PMSM双闭环平滑非奇异终端滑模控制
王艳敏 牛子铭 买永锋 葛杨

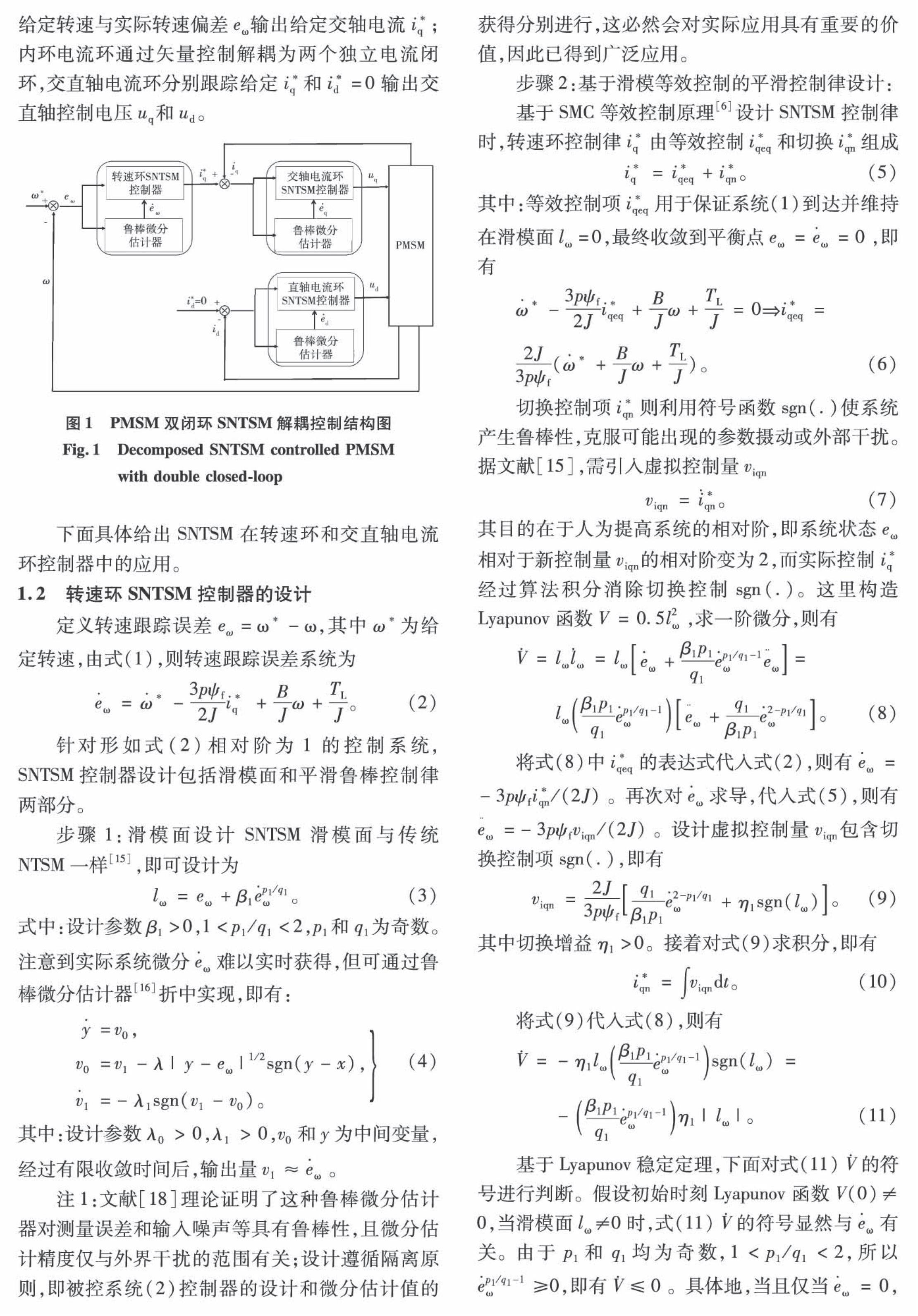

摘 要:针对传统滑模控制中高频切换控制特性不适用于永磁同步电机的双闭环矢量控制的问题,针对PMSM转速控制系统,提出一种基于鲁棒微分估计器的新型平滑非奇异终端SMC方法,理论上可完全克服抖振现象对PMSM的性能影响,提高系统的动静态特性。同时考虑到PMSM控制系统的非线性饱和特性造成的Windup现象,借鉴Antireset Windup PI控制,将转速SNTSM控制器的输入与输出电流之差作为反馈信号,克服Windup现象诱发的超调量、动静态性能变差等影响。基于李雅普诺夫稳定性理论,证明控制器的稳定性。通过仿真和实验验证所提控制方法的可行性和有效性,实现将SMC应用于PMSM的双闭环控制系统中,解决了交轴最大电流限幅造成的Windup问题,响应速度、无超调量、鲁棒性等性能得到优化。
关键词:滑模控制;永磁同步电机;非奇异终端滑模控制;抖振;windup
DOI:10.15938/j.emc.2020.03.017
中图分类号:TM 351文献标志码:A文章编号:1007-449X(2020)03-0138-09
Abstract:The traditional sliding mode control (SMC) is not suitable for the double closedloop vector control of permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSM), due to its highfrequency switching control characteristics. For the speed control system of PMSM, a smooth double closedloop nonsingular terminal sliding mode (SNTSM) control scheme based on a robust differential estimator is proposed. It could realize the freechattering SMC, overcome the influences of chattering problem on PMSM and improve the robustness and the response speed of the system. Focused on the windup phenomenon caused by nonlinear saturation characteristics of PMSM system, the difference between the input current and output current of speed SNTSM controller was taken as a feedback signal, as Antireset Windup PI