褐藻多糖对乳腺癌细胞活性的影响及机制探讨
郝剑,吴雄志(天津医科大学肿瘤医院国家肿瘤临床医学研究中心天津市“肿瘤防治”重点实验室,天津300060)
褐藻多糖对乳腺癌细胞活性的影响及机制探讨
郝剑,吴雄志
(天津医科大学肿瘤医院国家肿瘤临床医学研究中心天津市“肿瘤防治”重点实验室,天津300060)
摘要:目的观察褐藻多糖对人乳腺癌细胞株MCF-7、MDA-MB-231细胞活性的影响,并探讨其作用机制。方法将对数生长期的MCF-7、MDA-MB-231细胞(观察A组、B组)分别加入100、200 μg/mL褐藻多糖2 mL,对照A组、B组均加入等体积的DMEM培养基2 mL。用台盼蓝染色实验测算细胞增殖抑制率,用流式细胞仪检测细胞周期和凋亡细胞,用Western blot法检测细胞Caspase-8及磷酸化细胞外调节蛋白激酶( p-Erk)、Erk表达。结果随着褐藻多糖浓度增加、作用时间延长,观察A组、B组细胞增殖抑制率逐渐升高( P均<0.05) ;观察A组、B组G0/G1期细胞比例升高、S期及G2期细胞比例降低,细胞凋亡率增高,褐藻多糖浓度高者变化更明显,P均<0.05;观察A组、B组细胞Caspase-8表达升高、p-Erk表达下降,褐藻多糖浓度高者变化更明显,P均<0.05。结论褐藻多糖可抑制MCF-7、MDA-MB-231细胞增殖,阻滞细胞周期于G0/G1期,促进细胞凋亡;该作用可能是通过上调细胞Caspase-8表达、下调p-Erk表达水平实现。
关键词:褐藻多糖;乳腺癌;细胞周期;细胞凋亡;半胱氨酸天冬氨酸蛋白酶8;细胞外调节蛋白激酶doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2015.30.002
Effects of Fucoidan on cell viability of breast cancer and its mechanism
HAO Jian,WU Xiong-zhi
( Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital,National Clinical Research Center for Cancer,Key Laboratory of Cancer Prevention and Therapy,Tianjin 300060,China)
Abstract:Objective To observe the effects of Fucoidan on cell viability of breast cancer cell lines MCF-7 and MDAMB-231 and to investigate its possible mechanism.Methods The breast cancer cell lines MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 in the logarithmic phase ( observation group A and B) were respectively treated with 2 mL Fucoidan ( 100 ug/mL and 200 ug/mL).The control group A and B were treated with the same volume of DMEM culture medium.The cell proliferation inhibition rate was detected by Trypan blue staining,cell cycle and apoptosis cells were analyzed by flow cytometry,and the expression of Caspase-8,phosphorylation Erk ( p-Erk) and total Erk was detected by Western blotting.Results With the increased Fucoidan concentration and the prolonged time,the cell proliferation inhibition rates of the observation groups A and B were increased ( all P<0.05),the cell proportion in the G0/G1phase of the observation groups A and group B was increased,the cell proportion in the S phase and G2was reduced,the apoptosis rate was increased,and the changes in the high concentration Fucoidan group were more significant ( all P<0.05).The expression of Caspase-8 was increased and the Erk expression was decreased in the observation groups A and B,and the changes in the high concentration Fucoidan group were more significant ( all P<0.05).Conclusion Fucoidan could inhibit the proliferation of MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cell lines,arrest the breast cells in G0/G1phase,and also promote the apoptosis.This mechanism may be achieved by activating the expression of Caspase-8 and down-regulating the p-Erk expression.
