熵格子Boltzmann方法的重整化群代数湍流模型
刘 强,谢 伟,张再夫,田斌斌,邱辽原
(中国舰船研究设计中心,武汉 430064)
熵格子Boltzmann方法的重整化群代数湍流模型
刘 强,谢 伟,张再夫,田斌斌,邱辽原
(中国舰船研究设计中心,武汉 430064)
重整化群理论所建立的湍流模型能够最大程度地减小模型经验性,因此文章尝试将重整化群代数湍流模型引入到熵格子Boltzmann方法中,建立新型的计算模型以对高雷诺数湍流进行模拟研究。同时为了进行比较研究,还建立了熵格子Boltzmann方法的标准大涡模拟模型。完成了对高雷诺数湍流绕流场的模拟计算。结果表明:所建立的熵格子Boltzmann方法重整化群代数湍流模型能够有效地模拟高雷诺数湍流流动问题;其对紧贴壁面处较小尺度湍涡的模拟结果趋近于大涡模拟的结果;重整化群代数湍流模型在对高雷诺数湍流的模拟中表现出耗散模型的特征。
熵格子Boltzmann方法;重整化群;代数湍流模型;大涡模拟;高雷诺数
0 引 言
格子Boltzmann方法(Lattice Boltzmann Method,简称LBM)可以被认为是气体动理论中Boltzmann方程的一种简化形式的特殊离散格式[1]。Boltzmann方程基于分子处于某一状态的概率计算和统计理论建立,由此决定了LBM本质上是一种介观方法[2-3],其对物质的描述层次介于微团层次和分子层次之间。熵格子Boltzmann方法(Entropic Lattice Boltzmann Method,简称ELBM)是格子Boltzmann方法研究的一个分支,其对LBM的改进有效提高了数值模拟的稳定性。
相比LBM在其他领域所取得的进展,基于LBM的湍流研究并不够充足[3]。到目前为止,使用LBM对湍流流动问题的直接数值模拟仍然受到雷诺数的限制。为了进一步提高湍流模拟的雷诺数,Succi等[4]最早将k-ε湍流模型引入到LBM中。近期受到广泛关注的是基于LBM的亚格子尺度模型研究,包括Premnath等[5]所引入的动态亚格子尺度模型,Dong等[3]所关注的惯性区一致模型,向先亚格子模型[6]及二次内单元模型[7]等。然而至今,尚未见到基于ELBM的重整化群(Renormalization Group,简称RNG)代数湍流模型的相关研究。由于代数湍流模型计算效率高,并且基于重整化群理论的湍流模型系数均由理论推导得来,其可以有效减少模型的经验性,在本研究中尝试将重整化群代数模型理论引入到熵格子Boltzmann方法中,从而建立了ELBM-RNG代数模型,基于此编写了高雷诺数湍流模拟的计算程序。此外,本研究同时编写了基于ELBM的大涡模拟亚格子尺度模型(ELBM-LES)的计算程序,并将两种模型的模拟计算结果进行了比较分析。
1 熵格子Boltzmann方法重整化群代数湍流模型理论
1.1 熵格子Boltzmann方法理论
熵格子Boltzmann方法的通用形式可写为:
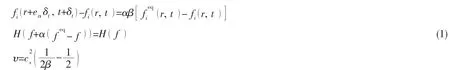
其中:速度分布函数 f是空间位置矢量r( x,y, )z 、分子速度矢量及时间 t的函数,eα表示离散速度模型,δt表示时间间隔表示平衡态分布函数,υ为运动粘度,cs为格子声速,Boltzmann所
定义H函数(H function)的离散形式写为:

其中:ωi为相应权系数。
所选用平衡态分布函数的形式如下式所示:
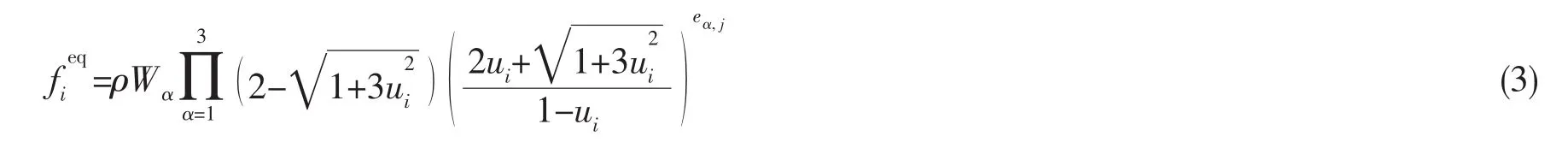
其中:Wα表示权系数。
1.2 重整化群代数湍流模型理论
湍流分析重整化群理论的结果表示为:

