水轮机调节系统非线性模型预测控制器设计
周文军
水轮机调节系统非线性模型预测控制器设计
周文军
(国电大渡河流域水电开发有限公司龚嘴水力发电总厂,四川省 乐山市 614900)
基于麦克劳林展开公式,对水轮机调节系统(hydro-turbine governing system,HTGS)中的非线性项进行近似处理,引入Takagi-Sugeno (TS)模糊控制处理麦克劳林展开式中的非线性项,建立水轮机调节系统的TS模糊模型。基于TS模糊模型以及所定义的目标函数,设计了一种适用于水轮机调节系统的非线性模型预测控制器(nonlinear model predictive controller,NMPC)。考虑到水轮机调节系统的约束问题,引入二次规划(quadratic programming,QP),求解系统约束下的最优控制器输出。通过数值模拟评估所设计的基于二次规划的非线性模型预测控制器(quadratic programming-based nonlinear model predictive controller,QPNMPC)的性能,模拟结果表明:所设计的QPNMPC控制器能够有效地控制水轮机调节系统的输出功率,且相比于传统的PID控制器具有一定的优点。
水轮机调节系统;Takagi-Sugeno模糊控制;模型预测控制;二次规划;系统约束
0 引言
作为一种清洁能源,水电的高效利用对于能源可持续发展具有重要意义。水轮机调节系统(hydro-turbine governing system,HTGS)是水电站的核心组件之一,良好的HTGS控制系统是水电站安全稳定运行的重要保证。目前,HTGS控制系统大多是基于PID控制律而设计的。虽然PID控制算法具有结构简单、易于实现等优点;但是,PID控制算法完全是基于当前的被控对象输出与被控对象输出目标值之差而计算出当前控制输入的,难以适应不同的运行工况。例如,当输出功率目标值大幅变化时,为得到较好的控制效果,一些电厂采用“阶梯式”方法对输出功率目标值进行处理,将输出功率目标值的一次变化转化为若干段“阶梯”形变化,以防止PID控制器计算出较大的控制输入。
为提高HTGS的控制效果,一些研究人员设计出了适应性更强的控制器,并通过数值模拟评估了控制器的性能。例如:Yi等人[1]设计出了一种输出反馈控制器;周建中等人[2]采用引力搜索算法优化PID控制器的参数;Simani等人[3]设计出了一种容错控制系统;桂小阳等人[4]设计出了一种自适应控制器;Wang等人[5]基于线性矩阵不等式设计出了一种鲁棒控制系统;寇攀高等人[6]设计出了一种滑模变结构控制系统;Yuan等人[7]基于反馈线性化方法设计出了一种模糊-滑模控制器,模糊控制系统用于控制器输出的自适应调节,以减小滑模控制系统所固有的高频抖振问题。虽然文献[1-7]中取得了有价值的成果,但是这些控制算法都无法在控制器设计阶段考虑系统约束。实际水电站中,水轮机的运行受到机械限制,因此有必要考虑水轮机调节系统的约束问题。
模型预测控制(model predictive control,MPC)能够在控制器设计阶段考虑系统约束,是一种基于被控对象模型的最优控制算法。系统约束在工业过程中普遍存在,因此MPC在工业控制以及理论探索中得到了广泛关注[8-10]。例如:Wang等人[11-12]设计出了适用于压水堆发电系统的MPC控制器;Sindareh-Esfahani等人[13]基于分段线性模型设计出了一种余热蒸汽发生器MPC控制系统;Kujundžić等人[14]基于MPC算法设计出了一种电池的最优充电策略;Lim等人[15]针对汽车制冷系统设计出了一种MPC控制器。MPC算法通常是基于线性模型[13, 16-18],根据所定义的目标函数,对控制器输出求导,得出最优控制器输出。被控对象建模对于基于被控对象模型而设计的控制器具有至关重要的意义,模型的准确性对控制器的性能具有较大的影响。HTGS具有非线性的特点,本文基于麦克劳林展开公式和TS模糊控制系统处理HTGS的非线性项,建立了HTGS的TS模糊模型。对于非线性被控对象的建模,传统的建模方法通常是采用单个模型描述控制系统;而Takagi-Sugeno (TS)模糊控制系统通常采用多个子系统模型来描述整个被控对象。基于隶属度函数,TS模糊控制系统能够将多个简单的局部子系统结合起来,以描述复杂的被控对象。因此,TS模糊控制系统广泛应用于非线性被控对象的建模[19-21]。
首先,采用文献[1]中的HTGS模型,基于麦克劳林展开公式和TS模糊控制系统,处理HTGS的非线性项,建立了HTGS的TS模型;其次,根据所建立的TS模型和所定义的目标函数,通过求导得出了MPC控制律;最后,考虑HTGS的系统约束,引入二次规划(quadratic programming,QP)求解系统约束下的最优控制器输出。并设计仿真实验与传统的PID控制器进行对比,以验证所设计的基于二次规划的非线性模型预测控制器(quadratic programming-based nonlinear model predictive controller,QPNMPC)的有效性和优点。
1 HTGS模型
基于文献[1],本文引入了HTGS数学模型,基于麦克劳林展开公式,对HTGS数学模型中的非线性项进行近似处理,并引入TS模糊控制系统,处理麦克劳林展开式中的非线性项,得到了HTGS数学模型的TS模糊模型,为计算最优的控制输入,对TS模糊模型进行了扩增处理。
1.1 数学模型
考虑压力引水系统、发电机系统、液压伺服系统和水轮机系统,HTGS数学模型[1]可表示为


