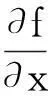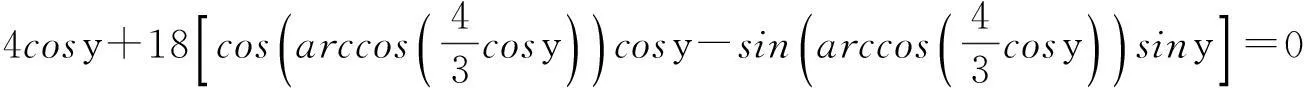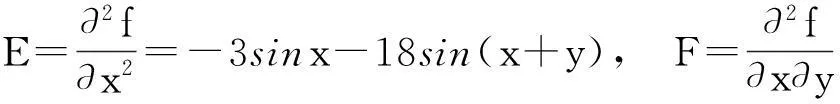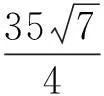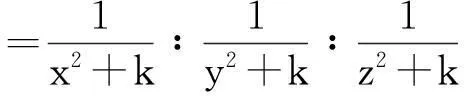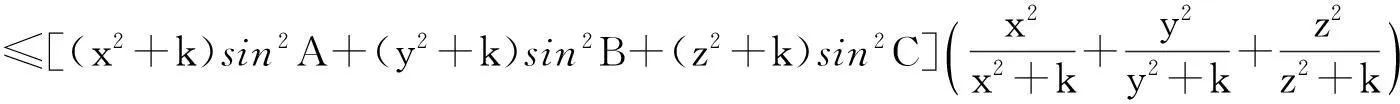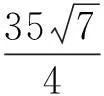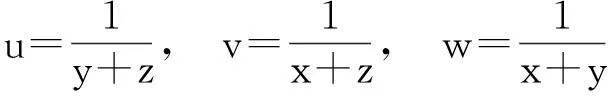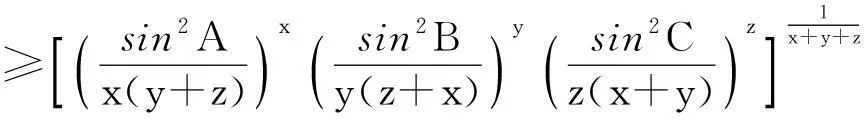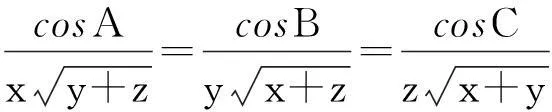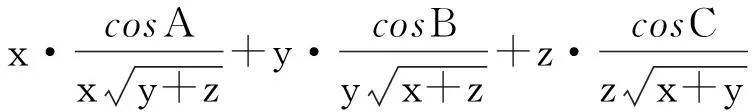一道全国大学生数学竞赛试题的解法及推广
一道全国大学生数学竞赛试题的解法及推广
王永喜1,王泽文1,刘冰2,邱淑芳1
(1.东华理工大学理学院,南昌330013;2. 南昌二中,南昌330038)
[摘要]给出了一道全国大学生数学竞赛试题的三种解答, 在此基础上研究了三角形三内角正弦的线性和最大值问题, 从而推广了竞赛试题中的结论. 最后, 研究了三内角正弦的指数之积以及余弦的指数之积的上界问题.
[关键词]大学生数学竞赛; 三角形; 嵌入不等式; 正弦定理; 余弦定理
[收稿日期]2014-11-15
[基金项目]江西省高等学校教学改革研究课题(JXJG-13-6-7); 江西省青年科学家培养计划(20122BCB23024); 江西省自然科学基金(20142BAB201008)
[中图分类号]O151.2[文献标识码]C
考虑2011年第三届全国大学生数学竞赛(数学类)的一道赛题:
对于△ABC, 求3sinA+4sinB+18sinC的最大值.
解法1该解法是依据全国大学生数学竞赛组委会给出的参考解答给出的, 但有所不同.
三角形三个角A,B,C的取值范围为
(A,B,C)∈D≡{(α,β,γ)|α>0,β>0,γ>0且α+β+γ=π}.
首先, 考虑3sinA+4sinB+18sinC在D的闭包
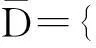
上的最大值. 于是,有



