Dynamic Update Scheme of Spectrum Information Based on Spectrum Opportunity Incentive in the Database-Assisted Dynamic Spectrum Management
Zhang Yu ,Chen Yong,,* ,He Panfeng ,Cai Yueming
1 Sixty-third Research Institute,National University of Defense Technology,Nanjing 210007,China
2 College of Communications Engineering,Army of Engineering University,Nanjing 210007,China
Abstract: To solve the problem of delayed update of spectrum information (SI) in the database assisted dynamic spectrum management (DB-DSM),this paper studies a novel dynamic update scheme of SI in DB-DSM.Firstly,a dynamic update mechanism of SI based on spectrum opportunity incentive is established,in which spectrum users are encouraged to actively assist the database to update SI in real time.Secondly,the information update contribution (IUC) of spectrum opportunity is defined to describe the cost of accessing spectrum opportunity for heterogeneous spectrum users,and the profit of SI update obtained by the database from spectrum allocation.The process that the database determines the IUC of spectrum opportunity and spectrum user selects spectrum opportunity is mapped to a Hotelling model.Thirdly,the process of determining the IUC of spectrum opportunities is further modelled as a Stackelberg game by establishing multiple virtual spectrum resource providers(VSRPs) in the database.It is proved that there is a Nash Equilibrium in the game of determining the IUC of spectrum opportunities by VSRPs.Finally,an algorithm of determining the IUC based on a genetic algorithm is designed to achieve the optimal IUC.Theoretical analysis and simulation results show that the proposed method can quickly find the optimal solution of the IUC,and ensure that the spectrum resource provider can obtain the optimal profit of SI update.
Keywords: database-assisted dynamic spectrum management;Hotelling;information updating contribution;spectrum information updating;Stackelberg
I.INTRODUCTION
1.1 Background
Dynamic spectrum management (DSM),a promising technology that can improve spectrum efficiency,has attracted the attention of scholars from different countries [1-5].It is regarded as one of the eight potential technologies of the next generation wireless network (XGNet),and an important way to improve spectrum efficiency and optimize network deployment[6].DSM mainly includes the model-based DSM[1],the trade-based DSM[2,3]and the data-driven DSM[4,5].According to the acquisition method of spectrum data,the data-driven DSM is divided into the DSM based on spectrum sensing[7],the database assisted DSM (DB-DSM) [8,9] and the DSM based on spectrum prediction [10].DB-DSM is regard as the most easily implemented mode,which has been concerned and developed by many countries.For example,Federal Communications Commission of the United States requires that all dynamic spectrum access networks working in the TV white space band can connect to the database to obtain spectrum opportunity,and designates 10 companies such as Microsoft and Google to be responsible for establishing,operating,storing and distributing databases related to the authorized network and its spectrum usage[11].[12]proposed a three-tier spectrum sharing system model for federal government owned frequency bands,including the exclusive federal basic access,secondary access registered in the database for paying short-term use and general authorized access for opportunistic low-power free use without any federal users or secondary access users.The XGNet is an integrated heterogeneous,large-scale,large-capacity,large bandwidth and ultra-low delay autonomous network,which includes different access modes such as mobile cellular,satellite communication and UAV Communication,and spans multi domain virtual space such as space,air,ground and deep sea[13].In addition to developing Terahertz and other high-band spectrum resources,the medium and low band spectrum resources used by 2G/3G/4G/5G networks still need to be used,and DSM is still one of the effective ways to solve the shortage of spectrum resources [13].Therefore,the data-driven DSM is regarded as the core key technology of the next generation heterogeneous wireless networks (XGHetNet),and is the development trend of spectrum management in the future [14].The super dense and highly dynamic characteristics of the XGHetNet bring many problems to spectrum management: i.spectrum users frequently join and exit the wireless network,and the occupation state of spectrum resources changes frequently.ii.the spectrum user’s mobility leads to frequently change in its geographical location,the electromagnetic environment of the user changes dynamically,and the available spectrum resources change dynamically with the change of the user’s spatial location.iii.malicious users implement sudden interference,and the occupation state of spectrum resources changes.iv.the use mode of spectrum resources is mobile,and the available spectrum resources change dynamically.Therefore,the dynamic update of spectrum information(SI)is a key problem to be solved in DSM of XGHetNet.
Due to the lack of timely updating of SI in the DBDSM,it is difficult to meet the need of real-time SI in high dynamic environment.Therefore,[15] and [16]proposed the spectrum sensing method based on the database,which took into account the protection of primary users and the improvement of spectrum efficiency.The proposed method could reduce the sensing demand for existing users and improve the timeliness of SI updating in the database.Considering the potential interference of spectrum sharing to existing users,[17] established a robust and secure spectrum sharing database and proposed the concept of fuzzy spectrum use mode to support SI real-time processing and policy updating.To solve the key problems of spectrum scarcity,large-scale access and lowpower reliable communication in machine communication,[18]designed a database driven adaptive MAC protocol to actively select the available spectrum map or local sensing scheme to maximize the throughput.Deo to its decentralization,transparency,invariance,availability and security,blockchain is more suitable for dynamic spectrum sharing mode.Therefore,some scholars have also carried out relevant research.[19]summarized the usage scenarios and future challenges of database assisted spectrum prediction in 5G network.[20]analyzed the potential applications,advantages and disadvantages of blockchain technology in four sharing modes: primary user collaborative sharing,secondary user collaborative sharing,secondary user non-collaborative sharing and primary user noncollaborative sharing.To cope with many challenges faced by large-scale spectrum sharing in 5G heterogeneous networks,such as lack of incentive mechanism,privacy leakage,security threats and so on,[21] has developed a framework of privacy protection,incentive compatibility and spectrum effectiveness based on blockchain,which provided reliable privacy and security guarantee for spectrum sharing and effectively encouraged the primary users to share their used spectrum resources,and achieved low complexity and efficient spectrum allocation.[22]proposed a blockchain verification protocol as a method for enabling and securing spectrum sharing in moving cognitive radio networks.The blockchain protocol facilitated the transactions between primary and secondary users and is used to validate and save each user’s virtual wallet.
