基于VMD-MPC法的并网型微电网多时间尺度能量协调优化调度
赵凤展,张启承,张 宇,杜松怀,郝 帅,苏 娟,赵婷婷
·农业生物环境与能源工程·
基于VMD-MPC法的并网型微电网多时间尺度能量协调优化调度
赵凤展1,张启承1,张 宇2,杜松怀1,郝 帅1,苏 娟1,赵婷婷2
(1. 中国农业大学信息与电气工程学院,北京 100083; 2. 国网北京市电力公司,北京 100031)
对于含有不同类型储能和分布式电源(Distributed Generation, DG)的并网型微电网,如何优化调度这些设备以提高设备的使用寿命同时平抑DG出力和负荷的波动性与不确定性对配电网的影响具有重要的研究意义。该研究提出一种基于变分模态分解(Variational Modal Decomposition, VMD)和模型预测控制(Model Predictive Control, MPC)相结合的、多时间尺度滚动优化兼具反馈矫正的微电网优化调控模型,该模型在调度过程中考虑了不同类型储能和可控微电源在不同时间尺度上的运行特性,设计了1 h和15 min相结合的调度控制策略,有效解决了含多种微电源及储能设备的微电网的经济优化调度问题;最后,通过算例对比验证了此模型能比较显著地降低铅酸蓄电池充放电频率和系统的运行成本、改善了调度经济性,证明了该方法的有效性和优越性。
模型;预测;控制;并网型微电网;变分模态分解;多时间尺度;可控微电源;能量优化调度
0 引 言
分布式光伏(Photovoltaic,PV)在电网中的渗透率不断提高。PV以微电网形式接入配电网被认为是提高分布式电源(Distributed Generation,DG)消纳能力的一种友好的接入方式[1-3]。并网型微电网的控制策略改善了DG的不确定性对配电网的影响[4-7]。以往并网型微电网协调优化调度采用传统单断面优化调度,即根据某一采样时刻微电网各分布式单元功率进行优化计算,得到这一时刻各分布式单元最优出力值,但这种开环优化方法效率低,优化性能差,无法作为微电网最优调度结果。模型预测控制(Model Predictive Control,MPC)采用某一时刻微电网各分布式单元预测功率进行优化计算,得到各分布式单元最优出力值进行计划控制[8-13]。随着负荷、PV预测方法的逐渐完善及预测精度逐步提高[14-19],采用分布式单元预测功率进行优化的微电网模型预测控制理论正越来越受到学者的关注。模型预测控制采用日前最优经济调度、日内模型预测控制滚动优化反馈校正的思路[20-25],在日前根据短期预测结果计算成本最低调度方案,在日内根据超短期预测结果提前计算设备出力变化量从而对出力进行调整,同时结合系统实时状态进行闭环反馈校正,最大限度地消除了DG不确定性的影响,确保了日前计划的合理性及系统运行的稳定性。
微电网中不同的可控微电源(Controllable Micro-Source,CMS)含有不同时间尺度的运行特性,有些CMS可以进行短时间、高强度能量调度,有些CMS只能进行长时间、缓慢能量调度,在并网型微电网协调优化调度中,应当考虑这些CMS在时间上运行特性的不同,针对性的设计多时间尺度的控制模型[26]。
变分模态分解(Variational Mode Decomposition,VMD)是一种非递归、变模式的信号分解方法[27],VMD可以将负荷序列分解为一系列频率尺度由低到高的有限带宽子序列。在电力系统负荷预测过程中已经应用VMD方法对原始负荷值进行分解得到一系列频率尺度由低到高的子序列并分别建立预测模型[28-29]。本文设计了一套基于变分模态分解和模型预测控制(VMD-MPC)的并网型微电网多时间尺度能量协调优化调度策略,该方法采用VMD得到不同频率尺度的日PV、负荷子序列,并对应各CMS在不同时间尺度上的运行特性建立多个不同时间尺度的协调优化调度模型,利用各模型计算相加得到各CMS调度结果。算例证明了该策略的有效性和经济性。
1 变分模态分解及应用
本文采用变分模态分解VMD将日负荷、光伏序列分解为一系列频率尺度由低到高的有限带宽子序列。VMD采用非递归、变模态原理将信号分解成一系列有限带宽子序列;VMD具有更好谐波分离能力,并且每个分序列具有更好波动特性[27]。VMD具体分解步骤详见文献[27-28]。
采用VMD将当日24 h的96个时刻的负荷值(每15 min一个测量值)、PV预测功率值分解为一系列频率尺度由低到高的有限带宽子序列。以日负荷为例说明,将日负荷序列通过VMD分解为负荷子序列1、2、3、4,其结果如图1所示。
