碰撞诱导解离和高能碰撞解离方式在褐藻胶寡糖结构分析中的比较和应用
宋 妮,张秀丽,王 聪,吕志华,任素梅
(中国海洋大学医药学院,海洋药物教育部重点实验室,山东 青岛 266003)
碰撞诱导解离和高能碰撞解离方式在褐藻胶寡糖结构分析中的比较和应用
宋 妮,张秀丽,王 聪,吕志华,任素梅
(中国海洋大学医药学院,海洋药物教育部重点实验室,山东 青岛 266003)
利用组合式高分辨质谱仪(LTQ Orbitrap XL)对均一褐藻胶寡糖,包括甘露糖醛酸寡糖和古洛糖醛酸寡糖进行二级质谱分析,比较了常规的碰撞诱导解离(CID)和高能碰撞解离(HCD)在寡糖结构分析中的差异,并应用HCD技术分析甘露糖醛酸寡糖和古洛糖醛酸寡糖的结构差异。研究发现,HCD可避免CID中的1/3效应,而且可以提供更多的糖环断裂碎片信息,如2,5A2(m/z291)、2,4A(m/z235、411)、2,5A脱水(m/z101、277、453)以及Z2脱羧碎片(m/z307、483、659)等,进一步验证了Z2脱羧碎片是区别甘露糖醛酸与古洛糖醛酸的特征碎片。同时,HCD能够提供丰富的裂解碎片信息,这为褐藻胶寡糖的结构解析提供了依据。
组合式高分辨质谱仪(LTQ Orbitrap XL);褐藻胶寡糖;碰撞诱导解离(CID);高能碰撞解离(HCD)
Abstract: Alginate homooligosaccharides including oligomannuronate (M) and oligoguluronate (G) with degree of polymerization from 2 to 7 were analyzed by linear ion trap-Orbitrap mass spectrometer (LTQ Orbitrap XL) using collision induced dissociation (CID) and high energy collision induced dissociation (HCD). First of all, comparison of CID MS/MS and HCD MS/MS of either M or G was conducted. Taking the trimannuronate (M3) as an example, CID MS/MS showed them/z369, 193 and 175 ions were assigned to C2/Y2, C1/Y1and B1/Z1, respectively, which were formed due to single glycosidic bond cleavage, while HCD MS/MS caused cleavage of all glycosidic bonds and showed weak A-type ions, such as0,2A (m/z309, 485),2,5A (m/z291, 467) and0,4A3ions (m/z471). Interestingly, an internal M produced a Zint-CO2ions atm/z307, which was unique and found only in HCD MS/MS. Furthermore, CID MS/MS and HCD MS/MS of M3 and triguluronate (G3) were executed. For CID, M3 and G3 did not show significant difference, and they gave identical glycosidic bond cleavage ions C1(m/z193), B1(m/z175) together with the dehydrated and decarboxylated ions (m/z157 andm/z131). These results suggest that it is impossible to differentiate the two residues at a nonreducing terminal of M3 and G3 by CID. However, a significant difference was observed in HCD spectra for M3 and G3. It was found that besides decarboxylation fragmentm/z307, debris2,4A3(m/z411),2,5A3(m/z467) and0,4A3(m/z471) were found in M3, whereas these ions were not found in HCD MS/MS of G3, thus demonstrating that HCD MS/MS can be used to differentiate M3 and G3. In the CID MS/MS of pentamannuronate (M5), fragment ions0,2A3(m/z837),0,4A3(m/z823) and2,5A3(m/z819) was found apparently, however, HCD displayed rich fragment ions in the low mass region, which should be ascribed to the characteristics of high-energy dissociation of HCD. For heptamannuronate (M7) and heptaguluronate (G7), doubly charged protonated species were collected as parent ions for CID and HCD. HCD MS/MS provided more fragment ions than CID MS/MS, especially, Zint-CO2ion (m/z307, 483, 659, 835 and 1 011) signal was apparently showed in M7 HCD spectra. Taken together, this work demonstrates that HCD MS/MS provides rich product ions and has no low mass cut off. The fragment ions in HCD spectra have high mass accuracy and resolution. These characteristics of HCD spectra complement the power of CID and allow easy spectrametric interpretation and high confidence in structural elucidation for alginate oligosaccharides.
