带有非线性传染率的传染病模型动力学分析
陕振沛
(西北民族大学 数学与计算机科学学院,甘肃 兰州 730030)
带有非线性传染率的传染病模型动力学分析
陕振沛
(西北民族大学 数学与计算机科学学院,甘肃 兰州 730030)

传染病模型;平衡点;稳定性;持续性
经典的传染病模型主要关心模型平衡点的存在性和全局稳定性.近年来,由于在传染病模型中出现了一些形式更为一般的传染率,这就使得传染病模型具有更复杂的动力学性态,从而用传统的分析方法难以取得完整的定性分析结果.但是,从流行病学的意义上来讲,研究疾病的持续性与研究疾病的最终行为有着同样重要的意义.关于流行病的持续性已有一些学者进行了研究[1-3].
在经典的流行病模型中通常采用双线性型和标准型的传染率,它们通常具有较简单的动力行为.当基本再生数小于1时,无病平衡点全局渐近稳定;当基本再生数大于1时,地方病平衡点全局渐近稳定.近来,文[4-5]分别引入了依赖种群密度的传染率 f(N)SI和饱和型传染率
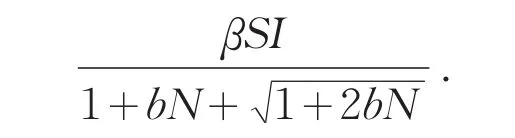
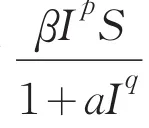
1 基本假设及模型
以S=S(t)、I=I(t)和R=R(t)分别表示t时刻易感者、染病者和恢复者的数量,并假设:
(1)K表示对种群的常数输入率
(2)d表示种群的自然死亡率
(3)α表示染病者的因病死亡率
(4)γ表示染病者的恢复率
(5)ε表示恢复者的免疫失去率,即恢复者中一部分将失去免疫而又成为易感者
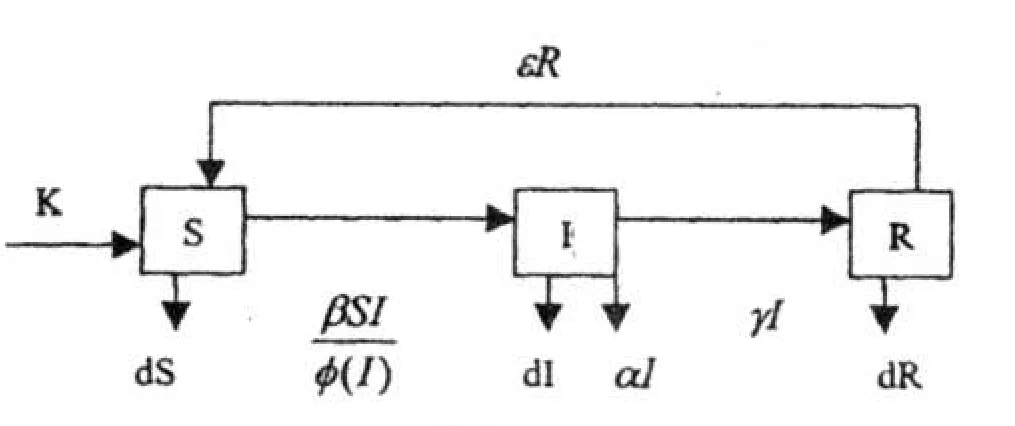
图1.疾病传染规律框图Fig.1 Diagram of the laws of disease transmission

2 SIS模型的分析


3 SIRS模型的分析


4 结论
[1]Wang W,Ma Z.Global dynamics of an epidemic model with delay[J].Nonlinear Analysis:Real World Applica⁃tions,2002,3:809-834.
[2]Wang W.Global Behavior of an SEIRS epidemic model time delays[J].Appl Math Lett,2002,15:423-428.
[3]Thieme R H.Persistence under relaxed point-dissipativity(with applications to an endemicmodel)[J].SIAM J Math Anal,1993,24:407-435.
[4]张娟,李建全,马知恩.带有种群密度制约接触率的SIR流行病模型的全局分析[J].工程数学学报,2004,21(4):259-267.
[5]Zhang J,Ma Z.Global dynamics of an SEIR epidemic model with saturating contactrate[J].Math Biol,2003,185:15-32.
[6]Liu W M,Hethcote H W,Levin S A.Dynamical behav⁃ior of epidemiological model withnonlinear incidence rates[J].J Math Biol,1987,25:359-380.
[7]Liu W M,Levin S A,Iwasa Y.In°uence of nonlinear inci⁃dence rates upon the behavior ofSIRSepidemiological models[J].J Math Biol,1986,23:187-204.
[8]Ruan S,Wang W.Dynamical behavior of an epidemic model with a nonlinear incidence rate[J].J Di®Equs,2003,188:135-163.
[9]Derrick W R,van den Driessche P.A disease transmission model in a nonconstant popula-tion[J].J Math Biol,1993,31:495-512.
Dynamic Analysis of Infectious Disease Model With Nonlinear Contagious Rate
SHAN Zhenpei
(School of Mathematics and Computer Science,Northwest Nationalities University,Lanzhou730030,China)
The paper introduced the nonlinear infection rates into SIS and SIRS type of infectious disease model with constant input,trying to get the complete results of the dynamic behavior.
infectious disease model;Balance;Stability;persistent
O 29
A
1674-4942(2011)01-0012-03
2010-11-05
西北民族大学研究生科研创新项目
毕和平

