Trends in research related to high myopia from 2010 to 2019: a bibliometric and knowledge mapping analysis
Xiao-Dan Zhang, Chun-Xia Wang, Hong-Hu Jiang, Shuo-Lan Jing, Jiang-Yue Zhao,Zi-Yan Yu
1Department of Ophthalmology, the Fourth Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University; Eye Hospital of China Medical University; Key Lens Research Laboratory of Liaoning Province, Shenyang 110005, Liaoning Province, China
2China Medical University, Shenyang 110122, Liaoning Province, China
Abstract
● KEYWORDS: high myopia; pathological myopia;bibliometric analysis; VOSviewer
INTRODUCTION
Myopia is the most common type of refractive error,and its prevalence is increasing drastically especially in East Asian[1]. Its global prevalence was predicted to raise from the 30% to 50%, and there would be nearly one billion people with high myopia (HM) by 2050[2]. In young adults of East Asia, the prevalence of myopia is high, about 80%-90%.Furthermore, pathological myopia (PM), a sight-threatening ocular disease, has been identified in nearly 30.8% of HM in China[3]. PM is one of the leading causes of global blindness,especially in East Asia, and its blinding complications include myopic macular degeneration, glaucoma-like optic neuropathy,retinal detachment, foveoschisis, posterior staphyloma, macular atrophy, and blindness and so on[4-8]. Therefore, this raises a number of ethical concerns and challenges for researchers and clinicians to reveal the pathological mechanism and to develop new preventive and therapeutic strategies.
Numerous documents have been published on academic journals on HM and PM in the past three decades. Bibliometric analysis and mapping knowledge domain (MKD) methods were carried out in this study to explore the HM research trends by using the Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC)database. Bibliometric analysis is a kind of publication analysis method using mathematical and statistical approach applied to evaluate the related literature. The distributions of profiles,the most influential and clusters of keywords were measured quantitatively[9]. MKD is a method to reveal the knowledge structure by graphic plotting scientifically and to classify the already known literature and reveal the hot spots of scientific knowledge via literature analysis software (VOSviewer and CiteSpace)[10]. Currently, keyword co-occurrence analyses,keywords burst analysis and co-citation analyses are used for knowledge mapping[11].
This study aimed to execute a global analysis of studies on HM categorically to assess the rise in publication number, source journals, author productivity, international collaborations,keyword co-occurrence analysis and co-citation analysis linked with HM. This brief summary of the keyword’s clusters showed the research progress and was supposed to shed some new lights for optometrist specialists on HM field.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Data Source and Research StrategyIn this research, we retrieved WoSCC (https://webofknowledge.com/) in the Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE) database online as data source, which is commonly regarded as a trustworthy source for academic and bibliometric research.
Data were collected in January 1, 2020. “High myopia” and“Pathological myopia” were retrieved as the topic terms,the time span was “from 2010 to 2019”, the document type was restricted to “article”, and the language was limited to“English” only. For the United Kingdom, publications of England, North Ireland, Scotland, and Wales were analyzed separately. Hong Kong is under the heading of China.
The retrieved data were stored as “Plain text” format with “full record and cited references” for further analyze. Raw data were initially downloaded from the WoSCC. The basic information of each document was gathered, such as author, journal,country, organization, keywords, title, abstract, and references.
Bibliometric and Visualized AnalysisVOSviewer software version 1.6.13 (www.vosviewer.com), a free software tool for constructing and visualizing bibliometric maps, was used in this study. These node-link maps may contain researchers,journals, individual publications, or important terms and they can be constructed based on co-authorship, co-citation, or cooccurrence relations. The manual for VOSviewer v. 1.6.13 is available online (https://www.vosviewer.com/documentation/Manual_VOSviewer_1.6.13.pdf)[12].
A total of 3544 articles containing complete research results were retrieved. The evaluation involved the following indictors obtained from the collected sample: 1) publication activity yearly; 2) top 10 most influential organizations; 3) top 10 countries with their numbers of publications and citations; 4)top 10 most productive co-cited authors and authors; 5) top 10 main source journals; 6) top 10 co-cited references; 7) top 22 most co-occurrence keywords.