Keywords: linear ion trap-Orbitrap mass spectrometer (LTQ Orbitrap XL); alginate homooligosaccharides; collision induced dissociation (CID); high energy collision induced dissociation (HCD)
褐藻胶是一种直链的多糖类化合物,结构单元是β-(1→4)连接的D-甘露糖醛酸(M)和α-(1→4)连接的L-古洛糖醛酸(G),其在人类疾病、植物生长和抑菌等方面具有生物活性。褐藻酸及其寡糖的活性和应用与褐藻酸中甘露糖醛酸和古洛糖醛酸的比例以及位置有着密切的关系[1-2]。近年来,电喷雾离子化-碰撞诱导解离-串联质谱(ESI-CID-MS/MS)技术促进了寡糖结构及其序列分析的发展[3-8]。如,张真庆等[9]利用Q-TOF质谱仪的CID技术对褐藻酸中甘露糖醛酸和古洛糖醛酸的异构体进行了MS/MS序列分析。
高能碰撞解离(HCD)是一项新型的质谱裂解技术,与传统的碰撞诱导解离(CID)相比,HCD能够提供稳定的高能裂解模式,可以改善CID裂解中产生的低质量碎片丢失(1/3 cut-off)效应。因此,将HCD应用到寡糖序列分析中,利用其高能特点可以提供不同断裂位点的糖链碎片;另外,因其与Orbitrap相连能够提供高精度的质量数(<3×10-6),可以直接给出元素组成,这更有助于寡糖碎片的结构分析[10-14]。
本研究将利用HCD对均一结构的褐藻胶寡糖,包括甘露糖醛酸寡糖和古洛糖醛酸寡糖进行二级质谱分析,并与传统的CID方式的结果进行比较,探索两种不同的碎裂方式在褐藻寡糖结构分析中的差异,以扩展高分辨质谱仪LTQ Orbitrap XL的高能碰撞解离模式在褐藻寡糖结构分析中的应用。
1 实验部分
1.1 仪器和试剂
LTQ-Orbitrap XL线性离子阱静电场轨道阱高分辨组合式质谱仪:美国Thermo Fisher公司产品。寡糖标准品:由中国海洋大学医药学院赵峡课题组提供,溶于50%乙腈水溶液中;乙腈(色谱纯):美国Honeywell公司产品;实验用水:Milli-Q制备的超纯水。
1.2 质谱条件
