基于神经网络的非线性多智能体系统自适应脉冲控制








摘要:针对状态不可测和存在外部未知扰动的非线性多智能体系统的一致跟踪问题,提出一种基于神经网络的分布式自适应脉冲控制方案。首先,构建复合扰动观测器,解决系统状态不可测与外部未知扰动耦合作用下的系统状态感知问题;然后,通过自适应脉冲更新律,实现神经网络权值参数的快速估计,提升系统的瞬态性能;接着,结合脉冲动态系统的Lyapunov稳定性理论,证明了闭环系统的一致最终有界性;最后,通过多单臂机械手系统的仿真实验,验证了该方案的有效性及优越性。
关键词:非线性多智能体;径向基函数神经网络;自适应控制;脉冲控制;观测器
中图分类号:TP13; TP183;"O231.2""""文献标志码:A """"""文章编号:1674-2605(2025)01-0003-10
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-2605.2025.01.003""""""""nbsp;""""""""""""开放获取
Adaptive Pulse Control of Nonlinear Multi-agent Systems """""""""""""""Based on Neural Networks
LUO Zhenfa
(Guangdong University of Technology, Guangzhou 510006,"China)
Abstract:"A distributed adaptive pulse control scheme based on neural networks is proposed for the consistent tracking problem of nonlinear multi-agent systems with unmeasurable states and external unknown disturbances. Firstly, construct a composite disturbance observer to solve the problem of system state awareness under the coupling of unmeasurable system states and external unknown disturbances. Then, by using an adaptive pulse update law, the neural network weight parameters can be quickly estimated to improve the transient performance of the system. Furthermore, based on the Lyapunov stability theory of pulse dynamic systems, it is proved that all signals in the closed-loop system are uniformly ultimately bounded. Finally, the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed scheme were verified through simulation experiments of a multi arm robotic arm system.