1.2 TS模糊模型
TS模糊控制系统通常由IF-THEN规则表 述[21,24]。模糊规则:




基于HTGS数学模型,通过单点模糊化、代数积算子推理和平均加权反模糊化方法,可得到TS全局模型为
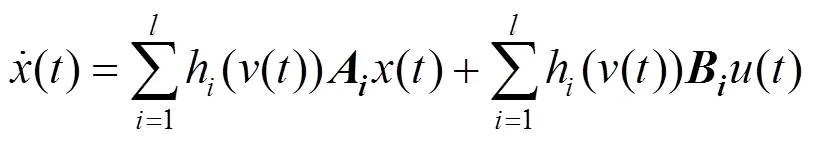






联立式(1)、(2),式(4)、(5)和式(9)、(10),可以得到水轮机调节系统的TS模糊模型为:




式(11)、(12)的离散化形式可以分别表示为:

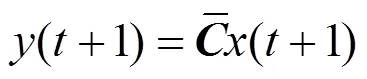


2 控制器设计
基于HTGS的TS模糊模型,设计出了MPC控制器,引入QP,求解系统约束下的最优控制器输出。
2.1 MPC控制系统

定义

可以得到

联立式(17)、(18),得到


式(20)的求解过程见附录A。
2.2 二次规划(QP)
在实际水电站中,水轮机导叶开度的变化和变化率是受限制的,从式(1)中的第4个微分方程可以看出导叶开度与系统输入是相关联的,因而系统输入和系统输入变化率也是受限制的。基于此,本文引入QP,求解系统约束下的最优控制器输出。系统输入的约束考虑为:



联立式(19)和式(23),可以得到

联立式(24)和附录A中的式(A5),可以得到




联立式(26)和式(28),可以得到

基于式(23)和式(29),引入QP,最小化

服从于



3 仿真实验

图1 sind的近似值与真实值
Fig. 1 The approximation and the actual value of sind

图2 h1(d(t))和h2(d(t))的隶属度函数

图3 r1(d(t))和r2(d(t))的隶属度函数

从仿真结果可以看出,当输出功率设定值改变时,PID控制器和所设计的QPNMPC控制器都快速地响应,并且输出功率都能够稳定在设定值。相比于PID控制器,所设计的QPNMPC控制器能够更快地稳定在功率设定值。并且,PID控制器具有较明显的超调,所设计的QPNMPC控制器没有明显的超调。这是因为PID控制器完全独立于被控对象模型,难以适应不同的运行工况。而本文所设计的QPNMPC控制器是基于被控对象模型,并且考虑了HTGS的系统约束而设计的。
图4 相对输出功率
Fig. 4 Relative output power

