重庆地区畜禽源大肠杆菌耐药性变化分析





摘要:【目的】对比重庆地区近10年来畜禽源大肠杆菌对常用抗菌药物的耐药率及部分可水平转移耐药基因阳性率的变化趋势,为该地区大肠杆菌耐药性的科学控制提供参考依据。【方法】从重庆市12个区县的13个养殖场采集畜禽粪便样本,经细菌分离纯化后共获得157株大肠杆菌(2007—2008年76株,2020年81株),通过体外抑菌试验检测受试大肠杆菌对18种抗菌药物的敏感性,采用PCR检测39株多重耐药大肠杆菌中的17种可水平转移耐药基因,利用MLST分型和系统进化分群探析其分子进化关系,并根据耐药谱对9株多重耐药大肠杆菌进行全基因组测序。【结果】重庆地区畜禽源大肠杆菌的多重耐药率由2007—2008年的96.05%降至2020年的75.31%,对四环素类(土霉素和米诺环素)、酰胺醇类(氟苯尼考)、氟喹诺酮类(恩诺沙星和环丙沙星)、氨基糖苷类(链霉素、庆大霉素和阿米卡星)的耐药率由13.16%~85.53%降至0~45.68%,耐药谱以五重~六重为主转变为以二重~四重为主。相对于2007—2008年分离菌株,2020年分离菌株对磺胺类(sul1)、β-内酰胺类(blaTEM)、氨基糖苷类[aadA1和aph(3')-Ia]和多肽类(mcr-1)耐药基因的检出率呈下降趋势,但对酰胺醇类(floR)和喹诺酮类(qnrS)耐药基因的检出率呈上升趋势。选取的39株受试大肠杆菌存在29种ST型,其中3种为新发现的ST型,分别是ST12677、ST12678和ST12679;系统进化分群分布相似,可分为A群、B1群和D群。受试大肠杆菌检出可水平转移耐药基因的个数和种类较丰富,其中,2007—2008年分离菌株检出10~14个(4~7类)可水平转移耐药基因,2020年分离菌株检出9~18个(6~10类)可水平转移耐药基因。【结论】重庆地区畜禽源大肠杆菌对部分抗菌药物的耐药性明显下降,多重耐药现象得到一定程度的缓解,但部分菌株仍携带大量可水平转移耐药基因,因此其水平传播方式及控制措施还有待进一步探究,应根据耐药性变化趋势建立适宜的替抗方案,以逐步改善多重耐药现状及维护公共卫生安全。
关键词:大肠杆菌;抗菌药物;多重耐药性;耐药基因;重庆地区
中图分类号:S852.61文献标志码:A文章编号:2095-1191(2024)10-3179-11
Changes in drug resistance of poultry and livestock sourced Escherichia coli in Chongqing
ZHOU Jie,MU Hang,WANG Shu-bo,HU Jun,GAO Wei,WU Jun-wei,WEI Shu-yong*
(College of Veterinary Medicine,Southwest University,Chongqing 402460,China)
Abstract:【Objective】To compare the changes in antimicrobial resistance rates and the prevalence of horizontally transferable drug resistance genes in Escherichia coli from livestock and poultry in Chongqing over the past decade,pro-viding scientific basis for controlling E.coli antimicrobial resistance in this region.【Method】Fecal samples were collected from livestock and poultry on 13 farms across 12 districts in Chongqing.A total of 157 E.coli strains(76 from 2007–2008 and 81 from 2020)were obtained after bacterial isolation and purification.Antimicrobial susceptibility to 18 antibiotics was evaluated through in vitro bacteriostatic tests.PCR was used to detect 17 horizontally transferable drug resistance genes in 39 multi-drug resistant E.coli strains.Molecular evolution relationships were analyzed using multilocus sequence typing(MLST)and phylogenetic clustering.Nine multidrug resistant E.coli strains were selected for whole-genome se-quencing based on their resistance spectrum.【Result】The multi-drug resistance rate of livestock and poultry E.coli in Chongqing decreased from 96.05%during 2007–2008 to 75.31%in 2020.Resistance rates to tetracyclines(oxytetracy-cline,minocycline),amphenicols(florfenicol),fluoroquinolones(enrofloxacin,ciprofloxacin),and aminoglycosides(streptomycin,gentamicin,amikacin)declined from 13.16%-85.53%to 0-45.68%.The resistance spectrum shifted from predominantly five-to six-drug resistance to two-to four-drug resistance.Compared to 2007–2008 isolates,2020 isolatesshowed decreased detection rates of resistance genes for sulfonamides(sul1),β-lactams(blaTEM),aminoglycosides[aadA1 and aph(3')-Ia and polymyxins(mcr-1),but increased detection rates for genes related to amphenicols(floR)and quinolones(qnrS).Among the 39 tested strains,29 sequence types(STs)were identified,including 3 novel STs:ST12677,ST12678,and ST12679.Phylogenetic clustering revealed similar distributions,with all isolates grouped into A,B1,and D clusters.Horizontally transferable drug resistance genes were abundant in quantity and types,with isolatesfrom 2007–2008 carrying 10-14 genes(4-7 types)and those from 2020 carrying 9-18 genes(6-10 types).【Conclusion】While resistance of E.coli strains from livestock and poultry to certain antibiotics has greatly declined in Chongqing,and multi-drug resistance has been alleviated to some extents,some strains still carry a substantial number of transferable drugresistancegenes.This highlights the importance of further investigation into horizontal transmission mechanisms and con-trolstrategies.Developing suitable alternative antimicrobial programs based on resistance trends may help mitigate multi-drug resistance and safeguard public health.