电喷雾离子源(ESI),喷雾电压3 kV,离子传输毛细管温度275 ℃;干燥气为氮气,压力0.05 MPa;CID和HCD碰撞气均为氦气,负离子模式检测;CID归一化碰撞能量采用15%~25%,HCD碰撞能量采用45~60 eV。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 甘露糖醛酸及古洛糖醛酸二糖、三糖的二级质谱解析
分析了较复杂的褐藻胶三糖——甘露糖醛酸三糖和古洛糖醛酸三糖,其二级质谱解析示于图1[10]。甘露糖醛酸三糖的分子离子峰为m/z545,糖苷键断裂产生m/z369、193和175碎片离子,分别记做 C2/Y2、C1/Y1和B1/Z1,它们是源于还原端和非还原端的离子碎片,是吡喃糖醛酸三糖的特征碎片离子。
本研究还分析了甘露糖醛酸三糖CID和HCD谱图的差异,其二级质谱采集信息示于图2。将产生跨环断裂碎片的区域放大10倍后,CID MS/MS给出了所有的糖苷键断裂碎片C2/Y2(m/z369)、B2/Z2(m/z351)、C1/Y1(m/z193)和 B1/Z1(m/z175)。糖环断裂仅显示了0,2A(m/z309和m/z485),而HCD MS/MS除了给出糖苷键断裂碎片外,还给出了所有的A型碎片离子,如0,2A(m/z309和m/z485)、2,5A(m/z291和m/z467)、0,4A3(m/z471)和2,4A(m/z235和m/z411),以及甘露糖醛酸三糖区别于古洛糖醛酸三糖特殊的Zint脱羧碎片m/z307[10],其中2,4A(m/z235和m/z411)是首次被检测到。
对比甘露糖醛酸三糖和古洛糖醛酸三糖的CID和HCD谱图的主要对照特征峰和峰高可以发现,两种寡糖的CID谱图没有明显差异,所有差异均显示在HCD谱图中。除Z2脱羧碎片m/z307外,在古洛糖醛酸三糖的HCD中未见碎片2,4A3(m/z411)、2,5A3(m/z467)和0,4A3(m/z471),这可作为区别两种寡糖的特殊碎片。
通过比较甘露糖醛酸二糖和古洛糖醛酸二糖的CID和HCD二级质谱图发现,同一二糖的CID和HCD之间无明显差异。这是因为在二糖中没有中间糖环,在原三糖HCD谱中发现的脱羧碎片也就不存在了。
2.2 甘露糖醛酸和古洛糖醛酸四、五糖的二级质谱解析