1.2 Motivations
However,the traditional user sensing and database assisted DSM needs to consume a lot of energy and additional spectrum resources to update SI.For the Internet of Things (IOT) nodes with limited energy,their energy resources are very valuable.Selfish IOT nodes will not easily consume energy and spectrum resources to update SI in real time.Therefore,aiming at the problem that the dynamic update of SI is not timely in the DB-DSM,this paper constructs a dynamic update mechanism of SI based on spectrum opportunity incentive,and proposes a determination method of information updating contribution (IUC) based on Hotelling and Steinberg game model.Then an algorithm of determining the IUC based on a genetic algorithm is designed to achieve the optimal IUC.The main contributions of this paper are summarized as follows:
• A dynamic update model of SI based on spectrum opportunity incentive is established to encourage spectrum users to actively assist database to update SI in real time.In this model,the database,as the spectrum manager,divides the spectrum resources into a series of spectrum opportunities according to different dimensions of spatial,time,frequency and energy.An appropriate spectrum access cost of each spectrum opportunity is determined.Spectrum users can transmit their real-time channel experience information to the database in exchange for spectrum opportunities.Their contributions in assisting the database to update SI are shared and recognized in the whole HetNet.
• The IUC of spectrum opportunity is applied to describe the cost of spectrum users in exchange for spectrum opportunities,and the profit of SI update obtained by the database from spectrum allocation.It not only describes the contribution of spectrum users in assisting the database in SI update in the HetNet,but it also can describe the quality of spectrum opportunity.The database determines the IUC paid by spectrum users to access the spectrum according to the quality of spectrum resources and the spectrum user’s preference.Only spectrum users who contribute to SI update can get access to spectrum opportunities.The greater the IUC paid by spectrum users,the more spectrum opportunities they can obtain.
• The process that the database determines the IUC of spectrum opportunities and spectrum users select spectrum opportunities is modelled as a Hotelling model.Multiple virtual spectrum resource providers (VSRPs) are established to determine an appropriate IUC with different quality in the database,which is modelled as a Stackelberg game.
• The impact of spectrum resource heterogeneity on the IUC and the utility of SI update is analyzed.It is proved that there is a Stackelberg equilibrium and a multivariate nonlinear problem with some nonlinear constraints.An algorithm of determining the IUC based on a genetic algorithm is designed to ensure the realizability of the proposed mechanism of SI.Simulation further verifies that the proposed method can quickly determine the optimal IUC,so as to ensure that the database can obtain the optimal profit of SI update.
1.3 Organization of this Paper
The rest of this paper is organized as follows.The system model is presented in Section II.In Section III,the detailed optimization problem formulation is provided.In Section IV,the determination method of the IUC based on genetic algorithm is proposed.In Section V,simulations are conducted to characterize the performance of the proposed schemes.Finally,conclusions are drawn in Section VI.
II.SYSTEM MODEL
2.1 Network Architecture of the Distributed DB-DSM
Consider the network architecture of the distributed DB-DSM as shown in Figure 1,which is mainly composed of the spectrum database and multiple heterogeneous spectrum users.The spectrum database is mainly composed of multiple databases that are distributed and store SI that includes the available spectrum resources,the requirements of spectrum users,the contribution of spectrum users,the electromagnetic environment and so on.SI will be shared on the whole interconnected databases.The database will ensure that the contribution of all spectrum users in SI updating can be recognized in the whole network.The main tasks of the database mainly include:
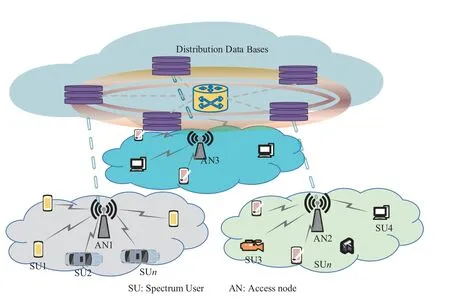
Figure 1.The network architecture of the distributed DBDSM.
• As a spectrum resource manager,the database divides all spectrum resources into a series of channels according to the multi-dimensional domains of space,time and frequency,and provides spectrum users with spectrum use schemes and spectrum access opportunities,namely as spectrum opportunities.
• As a SI collector,it should not only use the existing spectrum monitoring equipment or station to collect spectrum data such as background noise,electromagnetic signal and spectrum interference,but also build a SI updating model to encourage spectrum users to proactively assist in collecting channel experience information in real time.
• As a SI provider,we should not only integrate and process the spectrum data obtained from multiple channels and extract SI,such as the number of available channels,channel bandwidth,channel occupancy status,central frequency,electromagnetic environment and geographic information,but also ensure that the contribution of spectrum users in the SI updating can be recognized by these interconnection databases.The mapping relationship between the IUC and the spectrum opportunity is also established.
In network architecture of the distributed DB-DSM,spectrum users areK(K ≥1) HetNets or single devices with different spectrum requirements,including existing spectrum users and new spectrum users.The new spectrum users mainly refer to spectrum users with new requirements of the signal transmission.They will determine their requirements of spectrum and select appropriate spectrum opportunities according to the spectrum use schemes released by the database and their own resource constraints.Existing spectrum users mainly refer to spectrum users who are using spectrum to transmit their signals.New spectrum users will become existing spectrum users after accessing the spectrum.Existing spectrum users will release the occupied spectrum after completing their own services.The release or occupation of spectrum will directly affect the status of available spectrum.For existing spectrum users with mobility,when they leave the service area of DSM network,they will switch the spectrum according to the available spectrum,and release the previously occupied spectrum,and reapply for accessing new spectrum opportunity as a new spectrum user.