Key words:Fucoidan,breast carcinoma; cell cycle; apoptosis; caspase;extracellular signal-regulated kinases
褐藻是一种软坚散结中药,褐藻多糖是其主要活性成分。褐藻多糖具有抗氧化、抗肿瘤、抗病毒、抗血栓、降血脂、调节免疫等多种功能[1~5],但具体作用机制尚不清楚。细胞凋亡具有内源性和外源性
两条信号通路,两条信号通路最终均会激活凋亡蛋白Caspase-8[6]。在肿瘤细胞增殖过程中,丝裂素活化蛋白激酶( MAPK)/细胞外调节蛋白激酶( Erk)信号通路发挥重要作用,其与细胞周期、细胞凋亡密切相关[7,8]。2013年6月~2014年5月,我们观察了褐藻多糖对人乳腺癌细胞株MCF-7、MDA-MB-231细胞活性的影响,并探讨其机制。现报告如下。
1 材料与方法
1.1材料褐藻多糖购自南京泽朗医药科技有限公司,溶于PBS中以5 mg/μL的质量浓度储存备用; MCF-7、MDA-MB-231由天津市肿瘤医院肿瘤研究所提供,用含10%胎牛血清的DMEM(高糖)培养基培养于37℃、5% CO2恒温箱中;流式细胞仪、凋亡试剂盒购于BD公司(美国),PI购于鼎国生物试剂有限责任公司; Western blot相关仪器购于北京六一器械厂,单克隆抗体Erk(鼠源)、羊抗鼠单克隆二抗购于Sigma公司,单克隆抗体Caspase-8(兔源)购于Ebcam公司。
1.2细胞增殖抑制率测算取对数生长期的MCF-7、MDA-MB-231细胞,分别消化、计数,接种于24孔板,1×104/孔。细胞贴壁后,MCF-7、MDA-MB-231细胞(观察A组、B组)分别加入100、200 μg/mL褐藻多糖2 mL,对照A组、B组均加入等体积的DMEM培养基2 mL,每组每浓度18个复孔,分别于培养2、3、4、5、6 d收集3个复孔的细胞,加入0.4%台盼蓝溶液进行细胞计数,计算两组细胞增殖抑制率。细胞增殖抑制率= (对照组平均细胞数-实验组平均细胞数)/对照组平均细胞数×100%。
1.3细胞周期和细胞凋亡检测细胞处理及分组同1.2,接种浓度为5×104/孔,每组每浓度3个复孔。收集培养96 h后的细胞,制成单细胞悬液;采用流式细胞仪检测,行AnnexinV-FITC/PI荧光染色,操作均严格按照试剂盒说明书进行。观察各细胞周期的细胞比例,计算细胞凋亡率。