controller does, to overcome the influence such as overshoot, bad dynamic and static performances. Based on the Lyapunov theorem, the stability of controllers was proved. Simulation and experiment results proved the proposed method.
Keywords:sliding mode control; permanent magnet synchronous motor; nonsingular terminal sliding mode; chattering; windup
0 引 言
永磁同步电机(permanent magnet synchronous motors,PMSM)以其效率高、运行可靠、力能指标好、质量轻、体积小等优点,目前在汽车船舶、风机水泵、医疗器械等领域应用前景广阔[1-2]。然而,PMSM的转速、电流、电压等输入/输出量之间存在复杂的影响关系,尽管利用矢量控制技术可实现PMSM的模型解耦,但是耦合作用不等于简单的干擾,PMSM的内部参数摄动和负载等外部扰动,仍对系统的稳定性及各项动静态性能指标产生严重影响。如何实现强鲁棒性、高性能的PMSM控制策略研究仍具有重要的研究价值[3-5]。
大量文献表明滑模控制(sliding mode control,SMC)以其实现简单、抗干扰能力强等优点而成为一种有效控制非线性系统的手段[6-7]。目前,SMC在PMSM中的应用仍以传统SMC为主,其中应用最为广泛的方法包括线性滑模[6]、终端滑模[8]和非奇异终端滑模(nonsingular terminal sliding mode,NTSM)[9],例如文献[10-11]。一方面,抖振问题[6]严重制约其实际应用。考虑到实际系统硬件电路的实现,理论上无限快的SMC切换控制sgn(.)只能通过有限频率的功率器件实现,进而诱发高频抖振现象,使得实际PMSM控制器输出表现为光滑的理论计算值与有限频率和幅值的锯齿信号的叠加,从而降低系统的动静态性能,造成电机磨损和发热,甚至破坏其稳定性。另一方面,尽管采用诸如滞环调制、积分器/低通滤波等多种措施可以有效抑制高频抖振信号,然而传统的SMC在PMSM的应用多采用诸如“外环PI+内环SMC”的复合形式,难以扩展到双闭环SMC控制。从理论上分析,外环SMC控制器的输出sgn(.)作为输入送到内环,即意味着内环SMC控制器设计时需要对高频切换信号sgn(.)求导,这显然是个难题。
同时,Windup现象也是影响PMSM系统控制性能的一个突出问题。PMSM控制系统包含复杂的非线性饱和特性,例如逆变器的限幅作用等,使得控制器参考输入值和反馈值不相等,进而出现 Windup现象,造成超调量过大,甚至系统失稳的现象。相比于PI控制的AntiWindup方法[12],例如条件作用技术和系统综合法,目前在PMSM滑模控制系统的研究还略显薄弱,但Windup问题依然存在,有必要在SMC控制器设计时进行考虑。