Key words:Escherichia coli;antimicrobial agents;multi-drug resistance;resistance genes;Chongqing
Foundation items:Youth Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China(32302852);Fundamental Re-search Fund for the Central Universities(XDJK2020C021)
0引言
【研究意义】大肠杆菌(Escherichia coli)是肠杆菌科(Enterobacteriaceae)的代表菌种,主要存在于人类及动物的胃肠道等器官中。由于长期大量甚至不合理使用抗菌药物,导致动物源细菌的耐药性及多重耐药性(Multi-drug resistance,MDR)现象泛滥,严重阻碍了细菌性疾病的治疗(杨承霖等,2020;徐军,2021;杨影影等,2022)。在细菌已产生耐药性的情况下,由于水平基因转移(Horizontal gene transfer,HGT)的存在,减少抗菌药物使用并不足以逆转其耐药性(李嘉敏和张玲,2023)。大肠杆菌被认为是耐药基因的存储库和HGT源头菌(方光远等,2023;吴玉双,2023),携带可水平转移耐药基因的大肠杆菌通过环境、接触和食物链等途径在自然界广泛传播,进而造成环境污染、食品安全及人体健康等全球性公共卫生问题(Mandal et al.,2022),因此延缓和控制其多重耐药现象已成为全球关注的热点。【前人研究进展】我国作为全球抗菌药物的生产和使用大国,抗菌药物滥用情况曾经十分严重。2009—2019年,我国兽用抗菌药物使用量占兽用化学药品总用量的69.6%~74.1%,且药物残留在食用产品中的检出率超过90.0%(程兆康等,2022;涂闻君等,2022)。自20世纪90年代以来,大肠杆菌耐药率呈直线上升趋势,其中β-内酰胺类、氨基糖苷类、四环素类、磺胺类和喹诺酮类药物的耐药增长率均在10%~30%(张玉杰等,2023)。近年来,部分畜禽源大肠杆菌的耐药率仍保持在高水平,如猪(张锦熙,2021;张兆天等,2023)、牛(孙月等,2023)、羊(杨莉等,2023;张洪浩等,2023)、兔(王莉等,2023)、鸡(高笑等,2023;刘挺等,2023)、鸭(宋毅等,2023)等养殖动物源大肠杆菌对氨苄西林、庆大霉素、四环素、恩诺沙星和复方新诺明等药物的耐药率均在50%以上。为保障动物性食品安全及合理控制动物源细菌耐药性发展,我国逐步规范抗菌药物的管理,减量、限制和禁止了部分抗菌药物的生产与使用(巨向红,2023)。我国自实施“减抗”政策以来,各类抗菌药物使用量呈明显的下降趋势(侯薄等,2017;徐军,2021;王翠月等,2022)。据统计,2018年我国兽用抗菌药使用总量较2014年下降了57.03%,2020年的兽用抗菌药物使用总量较2017年下降了21.90%。此外,临床分离菌也逐渐恢复了对部分抗菌药物的敏感性,如恩诺沙星和黏菌素等(Du etal.,2020;Wang et al.,2020;张译心,2022;Shen et al.,2022;蒋宇轩等,2023)。【本研究切入点】川渝地区是我国畜禽养殖的重要区域,但在“减抗”等相关政策实施下该地区畜禽源大肠杆菌耐药性和耐药基因的变化尚缺乏足够研究数据。【拟解决的关键问题】对比重庆地区近10年来畜禽源大肠杆菌对常用抗菌药物的耐药率及部分可水平转移耐药基因阳性率的变化趋势,为该地区大肠杆菌耐药性的科学控制提供参考依据。
1材料与方法
1.1试验材料
2007—2008年及2020年分别从重庆市荣昌、大足、铜梁等12个区县的13个养殖场采集畜禽粪便样本,经分离鉴定共获得157株大肠杆菌,其中,2007—2008年76株,占48.41%,2020年81株,占51.59%。鸡源大肠杆菌81株,占51.59%;猪源大肠杆菌76株,占48.41%。标准菌株ATCC25922购自中国兽医药品监察所;米诺环素(S1038)等16种药敏纸片及MH琼脂(M0202)和麦康凯琼脂(M0004-1)培养基购自杭州微生物试剂有限公司;土霉素(Z21088)购自温州市康泰生物科技有限公司;多黏菌素B(MB1188)购自大连美仑生物技术有限公司;MH肉汤(HB6231)和LB肉汤(HB0128)培养基购自海博生物技术有限公司;2×Taq Master Mix(P112-01)购自南京诺唯赞生物科技股份有限公司;DL2000 DNA Marker(B500350)购自生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司;绿色荧光核酸染料(G8140)购自北京索莱宝科技有限公司;HiPure Bacterial DNA Kit(D3146)购自上海迈跟生物科技有限公司。
1.2试验方法
1.2.1耐药表型检测参照CLSI推荐的方法进行体外抑菌试验(阮紫涵等,2022)。采用纸片扩散法和微量肉汤稀释法(多黏菌素B)分别测定157株受试菌株对18种抗菌药物的敏感性,比对分析不同时间来源菌株的耐药性差异,对3类及以上抗菌药物同时耐药的菌株即判定为多重耐药菌株。