由图1可见,4个子序列反映了不同频率尺度上的日负荷曲线变化情况。子序列1、2为变化分量,子序列1反映了曲线的总体变化趋势,子序列2反映了曲线的变化形状;子序列3、4为波动分量,反映了曲线不同频率尺度的随机波动细节。
2 模型预测控制
模型预测控制(Model Predictive Control,MPC)是一种基于滚动优化和反馈校正方法的有限时域内闭环优化控制模型。MPC在日前进行最优经济调度,得到下一日的基本调度计划,并将该调度计划提前下达至各CMS,并在下一日对其进行实时反馈校正。MPC日内反馈校正的机理为:在每一采样时刻,考虑当前系统的运行状态,以负荷和PV的超短期预测功率为输入量,在线求解一个有限时长内微电网的最优调度问题,得到当前时刻及一个有限时长内各CMS的调度结果,并只执行当前时刻调度结果,在下一个采样时刻,根据前一时刻调度后的系统状态,重复上述过程。本文参考文献[22]的MPC日内滚动优化调度模型,以文献[14]及文献[17]的负荷、PV超短期功率预测方法为基础,以负荷、PV的日前短期预测功率值与日内超短期预测功率值的差值作为扰动输入,以各CMS的功率增量作为控制变量,进行了MPC日内滚动优化调度。MPC流程图如图2所示。
3 多时间尺度日前优化调度模型
本文基于含有多种DG、储能装置和负荷的并网型微电网设计日前优化调度模型,微电网结构示意图如图3所示。
微电网内不同CMS在不同时间尺度上存在不同的运行特性:铅酸蓄电池(Lead-Acid Battery,LAB)适合功率的慢速调控,超级电容器(Supercapacitor,SC)适合功率的快速调控[30],两种储能优先向负荷进行供电,剩余电量输送至配电网,这部分剩余电量产生的利润纳入微电网-配电网的售电利润中;微型燃气轮机(Micro-Turbine,MT,常用于冷热电联供系统);小型生物质发电机(Biomass Power Generation,BPG,装设于城市垃圾处理厂或农村秸秆处理厂中,采用环保燃烧发电模式)功率较小,既适应于功率快速调控、又适应于功率慢速调控,本文采用线性模型实现机组的简化计算。
为了实现微电网各CMS的高效调控和系统整体的经济运行,本文设计了考虑不同储能调控特性与多CMS协调优化调控的多时间尺度日前优化调度模型,具体设计如下:首先输入日前短期预测得到的负荷和PV功率序列,并经VMD分解得到表征不同频率尺度的4个子序列:子序列1、2代表序列的趋势和形状分量,将用于微电网内功率的缓慢调度,即长时间尺度协调优化调度模型;子序列3、4代表序列变化的波动分量,将用于微电网内功率的快速调度,即短时间尺度协调优化调度模型。由此,对应设计了两个时间尺度的4个协调优化调度模型:长时间尺度调度模型每隔1 h优化一次,即执行时长为1 h;短时间尺度调度模型每隔15 min优化一次,即执行时长为15 min。
3.1 长时间尺度日前优化调度模型
长时间尺度优化控制模型以1 h作为时间间隔,设计思路为:从负荷、PV的子序列1、2的96个采样时刻值中抽取24个整点时刻值作为输入值,以LAB、MT、BPG出力/充放电功率为控制变量,构建2个长时间尺度成本模型,滚动求解微电网未来24个整点时刻LAB、MT、BPG出力/充放电功率及公共耦合点电网联络功率PCC(Point of Common Coupling)。
3.1.1 优化目标
为保证并网型微电网系统的运行经济性,长时间尺度优化控制模型的优化目标为系统调度成本最小,调度成本包括运行成本和环境成本,即
式中()为时刻并网型微电网调度成本,单位为美元($),()为时刻运行成本函数,()为时刻环境成本函数,、是多目标的权重系数。运行成本和环境成本具体如下:
1)运行成本函数,包括各DG发电成本函数、LAB运行成本、微电网与配电网之间交易成本,具体为
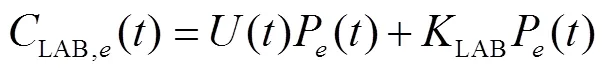
2)环境成本函数,包括各DG及LAB 的污染排放总成本,具体为
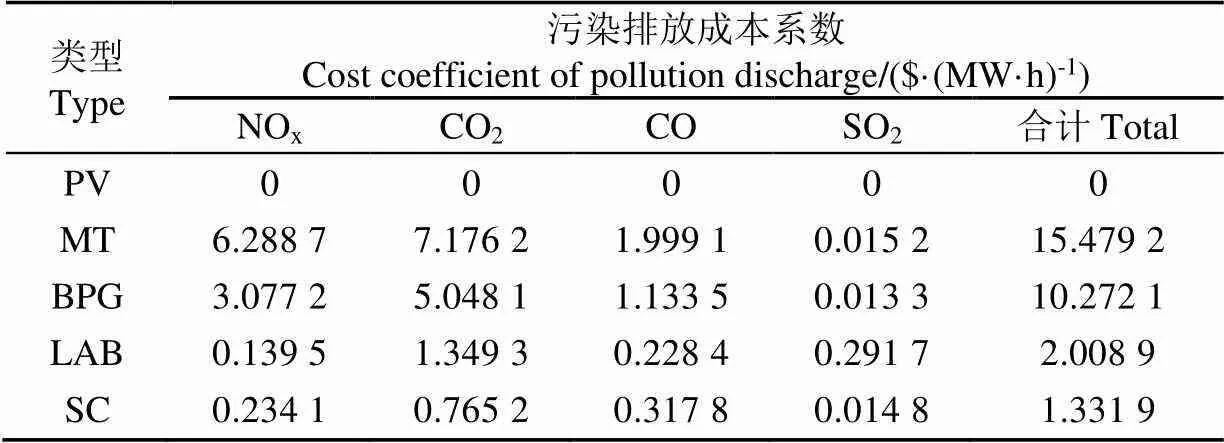
表1 DG及LAB、SC污染排放总成本系数
注: PV, Photovoltaic; MT, Micro-Turbine; BPG, Biomass Power Generation; LAB, Lead-Acid Battery; SC, Supercapacitor.
