E- 选择素在胃癌中的表达及其血行转移中作用的研究
季福建,刘选文,于 哲,房学东*,郭惠玲*
(1.吉林大学中日联谊医院新民院区普通外科,吉林长春130021;2.吉林市中心医院普通外科,吉林吉林132602)
E- 选择素在胃癌中的表达及其血行转移中作用的研究
季福建1,刘选文2,于 哲1,房学东1*,郭惠玲1*
(1.吉林大学中日联谊医院新民院区普通外科,吉林长春130021;2.吉林市中心医院普通外科,吉林吉林132602)
目的 通过检测黏附分子E-选择素在胃癌中的表达,进一步探讨E-选择素与胃癌淋巴转移及远处转移之间的关系。方法 选取2011年6月至2013年6月在吉林大学中日联谊医院行胃癌根治术的患者,从中随机选取53例经术后病理诊断为腹膜转移者作为病例组;随机选取50例术前常规检查、手术过程中的探查均未发现明确腹膜转移者作为对照组,对E-选择素的表达情况与临床病理参数之间的关系进行分析。结果 腹膜转移组中E-选择素阳性率为86.8%,对照组中E-选择素阳性率为18.0%。E-选择素阳性表达主要在血管内皮细胞的胞浆上,此外肿瘤细胞胞膜上亦可见E-选择素的表达。结论 E-选择素在胃癌大网膜转移灶中的毛细血管内皮细胞上有表达,且随着病变的进展也呈现出一个逐渐上升的趋势,所以E-选择素很可能是胃癌腹膜转移的一个重要的分子生物学标志物。
黏附分子;E-选择素;腹膜转移;胃癌
(Chin J Lab Diagn,2015,19:1469)
研究表明细胞黏附分子中E-选择素(E-selectin)与多种肿瘤的转移密切相关[14]。本文应用免疫组化的方法对43例胃癌合并远处转移蜡块标本E-selectin表达进行检测,探讨E-selectin在胃癌的表达情况及其在血行转移中的作用。
1 材料与方法
1.1 研究对象
选取2011年6月至2013年6月在吉林大学中日联谊医院行胃癌根治性手术的术后蜡块标本,选取53例胃癌患者术后病理诊断为腹膜转移,其中男性32例,女性21例,年龄49±18岁;原发灶肿瘤≤5cm为16例,>5cm为37例;浸润深度T2:4例,T3:11例,T4:38例;淋巴结转移:N1:8例,N2:17例,N3:28例;肿瘤分化程度:高、中分化腺癌:8例,低分化腺癌:27例,印戒细胞癌:13例,粘液腺癌:5例;转移病灶部位:腹壁或大网膜转移:53例;全部病例术前均未接任何治疗。对照组病例为:随机选出50例蜡块标本,50例胃癌患者术后病理均未发现腹膜转移,50例胃癌腹膜未见转移的标本中,男性31例,女性19例,年龄46±17岁;原发灶肿瘤≤5cm为37例,>5cm为13例;浸润深度T2:22例,T3:19例,T4:9例;淋巴结转移:N1:21例,N2:17例,N3:21例;肿瘤分化程度:高、中分化腺癌:36例,低分化腺癌:11例,印戒细胞癌:3例,粘液腺癌:0例。所有病例术前均未接受相关治疗。
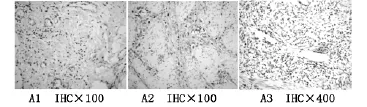
图1 E-选择素在胃癌腹膜转移灶中(血管内皮细胞)的表达(A1、A2为阳性表达,A3为阴性表达)
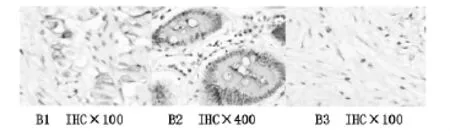
图2 E-选择素在胃癌肿瘤细胞膜上的表达(B1在肿瘤细胞膜上的阳性表达,B2在肿瘤细胞膜上的阳性表达,B3在肿瘤细胞膜上的阴性表达)
腹膜转移组中,浸润深度为T2、T3、T4的E-选择素阳性染色率分别为25%、72.7%、97.3%;淋巴结癌转移N1、N2、N3的E-选择素阳性染色率分别为62.5%、82.3%、96.4%;各组之间有显著差异(P均<0.05)(见表2)。
1.2 试验方法
运用SP免疫组化染色法。以胃癌无远处转移病例作为阴性对照,具体步骤按试剂盒进行。
1.3 结果判定标准
E-选择素以整张切片中阳性(棕黄色)染色血管≥5条为阳性。阴性对照选取胃癌患者无远处转移者。
1.4 统计学处理
采用SPSS17.0统计学软件进行统计分析,计数资料采用χ2检验,计量资料多个样本均数间比较采用方差分析,两样本均数间比较采用t检验。P<0.05认为有显著性差异,具有统计学意义。
2 结果
腹膜转移组中E-选择素阳性率为86.8%,未见转移组中E-选择素阳性率为18.0%(见表1)。E-选择素阳性表达主要在血管内皮细胞的胞浆上,此外肿瘤细胞胞膜上亦可见E-选择素的表达(见图1、2)。