1.2.2耐药基因检测根据耐药谱,提取39株(2007—2008年分离菌株16株,2020年分类菌株23株)多重耐药大肠杆菌的基因组DNA。参照Gene-Bank已公布的17种耐药基因序列,使用Primer 5.0设计耐药基因扩增引物(表1),并委托生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司合成。PCR反应体系25.0μL:2×Taq Master Mix 12.0μL,DNA模板2.0μL,上、下游引物各1.0μL,ddH2O 9.0μL。扩增程序:94℃预变性4 min;94℃30 s,退火30 s,72℃30 s,进行30个循环;72℃延伸7 min。PCR扩增产物使用1.0%琼脂糖凝胶电泳和凝胶成像分析系统进行检测。
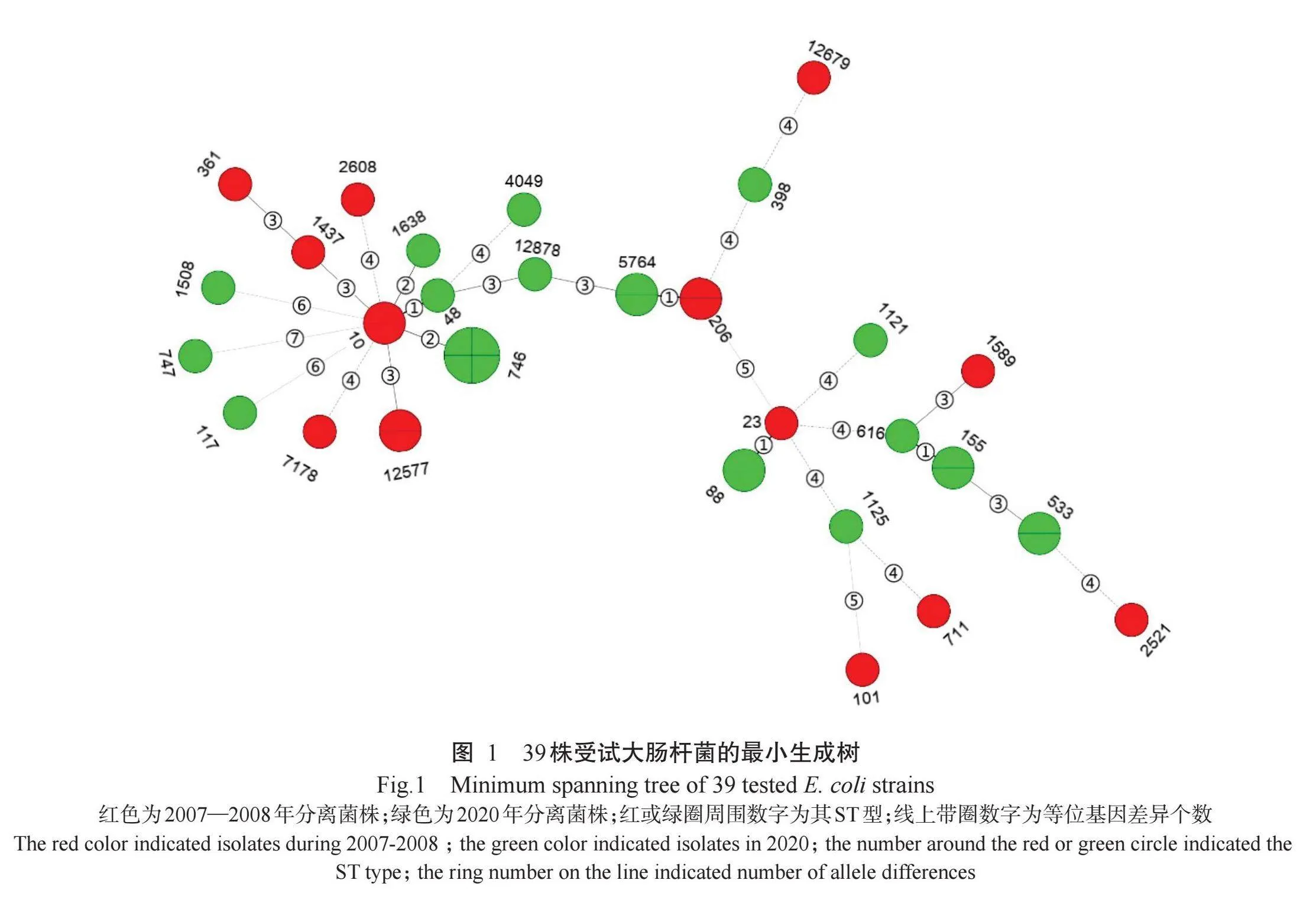
1.2.3 MLST分型及聚类分析以MLST网站(http://mlst.ucc.ie/mlst/dbs/Ecoli)提供的7对管家基因为目的基因,对上述39株多重耐药大肠杆菌进行MLST分型,引物序列信息见表1。PCR反应体系及扩增程序同1.2.2,扩增产物送至生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司进行双向测序,经BioNumerics 8.0校对及拼接与剪切后,提交至MLST网站的电子数据库进行匹配,以获得菌株的7个等位基因编号、序列型及克隆群(Complex clone,CC),未完全匹配和定型的菌株则获得新ST型,并通过Categorical法计算相似性系数,构建最小生成树。
1.2.4系统进化群分配根据Clermont等(2000)报道的三重PCR,以chuA、yjaA和TspE4.C2基因为目的基因同时进行PCR扩增,引物序列信息见表1。对上述39株多重耐药大肠杆菌主要进化群(A、B1、B2、D)进行分配,PCR反应体系及扩增程序同1.2.2。系统进化群判定标准:扩增出chuA基因条带或同时出现chuA和TspE4.C基因2种条带的菌株属于D群;同时出现chuA和yjaA基因2种条带或chuA、yjaA和TspE4.C2基因3种条带的菌株属于B2群;扩增后无条带或仅出现yjaA基因条带的菌株属于A群;只出现TspE4.C2基因条带的菌株属于B1群。
1.2.5全基因组测序根据耐药谱,选择9株(2007—2008年分离菌株4株,2020年分离菌株5株)受试菌株,使用MagPure bacterial DNA Kit提取基因组,委托生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司通过Illumina HiSeq测序平台完成全基因组测序,然后将基因序列输入CARD耐药基因数据库进行BLAST比对分析,筛选出耐药相关基因。
2结果与分析
2.1耐药表型检测结果
重庆地区畜禽源大肠杆菌多重耐药率为85.35%(134/157),其中,2007—2008年分离菌株的多重耐药率为96.05%(73/76),2020年分离菌株的多重耐药率为75.31%(61/81)。就抗菌药物而言,2020年分离菌株对四环素类(土霉素和米诺环素)、酰胺醇类(氟苯尼考)、氟喹诺酮类(恩诺沙星和环丙沙星)、氨基糖苷类(链霉素、庆大霉素和阿米卡星)药物的耐药率较2007—2008年分离菌株呈明显下降趋势,由13.16%~85.53%降至0~45.68%(表2)。此外,157株受试大肠杆菌的耐药谱型多且分散(表3),2007—2008年分离菌株以五重~六重耐药为主,占70.00%以上;2020年分离菌株以二重~四重耐药为主,占80.00%以上。
2.2耐药基因检测结果
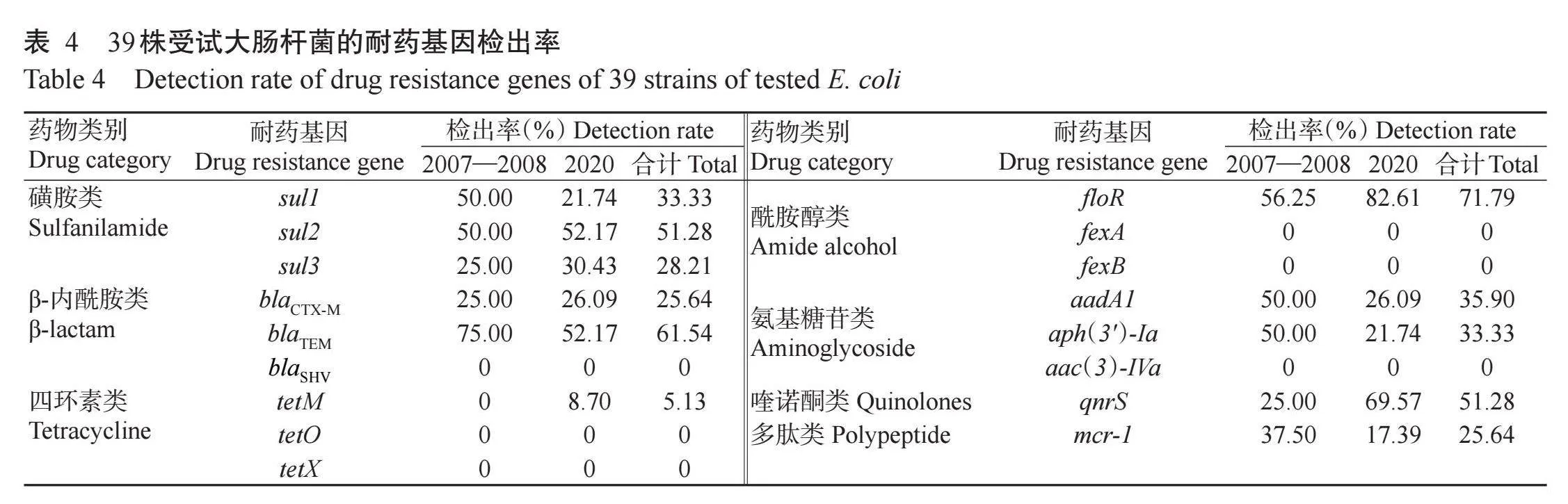
在17种可水平转移耐药基因中,有sul1、sul2、sul3、blaCTX-M、blaTEM、tetM、floR、aadA1、aph(3')-Ia、qnrS及mcr-1等11种耐药基因被检出(表4)。相对于2007—2008年分离菌株,2020年分离菌株对磺胺类(sul1)、β-内酰胺类(blaTEM)、氨基糖苷类[aadA1和aph(3')-Ia]和多肽类(mcr-1)耐药基因的检出率呈下降趋势,对酰胺醇类(floR)和喹诺酮类(qnrS)耐药基因的检出率则呈上升趋势。
2.3 MLST分型及聚类分析结果
39株受试大肠杆菌存在29种ST型,其中3种为新发现的ST型,分别是ST12677、ST12678和ST12679。2007—2008年分离菌株与2020年分离菌株无交叉ST型,2007—2008年分离菌株检出13种ST型,其优势ST型为ST206、ST10和ST12677,各占12.50%(2/16);2020年分离菌株检出16种ST型,其优势ST型为ST746,占17.39%(4/23)。ST聚类分析结果(表5)显示,29种不同的ST型聚类为6个克隆群,且以ST10 Cplx为优势克隆群。在6个克隆群中,ST23 Cplx、ST10 Cplx和ST206 Cplx同时存在于不同年份的分离菌株样本中,构成了较小的克隆系。此外,ST10与ST48和ST1638,ST88与ST23,ST206与ST5764具有较近的亲缘关系(图1)。
2.4系统进化分群结果
以chuA、yjaA和TspE4.C2基因为目的基因进行三重PCR扩增,结果(表5)显示,39株受试大肠杆菌可分为A群(26株,占66.67%)、B1群(11株,占28.20%)和D群(2株,占5.13%)。其中,2007—2008年分离菌株样本可分为A群(12株,占75.00%)和B1群(4株,占25.00%);2020年分离菌株样本可分为A群(14株,占60.87%)、B1群(7株,占30.43%)和D群(2株,占8.70%)。