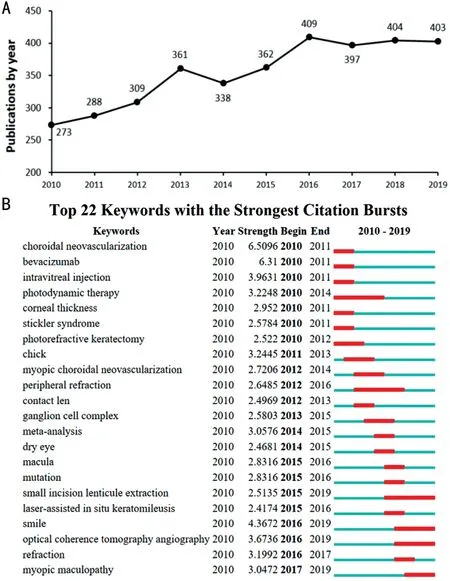
Figure 1 The publication trends and keywords of HM study from 2010-2019 A: The annual number of publications in HM research from 2010 to 2019; B: Burst analysis of keywords.
Co-occurrence network of keywords was used to build the knowledge map of HM academic research. Keywords are applied to state the theme of the scientific literature, and the clustering of related keywords form co-occurrence keyword clusters in order to explore the knowledge hotspots and structure in the field of HM.
In this research, we also used CiteSpace 5.6.R2 (Drexel University, Philadelphia, PA) to analyze keywords showing strong citation bursts, to represent predictors of research frontiers. The Web of Science is the original input data source for CiteSpace.
RESULTS
Annual Distribution of PublicationsBy WoSCC based analysis, 3544 documents on HM from 2010 to 2019 has been collected. Published articles increased in the past decade from 273 articles to 403 articles (Figure 1A). The top 22 keywords with the strongest citation bursts were extracted via keywords burst analysis. The keyword “smile” showed burst from 2016 (Figure 1B), consistent with the boost of publications. “Choroidal neovascularization”, “bevacizumab”,“intravitreal injection”, and “photodunamics therapy” are the keywords burst from 2010, in accordance with the emergence of therapies for neovascular maculopathy.
Country AnalysisCountry analysis revealed that 3544 documents were from 87 countries and regions. The top 10 countries and regions have published 3529 documents in HM field, accounting for 99.6% of total documents (Table 1). China is the most published country (988, 27.9%), followed by the United States (759, 21.4%) and Japan (303, 8.5%). Citations are always used as an important indicator of academic impact.Citation analysis showed that the United States had 12 312 citations and ranked the top one, followed by China (9901 citations) and Japan (6541 citations).
Country co-authorship analysis revealed the influential countries and the degree of communication between countries in HM field. The larger nodes indicate the country has greater influence; the distance and thickness of connection between nodes indicated their cooperative relationships in HM field.The United States cooperated with many countries in HM field intensely, for example, Canada, Brazil, Germany, and Sweden,indicating that geographical distance is not important factors that influence cooperation relationships (Figure 2).
Distribution of Main Research OrganizationsResearch organization analysis showed that the 3544 documents from 3068 organizations. The top 10 organizations published 931 documents, accounting for 26.3% of the total (Table 2). Coauthorship analysis revealed knowledge domain map of research organizations’ distribution in HM field (Figure 3),node size representing the publications number and links between nodes representing the cooperation intensity.
Distribution of Authors and co-Authorship of Research GroupsAuthors analysis showed more than 12 238 authors published documents about HM. Among these authors, Jonas JB (80 publications) ranked the first, followed by Ohno-Matsui K (77 publications) and Saw SM (41 publications), indicating their great contribution in the field of HM. Author co-citation analysis showed Saw SM (953 co-citations) ranked first,followed by Jonas JB (647 co-citations) and Wong TY (513 co-citations), indicating their relative influence in HM research(Table 3).