3.1.2 约束条件
1)功率平衡约束[5]
2)联络线传输功率约束[6]
3)DG出力上下限约束[5]
4)DG出力爬坡约束[6]
5)LAB充放电功率限值约束[22]
6)LAB剩余容量约束[22]
由于LAB充放电效率及漏电等限制,在[-1,]()时段内向LAB进行充放电电量并不能完全转化为储能容量。LAB充电时,时刻的剩余容量为
LAB放电时,时刻的剩余容量为
则LAB剩余容量约束为
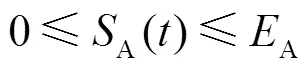
7)LAB周期性电量约束
为了保证一日内第个LAB调度的周期性,当日LAB的充电电量应等于当日LAB的放电电量,即
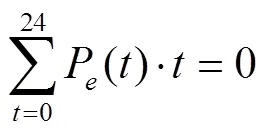
3.2 短时间尺度日前优化调度模型
短时间尺度优化控制模型以15 min作为时间间隔,设计思路为:以负荷、PV的子序列3、4做为输入值,以SC、MT、BPG出力/充放电功率为控制变量,构建2个短时间尺度成本模型,滚动求解微电网未来96个时刻的SC、MT、BPG出力/充放电功率及PCC联络功率。
3.2.1 优化目标
短时间尺度优化控制模型的优化目标同样为系统调度成本最小,系统调度成本同样包括运行成本和环境成本,具体如下:
1)运行成本函数,包括各DG发电成本函数、SC运行成本、微电网与配电网之间交易成本,具体为
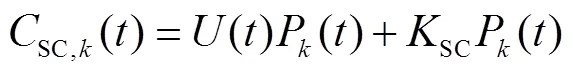
2)环境成本函数,包括各DG及SC的污染排放总成本,具体为
3.2.2 约束条件
短时间尺度优化控制的约束条件与长时间尺度优化控制的约束条件基本相同,不同之处如下:
1)功率平衡约束[5]
2)SC充放电功率限值约束[22]
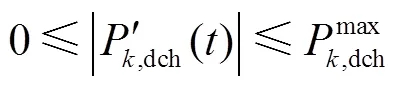
3)SC剩余容量约束[22]
SC充电时,时刻的剩余容量为
SC放电时,时刻的剩余容量为
SC剩余容量约束为
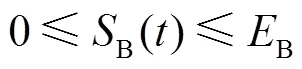
4)SC周期性电量约束
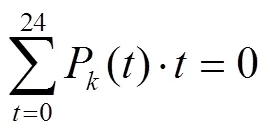
4 基于变分模态分解-模型预测控制的多时间尺度能量协调优化调度策略
本文设计一套基于VMD-MPC的并网型微电网多时间尺度能量协调优化调度策略,其主要思路为:采用VMD将日前负荷和PV的预测功率分别分解为4个不同频率尺度的子序列,并对应各子序列设计2个长时间尺度优化控制模型和2个短时间尺度优化控制模型,各控制模型针对含不同时间尺度运行特性的CMS及各自的控制目标分别执行单独的模型预测控制,各CMS功率相加得到微电网日前调度计划;在日内对各CMS的功率进行反馈校正。该策略流程图如图4所示。该策略具体步骤如下:
步骤1:将日前负荷、PV的96个时刻的短期预测数据进行VMD分解,得到4个子分量。
步骤2:从负荷、PV的子序列1、2的96个采样时刻值中抽取24个整点时刻值作为长时间尺度协调优化调度模型的输入数据。
步骤3:以1h为时间间隔的子序列1和子序列2分别输入长时间尺度协调优化调度模型1、模型2,以15 min为时间间隔的子序列3和子序列4分别输入短时间尺度协调优化调度模型3、模型4,4个优化模型根据不同负荷、PV子序列计算得到时刻LAB、SC、MT、BPG的出力/充放电功率及PCC联络功率结果。