1.4细胞Caspase-8、Erk、p-Erk表达检测细胞处理及分组同1.2,接种浓度1×106/孔,每组每浓度3个复孔。收集培养96 h后的细胞,裂解细胞提取蛋白。采用Western blot法检测Caspase-8、Erk、p-Erk的表达水平,以β-actin为空白对照,操作均严格按照试剂盒说明书进行。
1.5统计学方法采用SPSS17.0统计软件。计量资料以珋x±s表示,采用单因素方差分析;计数资料用率表示,组间比较用χ2检验。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1各组细胞增殖抑制率比较见表1。
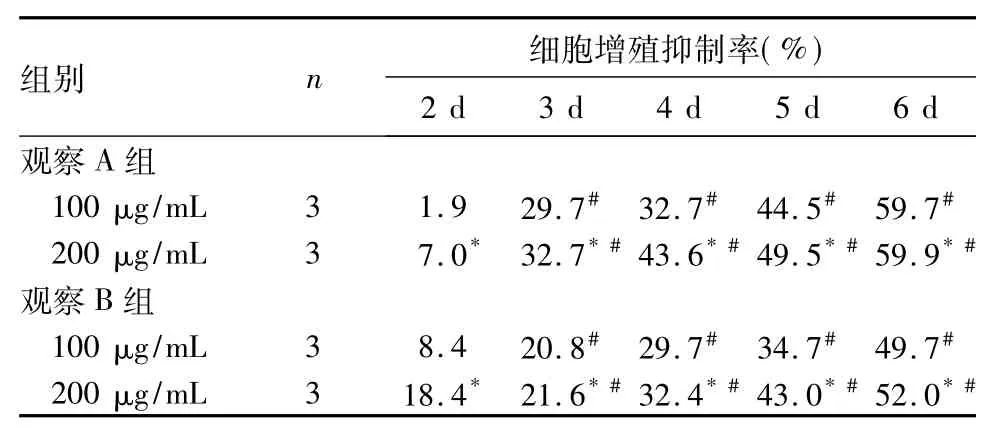
表1 两组细胞增殖抑制率比较
2.2各组细胞周期、细胞凋亡率比较见表2。
表2 各组细胞周期及细胞凋亡率比较( %,±s)
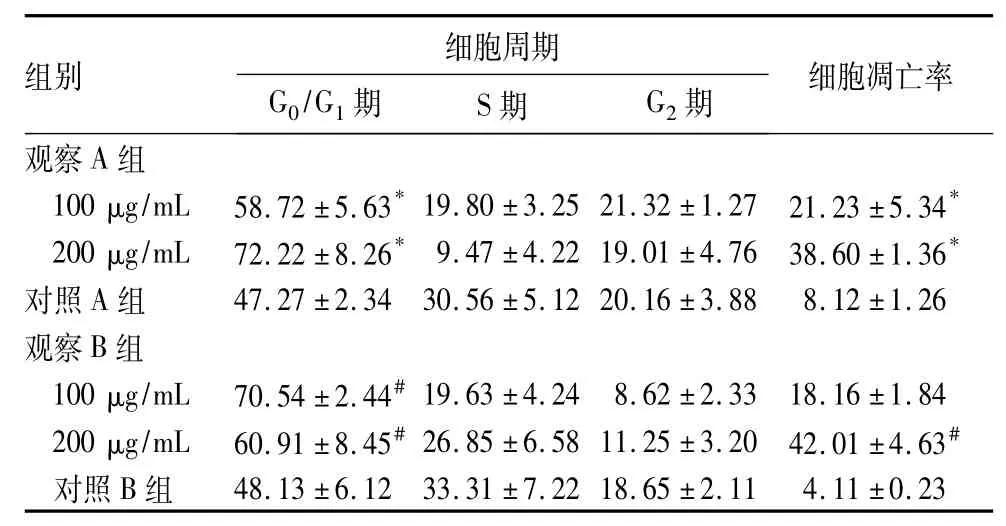
表2 各组细胞周期及细胞凋亡率比较( %,±s)
注:与对照A组比较,*P<0.05;与对照B比较,#P<0.05。
组别 细胞周期G0/G1期 S期 G2期 细胞凋亡率观察A组100 μg/mL 58.72±5.63*19.80±3.25 21.32±1.27 21.23±5.34*200 μg/mL 72.22±8.26*9.47±4.22 19.01±4.76 38.60±1.36*对照A组 47.27±2.34 30.56±5.12 20.16±3.88 8.12±1.26观察B组100 μg/mL 70.54±2.44#19.63±4.24 8.62±2.33 18.16±1.84 200 μg/mL 60.91±8.45#26.85±6.58 11.25±3.20 42.01±4.63#对照B组48.13±6.12 33.31±7.22 18.65±2.11 4.11±0.23
2.3各组细胞Caspase-8、Erk、p-Erk表达比较观察A组、B组细胞Caspase-8表达增加,p-Erk表达减少。见图1。
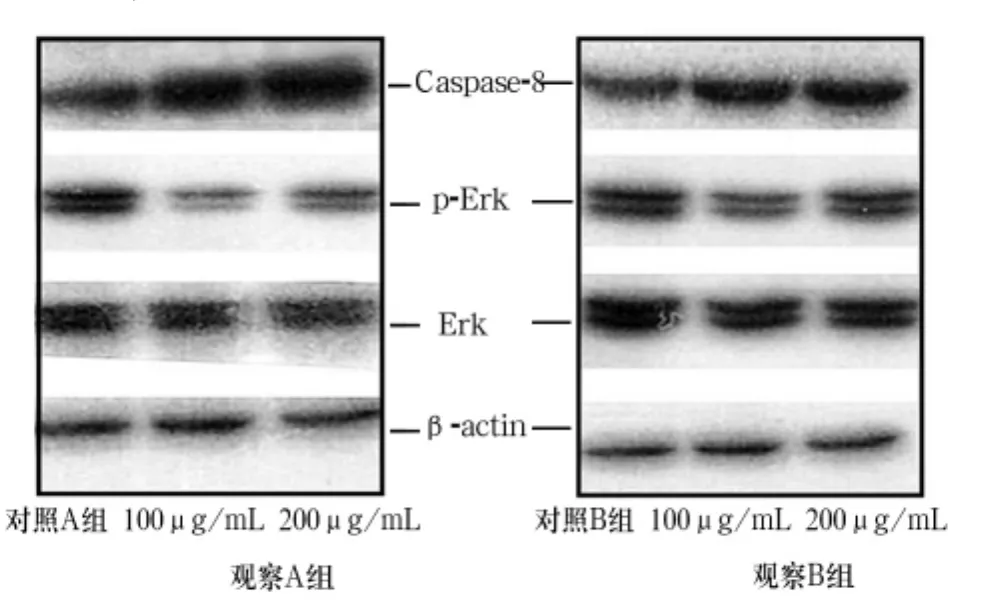
图1 各组细胞Caspase-8、Erk、p-Erk表达( Western blot)
3 讨论
褐藻多糖可促进肝癌、肺癌、黑色素瘤、胃癌等多种肿瘤细胞[9,10]的凋亡及自我吞噬[11],诱导人单核树突细胞、T细胞和自然杀伤细胞的分化成熟[12,13]。既往研究发现,褐藻多糖可通过内源性和外源性凋亡机制直接促进MCF-7细胞株的凋亡,同时还可增强化疗药物的疗效[14~18]。本研究结果发现,不同浓度褐藻多糖均可促进观察A组、观察B组的细胞增殖抑制率,同时褐藻多糖可阻滞两组细