Co-authorship analysis showed the knowledge domain map of research groups’ distribution in the field of HM (Figure 4). Node size is consistent with the number of publications. Cooperative relationship between authors was shown by links between nodes, and greater link strength indicates higher cooperation density.
Distribution of Source JournalsPublications about HM were from 359 journals. Top 10 journals are shown in Table 4. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science published the highest number of documents (288, 8.1%), followed by Journal of Cataract and Refractive Surgery (196, 5.5%) and Journal of Refractive Surgery (156, 4.4%). The top three journals accounted for 42.2% of all the publications.
Distribution of Cited References: Knowledge Bases of HM studyCo-cited reference analysis revealed the scholarly publications constitution of HM research. In the total 49 210 cited references, 320 cited references met the threshold (the minimum number threshold set as 30). The top 10 co-cited references were shown in Table 5.

Figure 2 Distribution of main research countries and regions in HM study The minimum number of documents of a country or region was set as 5. Of the 87 countries and regions that were involved in HM research, 52 countries and regions met the threshold.
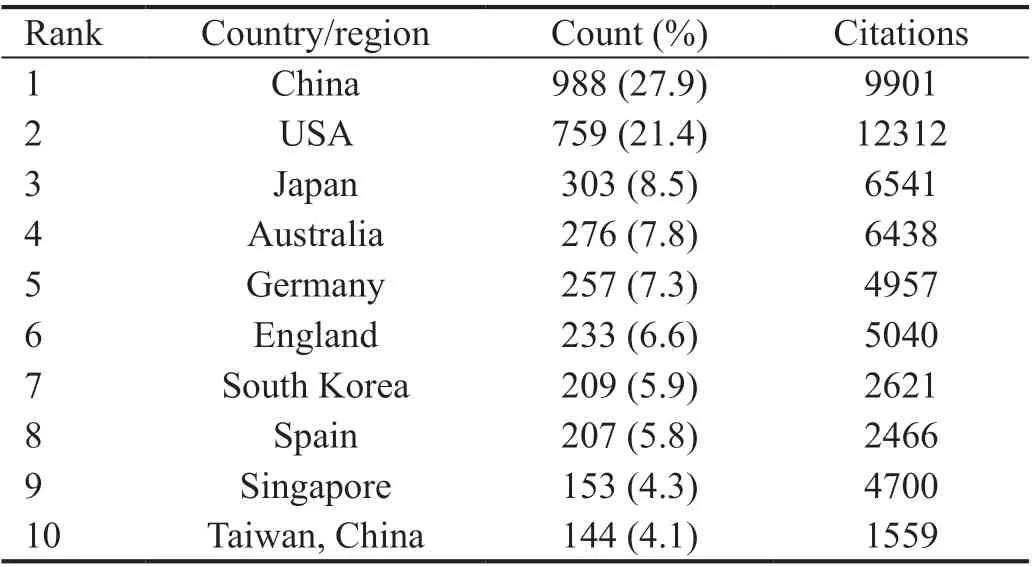
Table 1 Top 10 productive countries/regions in HM study, 2010-2019
If the minimum number of citations of a document was set as 50, 163 documents met the threshold through citation analysis of the 3544 documents, node size corresponding to the number of citations (Figure 5).
Distribution of Keywords: Hotspots of HM StudyHighfrequency keywords co-occurrence analysis identified hotspots of HM network. The minimum co-occurrence number of a keyword equaled to 15. Totally 126 keywords met the threshold in the sample number of 8294 keywords that involved in HM.Through network analysis, the keywords were clustered based on similarities. The 6 main clusters in order were red, green,blue, yellow, purple, and light blue (Figure 6) and the top 10 keywords of each cluster were listed (Table 6).
DISCUSSION
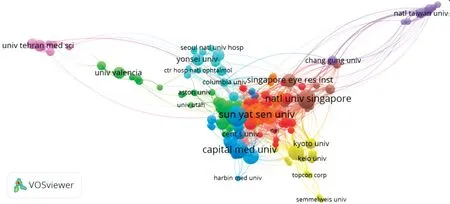
Figure 3 Collaboration network of main research organizations in HM study The minimum number of documents of an organization was set as 10. Of the 3068 organizations that were involved in HM research, 171 organizations met the threshold.