2.2 Dynamic Update Process of Spectrum Information
The traditional acquisition methods of SI,which use special spectrum sensing equipment,require additional hardware resources and be greatly affected by the cost of equipment.It is difficult to deploy special spectrum sensing equipment in some time or space,and obtain the end SI in real time.The spectrum user with a receiver is essentially a spectrum sensing node with channel experience information.The database can update SI based on the channel experience information of these ubiquitous spectrum users.However,most spectrum users are selfish and rational.No one is willing to actively spend their resources to transmit additional channel experience information to the database.Therefore,we establish a real-time dynamic update model of SI based on spectrum opportunity incentive.The database in the model will determine the spectrum access cost for each spectrum opportunity,and spectrum users will obtain the spectrum opportunity by transmitting the channel experience information to the database.
In this model,the IUC is defined to describe the access cost of spectrum opportunities,which is the contribution degree of spectrum users assisting the database to dynamically collect SI,which is quantitatively described by the throughput of spectrum users transmitting its channel experience information to the database.It is not difficult to understand that the higher the IUC paid by spectrum users,the more spectrum opportunities they can obtain.The database is responsible for recording the IUC paid by spectrum users and sharing them in the interconnected DSM network.To meet their own service needs,rational spectrum users will comprehensively consider the IUC of spectrum opportunities,the cumulative value of their own IUC,spectrum requirements and resource constraints.
Under the distributed DB-DSM network architecture,the main implementation process of the dynamic update model of SI based on spectrum opportunity incentive is shown in Figure 2.Firstly,the database broadcasts SI to all new spectrum users through the public control channel.After receiving SI,new spectrum users will feedback their spectrum demands including the plan of spectrum use,the service type and other contents to the database.After completing the collection of spectrum demands,the database determines the IUC(namely the spectrum access cost)and broadcasts them to all new spectrum users.New spectrum users select and access the channel with considering the spectrum demand,their resource constraints and IUC,and feedback their decisions of spectrum access to the database.After new spectrum users accessing the spectrum opportunities,they need to transmit the channel experience information to the database while transmitting their own electromagnetic signals.Spectrum users will vacate the channel after completing their transmission.The database dynamically updates SI in real time according to the spectrum data obtained by spectrum monitoring,the access or leave status of spectrum users and the submitted SI of spectrum users,which can provide real-time SI for the access of other spectrum users.
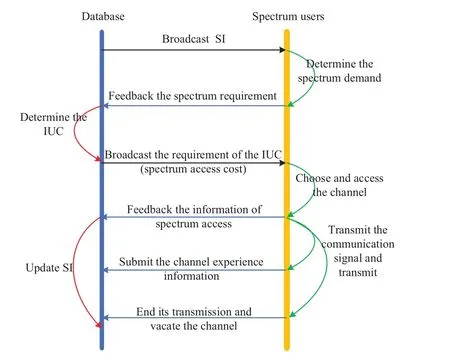
Figure 2.The main implementation process of the dynamic update of SI based on spectrum opportunity incentive.
III.METHOD FOR DETERMINING THE IUC
From the dynamic update process of SI described in Section 2.2,the dynamic update of SI includes two processes.One is that the spectrum resource provider(SRP)determines the IUC of spectrum opportunities,which is the key and foundation of the dynamic update of SI in this paper.The other is that spectrum users select and access spectrum opportunities according to the IUC of spectrum opportunities determined by SRPs.In order to enable balanced application of different types of channels,the SRP must consider the requirement of spectrum users when determining the IUC of spectrum opportunities.Therefore,we first define the spectrum utility function of spectrum users before establishing the model of determining the IUC of spectrum opportunities.
3.1 Defining the Utility Function of Spectrum User
The better the spectrum characteristics and channel quality of spectrum opportunities spectrum users choose,the more IUC they consume,and vice versa.If the consumption of the IUC exceeds the limitation of their own resources,spectrum users will not choose the spectrum opportunity,and the spectrum utility is 0.Meanwhile,spectrum users will pay the penalty costs due to the interference to the existing spectrum users.Similar to[23],the database divides all available channels intoMtypes,and each type of channels has the same spectrum characteristics and quality.Spectrum users are also divided intoKtypes,and each type of spectrum users has the same spectrum requirements.Therefore,the spectrum utility obtained by thej-th type of spectrum users choosing thei-th type of channels is expressed as
Spectrum users with limited energy will be more cautious about the power cost required to transmit SI,and their power cost has a greater impact on the profit of spectrum users.A greater weight of preferenceβjis given to the power cost.Spectrum users with abundant energy want to obtain better transmission performance,and their channel quality has a greater impact on the profit of spectrum users.A greater weight of preferenceαjis given to the channel quality.For the exclusive spectrum access mode,the interference to existing spectrum users is mainly adjacent channel interference,and its interference factorsχjhave little impact on the profit of spectrum users.For the shared spectrum access mode,the interference to existing spectrum users includes co-channel interference and adjacent channel interference,and its interference factorsχjhave a relatively large impact on the profit of spectrum users.
To sum up,spectrum users need to consider not only the channel quality,but also the IUC of spectrum opportunity and the interference level of existing spectrum users when choosing spectrum opportunities.
3.2 Defining the Utility Function of SI Updating Obtained by the Database
According to the network architecture of distributed DB-DSM given in Section 2.1,the database is not only a SRP but also a SI collector.As a SRP,it provides spectrum opportunities for spectrum users in an exclusive dynamic sharing mode.If some spectrum opportunities are selected by a spectrum user,they cannot be provided for other spectrum users,which is described as spectrum opportunities are consumed.As a SI collector,it will obtain profit of SI update by providing spectrum opportunities for spectrum users.Refer to[23,24],the cost of spectrum opportunities occupied is measured by the reduction of channel capacity,and the utility function of SI update obtained by the database can be given by
whereϑiis the preference of spectrum users for theith type of channels.is the lower bond of the preference of spectrum users for thei-th type of channels.is the upper bound of the preference of spectrum users for thei-th type of channels.Niis the number of spectrum users selecting thei-th type of channels.g(ϑ)is the probability distribution function of the preference of spectrum users.