步骤4:若为整点时刻,则最终各CMS有功功率为4个优化模型计算的各CMS有功功率相加;若不为整点时刻,则最终各CMS有功功率为优化模型3、模型4计算的各CMS有功功率加时刻之前最近整点时刻的优化模型1、模型2计算的各CMS有功功率。
步骤5:在日内每时刻对各CMS的功率进行反馈校正。
步骤6:调度时刻更新为下一15 min,根据调度后的系统状态及下一时刻PV、负荷的超短期预测数据,重复上述过程。
5 算例分析
5.1 算例设计
1)实例介绍:本文采用中国北方某地电网一实际光伏发电微电网进行基于VMD-MPC的并网型微电网多时间尺度协调优化调度仿真,微电网LAB、SC、MT、BPG设备数量均为1,其参数如表2所示,当日各时段电力市场单位能量交易价格见文献[20]。
2)起始数据:微电网内各设备起始功率如表3所示,LAB、SC起始容量分别为40、20 kW·h。
3)输入数据:本算例输入数据为2019年2月25日典型日的PV、负荷96个时刻的预测功率。
4)输出数据:当日96个时刻MT、BPG、LAB、SC、PCC的出力/充放电功率/联络功率。
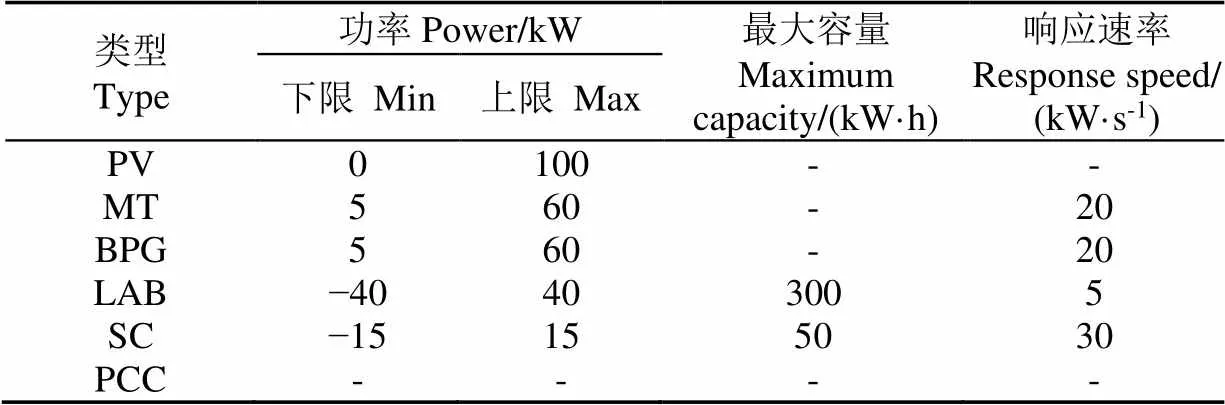
表2 微电网内各设备参数
注:PCC, Point of Common Coupling.
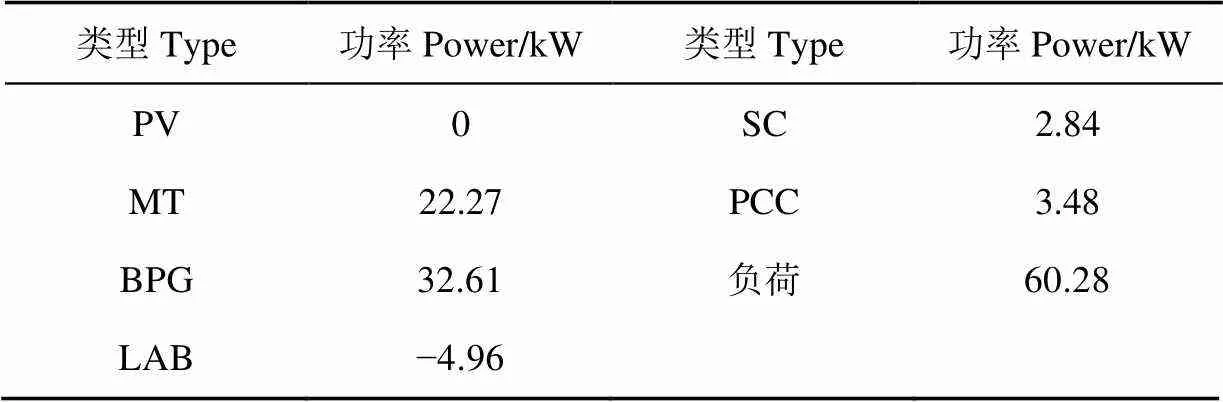
表3 微电网内各设备起始功率
5.2 计算结果及分析
5.2.1 功率调度效果分析
图5给出了当日96个时刻PV、负荷预测功率及LAB、SC、MT、BPG的出力/充放电功率及PCC联络功率计算结果。由图5可以看出:
1)PV:在7:00-18:00期间PV面板接受光照,因此该时段PV出力。
2)负荷LOAD:负荷在当日波动较大,由于工作生产及居家生活需要,负荷在上午及傍晚增长较大。
3)LAB:LAB进行长时间尺度优化调度,相邻1h时段充放电功率变化缓慢,没有出现突变情况;同时可以看出,凌晨至早晨负荷变化较小,LAB基本不工作;7:00-16:00期间PV出力,微电网电量充足,LAB存储电量;16:00-24:00期间PV出力降低,LAB放电。
4)SC:SC进行短时间尺度优化调度,相邻15 min时段充放电功率变化迅速,与负荷功率曲线对比可知SC对负荷突增有很好的跟踪性能;在12:30时刻,SC放电功率为7.73 kW,微电网向配电网售电功率为11.46 kW,说明SC在向负荷供电后仍有多余电量通过PCC输入配电网中,产生的利润纳入微电网-配电网的售电利润中,减小了微电网运行成本。
5)MT、BPG:由于MT、BPG成本及污染较高,MT、BPG一天内出力基本稳定,无较大波动,说明该策略能最大限度地采用可再生能源供电。
6)PCC:凌晨至早晨负荷较小,微电网向配电网购电;白天PV出力,微电网电量充足,微电网向配电网售电;傍晚至凌晨微电网负荷升高,微电网电量不足,但电价较高,微电网购电量较少,负荷缺额主要由LAB供给。
5.2.2 2种储能运行效果分析