Keywords:"nonlinear multi-agent system; radial basis function neural network; adaptive control; pulse control; observer
0 引言
多智能体系统通过多个子系统之间的协同合作来完成各类复杂任务,广泛应用于机器人、航天器和无人机等领域[1-3]。一致跟踪控制作为多智能体系统协同合作的基本问题之一,吸引了大批学者开展研究,并取得了一定成果[4-6]。但这些研究大多集中于线性多智能体系统。对于非线性多智能体系统,特别是不确定非线性多智能体系统,其一致跟踪控制没有得到充分研究。
随着人工智能技术的快速发展,神经网络因具有良好的非线性逼近能力,被广泛应用于不确定非线性系统的自适应控制设计中。文献[7]针对高阶非线性多智能体系统,提出一种基于观测器的自适应神经网络一致跟踪控制策略,解决了系统状态不可测的问题。文献[8]讨论了不确定非线性系统的自适应神经网络输出反馈控制问题,通过其设计的干扰观测器,避免了未知扰动的影响。文献[9]提出一种基于最小学习参数的分布式多智能体系统的自适应神经网络一致跟踪控制协议,有效减少了在线学习的参数量。在自适应神经网络控制设计中,神经网络权值参数的估计十分重要,快速的自适应权值参数估计,可以改善系统的瞬态性能,获得更好的控制效果。为此,文献[10-11]设计了一种预估器来代替传统的动态面误差,由于预估误差具有额外的可调参数,加快了神经网络权值参数的估计速率,但额外的预估器使系统控制结构更加复杂,并增加了计算负担。因此,为了获得更好的瞬态性能,仍需进一步研究自适应神经网络控制。
脉冲控制可以提高系统的控制性能,具有控制动作快、结构简单、鲁棒性强等特点,在实际系统工程中得到广泛的研究与应用。文献[12]设计了脉冲反馈控制律,对给定的参考信号具有较好的跟踪效果。文献[13]引入脉冲观测器,通过合理利用原始输出来改善跟踪性能。文献[14]设计了自适应脉冲反馈控制方案,有效提高了系统的同步性能。将脉冲控制与自适应神经网络控制相结合,可获得更好的系统瞬态性能,这对控制理论的研究和应用具有重要意义。
本文针对状态不可测和存在外部未知扰动的非线性多智能体系统,设计一种基于神经网络的分布式自适应脉冲控制方案,以实现多智能体系统的一致跟踪控制。首先,构建复合扰动观测器,同时考虑了外部扰动和神经网络逼近误差,提高了系统的控制性能;然后,提出一种自适应脉冲更新律,实现神经网络权值参数的快速估计;接着,基于反步递推方法,设计自适应脉冲控制器;最后,建立一个脉冲动态系统,利用扩展的Lyapunov稳定性理论,证明了闭环系统的一致最终有界性。
1 相关内容
1.1 图论知识
1.2 问题描述
1.3 RBF神经网络
1.4 脉冲动态系统
2 方案设计
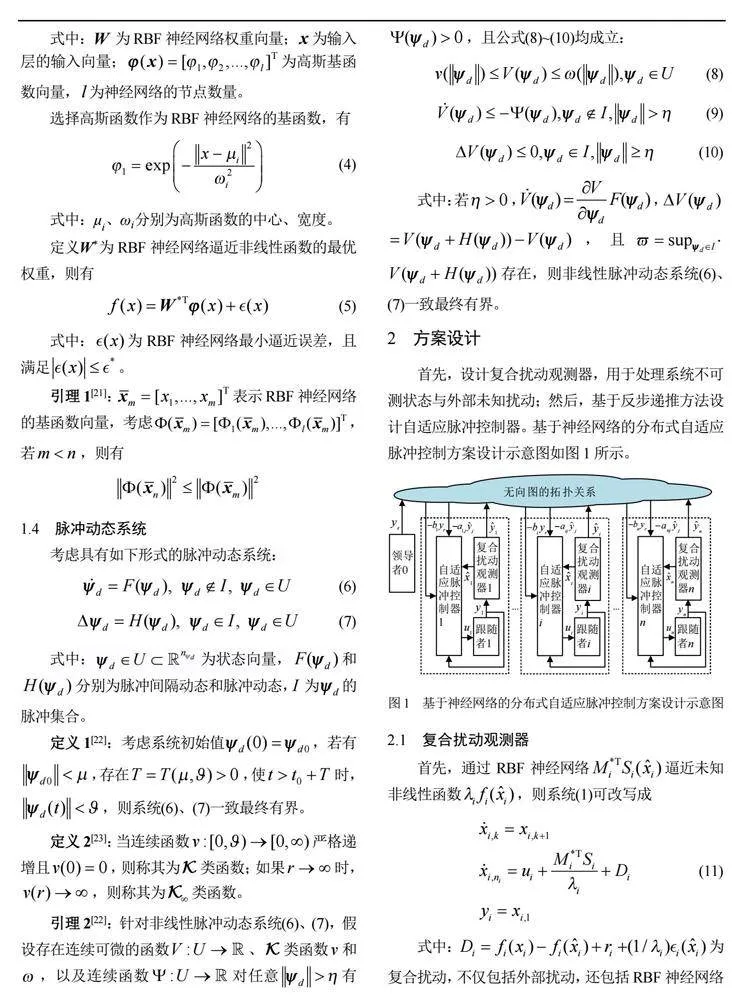