其中:ν0为分子动力粘度表示空间维度,ε=4+y-d,参数y用以表征不同的流动情形,对于强非平衡流动y>-2。此处参量ε并非指通常所指代的耗散率,表示网格单元体积内的平均能量耗散率,Sd表示d维空间下单位球体的面积,,λ0表示所求摄动解的阶数(0 阶则 λ0=0),D0=ν0kBT/ρ,kB为 Boltzmann 常数,T 为流体温度,ρ为流体密度,湍流谱空间的截断波数Λ与积分尺度有如下关系:

而惯性区湍流能量:

其中:由重整化群理论得到的Kolmogorov常数Ck的理论值Ck=1.607 5。
因此,在大于截断波数Λ的所有波数范围内对公式(6)进行积分,可得到湍动能的表达式:

在高雷诺数情况下可将重整化的湍流粘度写为:

其中:取重整化群的理论值Cμ=0.084 5。
于是这样就可以将混合长度用惯性尺度表达,将公式(7)代入公式(8)得到:

这样,就可以用混合长度替代截断波数,将公式(4)重写为:

2 数值模拟计算
尝试将重整化群代数湍流模型引入到熵格子Boltzmann方法中,对雷诺数为Re=1.0×106的圆柱绕流场进行了模拟研究。为了进行比较研究,同时建立了基于熵格子Boltzmann方法的大涡模拟标准Smagorinsky亚格子尺度模型,在相同计算网格下对相同的计算模型进行了模拟计算。其中ELBM-LES表示熵格子Boltzmann方法的大涡模拟标准Smagorinsky亚格子尺度模型,ELBM-RNG algebraic表示熵格子Boltzmann方法的重整化群代数湍流模型。

图1 二维圆柱绕流场计算域Fig.1 Computational domain of 2-D flow field around a circular cylinder
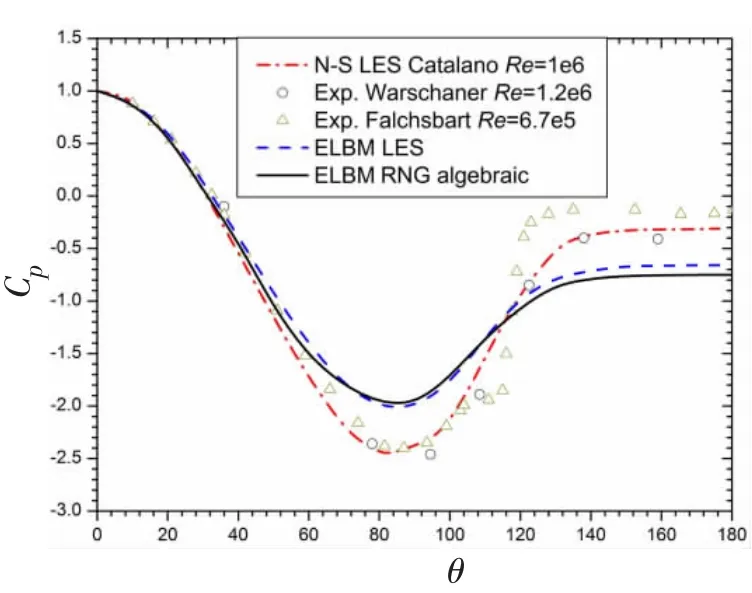
图2 圆柱表面压力系数分布Fig.2 Pressure coefficient distribution on the circular cylinder surface
所建立的计算域形式如图1所示,其中D表示圆柱的直径。为了提高模拟计算的效率和准确性,研究中使用了具有3重网格的多重网格技术,具体可参见文献[8]。离散速度模型使用D2Q9模型,边界条件采用非平衡态外推格式。
圆柱绕流场尾流区位置x/D=0.75处的流向速度分量分布如图3所示,其中x表示流向方向上距圆柱中心的距离,y表示纵向坐标(圆柱中心的纵向坐标参照为0),U0为特征速度的大小。图4所示为尾流区位置x/D=1.5处的流向速度分量分布。
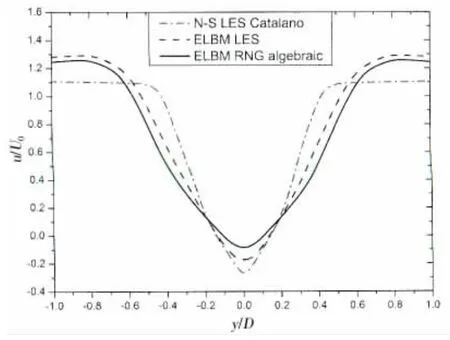
图3 x/D=0.75处的时间平均流向速度分量分布 Fig.3 Time-averaged flow direction velocity component distribution at x/D=0.75