LAB、SC的荷电状态即剩余容量如图6所示。由图5、图6结合看出,0:00-7:00期间LAB剩余容量变化较小;以16:00为分界线,LAB在7:00-16:00期间充电,剩余容量增大,在16:00-24:00期间放电,剩余容量减小;而SC则根据负荷波动进行充放电,剩余容量变化频率较大,但变化量较小。由此再一次证明LAB具有长时间尺度功率调度的作用,SC具有短时间尺度功率调度的作用。
5.3 方法对比及分析
分别采用策略1:没有VMD且非预测控制的传统有功调度策略(Traditional strategy);策略2:文献[22]的MPC多时间尺度调度策略(MPC);策略3:本文所提的VMD-MPC多时间尺度调度策略(VMD-MPC)进行仿真,并对功率调度效果、运行成本进行对比,以验证本文所提调度策略具有更高的实用性及经济性。其中策略1、策略2的时间间隔均为15min。
5.3.1 功率调度效果对比分析
通过分析3种策略每时刻的LAB充放电功率,验证各策略的功率调度效果优劣。采用3种策略得到的LAB充放电功率如图7所示。由图7看出,由于采用了低频率尺度的负荷、PV子分量进行1h尺度的优化调度,策略3的LAB充放电功率较前两者相比变化更缓慢,说明本文所提的VMD-MPC调度策略更具可行性。
5.3.2 运行成本对比分析
采用3种策略得到的每时段系统运行成本如图8所示。可以看出图8的3条成本曲线呈现出的相同趋势为:凌晨负荷需求较低,成本较小;白天微电网向配电网售电,成本较小;傍晚微电网从配电网购入电量,期间电力交易价格较高,因此成本较大。同时,比较这3条成本曲线可见,由策略3得到的运行成本曲线在当日各时段都为最低值。将3种策略当日96个时刻的系统运行成本分别相加,得到当日总成本依次为:192 272、174 388、155 031美元。策略3当日总成本与前2种策略相比分别下降了19.37%、11.10%,由此可见,本文所提的VMD-MPC调度策略可以有效降低微电网运行成本,更具经济性优势。
6 结 论
本文采用VMD将原始PV和负荷预测功率序列分解为不同频率尺度的子序列,并考虑微电网中各CMS在不同时间尺度上的运行特性,设计了以成本最低为目标的多个不同时间尺度的协调优化调度模型及一套基于VMD-MPC的多时间尺度协调优化调度策略。该策略利用由VMD分解得到的不同频率尺度的PV、负荷子序列分别控制不同时间尺度运行特性的CMS,实现了微电网各CMS的差异化控制。
算例分析及对比表明,本文所提的VMD-MPC多时间尺度协调优化调度策略具有2个方面的特点及优势:1)实现了储能设备的优化利用。本策略考虑了不同类型储能(铅酸蓄电池和超级电容器)的运行特性,设计了长、短时间尺度能量协调优化调度策略,更有利于储能运行及延长寿命。2)算例当日总成本较对比策略分别下降了19.37%和11.10%,此策略显著降低了系统的运行成本、改善了调度经济性。
在本文提出的微电网多时间尺度协调优化调度策略的基础上,可以进一步研究包含更多能源类型、更多场景的综合能源系统的多时间尺度协调优化调度问题。
[1] 王成山,王瑞,于浩,等. 配电网形态演变下的协调规划问题与挑战[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2020,40(8):2385-2396.