3.3 Game Model of Determining the IUC
It is assumed that each type of channels is managed by a VSRP.Therefore,there areMVSRPs in the DB-DSM.The VSRP determines a reasonable IUC for each type of channels it manages according to the spectrum characteristics and channel quality.Meanwhile spectrum users carrying different services also have different requirements on the number of channels and channel quality.They will choose appropriate spectrum opportunities according to their own resource constraints and spectrum requirements,as well as the IUC of spectrum opportunities.
Considering that the interactive process of the VSRPs determining the IUC of spectrum opportunities and spectrum users selecting spectrum opportunities is similar to the problem of monopoly competition in economics,the interactive process of them is modelled as a Hotelling model,whereMVSRPs are equivalent to the monopolizing enterprises in the market.They provide different types of spectrum opportunities for spectrum users.The model of VSRPs determining the IUC for each type of channels is mapped to the pricing problem of enterprises for their own products.Spectrum users are equivalent to the users in the monopoly market and will choose appropriate spectrum opportuities.
Just like the commodity market,the VSRPs analyze spectrum user’s preference based on historical data of spectrum user’s selection of spectrum opportunities,determine or adjust the IUC to maximize their profit of SI updating.Considering that there is a sequence and mutual influence in the process of determining these IUC by VSRPs,similar to [25],the process of determining these IUC by VSRPs is modelled as a Stackelberg game to solve “the pricing problem of the products”in the Hotelling model.
It is assumed that the channel resources are sorted according to the channel capacity and 0<C1<C2<···<CM.The spectrum users’preferences for the channels satisfy 0<ϑ1<ϑ2<···<ϑM.In Stackelberg game,without loss a generality,we assume that the leader is the VSRP with lowest channel quality and the followers are these VSRPs with higher channel qualities in the Stackelberg game.Obviously,there is an equilibriumbetween the spectrum user’s preferences [ϑi,ϑi+1] so that spectrum users can obtain the same profit whether they choose theith type of channels or the(i+1)th type of channels[23,24],namely as
Base on (4),the equilibriumof the spectrum user’s preferences in[ϑi,ϑi+1]is expressed as
It is assumed that the channel attenuation from the same spectrum user to the database is regarded as the same,is expressed as
Based on (2),(3) and (6),the utility function of SI updating obtained by theith VSRP is expressed as
From (7),the utility function of SI updating obtained by the first VSRP is a function of the IUC ofthe first type of channels and that of the second type of channels.The utility function of SI updating obtained by theMth VSRP is a function of the IUC of the(M-1)th and theMth type of channels.The utility function of SI updating obtained by theith VSRP is a function of the IUC of the(i-1)th,ith and(i+1)th type of channels.Therefore,the two-step or three-step Stackelberg game can be used to solve the problem ofMVSRPs determining the IUC in this section.
Proposition 1.When the spectrum users’preference for the ith type of channels is a uniform distribution in[ϑi,ϑi+1],there has a Stackelberg equilibrium solution and the IUC obtained by VSRPs is expressed as
The equations of the optimal response function of the IUC obtained by the VSRPs are expressed as
Proof.When the spectrum user’s preference forith type of channels is a uniform distribution in[ϑi,ϑi+1],the demand function of spectrum user for the first type of channels is expressed as
Based on(7),the IUC obtained by the first VSRP is expressed as
Similarly,the IUC obtained by theith VSRP is expressed as
Calculate the first-order partial derivative ofqifor the IUC obtained by VSRPs given in(11)to(13)and make them 0,which are the equations of the optimal response function given in (9).Calculate the secondorder partial derivative ofqifor the IUC obtained by VSRPs given in(11)to(13)to obtain these equations given in(14)to(16).
Sinceςj <0,ωj >0 and Δϑj >0,≥0 holds when.Therefore,when the spectrum user’s preference for theith type of channels is a uniform distribution in[ϑi,ϑi+1],there has a Stackelberg equilibrium solution.This completes the proof.
Proposition 2.When the spectrum user’s preference for the ith type of channels is a normal distribution with a meanand a variancein[ϑi,ϑi+1],there has a Stackelberg equilibrium solution and the IUCobtained by VSRPs are expressed as
The equations of the optimal response function of the IUC obtained by VSRPs are expressed as
Proof.When the spectrum user’s preference for theith type of channels is a normal distribution in[ϑi,ϑi+1],the proof process is similar to[24].The distribution function of spectrum user’s preference for the first type of channels is
whereµ1is the mean of the distribution function of spectrum user’s preference for the first type of channels.The demand function of spectrum user for the first type of channels is expressed as
Sett=the demand function of spectrum user in(20)is transformed into
When≥µ1,the first part of(21)is expressed as
Based on (21),(23) and (25),the demand function of spectrum user in(21)is transformed into
Similarly,when< µ1,the demand function of spectrum user for the first type of channels is expressed as
Generally,the spectrum user’s preferences are distributed aroundwith high probability.Setµ1=the demand function of spectrum user for the first type of channels from(26)and(27)is expressed as
Similarly,the demand function of spectrum user for theith type of channels is derived and expressed as
where 1≤i <M.
Based on(28),(29),(30)and(7),the IUC obtained by theith VSRP in(17)can be obtained.
Calculate the first-order partial derivative ofqifor the IUC obtained by VSRPs given in (17) and make them 0,which can be the optimal response function equations given in (18).Calculate the second-order partial derivative ofqifor the IUC obtained by the first VSRP given in(17)to obtain(31).
IV.DETERMINATION ALGORITHM OF THE IUC BASED ON GENETIC ALGORITHM
According to the theoretical analysis and proof of the Section III,it can be seen that there has a Stackelberg equilibrium solution and it is a multi-objective optimization problem.It can be solved by solving the equations composed of the optimal response function of the IUC.