从实验数据可以看出,四糖和五糖具有相同的结果,本研究以甘露糖醛酸五糖和古洛糖醛酸五糖为例进行解析,结果示于图3。甘露糖醛酸五糖和古洛糖醛酸五糖的CID和HCD谱图示于图4。通过比较甘露糖醛酸五糖的CID和HCD谱图可以发现:HCD二级质谱图给出了通过糖苷键断裂产生的所有表征它们直链连接方式的碎片离子m/z175/193、m/z351/369、m/z527/545和m/z703/721;而在CID谱图中,因1/3效应缺失了m/z175/193。但是,在CID谱图中可见跨环断裂产生的碎片离子0,2A5(m/z837)、0,4A5(m/z823)和2,5A5(m/z819),而在HCD谱图中未见这3个特征峰。与三糖相同,甘露糖醛酸区别于古洛糖醛酸残基的Z离子脱羧碎片Zint-CO2(m/z307和m/z483)仅出现在HCD谱图中。还可以看到,HCD在低质荷比端提供了大量的碎片离子,弥补了CID的1/3效应,HCD谱比CID谱在低质荷比区域的信号和峰度高,CID谱则反之,这是由于HCD高能裂解的特点。

图1 甘露糖醛酸三糖(a)和古洛糖醛酸三糖(b)的二级质谱解析Fig.1 MS/MS analysis of trimannuronate (a) and triguluronate (b)

图2 甘露糖醛酸三糖和古洛糖醛酸三糖的CID(a, c)和HCD(b, d)谱图Fig.2 CID (a, c) and HCD (b, d) MS/MS spectrum of trimannuronate and triguluronate

图3 甘露糖醛酸五糖(a)和古洛糖醛酸五糖(b)的质谱解析Fig.3 MS/MS analysis of pentamannuronate (a) and pentaguluronate (b)

图4 甘露糖醛酸五糖和古洛糖醛酸五糖的CID(a,c)谱和HCD(b,d)谱Fig.4 CID (a, c) and HCD (b, d) MS/MS spectrum of pentamannuronate and pentaguluronate
比较甘露糖醛酸五糖和古洛糖醛酸五糖的CID以及HCD差异,发现与三糖的解析结果有相同的规律,M5和G5的CID谱图没有明显差异,M5的HCD谱图较G5仅多了Zint-CO2(m/z307和m/z483),进一步验证了Zint-CO2碎片离子是区别甘露糖醛酸寡糖与古洛糖醛酸寡糖的重要标志。通过比较发现,需要将CID和HCD结合起来才能得到五糖完整的解析信息。聚合度为2~5的两种类型寡糖的CID MS/MS和HCD MS/MS详细二级碎片信息列于表1。
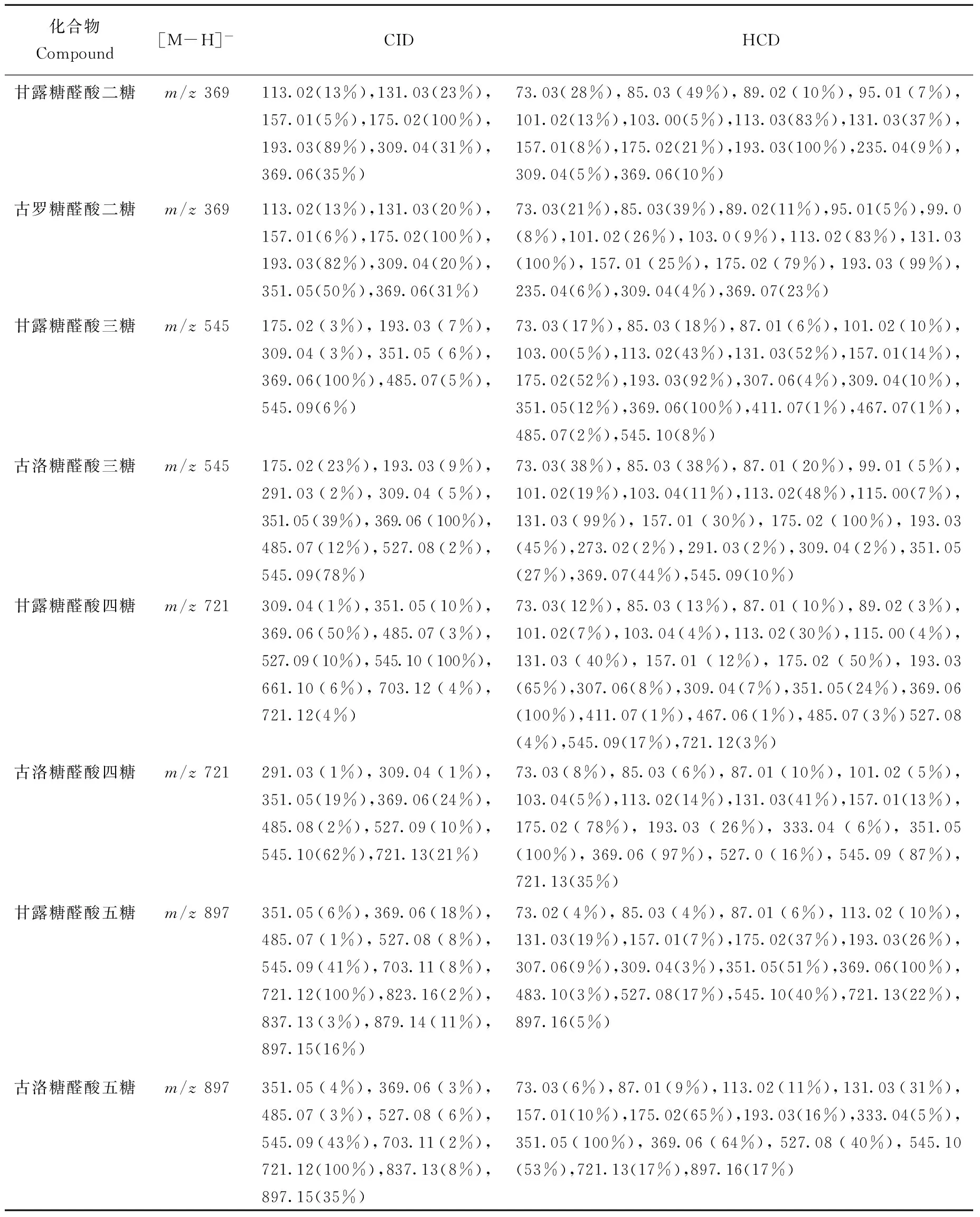