Table 2 Top 10 productive organizations in HM study, 2010-2019
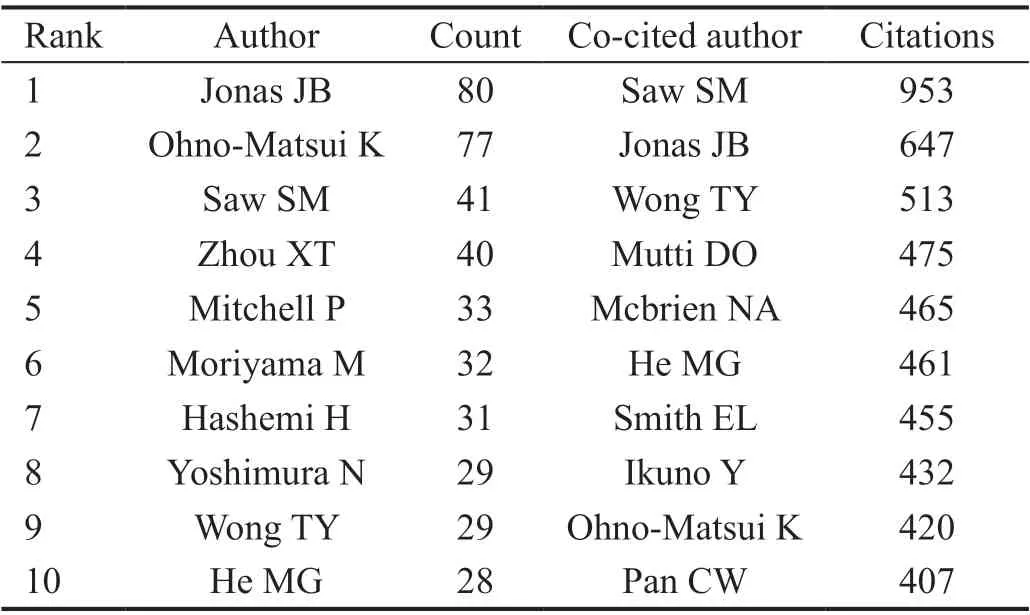
Table 3 Top 10 productive authors and co-cited authors in HM study, 2010-2019
The number of academic publications can reveal the development tendency in a field, and the variation of the number is an important research index. As shown in Figure 1A, 3544 documents on HM field from 2010 to 2019 were collected, and the number of annual publications rose in the past decade. The strongest citation bursts keywords are considered to be an indicator of frontiers in basic and clinical research. Among the top 22 burst keywords (Figure 1B),“Choroidal neovascularization”, “bevacizumab”, “intravitreal injection”, and “photodunamics therapy” are the keywords burst from 2010, in accordance with the emergence of intravitreal anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF)injection and photodynamics in PM therapy. The keyword“SMILE” burst from 2016, many research projects evoked around this topic. In conformity to the line chart, the number of publications increased from 362 to 409 in 2016.
In the most productive countries analysis, China is the leading country in HM research, accounted for 27.9% of documents and ranked top one in citation numbers, followed by the United States (21.4%) and Japan (8.5%) (Table 1). Research organizations distribution analysis showed the most productive organizations and the most active collaborations in HM field.The most productive research institution was Sun Yat-sen University, followed by Fudan University, Capital Medical University and National University of Singapore (Table 2).Geographical distribution may play a role in prevalence rates indicating a high HM prevalence in Asian countries, especially in China and Singapore[3,13]. The country co-authorship analysis indicated that the United States is the key node cooperated with Japan, Singapore, Canada, Brazil, Germany and Sweden,and other countries (Figure 2).Constructing the analysis of the co-authorship and the information of author co-citations can provide valuable information for researchers to seek collaboration opportunities.In the co-authorship analysis, Jonas JB ranked the first,followed by Ohno-Matsui K and Saw SM; and the author co-citations analysis showed Saw SM ranked first, followed by Jonas JB and Wong TY, indicating their productive contribution and relative influence in HM research (Table 3).Academic journals distribution analysis showed the most published journals in HM field. The most published journal is Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science (288, 8.1%),followed by Journal of Cataract and Refractive Surgery(196, 5.5%) and Journal of Refractive Surgery (156, 4.4%).Publications of these three journals accounted for 42.2% of the total amount, showing that the United States contributed most in the publication of HM field (Table 4).