图4 x/D=1.5处的时间平均流向速度分量分布Fig.4 Time-averaged flow direction velocity component distribution at x/D=1.5
模拟计算得到圆柱绕流场内的流线分布、涡量分布及大尺度应变率张量大小的分布如图5-7所示。
可见,模拟计算所得到的圆柱表面压力系数及湍流绕流场速度分布与实验数据或已有的数值结果具有一致性,参见图2-4,所建立的熵格子Boltzmann方法重整化群代数湍流模型及大涡模拟亚格子尺度模型能够有效进行高雷诺数湍流的数值模拟。对比两个模型,尽管结果相近熵格子Boltzmann方法的大涡模拟计算表现略优于重整化群代数模型。
此外参见图5,两个模型对湍流绕流场内反向对称交替脱落卡门涡街的产生和演化过程也进行了有效的模拟预报。同时注意到,熵格子Boltzmann方法大涡模拟计算对紧贴壁面处较小尺度湍涡的模拟结果仍更加有效,然而重整化群代数湍流模型的结果已经趋于接近大涡模拟的结果,参见图5-6。
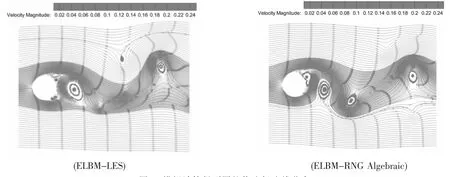
图5 模拟计算得到圆柱绕流场流线分布Fig.5 Streamline distribution calculated in the flow field around a circular cylinder
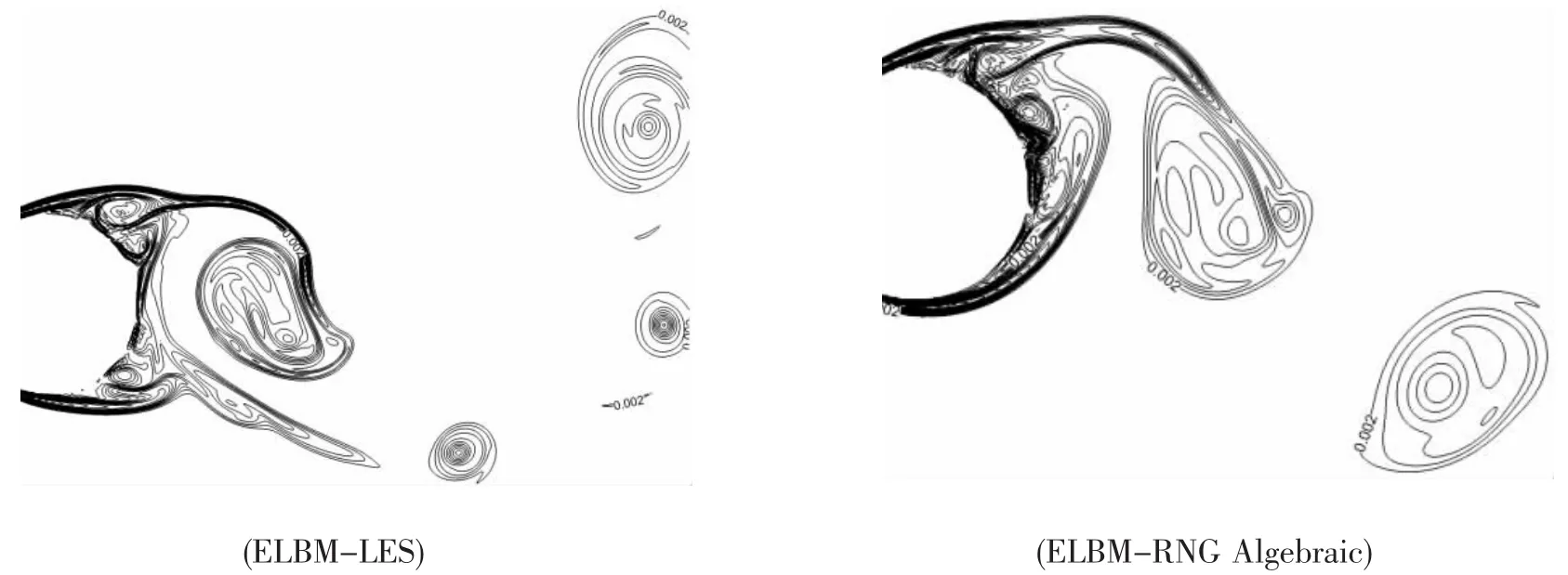
图6 模拟计算得到圆柱绕流场涡量分布Fig.6 Vorticity distribution calculated in the flow field around a circular cylinder
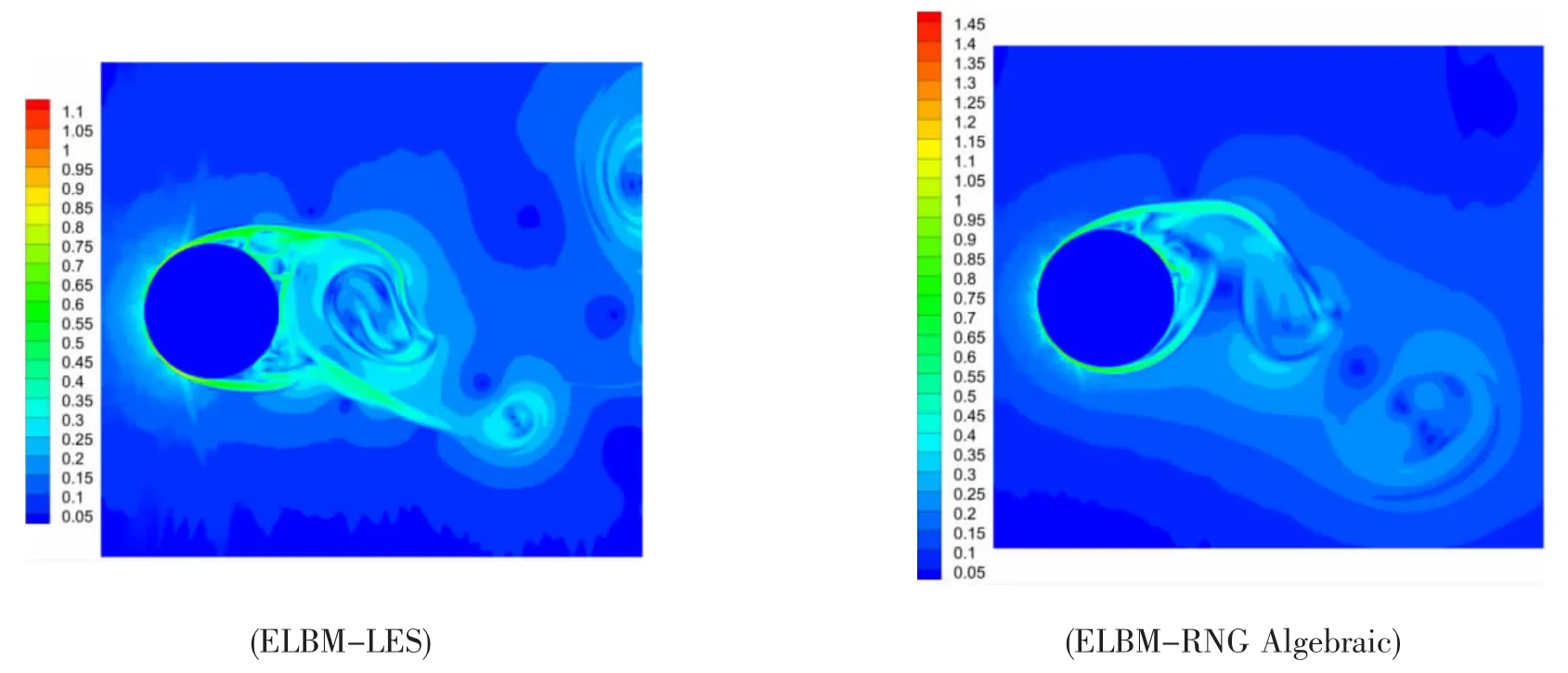
图7 模拟计算得到圆柱绕流场大尺度应变率张量大小分布Fig.7 Magnitude of large scale strain rate tensor distribution calculated in the flow field around a circular cylinder
由图7所示模拟计算得到高雷诺数湍流绕流场内应变率张量大小的分布可知,两个模型的结果能够基本表现出一致性。较大值的应变率张量均首先出现在圆柱壁面附近,随后跟随涡的交替向后脱落而值逐渐减小。说明熵格子Boltzmann方法的重整化群代数湍流模型体现了一定的耗散模型特征。
3 结 论
在基于H定理完成对LBM的改进后,ELBM成为一种稳定的数值格式,由此ELBM具有了模拟高雷诺数湍流的潜在能力。另一方面,建立在重整化群理论上的湍流模型最大程度地减小了模型经验性。本研究中尝试将重整化群代数湍流模型引入ELBM中,建立了高雷诺数湍流模拟的ELBM-RNG Algebric模型。为了进行比较研究,同时建立了ELBM-LES模型。编写了两个模型模拟计算高雷诺数圆柱绕流场的计算机程序。得到结论如下:
(1)所建立的熵格子Boltzmann方法重整化群代数湍流模型及大涡模拟亚格子尺度模型能够有效地模拟高雷诺数的湍流流动。
(2)熵格子Boltzmann方法的大涡模拟模型对流场压力及速度等宏观量的计算结果略优于熵格子Boltzmann方法重整化群代数模型的结果,重整化群代数湍流模型也表现出了较好的计算准确性。
(3)熵格子Boltzmann方法重整化群代数模型能够模拟尾迹区及壁面附近大尺度及较大尺度高雷诺数湍涡的形成和演化过程。对于紧贴壁面处较小尺度湍涡的形成和演化,其模拟结果与熵格子Boltzmann方法的大涡模拟结果也趋于接近。
(4)尽管重整化群代数湍流模型属于代数模型,然而在对高雷诺数湍流的模拟中表现出耗散模型的特征。