表1 8种寡糖在CID和HCD方式下的质谱碎片峰比较Table 1 Comparison of CID and HCD for 8 oligosaccharides
2.3 高聚合度甘露糖醛酸及古洛糖醛酸的二级质谱解析
对于聚合度高于5的寡糖,二级质谱采集选择双电荷或三电荷离子作为母离子。本研究以七糖为例进行解析,甘露糖醛酸七糖和古洛糖醛酸七糖的CID和HCD谱图示于图5。M7选择m/z624双电荷离子作为母离子,从图中可以看出,HCD谱给出的信息远多于CID谱,在糖苷键断裂的碎片中有丰富的糖环断裂碎片,尤其是Zint-CO2离子(m/z307、483、659、835、1 011)的信号在M7的HCD谱中很明显,但是在G7的HCD谱中未见,因此可以很容易地区分这两种寡糖。对于高聚合度的寡糖,HCD的优势明显高于CID。
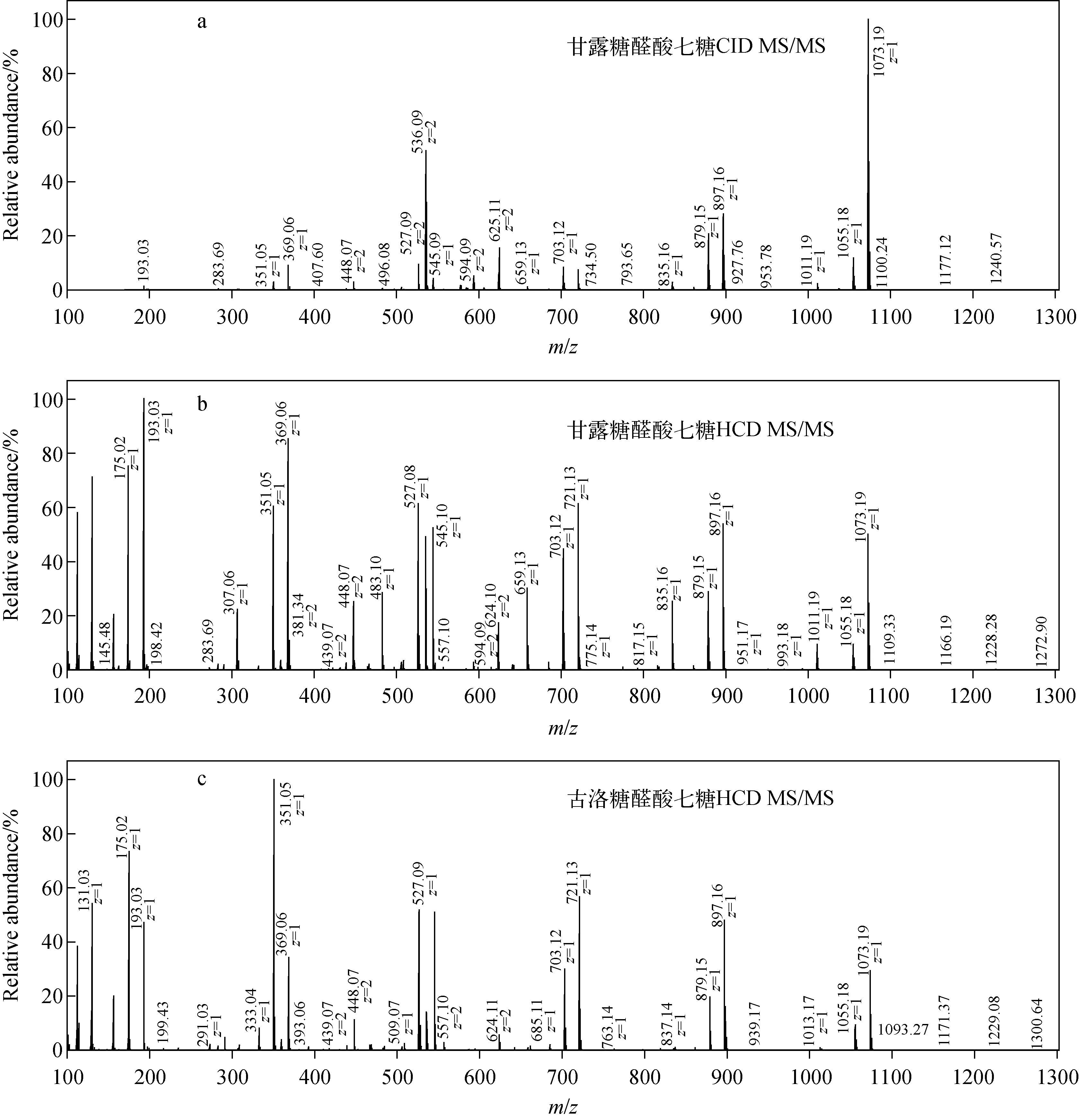
图5 甘露糖醛酸七糖和古洛糖醛酸七糖的CID谱和HCD谱Fig.5 CID and HCD MS/MS of heptamannuronate and heptaguluronate
3 结论
通过分析褐藻胶寡糖的HCD和CID二级质谱数据发现:对于聚合度较低的寡糖,HCD较CID能够给出更多的糖环断裂碎片和低质荷比碎片等信息,这是寡糖结构解析的关键;对于聚合度为4和5的寡糖,在高质荷比区域的CID信息较HCD信息更为丰富,因此需要综合两种裂解模式提供的信息进行解析;对于聚合度高于5的寡糖,HCD提供的信息远远多于CID模式。从数据分析发现,HCD通过检测Zint-CO2离子可以清晰地判断寡糖类型。对于褐藻胶寡糖的二级质谱分析,将HCD高能裂解的特点应用到寡糖结构解析,可以提供更多的糖环断裂碎片与高质量精度和高灵敏度的二级质谱数据,并且避免了CID技术中低质荷比数据缺失,有助于褐藻胶寡糖的结构解析。
[1] LIU Y, JIANG X L, LIAO W, et al. Analysis of oligoguluronic acids with NMR electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry and high-performance anion-exchange chromatography[J]. J Chromatogr A, 2002, 968(1/2): 71-78.