首先,设计复合扰动观测器,用于处理系统不可测状态与外部未知扰动;然后,基于反步递推方法设计自适应脉冲控制器。基于神经网络的分布式自适应脉冲控制方案设计示意图如图1所示。
2.1 复合扰动观测器
本文设计的自适应脉冲更新律,可在不产生高频振荡信号的前提下,快速自适应估计RBF神经网络的权值参数,从而提高多智能体系统的状态观测速率,改善系统瞬态性能。
2.2 自适应脉冲控制器
3 稳定性分析
首先,基于神经网络的分布式自适应脉冲控制方案建立一个脉冲动态系统,并给出主要的稳定性结果;然后,分别分析脉冲间隔动态和脉冲动态;最后,给出闭环系统的稳定性证明。
4 仿真验证
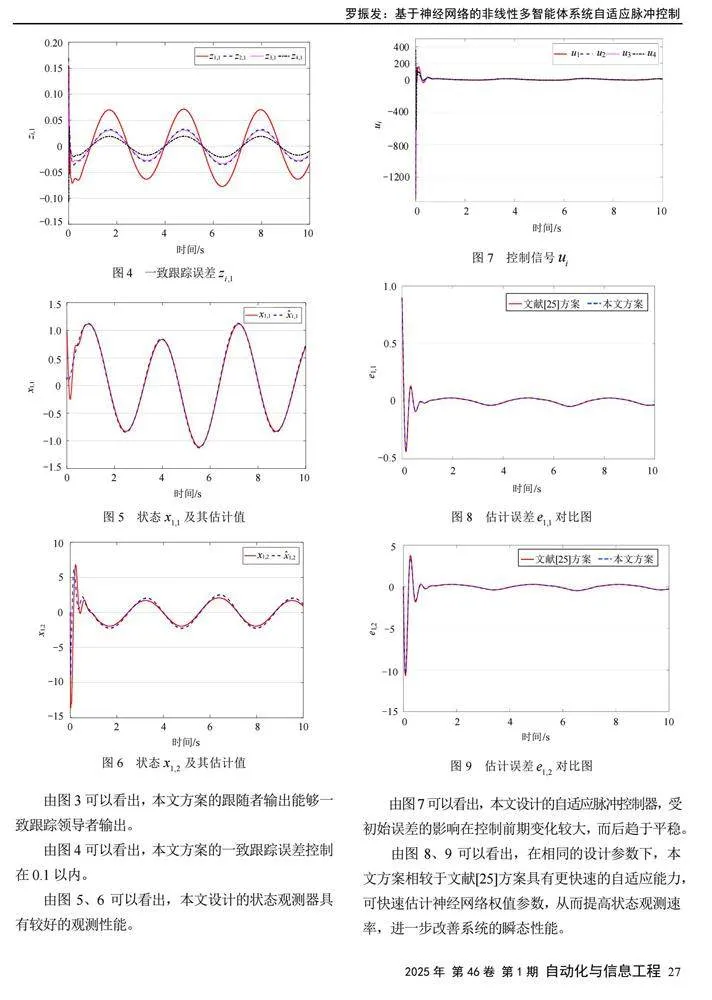
通过多单臂机械手系统的仿真实验,验证本文提出的基于神经网络的分布式自适应脉冲控制方案的有效性,并与文献[25]方案进行对比实验,验证本文方案的优越性。
在MATLAB平台上,利用本文提出的基于神经网络的分布式自适应脉冲控制方案对上述多单臂机械手系统进行仿真,结果如图3~9所示。其中,图8、9为本文方案与文献[25]方案的仿真效果对比图。
由图8、9可以看出,在相同的设计参数下,本文方案相较于文献[25]方案具有更快速的自适应能力,可快速估计神经网络权值参数,从而提高状态观测速率,进一步改善系统的瞬态性能。
5 结论
本文针对状态不可测和存在外部未知扰动的非线性多智能体系统,提出一种基于神经网络的分布式自适应脉冲控制方案,以解决系统的一致跟踪控制问题。本文提出的复合扰动观测器同时考虑了外部扰动和神经网络逼近误差,提高了系统的控制性能;自适应脉冲更新律快速实现神经网络权值参数的收敛,改善了闭环系统的瞬态性能;在脉冲动态系统中,通过扩展的Lyapunov稳定性理论证明了闭环系统的一致最终有界性。通过多单臂机械手系统的仿真对比实验,验证了本文方案的有效性和优越性。但本文方案对于其他类型的系统,如随机非线性系统、分数阶系统、切换非线性系统,是否具有普适性还有待进一步验证。同时,本文只考虑了系统状态不可测和存在外部扰动的情况,对于存在约束、控制增益未知的系统未进行研究,后续开展扩展研究十分必要。
©The author(s) 2024. This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/ by-nc-nd/4.0/)
参考文献
[1] DU H, WEN G, CHENG Y, et al. Distributed finite-time cooperative control of multiple high-order nonholonomic mo-bile robots[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2016,28(12):2998-3006.
[2] DU H, LI S. Attitude synchronization for flexible spacecraft with communication delays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2016,61(11):3625-3630.