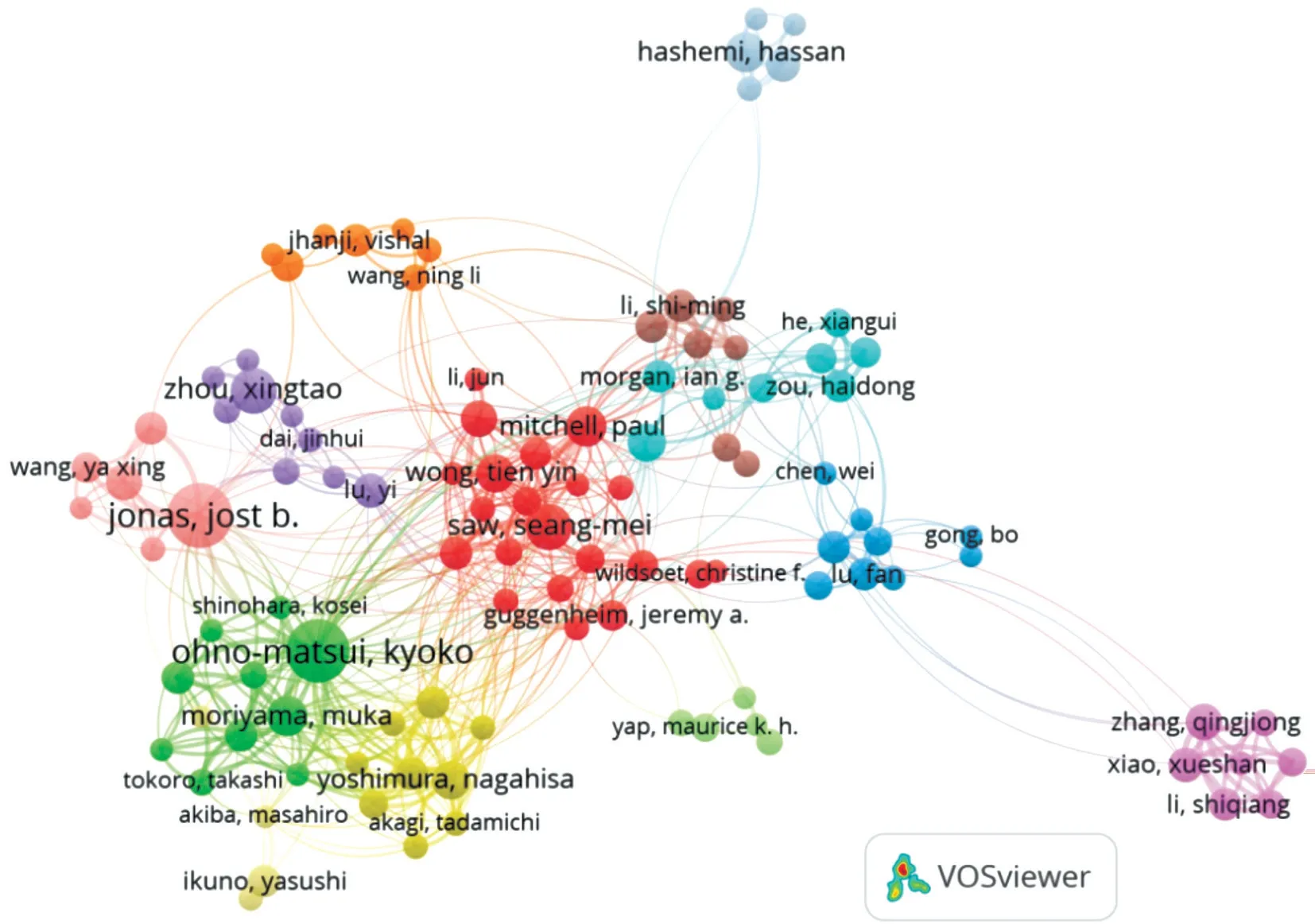
Figure 4 Co-authorship network of productive authors in HM study The minimum number of documents of an author was set as 10. Of the 12 238 authors that were involved in HM research, 145 authors met the threshold.