Wang Chengshan, Wang Rui, Yu Hao, et al. Problems and challenges of coordinated planning in distribution network configuration evolution[J]. Chinese Journal of Electrical Engineering, 2020, 40(8): 2385-2396. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] Danish M S S, Matayoshi H, Howlader H R, et al. Microgrid planning and design: resilience to sustainability[C]//2019 IEEE PES GTD Grand International Conference and Exposition Asia (GTD Asia), Bangkok, Thailand, 2019: 253-258.
[3] 李军徽,张嘉辉,穆钢,等. 计及负荷峰谷特性的储能调峰日前优化调度策略[J]. 电力自动化设备,2020,40(7):128-133,140.
Li Junhui, Zhang Jiahui, Mu Gang, et al. Optimal scheduling strategy for energy storage before peak and valley load characteristics[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2020, 40(7): 128-133, 140. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 严干贵,蔡长兴,段双明,等. 考虑电池储能单元分组优化的微电网运行控制策略[J]. 电力系统自动化,2020,44(23):38-46.
Yan Gangui, Cai Changxing, Duan Shuangming, et al. Microgrid operation Control Strategy considering grouping optimization of battery energy storage units[J]. Power System Automation, 2020, 44(23): 38-46. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 刘峪涵,汪沨,谭阳红. 并网型微电网多目标容量优化配置及减排效益分析[J]. 电力系统及其自动化学报,2017,29(9):70-75.
Liu Yuhan, Wang Feng, Tan Yanghong. Multi-objective optimal capacity configuration and emission reduction benefit analysis of grid-connected microgrid[J]. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2017, 29(9): 70-75. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 徐意婷,艾芊. 含微电网的主动配电网协调优化调度方法[J]. 电力自动化设备,2016,36(11):18-26.
Xu Yiting, Ai Qian. Coordinated optimal dispatch of active distribution network with microgrids[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2016, 36(11): 18-26. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 周烨,汪可友,李国杰,等. 基于多智能体一致性算法的微电网分布式分层控制策略[J]. 电力系统自动化,2017,41(11):142-149.
Zhou Ye, Wang Keyou, Li Guojie, et al. Distributed hierarchical control strategy for micro grid based on multi-agent consistency algorithm[J]. Power System Automation, 2017, 41(11): 142-149. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] Batiyah S, Zohrabi N, Abdelwahed S, et al. An MPC-based power management of a PV/battery system in an islanded DC microgrid[C]//2018 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo (ITEC), Long Beach, CA, 2018: 231-236.
[9] 乐健,廖小兵,章琰天,等. 电力系统分布式模型预测控制方法综述与展望[J]. 电力系统自动化,2020,44(23):179-191.
Le Jian, Liao Xiaobing, Zhang Yantian, et al. Review and prospect of distributed model predictive control methods for power systems[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2020, 44(23): 179-191. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] Zhang W, Zhang F, Zhang J, et al. Parameter optimization and model identification of identification model control based on improved generalized predictive control[C]//Proceedings of 2018 International Computers, Signals and Systems Conference (ICOMSSC 2018), Dalian, China, 2018: 732-736.
[11] 曾宇,刘友波,高红均,等. 基于模型预测控制的高压配电网负荷转供与储能电站协同运行[J/OL]. 电网技术:1-11. https://doi.org/10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst. 2020. 1575.
Zeng Yu, Liu Youbo, Gao Hongjun, et al. Model predictive control based collaborative operation of high voltage distribution network load transfer and energy storage power station[J/OL]. Grid Technology: 1-11. https://doi.org/ 10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2020.1575. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 刘颖明,王晓东,彭朝阳. 计及储能出力水平的平滑风电功率模型预测控制策略[J]. 电网技术,2020,44(5):1723-1731.
Liu Yingming, Wang Xiaodong, Peng Chaoyang. Smooth wind power model predictive control strategy considering storage output level[J]. Power Grid Technology, 2020, 44(5): 1723-1731. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 葛乐,张伟,严锋,等. 基于自适应模型预测控制的柔性互联配电网优化调度[J]. 电力自动化设备,2020,40(6):15-23.
Ge Le, Zhang Wei, Yan Feng, et al. Optimal scheduling of flexible interconnected distribution network based on adaptive model predictive control[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2020, 40(6): 15-23. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 姚程文,杨苹,刘泽健. 基于CNN-GRU混合神经网络的负荷预测方法[J]. 电网技术,2020,44(9):3416-3424.
Yao Chengwen, Yang Ping, Liu Zejian. Load forecasting method based on CNN-GRU hybrid neural network[J]. Power System Technology, 2020, 44(9): 3416-3424. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 陆继翔,张琪培,杨志宏,等. 基于CNN-LSTM混合神经网络模型的短期负荷预测方法[J]. 电力系统自动化,2019,43(8):131-137.
Lu Jixiang, Zhang Qipei, Yang Zhihong, et al. Short-term load forecasting method based on CNN-LSTM hybrid neural network model[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2019, 43(8): 131-137. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 王育飞,杨启星,薛花. 考虑混沌特征的增强型大脑情绪神经网络光伏发电功率超短期预测模型[J/OL]. 高电压技术,1-15. https://doi.org/10. 13336/j.1003- 6520.hve. 20201811.