[3] DONG X, HUA Y, ZHOU Y, et al. Theory and experiment on formation-containment control of multiple multirotor un-manned aerial vehicle systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Auto-mation Science and Engineering, 2018,16(1):229-240.
[4] WANG X, WANG H, LI C, et al. Consensus seeking in multiagent systems with Markovian switching topology under aperiodic sampled data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2018,50(12):5189-5200.
[5] WANG L, XIAO F. Finite-time consensus problems for networks of dynamic agents[J]. IEEE Transactions on Auto-matic Control, 2010,55(4):950-955.
[6] YU W, ZHENG W X, CHEN G, et al. Second-order consensus in multi-agent dynamical systems with sampled position data[J]. Automatica, 2011,47(7):1496-1503.
[7] CHEN C L P, WEN G X, LIU Y J, et al. Observer-based adaptive backstepping consensus tracking control for high-order nonlinear semi-strict-feedback multiagent systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2015,46(7):1591-1601.
[8] LIAN Y, XIA J, PARK J H, et al. Disturbance observer-based adaptive neural network output feedback control for uncertain nonlinear systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022,34(10):7260-7270.
[9] SHANG Y, CHEN B, LIN C. Consensus tracking control for distributed nonlinear multiagent systems via adaptive neural backstepping approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2018,50(7):2436-2444.
[10] PENG Z, WANG D, WANG J. Predictor-based neural dynamic surface control for uncertain nonlinear systems in strict-feedback form[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Net-works and Learning Systems, 2016,28(9):2156-2167.
[11] YANG Y, LIU Q, YUE D, et al. Predictor-based neural dynamic surface control for bipartite tracking of a class of nonlinear multiagent systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021,33(4):1791-1802.
[12] TUMA T, PANTAZI A, LYGEROS J, et al. Nanopositioning with impulsive state multiplication: A hybrid control approach [J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2012, 21(4):1352-1364.
[13] YU H, CHEN T. Event-triggered tracking control with filtered outputs and impulsive observers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020,52(6):4981-4992.
[14] ZHU D, WANG R, LIU C, et al. Synchronization of chaotic-oscillation permanent magnet synchronous generators networks via adaptive impulsive control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits"and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2019,67(10):2194-2198.
[15] ZHOU Q, DU P, LI H, et al. Adaptive fixed-time control of error-constrained pure-feedback interconnected nonlinear sys-tems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2020,51(10):6369-6380.
[16] SUI S, TONG S. Finite-time fuzzy adaptive PPC for nonstrict-feedback nonlinear MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022,53(2):732-742.
[17] CHEN D, LIU X, YU W, et al. Neural-network based adaptive self-triggered consensus of nonlinear multi-agent systems with sensor saturation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2021,8(2):1531-1541.
[18] LU S, CHEN M, LIU Y, et al. Adaptive NN tracking control for uncertain MIMO nonlinear system with time-varying state constraints and disturbances[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022,34(10):7309-7323.
[19] ZHANG Y, SUN J, LIANG H, et al. Event-triggered adaptive tracking control for multiagent systems with unknown distur-bances[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2018,50(3):890-901.
[20] WANG X, WANG H, HUANG T, et al. Neural-network-based adaptive tracking control for nonlinear multiagent systems: The observer case[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021,"53(1):138-150.
[21] SUN Y, CHEN B, LIN C, et al. Adaptive neural control for a class of stochastic nonlinear systems by backstepping ap-proach[J]. Information Sciences, 2016,369:748-764.
[22] HADDAD W M, CHELLABOINA V S, NERSESOV S G. Impulsive and hybrid dynamical systems: stability, dissipa-tivity, and control[M]. Princeton University Press, 2006.
[23] KHALIL HK. Nonlinear systems third edition[M]. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall,"2002.
[24] CHEN B, LIU X, LIU K, et al. Direct adaptive fuzzy control of nonlinear strict-feedback systems[J]. Automatica, 2009,45(6): 1530-1535.
[25] CHEN M, GE S S. Adaptive neural output feedback control of uncertain nonlinear systems with unknown hysteresis using disturbance observer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2015,62(12):7706-7716.
作者简介:
罗振发,男,1999年生,硕士研究生,主要研究方向:自适应控制、神经网络。E-mail:"m18379124404@163.com