胞于细胞周期的G0/G1期;增加细胞凋亡率。
细胞凋亡是程序性细胞死亡的一种形式,对维持生物体的正常生长、发育起重要作用,凋亡信号通路的变异是肿瘤发生发展的重要机制之一。细胞凋亡途径主要分为内源性凋亡和外源性凋亡。内源性凋亡也称为线粒体通路,当细胞接受死亡信号后通过信号转导,导致线粒体内的cytC释放入细胞质,并结合凋亡蛋白水解酶激活因子及Caspase-9前体,形成凋亡小体,激活下游的凋亡蛋白Caspase-8、Caspase-3[2]。外源性通路是通过死亡配体与细胞膜上死亡受体结合,形成死亡诱导信号复合体,激活下游Caspase-8、Caspase-3。因此,Caspase-8在内源性、外源性信号通路中均占据重要作用。MAPK级联是细胞内重要的信号转导途径,它将细胞外刺激传递至细胞核,参与细胞的生长、发育、分化等一系列生理过程,并在细胞的恶性转化和肿瘤的发生、发展中起重要作用。近来研究发现,乳腺癌中MAPK/Erk信号转导通路明显激活,p-Erk是Erk的活性形式,可通过磷酸化活化转录因子而调控特定基因的表达。研究发现,p-Erk的表达水平与乳腺癌增殖、凋亡、临床病理分型相关[19~22]。本研究结果显示,观察A组、B组细胞Caspase-8表达均增加、p-Erk表达均减少,且褐藻多糖浓度高者变化更明显。因此,我们推测褐藻多糖可能通过下调Erk磷酸化信号通路,诱导Caspase-8表达,阻滞乳腺癌细胞于细胞周期的G0/G1期,抑制乳腺癌细胞的增殖。
参考文献:
[1]刘宪丽,刘东颖,汪艳秋,等.褐藻多糖硫酸酯免疫调节和抗肿瘤活性研究[J].中国微生态学杂志,2010( 12) : 1074-1076.
[2]崔艳秋,罗鼎真,王晓民.褐藻多糖硫酸酯的抗炎与抗氧化活性研究进展[J].药学学报,2008,43( 12) : 1186-1189.
[3]陆艳娟,李晓林,李晓梅,等.褐藻多糖硫酸酯对老龄小鼠抗氧化酶活性的实验研究[J].中国老年学杂志,2006,26( 9) : 1220-1221.
[4]马浩,夏亚穆.褐藻多糖硫酸酯的生物活性及应用前景[J].化学与生物工程,2013,30( 1) : 7-10.
[5]Senthilkumar K,Manivasagan P,Venkatesan J,et al.Brown seaweed fucoidan: biological activity and apoptosis,growth signaling mechanism in cancer[J].INT J Bio Macromol,2013( 60) : 366-374.