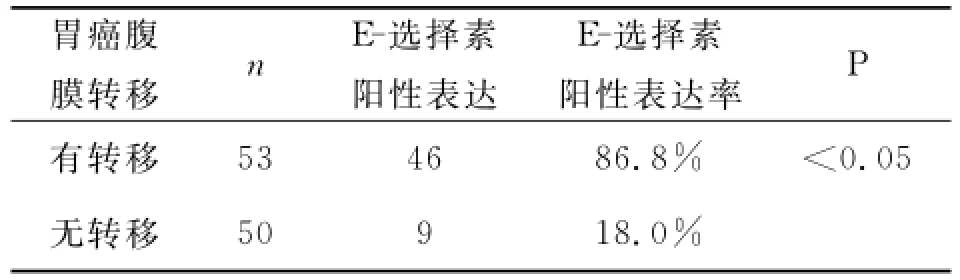
表1 E-选择素在胃癌腹膜转移与腹膜无转移中的表达
3 讨论
乳腺癌和结肠癌血清中E-selectin表达高者其分期较晚,预后较差[5]。而E-selectin在胃癌中的研究报道却极少,E-selectin是否也可以作为胃癌的肿瘤标记,特异性的应用于胃癌的转移状态?通过本次实验结果显示E-selectin可能是协同胃癌进展、侵袭及远处转移的一个重要的分子标志物,高表达E-选择素的胃癌更具侵袭性和转移性。
E-selectin介导血管内皮细胞与白细胞黏附起始阶段白细胞滞留和滚动的重要分子,还可介导肿瘤细胞与内皮细胞之间的黏附,在肿瘤转移过程中起着重要的作用[6],因此选择素作为黏附分子家族中的成员在血小板及血管内皮细胞上的表达可能是肿瘤转移发展的前提条件。E-selectin能特异性的识别肿瘤细胞表面上选择素的配体SleX及Slea,并与之结合,使肿瘤细胞与血管内皮细胞的识别和黏附,并在肿瘤转移中发挥重要作用[7]。本研究发现E-selectin的表达可能与胃癌血行转移有着密切的联系,E-selectin在有远处转移的胃癌组织中表达明显高于无远处转移者,说明E-selectin有利于胃癌细胞的远处转移,这也说明E-selectin在胃癌中的表达促使肿瘤细胞在血液中黏附于血管的内皮细胞上,从而造成血行转移。早期诊断是治愈肿瘤的关键,而肿瘤标志物检测技术的出现使早期诊断肿瘤起到了很大的促进作用。
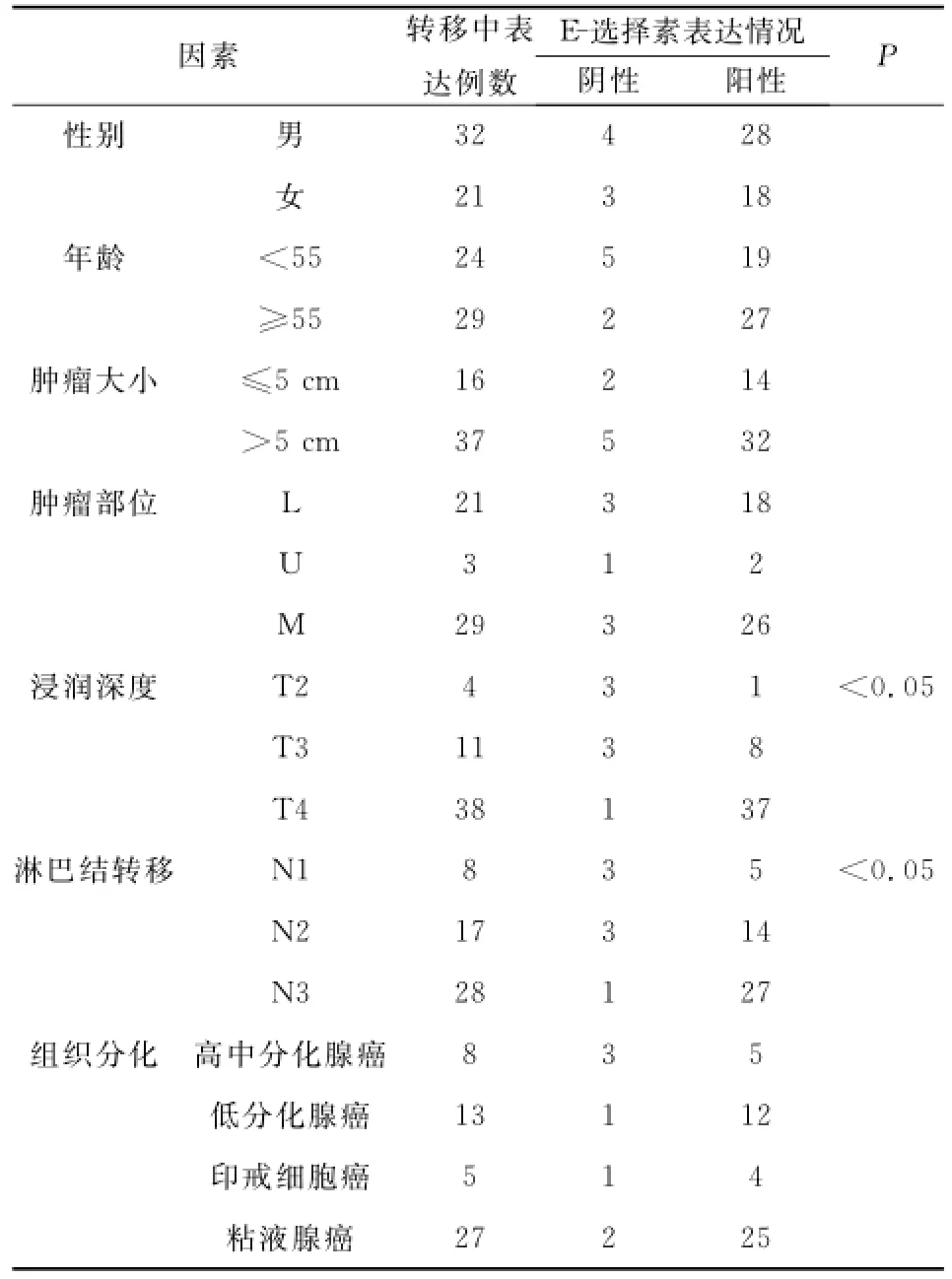
表2 胃癌腹膜转移灶中E-选择素的表达与临床病理参数间的关系
[1]Song G,Ohashi T,Sakamoto N,et al.Adhesive force of human hepatoma hepG2Cells to endothelial cells and expression of e-selectin[J].Mol Cell Biomech,2006,3(2):61.
[2]Harp AJ,Waters TE,Goff JP,et al.Expression of lymphocyte borning and adhesion molecules during intramammary infection of cows with serratia marcescens of streptococcus uberis:co-relation with bacterial colonization and clinical signa[J].Vet Immunol Immunopathol,2006,109(1):13
[3]Barthel SR,Gavino JD,Descheny L,et al.Targeting selectins and selectin ligands in inflammation and cancer[J].Expert Opin Ther Targets,2007,11(11):1473.
[4]Tremblay PL,Huot J,Auger FA.Mechanisms by which E-selectinregulates diapedesis of coloncancer cells under flowconditions[J].Cancer Res,2008,68(13):5167.
[5]Silva H C,Garcao F,Coutinho E C,et al.Soluble VCAM-1and E-selectin in breast cancer:relationship with staging and with the detection of circulating cancer cells[J].Neoplasma,2006,53(6):538.
[6]Liu J,Schuff Werner P,Steiner M.Double transfection improves small interfering RNA-induced thrombin receptor(PAR1)gene silencing in DU 145prostate cancer cells[J].FEBS Lett,2004,577(122):175.