2.5全基因组测序结果
9株受试大肠杆菌检出的外排泵家族基因相似,2007—2008年分离菌株和2020年分离菌株均检出MFS、RND、SMR家族的外排泵基因25~27个(表6)。此外,受试大肠杆菌检出可水平转移耐药基因的个数和种类较丰富,其中,2007—2008年分离菌株检出10~14个(4~7类)可水平转移耐药基因,2020年分离菌株检出9~18个(6~10类)可水平转移耐药基因。
3讨论
自抗菌药物被投入畜禽养殖业以来,细菌耐药性和兽药残留问题已受到广泛关注(徐军,2021;刘婷等,2023)。20世纪80年代,瑞典率先颁布了养殖业抗生素禁用的相关规定(刘婷等,2023),随后其他国家和地区也开始加入到抗生素减量使用行动中。21世纪以来,我国针对食品动物抗菌药物的生产和使用陆续出台了各项相关规定(巨向红,2023)。2003年,农业部公告第278号规定禁止恩诺沙星、氧氟沙星及环丙沙星用于产蛋鸡;2005年,农业部公告第560号规定禁止头孢哌酮、头孢噻肟等21种抗菌药用于食品动物;2015年,农业部公告第2292号规定停止生产用于食品动物的洛美沙星、培氟沙星、氧氟沙星、诺氟沙星等4种原料药的各种盐、酯及其制剂;2016年,农业部公告第2428号规定停止硫酸黏菌素用于动物促生长;2018年,农业部公告第2638号规定停止生产喹乙醇、氨苯胂酸、洛克沙胂等3种兽药的原料药及各种制剂;2020年,农业农村部公告第250号规定禁止氯霉素、万古霉素等21类药品及其他化合物用于食品动物。此外,Wang等(2020)通过比较2015—2018年我国黏菌素的产量与销量变化,并计算人类、畜禽源黏菌素耐药大肠杆菌的流行率及mcr-1基因丰度,指出我国对黏菌素用药限制等相关政策的实施对降低黏菌素耐药水平有显著影响。张译心(2022)分析全面禁止使用抗生素2年后四川成都地区猪源金黄色葡萄球菌的耐药性,结果发现部分分离株已恢复对氟喹诺酮类和恶唑烷酮类药物的敏感性。畜禽作为我国抗菌药物的主要消耗群体,极易产生多重耐药性(侯薄等,2017;刘婷等,2023)。本研究通过分析重庆地区畜禽源大肠杆菌在全面禁止使用抗生素前后2个阶段的耐药性变化,MLST分型和系统进化分群结果显示2007—2008年分离菌株和2020年分离菌株间存在一定的分子进化相关性,对重要抗菌药物如恩诺沙星和环丙沙星等的耐药率明显降低,耐药谱也明显缩短,与徐小明等(2018)、陈春林等(2019)的研究结果基本一致,究其原因可能与我国对氟喹诺酮类等药物使用政策的调整有关。此外,虽然受试大肠杆菌多重耐药株的检出率有所降低,但对氨苄西林及磺胺类药物的耐药率下降不明显,畜禽源大肠杆菌多重耐药的问题仍然存在。细菌耐药水平降低的同时,细菌性疫病的发生率逐年提升(孙泉云等,2022)。为此,农业农村部制定的《全国兽用抗菌药使用减量化行动方案(2021—2025年)》明确指出支持和鼓励兽用抗菌药替代产品的应用。已有研究表明,植物精油(李伟等,2021)、天然化合物(Zhang et al.,2021;巨向红,2023;Gao et al.,2023)、微生物发酵产物(王佰涛等,2022)、益生菌(王虎,2022)、中兽药(张莉等,2022;白飞英和吴文明,2023)、酸化及酶制剂(王恬和张昊,2023)等兽用抗菌药替代产品均具有良好的推广应用前景。
大肠杆菌具有较强的耐药基因积累能力(Poirel et al.,2018),是可水平转移耐药基因的重要宿主细菌(吴玉双,2023)。大量耐药基因可通过质粒等可移动遗传元件(Mobile genetic elements,MGEs)在不同菌株间水平转移,致使敏感菌株产生耐药性(Schink et al.,2012;刘五高等,2015;Alonso et al.,2017),如β-内酰胺类(blaCTX-M、blaTEM、blaSHV和blaCMY)、喹诺酮类[qnrS和aac(6')-Ib-cr]、氨基糖苷类[aadA、aph(3′)-Ia和aac(3)-Iva]、四环素类(tetA和tetB)、酰胺醇类(floR和cmlA)、磺胺类(sul1、sul2和sul3)、多肽类(mcr-1)及磷霉素类(fosA)等耐药基因(Call etal.,2010;Hou et al.,2012;Siqueira et al.,2016;Freitag et al.,2017;Liu et al.,2019)。本研究发现,2007—2008年分离菌株和2020年分离菌株携带的可水平转移耐药基因种类丰富且具有一定相似性,2020年分离菌株对sul1、sul2、sul3、blaCTX-M、blaTEM、tetM、floR、aadA1、aph(3')-Ia、qnrS及mcr-1等11个耐药基因的检出率与2007—2008年分离菌株间无明显规律变化,可能是大肠杆菌耐药机制呈多样性,PCR扩增仅能对有限数量的耐药基因进行检测,但在一定程度上也提示现阶段可水平转移耐药基因仍在畜禽源大肠杆菌中广泛存在,全基因组测序也验证了这一结论。
4结论
重庆地区畜禽源大肠杆菌对部分抗菌药物的耐药性明显下降,多重耐药现象得到一定程度的缓解,但部分菌株仍携带大量可水平转移耐药基因,因此其水平传播方式及控制措施还有待进一步探究,应根据耐药性变化趋势建立适宜的替抗方案,以逐步改善多重耐药现状及维护公共卫生安全。