(1)


上述过程与组委会给出的解答稍有不同, 即倒数第二步直接利用Cauchy-Schwartz不等式得到是“≤”成立, 这是因为我们认为用“=”不是直接的.考虑函数

在[0,π]上的最大值问题.对于函数f(C), 显然有
f(C)≥f(π-C),∀C∈[0,π/2].
于是, 由微积分中一元函数取极值的必要条件, 得

(2)
(2)式等价于
(8cosC-1)(27cos2C+32cosC+4)=0.

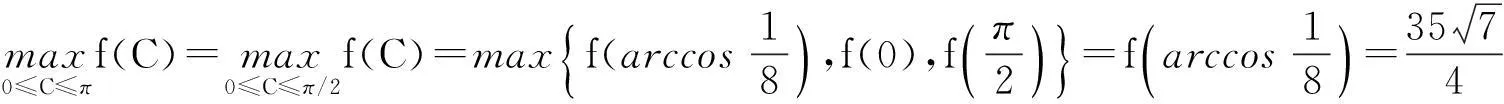

则有t>0且A=arctan(t)∈(0,π/2)⊂[0,π-C]. 因此, 成立
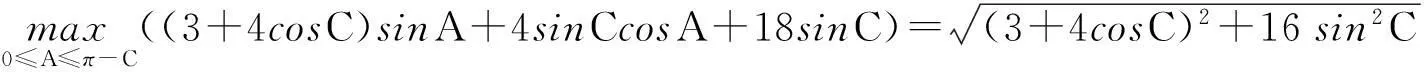
综上所述, 即得