According to Proposition 1,when the spectrum user’s preference for theith type of channels is a uniform distribution in[ϑi,ϑi+1],the equations composed of the optimal response function of the IUC obtained by VSRPs are expressed as
The constraints of(35)are given in
whereq=[q1,q2,···,qM] is the vector composed of variablesqi.The first constraintC1describes that the equilibrium point of the spectrum user’s preference for theith type of channels in [ϑi,ϑi+1].The second constraintC2describes that the received power of SI transmitted by spectrum users accessing to theith type of channels is not greater than that accessing to the(i+1)th.The third constraintC3describes that the received power of SI transmitted by spectrum users accessing to theith type of channels should be greater than 0.The fourth constraintC4describes that the IUC of theith VSRP should be greater than 0.The fifth constraintC5describes that there hasMtypes of channels.
According to Proposition 2,when the spectrum user’s preference for theith type of channels is a normal distribution in[ϑi,ϑi+1],the equations composed of the optimal response function of these IUC obtained by VSRPs are expressed as
The constraints of(37)are the same as those of(36).Obviously,(35) and (37) are nonlinear equations with nonlinear constraints.The solution of nonlinear equations mainly includes fixed point iterative algorithm,Newton algorithm,Gauss Newton algorithm,trust region algorithm,projection gradient algorithm,and so on.However,some of these algorithms require the iterated sequences to have accumulation points,and some algorithms require the equations to be monotonous.It is difficult to solve this problem of(35)or(37)with existing conventional algorithms.
Similar to[26],the minimum optimization problem(P1)used to solve(35)and(37)is given by
whereF(q)=Therefore,the problem of determining the IUC by VSRPs is transformed into a nonlinear programming problem with nonlinear inequality constraints.But the objective function of the optimization problem (P1) is very complex,and its concavity and convexity is difficult to be determined and guaranteed.There may be multiple minimum solutions.
Genetic algorithm,a search heuristic algorithm for solving optimization problems in the field of artificial intelligence,uses the search from the set of problem solutions to replace the search from a single problem solution.It has changed the traditional search idea and has a large coverage.It can solve the global optimization problem under the selection of appropriate adaptive functions.Therefore,in this section,the genetic algorithm is used to solve the optimization problem(P1),including population generation,individual fitness computing,selection and optimization of individual genetics,cross processing of two or more parents of the selection solution to create a new solution,changing some genes of individual in the group,obtaining individuals with optimal fitness and so on[27],which is described in Algorithm 1.

V.SIMULATION RESULTS
In this section,we aim to provide numerical results to evaluate and validate the proposed updating scheme of SI.The iterative algorithm for spectrum pricing is based on the distribution characteristics of spectrum user’s preference proposed in [23],the profit of which is defined to the received power of SI on the database,is used as a benchmark method for comparison.To ensure that no additional spectrum and time slots are consumed,spectrum watermarking technology is used to transmit the collected SI by spectrum users to the database [28].Then the signal of spectrum users is equivalent to noise interference for the database,namely as thatSimilar to[23],M=3,the set of channel capacity per unit bandwidth is set toC=[2,8,13]bps/Hz,N=[20,20],ΔJ=Jj,i-Jj,i+1=0.001mW,=1.5385mW,G=[2×10-6,3×10-6,1.5×10-6],ϑ=[1,5,9]and when the spectrum user’s preference forith type of channels is a normal distribution,=Δϑi.αj=1,χ=[120,100],β=[6× 10-6,5× 10-6],κ=[0.25,0.25,0.25],NP=200.
Figure 3 shows the convergence iterative performance of the IUC with different methods.The small figure at the bottom of Figure 3 shows the local enlarged diagram of the IUC of the first type of channels with the benchmark method.From Figure 3,the IUC will tend to be stable and balanced after the population of the two methods evolving to the 6th generation in genetic algorithm.The IUC will increase with the increase of channel quality.Although the convergence speed of the benchmark method is relatively faster than that of the proposed method,the IUC determined by the proposed method is generally higher than that by the benchmark method.Namely that the database can obtain higher profit from the updating of SI.
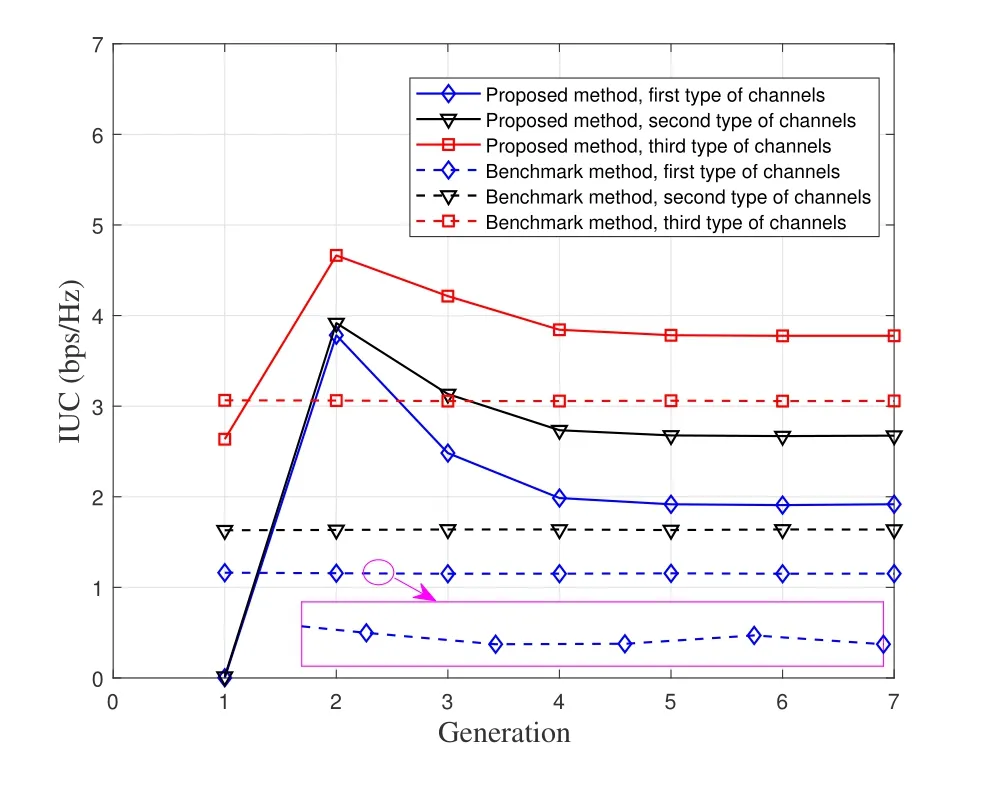
Figure 3.The convergence performance of the IUC with different methods.