Wang Yufei, Yang Qixing, Xue Hua. Ultra-short term prediction model of photovoltaic power generation based on enhanced brain emotional neural network considering chaotic characteristics [J/OL].High Voltage Technology, 1-15. https://doi.org/10.13336/j.1003-6520. hve. 20201811. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 肖白,刘庆永,牛强,等. 基于元胞负荷特性分析的RBF神经网络空间负荷预测方法[J]. 电网技术,2018,42(1):301-307.
Xiao Bai, Liu Qingyong, Niu Qiang, et al. Spatial load prediction method based on RBF neural network based on cellular load characteristics analysis[J]. Power Grid Technology, 2018, 42(1): 301-307. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 张金金,张倩,马愿,等. 基于改进的随机森林和密度聚类的短期负荷频域预测方法[J]. 控制理论与应用,2020,37(10):2257-2265.
Zhang Jinjin, Zhang Qian, Ma Yuan, et al. Short-term load frequency domain prediction method based on improved random forest and density clustering[J]. Control Theory and Application, 2020, 37(10): 2257-2265. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 王小杨,罗多,孙韵琳,等. 基于ABC-SVM和PSO-RF的光伏微电网日发电功率组合预测方法研究[J]. 太阳能学报,2020,41(3):177-183.
Wang Xiaoyang, Luo Duo, Sun Yunlin, et al. Research on the combination prediction method of daily power generation of PV micro-grid based on ABC-SVM and PSO-RF[J]. Journal of Solar Energy, 2020, 41(3): 177-183. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 孙惠娟,张乐乐,彭春华. 基于差异化需求响应模型预测控制的微网时域滚动优化调度[J/OL]. 电网技术:1-10. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2410.tm.20210107.1548.005.html.
Sun Huijuan, Zhang Lele, Peng Chunhua. Time-domain rolling optimal scheduling of micro-grid based on differential demand response model predictive control [J/OL]. Grid technology: 1-10. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2410.tm. 20210107.1548.005.html. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 王磊,周建平,朱刘柱,等. 基于分布式模型预测控制的综合能源系统多时间尺度优化调度[J/OL]. 电力系统自动化:1-13. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/ 32.1180.TP. 20210315.1837.004.html.
Wang Lei, Zhou Jianping, Zhu Liuzhu, et al. Multi-time scale optimal scheduling of integrated energy system based on distributed model predictive control [J/OL]. Automation of Electric Power Systems: 1-13. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/ 32.1180.TP.20210315.1837. 004.html. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 肖浩,裴玮,孔力. 基于模型预测控制的微电网多时间尺度协调优化调度[J]. 电力系统自动化,2016,40(18):7-14,55.
Xiao Hao, Pei Wei, Kong Li. Multi-time scale coordinated optimal dispatch of microgrid based on model predictive control[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2016, 40(18): 7-14, 55. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 董雷,陈卉,蒲天骄,等. 基于模型预测控制的主动配电网多时间尺度动态优化调度[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2016,36(17):4609-4617.
Dong Lei, Chen Hui, Pu Tianjiao, et al. Multi-time scale dynamic optimal dispatch in active distribution network based on model predictive control[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2016, 36(17): 4609-4617. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 窦晓波,晓宇,袁晓冬,等. 基于改进模型预测控制的微电网能量管理策略[J]. 电力系统自动化,2017,41(22):56-65.
Dou Xiaobo, Xiao Yu, Yuan Xiaodong, et al. Energy management strategy based on improved model predictive control for microgrid[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2017, 41(22): 56-65. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 张哲,王成福,董晓明,等. 基于分层模型预测控制的风电场电压协调控制策略[J]. 电力系统自动化,2019,43(11):34-42,94.
Zhang Zhe, Wang Chengfu, Dong Xiaoming, et al. Wind farm voltage coordination control strategy based on hierarchical model predictive control[J]. Power System Automation, 2019, 43(11): 34-42, 94. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 张颖,季宇,唐云峰. 基于MPC含分布式光伏配电网有功功率—无功功率协调控制[J]. 电力系统自动化,2017,41(21):140-146.
Zhang Ying, Ji Yu, Tang Yunfeng. Coordinated control of active and reactive power for distribution network with distributed photovoltaic based on model predictive control[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2017, 41(21): 140-146. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] Abdoos A A. A new intelligent method based on combination of VMD and ELM for short term wind power forecasting[J]. Neurocomputing, 2016, 203: 111-120.
[28] 赵凤展,郝帅,张宇,等. 基于变分模态分解BA-LSSVM算法的配电网短期负荷预测[J]. 农业工程学报,2019,35(14):190-197.