图5 控制器输出
4 结论
基于麦克劳林展开式,对HTGS的非线性项进行了近似处理;引入TS模糊控制系统,建立HTGS的TS模糊模型;基于所建立的TS模糊模型和所定义的目标函数,求解得出了MPC控制系统的最优控制器输出。最后,考虑HTGS的系统约束,引入QP求解系统约束下的优化问题。
将所设计的QPNMPC控制器与传统的PID控制器进行仿真对比,仿真结果表明:PID控制器和所设计的QPNMPC控制器都能够有效地跟踪功率设定值;相对于PID控制器,所设计的QPNMPC控制器能够更快地稳定在功率设定值,且具有更小的超调。但是,相对于PID控制器,所设计的QPNMPC控制器更加复杂,且计算量更大。总体而言,所设计的QPNMPC控制器能够准确、快速地跟踪功率设定值,没有明显的超调,具有一定的优点。
[1] Yi Y,Chen D,Li H,et al.Observer-based adaptive output feedback fault tolerant control for nonlinear hydro-turbine governing system with state delay[J].Asian Journal of Control,2020,22(1):192-203.
[2] 周建中,赵峰,李超顺.基于GSA的水轮机调速系统非线性PID控制参数优化方法研究[J].水电能源科学,2014,12:127-130.
Zhou J Z,Zhao F,Li C S.Nonlinear PID parameter optimization for hydraulic turbine governing system based on GSA[J].Water Resources and Power,2014,12:127-130.
[3] Simani S,Alvisi S,Venturini M.Fault tolerant control of a simulated hydroelectric system[J].Control Engineering Practice,2016,51:13-25.
[4] 桂小阳,梅生伟,刘锋,等.水轮机调速系统的非线性自适应控制[J].中国电机工程学报,2006,26(8):66-71.
Gui X Y,Mei S W,Liu F,et al.Adaptive nonlinear control for hydraulic turbine governor[J].Proceedings of the CSEE,2006,26(8):66-71.
[5] Wang B,Xue J,Wu F,et al.Robust Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy control for fractional order hydro-turbine governing system[J].ISA Transactions,2016,65:72-80.
[6] 寇攀高,周建中,张孝远,等.基于滑模变结构控制的水轮机调节系统[J].电网技术,2012,36(8):157-162.
Kou P G,Zhou J Z,Zang X Y,et al.An improved hydro-turbine governing system model and design of sliding mode variable structure controller[J].Power System Technology,2012,36(8):157-162.
[7] Yuan X,Chen Z,Yuan Y,et al.Design of fuzzy sliding mode controller for hydraulic turbine regulating system via input state feedback linearization method[J].Energy,2015,93:173-187.
[8] 叶嘉俊,魏焕政,李牧星.交直流混合微电网中双向AC/DC变换器模型预测控制策略[J].广东电力,2017(4):147-152.
Ye J J,Wei H Z,Li M X.Predictive control strategy for bidirectional AC/DC converter in AC/DC hybrid micri-grid[J].Guangdong Electric Power,2017(4):147-152.
[9] 段洁,孙正龙,张秀琦.基于模型预测控制的互联电网阻尼控制[J].广东电力,2016,29(6):78-81.
Duan J,Sun Z L,Zhang X Q.Damping control for interconnected power grid based on model predictive control[J].Guangdong Electric Power,2016,29(6):78-81.
[10] 蔡纯,潘凤萍.1000 MW超超临界机组汽温多模型预测控制研究[J].广东电力,2014,27(5):7-10.
Cai C,Pan F P.Study on multi-model prediction control on steam temperature of 1000 MW ultra-supercritical unit[J].Guangdong Electric Power,2014,27(5):7-10.
[11] Wang G,Wu J,Zeng B,et al.State-space model predictive control method for core power control in pressurized water reactor nuclear power stations[J].Nuclear Engineering & Technology,2017,49(1):134-140.
[12] Wang G,Wu J,Zeng B,et al.Design of a model predictive control method for load tracking in nuclear power plants[J].Progress in Nuclear Energy,2017,101:260-269.
[13] Sindareh-Esfahani P,Tabatabaei S S,Pieper J K.Model predictive control of a heat recovery steam generator during cold start-up operation using piecewise linear models[J].Applied Thermal Engineering,2017,119,516-529.
[14] Kujundžić G,Šandor Ileš,Matuško J,et al.Optimal charging of valve-regulated lead-acid batteries based on model predictive control[J].Applied Energy,2017,187:189-202.