Figure 5 Citation analysis of documents The minimum number of citations of a document was set as 50. Of the 3544 documents, 163 documents met the threshold.
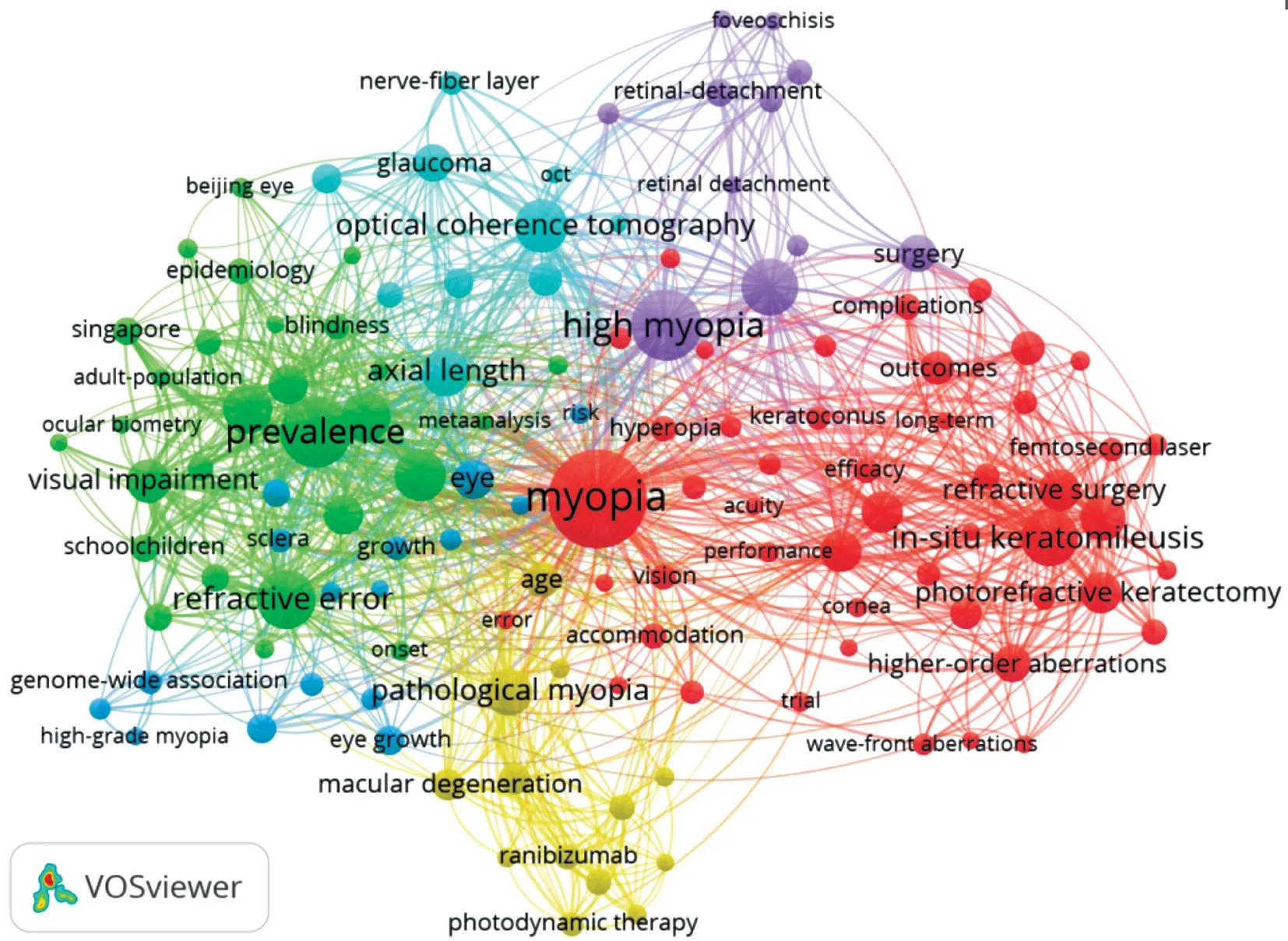
Figure 6 Co-occurrence network of keywords in HM study The minimum number of occurrences of a keyword was set as 40. Of the 8294 keywords that were involved in HM research, 126 keywords met the threshold.