Zhao Fengzhan, Hao Shuai, Zhang Yu. et al. Short-term load forecasting for distribution transformer based on VMD-BA-LSSVM algorithm[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2019, 35(14): 190-197. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 梁智,孙国强,李虎成,等. 基于VMD与PSO优化深度信念网络的短期负荷预测[J]. 电网技术,2018,42(2):598-606.
Liang Zhi, Sun Guoqiang, Li Hucheng, et al. Short-term load forecasting based on VMD and PSO optimized deep belief network[J]. Power System Technology, 2018, 42(2): 598-606. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] Yao Liangzhong, Yang Bo, Cui Hongfen, et al. Challenges and progresses of energy storage technology and its application in power systems[J]. Journal of Modern Power Systems and Clean Energy, 2016, 4(4): 519-528.
Multi-time scale coordinated optimal energy dispatch of grid-connected microgrid using VMD-MPC
Zhao Fengzhan1, Zhang Qicheng1, Zhang Yu2, Du Songhuai1, Hao Shuai1, Su Juan1, Zhao Tingting2
(1. College of Information and Electrical Engineering, China Agricultural University, Beijing 100083, China;2. State Grid Beijing Electronic Power Company, Beijing 100031, China)
Distributed Photovoltaic (PV) is ever increasing in the power grid, as the current PV generation rapidly developed. However, it is difficult to directly coordinate the PV into the conventional power grid, due mainly to the intermittent and uncertain nature of PV power generation. As such, there is a great impact on the power flow of a system, particularly the volatility and uncertainty of the output and load demands of Distributed Generation (DG) power in grid-connected microgrids. A friendly way is widely expected that the PV can access the distribution network in the form of a microgrid for the enhanced DG absorption capacity. It is highly urgent to reduce the impact of such volatility and randomness on the energy transmission between microgrids and distribution networks. In this study, a multi-time scale coordinated optimization was performed on energy scheduling strategies using a Variational Modal Decommission-Model Predictive Control (VMD-MPC). Specifically, an MPC was a sort of optimal control with a closed-loop over a finite time domain, suitable for the nonlinear, time-varying, and uncertainty of the system. There was no differentiation scheduling on the forecast of PV power for each Controllable Micropower (CMS)in the microgrid operation because the load was directly applied in the previous multiple-time scale scheduling using MPC optimization. Consequently, some CMS (such as a Lead-Acid Battery, LAB) was run in a short time, high strength, and energy scheduling, whereas, some CMS (such as a Super Capacitor, SC) was only for a long and slow energy scheduling. Thus, the operating characteristics of CMS in different time scales should be considered in the optimization of scheduling. A VMD was utilized to acquire the different loads and subsequence in the PV series of frequency scales, thereby achieving the multiple coordinated optimization scheduling CMS models in different time scales. The scheduling model included a longtime scale of 1 hour and 15 min interval time for a short scale. Dispatching LAB, Micro gas Turbine (MT), and small Biomass Generator (BPG) were usually responded to the signals of a long-time scale. Scheduling SC, MT and BPG were responded to the signals of a short-time scale. The final scheduling was achieved for each CMS to realize the differentiated optimal processing of signals on different time scales, where the calculated values of each model were summed up. Then a feedback correction model was constructed to form a closed-loop control using the day-ahead scheduling, where the difference between the ultra-short-term forecast within the day and the day-ahead forecast was taken as the disturbance input, while the current operating state of the system was taken as the parameter, and the power increment of each CMS was taken as the control variable. The feedback correction effectively enhanced the robustness, while reduced the impact of the system that resulted from the uncertainty of load and PV output. As such, the optimal energy scheduling strategy effectively coordinated the grid-connected microgrids with multiple micro power sources and time scales. Taking a PV microgrid in North China as an example, an MATLAB software was used to simulate and verify the model, indicating optimal scheduling. Better feasibility, effectiveness, and economy of strategy were achieved from the perspectives of power scheduling and operating cost, compared with the traditional active power and MPC multi-time scale scheduling strategy. Accordingly, this finding can provide a practical and effective technical approach for high-permeability microgrids in energy trading under the environment of multiple renewable energy consumption and electricity market.
models; prediction; control; grid-connected microgrid; variational mode decomposition; multi-time scale; controllable micro-source; optimal energy dispatch
2020-12-07
2021-03-23
国家重点研发计划项目(2016YFB0900101);国家电网公司总部科技项目(52272216002N)
赵凤展,博士,副教授,研究方向为智能配电网与微网分析、控制与评价。Email:zhaofz@cau.edu.cn
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2021.07.023
TM 731
A
1002-6819(2021)-07-0190-09
赵凤展,张启承,张宇,等. 基于VMD-MPC法的并网型微电网多时间尺度能量协调优化调度[J]. 农业工程学报,2021,37(7):190-198. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2021.07.023 http://www.tcsae.org
Zhao Fengzhan, Zhang Qicheng, Zhang Yu, et al. Multi-time scale coordinated optimal energy dispatch of grid-connected microgrid using VMD-MPC[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2021, 37(7): 190-198. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2021.07.023 http://www.tcsae.org