[7]Feist ritzer C,Riewald M.Endothelial barrier protection by activated protein C through PAR1-dependent sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor-1cross activation[J].Blood,2005,105(8):3178.
A study of E-selectin expression and its effect on hematogenous metastasis in gastric cancer
JI Fu-jian,LIU Xuan-wen,YU Zhe,et al.(Department of General Surgery,Xinmin Branch of the China-Japan Union Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun130021,China)
Objective To test the expression level of adhesion molecule E-selectin in gastric cancer and then investigate the association between E-selectin and lymph node metastasis and distant metastasis of gastric cancer.Methods We chose patients who underwent radical gastrectomy from June 2011to June 2013in the China-Japan Union Hospital of Jilin University,from which 53cases who were diagnosed with peritoneal metastasis through postoperative pathology and 50cases who were found with no definite peritoneal metastasis through preoperative routine inspections and intraoperative exploration were randomly selected as peritoneal metastasis group and control group,respectively.Then we analyzed the association between E-selectin expression and clinical pathologic parameters.Results The E-selectin positive rate of peritoneal metastasis group and control group is 86.8%and 18.0%,respectively.E-selectin is mainly expressed on the cytoplasm of vascular endothelial cells and can be seen on the cell membrane of tumor cells.Conclusion Since E-selectin is expressed on the cytoplasm of vascular endothelial cells in gastric cancer omentum metastatic le-sions and the level is increasing with the progress of gastric cancer,it is probably a molecular biomarker for peritoneal metastasis in gastric cancer.
Adhesion molecule;E-selectin;Peritoneal metastasis;Gastric cancer
R735.2
A
2014-07-23)
1007-4287(2015)09-1469-03
*通讯作者