Figure 4 shows the convergence performance of the IUC of the first type of channels with two cases.The first case is that spectrum user’s preference obeys a normal distribution.The second case is that spectrum user’s preference obeys a uniform distribution,respectively.Before the third generation,the dynamic change of the IUC of the first type of channels in the first case is relatively larger than that in the second case.Since the third generation,the variation trend of the IUC obtained by the two methods is the same,and gradually converges to the equilibrium point in the fifth or sixth generation.Although the performance of the IUC in the first case is higher than that in the second case,it is not so obvious.Therefore,the distribution function of the spectrum user’s preference has little impact on the IUC.In addition,the spectrum user density has some impact on the convergence performance of the IUC in first case.The larger the spectrum user density,the slower the convergence.In second case,the spectrum user density has little impact on the convergence performance of the IUC.
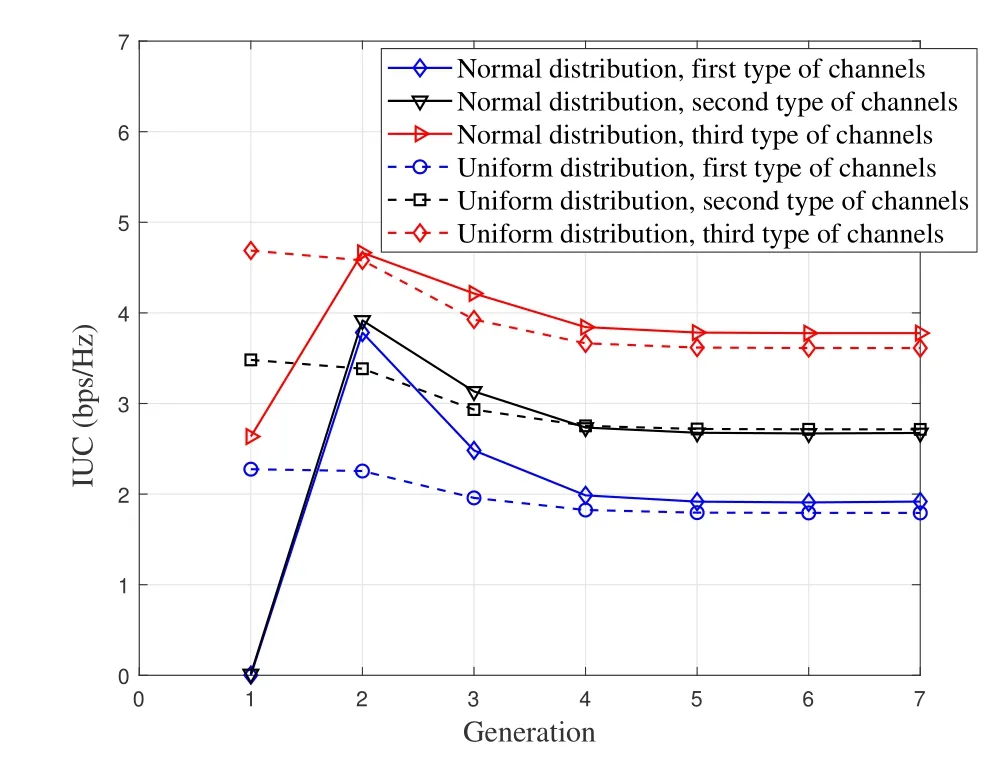
Figure 4.The convergence performance of the IUC of the first type of channels with two cases: spectrum user’s preference obeys a normal distribution and a uniform distribution,respectively.
Figure 5 shows the impact of the spectrum users’preference on the IUC,where the difference of spectrum user’s preference represents the difference of spectrum user’s preference for two adjacent channel qualities when the channel quality is certain.To facilitate analysis and comparison,it is assumed that the differences of the spectrum user’s preference for two adjacent channel quality are equal,namely that Δϑ=ϑi-ϑi-1,i ∈[2,M].From Figure 5,we can see that the greater the difference of the spectrum user’s preference for two adjacent channel qualities is,the higher the difference of the IUC for two adjacent channel qualities is,and the better the transmission rate of SI is.Moreover,the difference of the IUC between the two adjacent channels firstly increases with the increase of the difference of spectrum user’s preference,but it begins to decrease after that it increases to a certain threshold,and finally tends to 0.The reason for this phenomenon is that when the spectrum user’s preference follows the normal distribution,the spectrum users are mainly distributed in the median area of[ϑi,ϑi+1].When the distribution span of spectrum user’s preference is very large and far from the boundary value(ϑiorϑi+1)of spectrum user’s preference,the spectrum user’s preference can only take the boundary value (ϑiorϑi+1).Therefore,although the difference of spectrum user’s preference is very large,there may also be the same IUC for different channels,which the difference of channel quality will not be reflected.