参考文献(References):
白飞英,吴文明.2023.中兽医药在减抗替抗养殖业中的发展趋势[J].中国禽业导刊,40(9):12-16.[Bai F Y,Wu W M.2023.Development trend of traditional Chinese veteri-nary drugs in antimicrobial reduction and substitute bree-ding industry[J].Guide to Chinese Poultry,40(9):12-16.]
陈春林,冯刚,秦杨,付利芝.2019.重庆地区鸡源大肠杆菌、沙门氏杆菌耐药性的测定与分析[J].黑龙江畜牧兽医,(12):85-88.[Chen C L,Feng G,Qin Y,Fu L Z.2019.Determination and analysis of drug resistance of Esche-richia coli and Salmonella from chickens in Chongqing[J].Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medi-cine,(12):85-88.]doi:10.13881/j.cnki.hljxmsy.2018.07.0325.
程兆康,杨金山,吕敏,罗小三.2022.我国畜禽养殖业抗生素的使用特征及其环境与健康风险[J].农业资源与环境学报,39(6):1253-1262.[Cheng Z K,Yang J S,LüM,Luo X S.2022.Antibiotics used in livestock and poultry bree-ding and its environmental and health risks in China:A review[J].Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environ-ment,39(6):1253-1262.]doi:10.13254/j.jare.2021.0567.
方光远,谈福利,张智敏,单星月,袁光苏,王喜国,陈俊红,胡志华,蒋加进,戴鼎震.2023.仔猪腹泻大肠杆菌耐药性和超广谱β-内酰胺酶基因检测分析[J].江苏农业科学,51(10):53-57.[Fang G Y,Tan F L,Zhang Z M,Shan X Y,Yuan G S,Wang X G,Chen J H,Hu Z H,Jiang J J,Dai D Z.2023.Detection and analysis of Escherichia coli drug resistance and extended-spectrumβ-lactamase gene of diar-rhea piglets[J].Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences,51(10):53-57.]doi:10.15889/j.issn.1002-1302.2023.10.007.
高笑,徐亚昆,丁鹏云,马胜男,潘玉善,苑丽,胡功政,贺丹丹.2023.鸡源携带黏菌素耐药基因mcr-1大肠杆菌的流行情况及耐药性研究[J].中国畜牧兽医,50(12):5148-5159.[Gao X,Xu Y K,Ding PY,Ma S N,Pan Y S,Yuan L,Hu G Z,He D D.2023.Prevalence and drug resistance analysis of Escherichia coli with colistin resistance gene mcr-1 from chickens[J].Chinese Animal Husbandryamp;Veterinary Medicine,50(12):5148-5159.]doi:10.16431/j.cnki.1671-7236.2023.12.036.
侯薄,王卫,付智星,余静.2017.养禽业抗生素使用现状及无抗养殖研究进展[J].食品工业,38(8):216-220.[Hou B,Wang W,Fu Z X,Yu J.2017.On the status of antibiotics usage and the progress in antibiotic-free breeding in poul-try farming[J].The Food Industry,38(8):216-220.]
蒋宇轩,袁琳,路娟娥,张悦,辛圆,吴昊.2023.动物源性黏菌素耐药基因mcr-1携带率变化及适应性代价的研究进展[J].黑龙江畜牧兽医,(19):22-28.[Jiang Y X,Yuan L,Lu J E,Zhang Y,Xin Y,Wu H.2023.Research progresson the changes in carriage rate and fitness cost of the animal-derived colistin resistance gene mcr-1[J].Heilong-jiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine,(19):22-28.]doi:10.13881/j.cnki.hljxmsy.2023.06.0007.