[1]He X,Luo L S.Theory of the lattice Boltzmann method:From the Boltzmann equation to the lattice Boltzmann equation[J].Physical Review E,1997,56:6811-6817.
[2]Huo Y,Rao Z.The numerical investigation of nanofluid based cylinder battery thermal management using lattice Boltzmann method[J].International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2015,91:374-384.
[3]Dong Y H,Sagaut P,Marie S.Inertial consistent subgrid model for large-eddy simulation based on the lattice Boltzmann method[J].Physics of Fluids,2008,20:035104.
[4]Succi S,Amati G,Benzi R.Challenges in lattice Boltzmann computing[J].J Stat.Phys.,1995,81:5-16.
[5]Premnath K N,Pattison M J,Banerjee S.Dynamic subgrid scale modeling of turbulent flows using lattice-Boltzmann method[J].Physica A,2009,388:2640-2658.
[6]Sagaut P.Toward advanced subgrid models for lattice-Boltzmann-based large-eddy simulation:Theoretical formulations[J].Computersamp;Mathematics with Applications,2010,59(7):2194-2199.
[7]Baker C M J,Buchan A G,Pain C C,et al.Quadratic inner element subgrid scale discretization of the Boltzmann transport equation[J].Annals of Nuclear Energy,2012,45:124-137.
[8]Stiebler M,Krafczyk M,Freudiger S,et al.Lattice Boltzmann large eddy simulation of subcritical flows around a sphere on non-uniform grids[J].Computersamp;Mathematics with Applications,2011,61(12):3475-3484.
[9]Catalano P,Wang M,Iaccarino G,et al.Numerical simulation of the flow around a circular cylinder at high Reynolds numbers[J].International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow,2003,24:463-469.
[10]Warschauer K A,Leene J A.Experiments on mean and fluctuating pressures of circular cylinders at cross flow at very high Reynolds number[C]//In:Proc.Int.Conf.on Wind Effects on Buildings and Structures.Tokyo,Japan,1971:305-315.