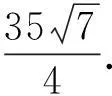
解法2 (配凑法)直接利用Cauchy-Schwarz不等式[1], 得
3sinA+4sinB+18sinC
=3sinA+4sinB+18sinAcosB+18sinBcosA
=3sinA(1+6cosB)+3cosA(6sinB)+4sinB
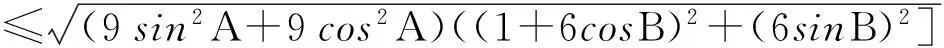
解法3因为0 3sinA+4sinB+18sinC=3sinA+4sinB+18sin(A+B). 为此, 在区域(0,π)×(0,π)上考虑二元函数 f(x,y)=3sinx+4siny+18sin(x+y) 的极值问题.由二元函数极值的必要条件, 得 (3) (4) 整理得 (16t-9)(3t2+16t+9)=0. (5) 对应t1有 对应t2有 又 那么 EG-F2=12sinxsiny+18sin(x+y)[3sinx+4siny]. 受此启发,考虑一般的问题: 对于△ABC, 求xsinA+ysinB+zsinC的最大值. 为此,先给出著名的嵌入不等式. 引理1[2-4]对于任一△ABC和任意的实数x,y,z和正整数n, 均有 x2+y2+z2≥(-1)n+12(yzcos(nA)+zxcos(nB)+xycos(nC)), (6) 当且仅当 x∶y∶z=sin(nA)∶sin(nB)∶sin(nC) 时不等式(6)取等号. 不等式(6)常称为Wolstenholme-Klamkin加权三角不等式. 定理1设x,y,z,k均是正数,且满足 对于任意三角形△ABC,有 (7) 其中上式等号成立当且仅当成立 (8) 在给出定理1证明之前, 先来证明一个引理. 则有 证由题设与正弦定理, 可知 a2∶b2∶c2=p(1-p)∶q(1-q)∶r(1-r)=p(q+r)∶q(p+r)∶r(p+q). 于是 sin(2A)∶sin(2B)∶sin(2C) =(a2(b2+c2-a2))∶(b2(c2+a2-b2))∶(c2(a2+b2-c2)) =(2pqr(q+r))∶(2pqr(r+p))∶(2pqr(p+q) =(q+r)∶(r+p)∶(p+q) 定理1的证明首先, 注意到对于给定的正数x,y,z, 满足 的k是唯一存在的. 由引理1, 可得 x2+y2+z2+2yzcos(2A)+2zxcos(2B)+2xycos(2C)≥0,x,y,z>0. 等号成立的条件是 x∶y∶z=sin(2A)∶sin(2B)∶sin(2C). 再利用二倍角公式有 (9) 用x2+k,y2+k,z2+k,k>0来代替上式中x,y,z, 则有 (x2+k)sin2A+(y2+k)sin2B+(z2+k)sin2C 上式等号成立的条件是 另一方面, 利用Cauchy-Schwarz不等式有 (xsinA+ysinB+zsinC)2 其中上式等号成立当且仅当 因此, 得到 即为 根据引理1知等号成立当且仅当 显然, 当x=3,y=4,z=18时, 由条件 可推出k=96, 故有 另一方面, 知道3sinA+4sinB+18sinC取极值时, 有 接着自然会思考一个问题,如何求解对应的余弦的线性组合的最大值问题, 如求xcosA+ycosB+zcosC 的最值问题. 为了简单起见,不妨设△ABC是锐角三角形, x,y,z都是正数的情形, 故得到如下结论[5-7]. 推论1设x,y,z为任意给定的正数, 则对于任一△ABC, 有 (10) 该定理的证明可直接由嵌入不等式得到[5]. 接下来考虑(sinA)x·(sinB)y·(sinC)z与(cosA)x·(cosB)y·(cosC)z的上界问题. 定理2设x,y,z是任意给定的正数, 对于任意三角形△ABC, 有 (11) 其中不等式成立当且仅当 证对于任意给定的正数x,y,z, 令 对u,v,w应用不等式(10)式, 得 再利用加权幂平均不等式[8], 得 即 所以 上式取等号当且仅当 定理3在锐角三角形△ABC中, 设x,y,z是任意给定的正实数, 则有 (12) 其中不等式取等号当且仅当 证利用推论1, 即在(10)式的x,y,z分别置换成 即有 然后, 利用加权幂平均不等式得 从而证得 [参考文献] [1]徐利治.数学分析的方法及例题选讲-分析学的思想、方法与技巧[M].大连∶大连理工大学出版社.2007. [2]Wu S, Debnath L. Generalization of the Wolstenholme cyclic inequality and its application[J]. Computers Mathematics with Applications January, 2007, 53: 104-114. [3]Wolstenholme J. A book of Mathematical Problems[M]. London: Cambridge Press, 1867: 250-257. [4]匡继昌.常用不等式[M].济南:山东科学技术出版社, 2004.10. [5]朱华伟.嵌入不等式-数学竞赛命题的一个宝藏[J].中等数学,2010, 1: 14-17. [6]杨学枝.数学奥林匹克不等式研究[M].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学出版社,2008:420-428. [7]沈虎跃.高中数学竞赛专题讲座-三角函数[M].杭州: 浙江大学出版社, 2007. [8]潘杰, 孟勇.关于一道数学竞赛试题[J].大学数学, 2013, 29(4): 103-105. Solutions to a Question of the Chinese Universities Mathematics Competitions and Its Generalization WANGYong-xi1,WANGZe-wen1,LIUBing2,QIUShu-fang1 (1. College of Science, East China Institute of Technology, Nanchang 330013, China; 2. Nanchang Second Middle School, Nanchang 330038, China) Abstract:This paper presents three methods are presented for solving a question of the Chinese universities mathematics competitions, and studies the maximization of the linear summation of three interior angles’ sines of a triangle which extends the conclusion of the competition question. Finally, the bounded problems of the products of the sines and cosines exponents of three interior angles are studied. Key words: universities mathematics competitions; triangle; embedding inequality; sine theorem; cosine theorem