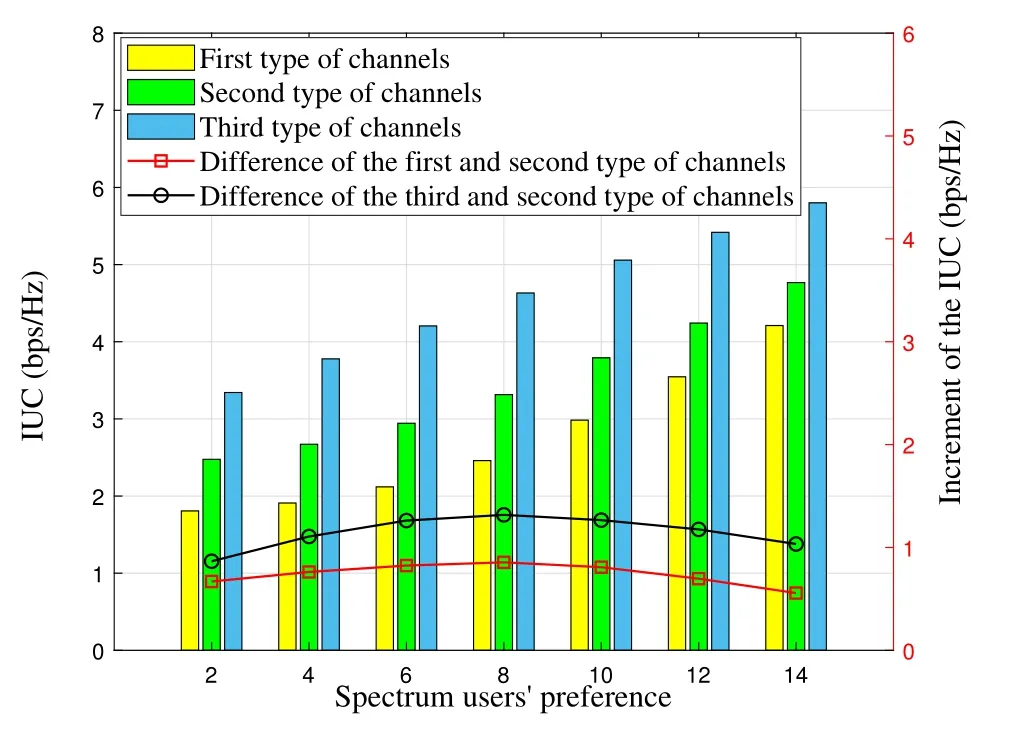
Figure 5.The impact of the spectrum users’preference on the IUC.
Figure 6 shows the impact of the number of populations involved in the computation on the IUC.It can be seen that when the number of populations is less than 110,the number of populations has a randomly impact on the IUC.When the number of populations is greater than or equal to 110,the increase of the number of populations has little or no impact on the IUC.The increase of populations will naturally increase the computation complexity.Therefore,it is necessary to find an appropriate value of the number of populations through repeated computation experiments to ensure the accuracy and stability of the IUC with low computational complexity.
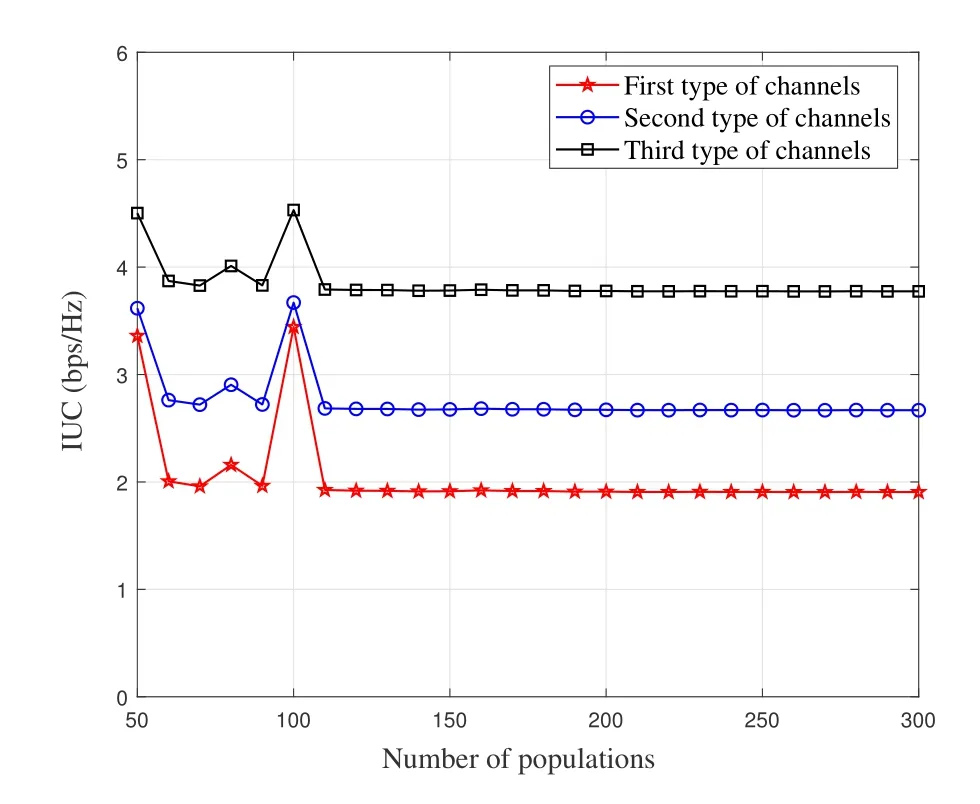
Figure 6.The impact of the number of populations involved in the computation on the IUC.
Figure 7 shows the impact of the channel quality difference between the two types of channels on the IUC,and the difference of the IUC is used to measure the channel quality difference of the two adjacent channels.When the difference of spectrum user’s preference is 4,the difference of the IUC will firstly increase and then decrease with the increase of the difference of the unit channel capacity(ΔCi=Ci+1-Ci),and achieve the maximum value when ΔC=7bps/Hz(To simply analysis,we set ΔC=ΔCi,1≤i ≤M).When the difference of the spectrum user’s preference is 5,the IUC will achieve the maximum when ΔC=6bps/Hz.That is because the utility of SI update is a function of the spectrum user’s preference,the channel quality and the cost of channel occupation.When the difference of the channel quality is small,spectrum users with high preference are more likely to choose high-quality channels.Then,the profit of SI update will be greater and the loss of available channel capacity will also increase.When ΔCachieves a certain value,the profit of SI update and the loss of available channel capacity are just balanced,and the maximum IUC can be obtained.As ΔCcontinues to increase,spectrum users with high preference will not choose these high-quality channels because the cost of channel occupation is too high.Spectrum users whose preference is distributed at both ends of the boundary are more sensitive to the channel quality.