[11]Zdravkovich M M.Flow around circular cylinders[M].Oxford:Oxford University Press,1997.
Renormalization group algebraic turbulence model in entropic lattice Boltzmann method
LIU Qiang,XIE Wei,ZHANG Zai-fu,TIAN Bin-bin,QIU Liao-yuan
(China Ship Development and Design Center,Wuhan 430064,China)
The renormalization group theory can furthest reduce the empirical value in turbulence models.A renormalization group algebraic turbulence model was introduced to the entropic lattice Boltzmann method,in order to establish a new model for high Reynolds number turbulent flow simulations.Meanwhile,with the view of comparative study,the standard large eddy simulation model in entropic lattice Boltzmann method was also established.Numerical simulations for the high Reynolds number turbulence were carried out.The results show that the renormalization group algebraic turbulence model established in entropic lattice Boltzmann method can effectively simulate high Reynolds number turbulent flows;as for the simulation of minor scale turbulent eddies,its results approach those of the LES model;the renormalization group algebraic turbulence model performs dissipation model features in the simulation of high Reynolds number turbulence.
entropic lattice Boltzmann method;renormalization group;algebraic turbulence model;large eddy simulation;high Reynolds number
O351.2
A
10.3969/j.issn.1007-7294.2017.11.001
1007-7294(2017)11-1317-06
2017-05-25
国家自然科学基金项目(51079032)
刘 强(1990-),男,博士,工程师,E-mail:liuqiang7012012@126.com;
谢 伟(1969-),男,研究员。