巨向红.2023.动物替抗天然产物的研究及应用进展[J].广东畜牧兽医科技,48(3):8-17.[Ju X H.2023.Research and application progress of natural alternatives to antibio-tics for animal[J].Guangdong Journal of Animal And Vete-rinary Science,48(3):8-17.]doi:10.19978/j.cnki.xmsy.2023.03.02.
李嘉敏,张玲.2023.水平基因转移促进细菌耐药性传播机制的研究进展[J].国际检验医学杂志,44(13):1630-1634.[Li J M,Zhang L.2023.Research progress on the mecha-nismofhorizontal gene transfer promoting bacterial anti-biotic resistance transmission[J].International Journal of Laboratory Medicine,44(13):1630-1634.]doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-4130.2023.13.019.
李伟,刘春海,韩建林,陶春卫,于光远,熊丽萍,杜丹,王源,陈静,初雷.2021.不同植物精油替抗方案对肉鸡生产性能的影响[J].养殖与饲料,20(12):21-25.[Li W,Liu C H,Han J L,Tao C L,Yu G Y,Xiong L P,Du D,Wang Y,Chen J,Chu L.2021.Effects of different plant essential oil substitution schemes on the production performance of broilers[J].Animals Breeding and Feed,20(12):21-25.]doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-427X.2021.12.007.
刘婷,阿永玺,李松涛,张沛.2023.我国畜禽养殖减抗探索及国外经验启示[J].北方牧业,(5):10-12.[Liu T,AY X,Li S T,Zhang P.2023.Exploration of reducing resistance of livestock and poultry breeding in China and its enligh-tenment from foreign experience[J].Northern Animal Hus-bandry,(5):10-12.]
刘挺,吕茜,赵文斌,赵婕霖,赵梦瑶,李帆,黄金虎,王丽平,王晓明.2023.江苏地区鸡源大肠杆菌的流行特征及耐药性调查[J].畜牧与兽医,55(8):44-50.[Liu T,LüQ,Zhao W B,Zhao J L,Zhao M Y,Li F,Huang J H,Wang L P,Wang X M.2023.Province and antimicrobicl resistance of Escherichia coli isolated from layers and broilers in the Jiangsu area[J].Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medi-cine,55(8):44-50.]
刘五高,丁友法,刘爱霞,黄黎俐,金晶,王伟.2015.质粒介导的耐药基因水平传播研究进展[J].中国卫生检验杂志,25(8):1288-1292.[Liu W G,Ding Y F,Liu A X,Huang L L,Jin J,Wang W.2015.Research progress of plasmid-mediated drug resistance gene horizontal transmission[J].Chinese Journal of Health Laboratory Technology,25(8):1288-1292.]
阮紫涵,黄安雄,王秀娟,黄玲利,郝海红.2022.CLSI、EUCAST和中国耐药判定标准概述[J].生物技术通报,38(9):47-58.[Ruan Z H,Huang A X,Wang X J,Huang L L,Hao H H.2022.Overview of CLSI,EUCAST,and sus-ceptibility breakpoints in China[J].Biotechnology Bulle-tin,38(9):47-58.]doi:10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2022-0695.
宋毅,李银涛,常维山,王祥锟,撒瑞雪,刘建华,苗立中.2023.山东部分地区鸭源大肠杆菌耐药性分析[J].现代畜牧兽医,(11):65-70.[Song Y,Li Y T,Chang W S,Wang X K,Sa R X,Liu J H,Miao L Z.2023.Analysis of drug resistance of duck Escherichia coli in some areas of Shandong[J].Modern Journal of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine,(11):65-70.]
孙泉云,朱九超,鞠龚讷.2022.饲料禁抗背景下规模猪场细菌性疫病的调查和监测[J].养猪,(4):116-117.[Sun Q Y,Zhu J C,Ju G N.2022.Investigation and monitoring of bacterial diseases in large-scale pig farms under the back-ground of feed prohibition[J].Swine Production,(4):116-117.]doi:10.3969/j.issn.1002-1957.2022.04.034.
孙月,王琪,毛伟,王博,董海燕,樊宏亮,郝普国,赵红霞.2023.内蒙古地区犊牛腹泻大肠杆菌耐药性分析及毒力基因检测[J].中国畜牧兽医,50(9):3811-3822.[Sun Y,Wang Q,Mao W,Wang B,Dong H Y,Fan H L,Hao P G,Zhao H X.2023.Drug resistance analysis and virulence gene detection of Escherichia coli casuing calf diarrhea in Inner Mongolia[J].Chinese Animal Husbandryamp;Veteri-nary Medicine,50(9):3811-3822.]doi:10.16431/j.cnki.1671-7236.2023.09.037.
涂闻君,曾政,赵明,侯峰清,蒋兵,方仁东,蒋佳利.2022.重庆市部分超市鸡肉中单增李斯特菌的耐药性与分子特征分析[J].西南大学学报(自然科学版),44(10):66-73.[Tu W J,Zeng Z,Zhao M,Hou F Q,Jiang B,Fang R D,Jiang J L.2022.Drug resistance analysis and molecular characterization of Listeria monocytogenes in the chicken meat from some supermarkets in Chongqing[J].Journal of Southwest University(Natural Science Edition),44(10):66-73.]doi:10.13718/j.cnki.xdzk.2022.10.008.
王佰涛,杨文玲,李灵平,雷高,刘德海.2022.微生物发酵饲料替抗机理研究进展[J].中国饲料,(1):10-13.[Wang B T,Yang W L,Li L P,Lei G,Liu D H.2022.Research progress on mechanism of microbial fermentation feed replacing antibiotics[J].China Feed,(1):10-13.]doi:10.15906/j.cnki.cn11-2975/s.20220103.
王翠月,陈大伟,马丽娜,唐修君,陆俊贤,刘茵茵,高玉时.2022.动物源性食品中氟喹诺酮类药物残留现状和检测方法研究进展[J].中国家禽,44(12):92-97.[Wang CY,Chen D W,Ma L N,Tang X J,Lu J X,Liu Y Y,Gao Y S.2022.Research progress of current status and detection methods of fluoroquinolones in animal derived food[J].China Poultry,44(12):92-97.]doi:10.16372/j.issn.1004-6364.2022.12.015.