[6]Evan GI,Vousden KH.Proliferation,cell cycle and apoptosis in cancer[J].Nature,2001,411( 6835) : 342-348.
[7]Roberts PJ,Der CJ.Targeting the Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the treatment of cancer[J].Oncogene,2007,26( 22) : 3291-3310.
[8]Hilger RA,Scheulen ME,Strumberg D.The Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK pathway in the treatment of cancer[J].Oncol Res Treatment,2002,25( 6) : 511-518.
[9]Koyanagi S,Tanigawa N,Nakagawa H,et al.Oversulfation of fucoidan enhances its anti-angiogenic and antitumor activities[J].Biochem Pharmacol,2003,65( 2) : 173-179.
[10]Kim EJ,Park SY,Lee JY,et al.Fucoidan present in brown algae induces apoptosis of human colon cancer cells[J].BMC Gastroenterol,2010,10( 1) : 96.
[11]Xue M,Ge Y,Zhang J,et al.Anticancer properties and mechanisms of fucoidan on mouse breast cancer in vitro and in vivo[J].PLoS One,2012,7( 8) : 43483.
[12]Park HS,Kim GY,Nam TJ,et al.Antiproliferative activity of fucoidan was associated with the induction of apoptosis and autophagy in AGS human gastric cancer cells[J].J Food Sci,2011,76( 3) : 77-83.
[13]Nagamine T,Hayakawa K,Kusakabe T,et al.Inhibitory effect of fucoidan on Huh7 hepatoma cells through downregulation of CXCL12[J].Nutri Cancer,2009,61( 3) : 340-347.
[14]Fitton J.Fucoidans: healthful saccharides from the sea[J].Cancer,2005,19( 20) : 21-22.
[15]Zhang Z,Teruya K,Yoshida T,et al.Fucoidan extract enhances the anti-cancer activity of chemotherapeutic agents in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 breast cancer cells[J].Mar Drugs,2013,11( 1) : 81-98.
[16]Zhang Z,Teruya K,Eto H,et al.Fucoidan extract induces apoptosis in MCF-7 cells via a mechanism involving the ROS-dependent JNK activation and mitochondria-mediated pathways[J].PLoS One,2011,6( 11) : 27441.
[17]Zhang Z,Teruya K,Eto H,et al.Induction of apoptosis by lowmolecular-weight fucoidan through calcium-and Caspase-dependent mitochondrial pathways in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells[J].Biosci Biotechnol Biochem,2013,77( 2) : 235-242.
[18]Yamasaki-Miyamoto Y,Yamasaki M,Tachibana H,et al.Fucoidan induces apoptosis through activation of Caspase-8 on human breast cancer MCF-7 cells[J].J Agr Food Chem,2009,57( 18) : 8677-8682.
[19]Zhu C,Cao R,Zhang SX,et al.Fucoidan inhibits the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma independent of angiogenesis[J].Evidbased Compl Alt,2013,53( 8) : 692549.
[20]Kwon MJ,Nam TJ.Porphyran induces apoptosis related signal pathway in AGS gastric cancer cell lines[J].Life Sci,2006( 79) : 1956-1962.
[21]Yoshida T,Sasahara Y,Miyakawa,S,Hattori M.Reduced T cell response to β-lactoglobulin by conjugation with acidic oligosaccharides[J].J Agric Food Chem,2005,53( 12) : 6851-6857.
[22]Davis TA,Volesky B,Mucci AA.Review of the biochemistry of heavy metal biosorption by brown algae[J].Water Res,2003,37 ( 7) : 4311-4330.
收稿日期:( 2015-05-08)
通信作者简介:吴雄志( 1975-),男,博士,主任医师,研究方向为中药抗癌机制研究及应用。E-mail: wuxingzhi@163.com
作者简介:第一郝剑( 1988-),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为软坚散结类中药的抗癌机制。E-mail: haojian1111520@126.com
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目( 81173376) ;新世纪优秀人才基金资助项目( NCET-11-1068)。
文章编号:1002-266X( 2015) 30-0005-03
文献标志码:A
中图分类号:R737.9