Table 4 Top 10 main source journals in HM study, 2010-2019
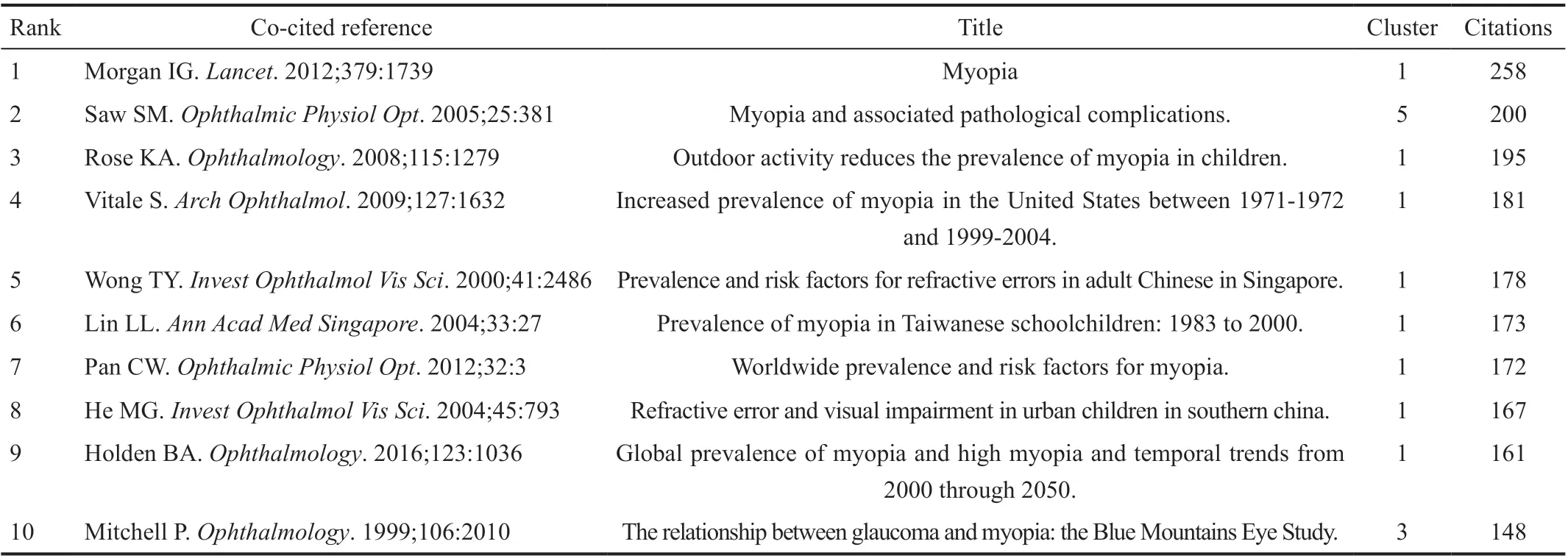
Table 5 Top 10 co-cited references in HM research, 2010-2019

Table 6 Co-occurrence analysis of keywords (Top 10 keywords in the 6 clusters)
Citation parameters were used to reveal associated topics within the high-quality collected articles. A great number of cited references can reveal the research background effectively via co-citation analysis. The top ten cited references mainly focused on etiology and clinical characteristics of myopia(Table 5).