王虎.2022.减抗形势下益生菌在畜禽生产中的应用[J].今日畜牧兽医,38(8):74-75.[Wang H.2022.Application of probiotics in livestock and poultry production under the situation of antimicrobial reduction[J].Today Animal Hus-bandry and Veterinary Medicine,38(8):74-75.]doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-4092.2022.08.041.
王莉,郭亚男,马晓燕,何生虎.2023.兔大肠杆菌病的耐药性研究进展[J].甘肃畜牧兽医,53(2):1-3.[Wang L,Guo YN,Ma X Y,He S H.2023.Research progress on drug resistance of rabbit colibacillosis[J].Gansu Animal Hus-bandry and Veterinary Medicine,53(2):1-3.]doi:10.15979/j.cnki.cn62-1064/s.2023.02.011.
王恬,张昊.2023.饲用抗生素替代物在畜禽生产上的研究进展[J].饲料工业,44(12):1-15.[Wang T,Zhang H.2023.Research progress of feed antibiotic substitutes on live-stock and poultry production[J].Feed Industry,44(12):1-15.]doi:10.13302/j.cnki.fi.2023.12.001.
吴玉双.2023.食源和人源产ESBLs大肠杆菌的分子分型与全基因组测序分析[D].石河子:石河子大学.[Wu Y S.2023.Molecular typing and whole genome sequencing analysis of food-derived and human-derived ESBLs-producing Escherichia coli[D].Shihezi:Shihezi Univer-sity.]doi:10.27332/d.cnki.gshzu.2023.000200.
徐军.2021.畜禽养殖中抗生素使用现状及改进措施[J].畜牧兽医科学(电子版),(22):126-127.[Xu J.2021.Present situation and improvement measures of antibiotics in animal epidemic disease control[J].Graziery Veterinary Sciences(Electronic Version),(22):126-127.]doi:10.3969/j.issn.2096-3637.2021.22.063.
徐小明,钟航,葛良鹏,孙静.2018.重庆某猪场大肠杆菌血清型鉴定及耐药性监测[J].四川畜牧兽医,45(10):22-24.[Xu X M,Zhong H,Ge LP,Sun J.2018.Serotype identifi-cation and drug resistance monitoring of Escherichia coliin a pig farm in Chongqing[J].Sichuan Animalamp;Veteri-nary Sciences,45(10):22-24.]
杨承霖,舒刚,赵小玲,王爽,林居纯.2020.2010—2016年四川省食品动物源大肠杆菌的耐药性研究[J].西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版),48(9):24-30.[Yang C L,Shu G,Zhao X L,Wang S,Lin J C.2020.Drug resistance of Escherichia coli isolates from food-animals obtained from 2010 to 2016 in Sichuan[J].Journal of Northwest Aamp;F University(Natural Science Edition),48(9):24-30.]doi:10.13207/j.cnki.jnwafu.2020.09.004.
杨莉,李婷,陈雪娇,徐景峨,韩勇,周伟,陶孟旭,李正兴,杨茂生,李美娟,蒲龄,周国松,张涛,田宇杰,卢昱希,周思旋.2023.贵州山羊大肠杆菌的分离鉴定及药敏试验[J].现代畜牧科技,(11):10-13.[Yang L,Li T,Chen X J,Xu J E,Han Y,Zhou W,Tao M X,Li Z X,Yang M S,Li M J,Pu L,Zhou G S,Zhang T,Tian Y J,Lu Y X,Zhou S X.2023.Isolation,identification and drug sensitivity test of Escherichia coli from Guizhou goat[J].Modern Animal Husbandry Scienceamp;Technology,(11):10-13.]doi:10.19369/j.cnki.2095-9737.2023.11.003.
杨影影,易开放,张俊锴,罗行炜,刘佩仪,韩荣嘉,胡功政.2022.猪链球菌临床分离株对利奈唑胺的耐药性及耐药机制研究[J].河南农业科学,51(1):141-145.[Yang Y Y,Yi K F,Zhang J K,Luo X W,Liu P Y,Han R J,Hu G Z.2022.Research on linezolid resistance and mechanism in clinical isolates of Streptococcus suis[J].Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences,51(1):141-145.]doi:10.1 5933/j.cnki.1004-3268.2022.01.017.
张洪浩,申茂恒,陈浩林,蒲龄.2023.安顺市羊场腹泻羔羊的大肠杆菌分离鉴定及耐药性分析[J].贵州畜牧兽医,47(4):60-62.[Zhang H H,Shen M H,Chen H L,Pu L.2023.Isolation,identification and drug resistance analysis of Escherichia coli from diarrhea lambs in Anshunsheepfarm[J].Guizhou Journal of Animal Husbandryamp;Veteri-nary Medicine,47(4):60-62.]doi:10.3969/j.issn.1007-1474.2023.04.019.
张锦熙.2021.哈尔滨市猪源大肠杆菌耐药性和耐药基因的检测分析[D].哈尔滨:东北农业大学.[Zhang J X.2021.Detection and analysis of drug resistance and drug resistance genes of porcine Escherichia coli in Harbin[D].Harbin:Northeast Agricultural University.]doi:10.27010/d.cnki.gdbnu.2021.000134.
张莉,陈丽园,李瑞.2022.减抗背景下中兽药在畜禽养殖中的应用研究[J].安徽农学通报,28(11):75-77.[Zhang L,Chen L Y,Li R.2022.Study on the application of Chi-nese veterinary drugs in livestock breeding under the back-ground of reducing antibody[J].Anhui Agricultural Scien-ce Bulletin,28(11):75-77.]doi:10.3969/j.issn.1007-7731.2022.11.025.
张译心.2022.禁抗后猪源金黄色葡萄球菌对恶唑烷酮类等药物耐药性调查及相关机制研究[J].现代畜牧兽医,(12):51-55.[Zhang Y X.2022.Investigation of drugresistance of swine-origined Staphylococcus aureus to oxa-zolidinones and other antibacterial agents and research onits relevant mechanisms after‘Antibiotic Prohibition’[J].Modern Journal of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine,(12):51-55.]