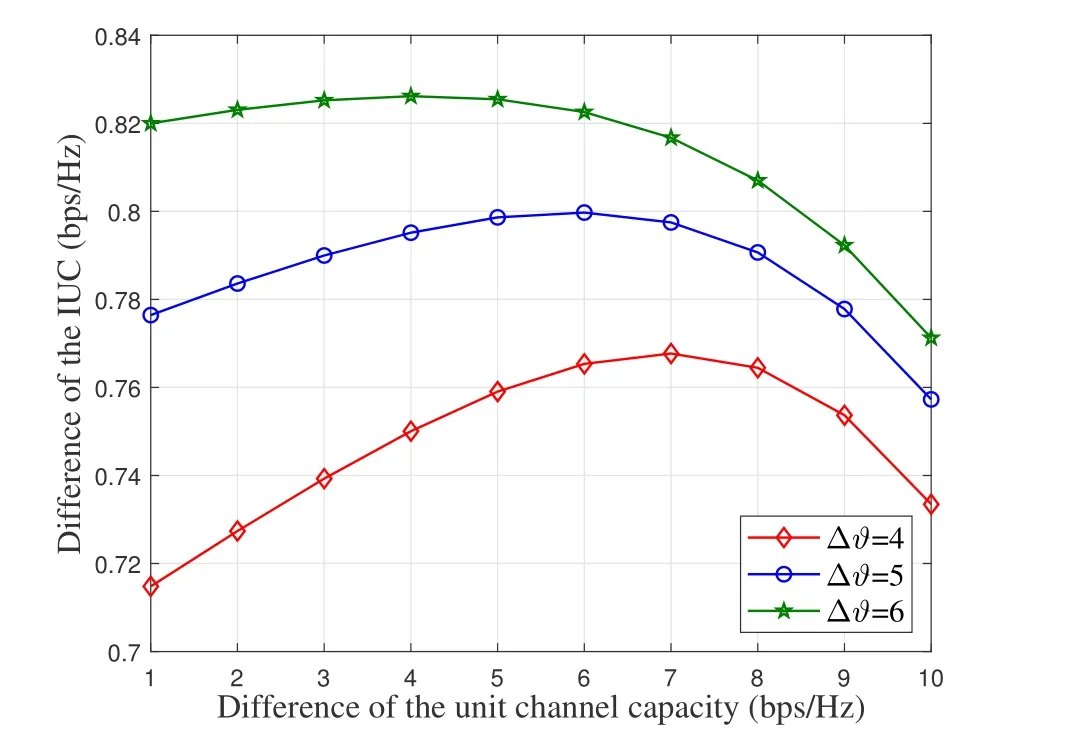
Figure 7.The impact of the channel quality difference between the two types of channels on the IUC.
Figure 8 shows the impact of the number of types of channels on the IUC,where the difference of the unit channel capacity is 5bps/Hz.From Figure 8,we can see that the IUC of the same channel generally decreases with the increase of the number of channel types.As shown in the dark blue histogram in Figure 8,the IUC of the first type of channels decreases with the increase of the number of channel types,but the reduction speed also decreases.The reason for this phenomenon are that the IUC of the first type of channels is related to the IUC of the second type of channels,the IUC of theith type of channels is related to the IUC of the (i-1)th type of channels and the(i+1)th type of channels.The IUC of theMth type of channels is related to the IUC of the(M-1)th type of channels.The influence of the IUC of high-quality channel on the IUC of low-quality channel is transmitted through the IUC of the medium channel quality.And this influence will gradually decrease with the increase of the number of channel types.
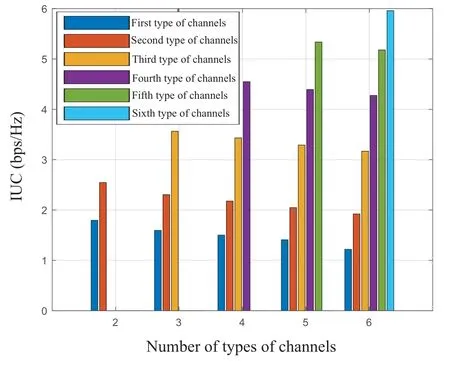
Figure 8.The impact of the number of types of channels on the IUC.
According to the above analysis,there is a correlation and mutual influence between the IUC of heterogeneous channels.The optimal IUC of heterogeneous channels can be found by multiple interactive iterations.The iterative optimization speed is related to the number of populations participating in the computation and the distribution of spectrum user’s preference.The IUC is related to some factors,such as the difference of channel quality,spectrum users’ preference and channel types.When the channel quality and the distribution of spectrum user’s preference are determined,the optimal value of the IUC can be found and determined.
VI.CONCLUSION
In this paper,we construct a dynamic spectrum management network framework assisted by distributed databases,and establish a dynamic update model of SI based on spectrum opportunity incentive.A method to determining the IUC based on Hotelling and Stackelberg game is established by constructing some VSRPs.The influence of the heterogeneity of spectrum resources on the IUC and the profit of SI updating is analyzed.It is proved that there has a Stackelberg equilibrium solution in the process of VSRPs to determine the IUC.A determination algorithm of the IUC based on genetic algorithm is designed to solve the optimization problem.Simulation results also show that there has a Stackelberg equilibrium solution in the process of VSRPs to determine the IUC.The proposed method can quickly and effectively obtain the optimal IUC to ensure that the optimal profit of SI updating can obtained.
- China Communications的其它文章
- Space/Air Covert Communications: Potentials,Scenarios,and Key Technologies
- Improved Segmented Belief Propagation List Decoding for Polar Codes with Bit-Flipping
- Scenario Modeling-Aided AP Placement Optimization Method for Indoor Localization and Network Access
- Off-Grid Compressed Channel Estimation with ParallelInterference Cancellation for Millimeter Wave Massive MIMO
- Low-Complexity Reconstruction of Covariance Matrix in Hybrid Uniform Circular Array
- Channel Estimation for Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface Aided Multiuser Millimeter-Wave/THz Systems