The keyword co-occurrence analysis displayed the highfrequency keywords which are considered to be on behalf of the search theme. The frontier discipline and internal structure of the related to HM literature mainly formed 6 clusters (colored red, green, blue, yellow, purple, and light blue; Figure 6), and each cluster was summarized a specific theme. The following 6 clusters were analyzed, regarding the characteristics and status of HM research.
Cluster 1 (red) is linked with the refractive surgery of HM. Extracting co-occurrence keywords included “insitu keratomileusis”, “laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis(LASIK)”, “refractive surgery”, “photorefractive keratectomy(PRK)”, “astigmatism”, “follow-up”, “higher-order aberrations”, “outcomes” and “moderate”[14-26].
Cluster 2 (green) represents keywords related to etiology and clinical characteristics of myopia. The extracted cooccurrence keywords included “prevalence”, “refractive error”,“children”, “risk-factors”, “population”, “visual impairment”,“progression”, “ametropia”, “school-children” and “outdoor activity”[2,27-63].
Cluster 3 (blue) is linked with the mechanism of eye growth.Extracting co-occurrence keywords included “eye”, “eye growth”, “form-deprivation myopia”, “association”, “sclera”,“genome-wide association”, “expression”, “growth”, “retina”and “susceptibility”[64-93].
Cluster 4 (yellow) represents keywords about management of PM, including “pathological myopia”, “age”, “macular degeneration”, “choroidal neovascularization”, “ranibizumab”,“secondary”, “photodynamic therapy”, “verteporfin” and“endothelial growth-factor”[4,94-102].
Cluster 5 (purple) represents keywords related to management of PM complications and treatment. The extracted cooccurrence keywords included “high myopia”, “eyes”,“surgery”, “retinal-detachment (RD)”, “vitrectomy”, “macular hole”, “management”, “posterior staphyloma”, “retinoschisis”and “foveoschisis”[103-109].
Cluster 6 (light blue) represents keywords related to myopiaassociated glaucoma-like optic neuropathy. The extracted co-occurrence keywords included “optical coherence tomography”, “axial length”, “glaucoma”, “thickness”, “openangle glaucoma”, “intraocular-pressure”, “choroidal thickness”,“nerve-fiber layer”, “reproducibility” and “OCT”[110-116].
This bibliometric analysis presented the overview and most influential hotspots of the research structure over the past decade in HM field. This study will expand researchers’understanding of investigation of HM nowadays and can give a direction that future research should concentrate on. However,there are some methodological limitations which may affect our analysis should be considered. Moreover, English was set as language restriction, linguistic bias may exist. Our study only used WoSCC database and didn’t include PubMed, Google Scholar and other search engine. The WoSCC database is updated quickly, and new publications should be included later.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank all reviewers for their valuable comments.
Foundations:Supported by Natural Science Key Research Project of the Education Department of Liaoning Province(No.ZD2020003); Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (No.2019-MS-376).
Conflicts of Interest: Zhang XD,None;Wang CX,None;Jiang HH,None;Jing SL,None;Zhao JY,None;Yu ZY,None.
 International Journal of Ophthalmology2021年4期
International Journal of Ophthalmology2021年4期
- International Journal of Ophthalmology的其它文章
- Prevalence and risk factors of dry eye disease in young and middle-aged office employee: a Xi’an Study
- YM155 inhibits retinal pigment epithelium cell survival through EGFR/MAPK signaling pathway
- Clinical features and treatment outcomes of intraocular lymphoma: a single-center experience in China
- A simple new technique for the induction of residual posterior vitreous cortex removal and membrane peeling
- Differential degeneration of rod/cone bipolar cells during retinal degeneration in Royal College of Surgeons rats
- Bilateral choroidal detachment and exudative retinal detachment following laser peripheral iridotomy in a case of ocular Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada’s disease