张玉杰,王晓旭,徐锋,沈莉萍,葛菲菲,刘健,唐聪圣,王建.2023.牛源大肠杆菌耐药性研究进展[J].中国奶牛,(10):29-36.[Zhang Y J,Wang X X,Xu F,Shen L P,Ge F F,Liu J,Tang C S,Wang J.2023.Progress on the antibio-tics resistance of Escheichia coli from bovine[J].China Dairy Cattle,(10):29-36.]doi:10.19305/j.cnki.11-3009/s.2023.10.006.
张兆天,靖豪杰,李嘉雯,宋雯雯,张迪,李妍.2023.河北地区猪源致病性大肠杆菌耐药性及相关基因型分析[J].今日畜牧兽医,39(6):12-15.[Zhang Z T,Jing H J,Li J W,Song W W,Zhang D,Li Y.2023.Analysis of drug resis-tance and related genotypes of pathogenic Escherichia coli from pigs in Hebei Province[J].Today Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine,39(6):12-15.]doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-4092.2023.06.006.
Alonso C A,Michael G B,Li J,Somalo S,Simón C,Wang Y,Kaspar H,Kadlec K,Torres C,Schwarz S.2017.Analysis of blaSHV-12-carrying Escherichia coli clones and plasmids from human,animal and food sources[J].Journal of Anti-microbial Chemotherapy,72(6):1589-1596.doi:10.1093/jac/dkx024.
Call D R,Singer R S,Meng D,Broschat S L,Orfe L H,Ander-son J M,Herndon D R,Kappmeyer L S,Daniels J B,Besser T E.2010.blaCMY-2-positive IncA/C plasmids from
Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica are a distinct component of a larger lineage of plasmids[J].Antimicro-bial Agents and Chemotherapy,54(2):590-596.doi:10.1128/AAC.00055-09.
Clermont O,Bonacorsi S,Bingen E.2000.Rapid and simple determination of the Escherichia coli phylogenetic group[J].Applied and Environmental Microbiology,66(10):4555-4558.doi:10.1128/AEM.66.10.4555-4558.2000.
Du Z,Wang M Y,Cui G Y,Zu X Y,Zhao Z Q,Xue Y.2020.The prevalence of amphenicol resistance in Escherichia coli isolated from pigs in mainland China from 2000 to 2018:A systematic review and meta-analysis[J].PLoS One,15(2):e0228388.doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0228388.
Freitag C,Michael G B,Kadlec K,Hassel M,Schwarz S.2017.Detection of plasmid-borne extended-spectrumβ-lactamase(ESBL)genes in Escherichia coli isolates from bovine mastitis[J].Veterinary Microbiology,200:151-156.doi:10.1016/j.vetmic.2016.08.010.
Gao J X,Yang Z,Zhao C Q,Tang X Z,Jiang Q,Yin Y L.2023.A comprehensive review on natural phenolic compounds as alternatives to in-feed antibiotics[J].Science China Life Sciences,66(7):1518-1534.doi:10.1007/s 11427-022-2246-4.
Hou J X,Huang X H,Deng Y T,He L Y,Yang T,Zeng Z L,Chen Z L,Liu J H.2012.Dissemination of the fosfomycin resistance gene fosA3 with CTX-Mβ-lactamase genes and rmtB carried on IncFII plasmids among Escherichia coli isolates from pets in China[J].Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy,56(4):2135-2138.doi:10.1128/AAC.05104-11.
Liu B T,Li X Y,Zhang Q D,Shan H,Zou M,Song F J.2019.Colistin-resistant mcr-positive enterobacteriaceae in fresh vegetables,an increasing infectious threat in China[J].In-ternational Journal of Antimicrobial Agents,54(1):89-94.doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2019.04.013.
Mandal A K,Talukder S,Hasan M,Tasmim S T,Parvin S,Ali Y,Islam M T.2022.Epidemiology and antimicrobial resis-tance of Escherichia coli in broiler chickens,farmworkers,and farm sewage in Bangladesh[J].Veterinary Medicineand Science,8(1):187-199.doi:10.1002/vms3.664.
Poirel L,Madec J Y,Lupo A,Schink A K,Kieffer N,Nord-mann P,Schwarz S.2018.Antimicrobial resistance in Escherichia coli[J].Microbiology Spectrum,6(4):26.doi:10.1128/microbiolspec.ARBA-0026-2017.
Schink A K,Kadlec K,Schwarz S.2012.Detection of qnr genes among Escherichia coli isolates of animal origin and complete sequence of the conjugative qnrB19-carrying plasmid pQNR2078[J].Journal of Antimicrobial Chemo-therapy,67(5):1099-1102.doi:10.1093/jac/dks024.
Shen Y B,Zhang R,Shao D Y,Yang L,Lu J Y,Liu C C,Wang X Y,Jiang J Y,Wang B X,Wu C M,Parkhill J,Wang Y,Walsh T R,Gao G F,Shen Z Q.2022.Genomic shift in population dynamics of mcr-1-positive Escherichia coli in Human carriage[J].Genomics Proteomicsamp;Bioinforma-tics,20(6):1168-1179.doi:10.1016/j.gpb.2022.11.006.
Siqueira A K,Michael G B,Domingos D F,Ferraz M M G,Ribeiro M G,Schwarz S,Leite D S.2016.Diversity of class 1 and 2 integrons detected in Escherichia coli iso-lates from diseased and apparently healthy dogs[J].Veteri-nary Microbiology,194:79-83.doi:10.1016/j.vetmic.2016.05.005.
Wang Y,Xu C Y,Zhang R,Chen Y Q,Shen Y B,Hu F P,Liu D J,Lu J Y,Guo Y,Xia X,Jiang J Y,Wang X Y,Fu Y L,Yang L,Wang J Y,Li J,Cai C,Yin D D,Che J,Fan R,Wang Y Q,Qing Y,Li Y,Liao K,Chen H,Zou M X,Liang L,Tang J,Shen Z Q,Wang S L,Yang X R,Wu C M,Xu S X,Walsh T R,Shen J Z.2020.Changes in colis-tin resistance and mcr-1 abundance in Escherichia coli of animal and human origins following the ban of colistin-positive additives in China:An epidemiological compara-tive study[J].The Lancet Infectious Disease,20(10):1161-1171.doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30149-3.
Zhang Q,Zhang Z Y,Zhou S Y D,Jin M K,Lu T,Cui L,Qian H F.2021.Macleaya cordata extract,an antibiotic alterna-tive,does not contribute to antibiotic resistance gene dissemination[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,412:125272.doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125272.
(责任编辑兰宗宝)

