calibration samples model(Rc)was 0.983 2,RMSECV was 1.78 mg/L, the correlation coefficient of prediction model(Rp)was 0.973 2,and RMSEP was 2.37 mg/L.The model results of the higher Rp value and the lower RMSEP value indicated that the method of SERS could accurately predict the malathion pesticide residues in Chinese cabbage.The five unknown concentration samples were prepared to verify the accuracy of the prediction models.The absolute values of relative deviation were calculated to be between 0.70%-9.84%.The predict recoveries were calculated to be between 99.30%-109.84%.These indicated that the SERS method was receivable and credible for rapid detection of malathion pesticide residues in Chinese cabbage.The t value was 1.589,less than t0.05,4= 2.776.The results of t test demonstrated that the difference between SERS and GC-MS was not significant.This study demonstrates that SERS is capable of detecting and identifying malathion pesticide residues in Chinese cabbage quickly and accurately.
spectrum analysis;pesticides;measurements;surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy;chinese cabbage; malathion;partial least squares(PLS);rapid detection
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.06.041
S634.1
A
1002-6819(2016)-06-0296-06
2015-09-23
2016-01-18
国家自然科学基金项目(31271612)
黄双根(1979-),男,江西新干人,博士生,江西农业大学副教授,主要从事农产品品质无损检测。镇江 江苏大学现代农业装备与技术教育部重点实验室,212013。Email:shuang19792@163.com
※通信作者:胡建平(1965-),男,江苏吴县人,教授,博导,主要从事精细农业研究。镇江 江苏大学现代农业装备与技术教育部重点实验室,212013。Email:hujp@ujs.edu.cn
中国农业工程学会会员:胡建平(E041200154S)