[15] Lim T H,Shin Y,Kim S,et al.Predictive control of car refrigeration cycle with an electric compressor[J].
Applied Thermal Engineering,2017,127:1223-1232.
[16] 王国旭,吴婕,曾碧凡,等.模型预测控制在压水堆堆芯功率控制中的应用[J].原子能科学技术,2018,51:480-484.
Wang G X,Wu J,Zeng B F,et al.Model predictive control method for core power control in pressurized water reactor[J].Atomic Energy Science and Technology,2018,51:480-484.
[17] Klaučo M,Kvasnica M.Control of a Boiler-Turbine Unit Using MPC-based Reference Governors[J].Applied Thermal Engineering,2017,110:1437-1447.
[18] 王国旭,吴婕,陈志杰,等.压水堆负荷跟踪模型预测控制器设计[J].核动力工程,2018,39:46-49.
Wang G X,Wu J,Chen Z J,et al.Design of a model predictive controller for load tracking in pressurized water reactor[J].Nuclear Power Engineering,2018,39:46-49.
[19] Assawinchaichote W,Nguang S K,Shi P,et al.H∞ fuzzy state-feedback control design for nonlinear systems with D-stability constraints:an LMI approach
[J].Mathematics and computers in simulation,2008,78(4):514-531.
[20] Assawinchaichote W,Nguang S K.Fuzzy H∞ output feedback control design for singularly perturbed systems with pole placement constraints:an LMI approach[J].IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems,2006,14(3):361-371.
[21] Nguang S K,Shi P.Fuzzy H∞ output feedback control of nonlinear systems under sampled measurements
[J].Automatica,2003,39(12):2169-2174.
[22] Xu B,Chen D,Zhang H,et al.Modeling and stability analysis of a fractional-order Francis hydro-turbine governing system[J].Chaos Solitons & Fractals,2015,75:50-61.
[23] Zhang R,Chen D,Ma X.Nonlinear predictive control of a hydropower system model[J].Entropy,2015,17(12):6129-6149.
[24] Wang G,Wu J,Zeng B,et al.A nonlinear adaptive sliding mode control strategy for modular high-temperature gas-cooled reactors[J].Progress in Nuclear Energy,2019,113:53-61.
附录A
式(20)的求解过程:





Design of a Nonlinear Model Predictive Controller for a Hydro-turbine Governing System
ZHOU Wenjun
(Gongzui Hydropower Plant, Guodian Dadu River Basin Hydropower Development Co., Ltd, Leshan 614900,Sichuan Province, China)
The nonlinear terms of the hydro-turbine governing system (HTGS) were approximated based on Maclaurin series. Takagi-Sugeno (TS) fuzzy control was introduced to handle the nonlinear terms of the Maclaurin series, and TS models of the HTGS were developed resultantly. Based on the TS fuzzy models and the defined cost function, a nonlinear model predictive control (NMPC) strategy was designed for the HTGS. Considering the constraints of the HTGS, quadratic programming (QP) was utilized to solve the optimal controller output under the system constraints. Simulations were conducted to assess the performance of the designed QP-based NMPC (QPNMPC) controller. Simulation results reveal that the proposed QPNMPC controller can effectively regulate the output power of the HTGS and that compared with the conventional PID controller the advantages of the proposed QPNMPC controller are demonstrated.
hydro-turbine governing system; Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy control; model predictive control; quadratic programming; system constraint
10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.19097
TK 73
2019-06-13。
(责任编辑 杨阳)