[2] HEYRAUD A, COLIN-MOREL P, GIROND S, et al. HPLC analysis of saturated or unsaturated oligoguluronates and oligomannuronates. Application to the determination of the action pattern ofHaliotistuberculataalginate lyase[J]. Carbohydr Res, 1996, 291(38): 115-126.
[3] CONBOY J J, HENION J D. The determination of glycopeptides by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry with collision-induced dissociation[J]. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom, 1992, 3(8): 804-814.
[4] YU G L, ZHAO X, YANG B, et al. Sequence determination of sulfated carrageenan-derived oligosaccharides by high-sensitivity negative-ion electrospray tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Anal Chem, 2006, 78(24): 8 499-8 505.
[5] YANG B, YU G L, ZHAO X, et al. Mechanism of mild acid hydrolysis of galactan polysaccharides with highly ordered disaccharide repeats leading to a complete series of exclusively odd-numbered oligosaccharides[J]. The FEBS Journal, 2009, 276(7): 2 125-2 137.
[6] ZHANG Y, FICARRO S B, LI S J, et al. Optimized orbitrap HCD for quantitative analysis of phosphopeptides[J]. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom, 2009, 20(8): 1 425-1 434.
[7] WU S, SALCEDO J, TANG N, et al. Employment of tandem mass spectrometry for the accurate and specific identification of oligosaccharide structures[J]. Anal Chem, 2012, 84(17): 7 456-7 462.
[8] ZHANG H T, ZHANG S, TAO G J, et al. Typing of blood-group antigens on neutral oligosaccharides by negative-ion electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Anal Chem, 2013, 85(12): 5 940-5 949.
[9] ZHANG Z Q, YU G L, ZHAO X, et al. Sequence analysis of alginate-derived oligosaccharides by negative-ion electrospray tandem mass spectrometry[J]. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom, 2006, 17(4): 621-630.
[10] RICHARD H, PERRY R, COOKS G, et al. Orbitrap mass spectrometry: instrumentation, ion motion and applications[J]. Mass Spectrom Rev, 2008, 27(6): 661-699.
[11] VALLVERDU-QUERALT A, JAUREGUI O, MEDINA-REMON A, et al. Improved characterization of tomato polyphenols using liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization linear ion trap quadrupole Orbitrap mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom, 2010, 24(20): 2 986-2 992.
[12] TCHOUMYCHOUA J, NJAMEN D, MBANYA J C, et al. Structure-oriented UHPLC-LTQ orbitrap-based approach as a dereplication strategy for the identification of isoflavonoids from Amphimas pterocarpoides crude extract[J]. J Mass Spectrom, 2013, 48(5): 561-575.
[13] CHARANDEEP S, CLEIDIANE G Z, ANDREW J C, et al. Higher energy collision dissociation (HCD) product ion-triggered electron transfer dissociation (ETD) mass spectrometry for the analysis ofN-Linked Glycoproteins[J]. J Proteome Res, 2012, 11(9): 4 517-4 525.
[14] O’BRIEN J P, BRODBELT J S. Structural characterization of gangliosides and glycolipids via ultraviolet photodissociation mass spectrometry[J]. Anal Chem, 2013, 85(21): 10 399-10 407.
Comparison and Application of Collision Induced Dissociation and High Energy Collision Induced Dissociation for Alginate Oligosaccharides Analysis
SONG Ni, ZHANG Xiu-li, WANG Cong, LV Zhi-hua, REN Su-mei
(KeyLaboratoryofMarineDrugs,SchoolofMedicineandPharmacy,OceanUniversityofChina,Qingdao266003,China)
O657.63
A
1004-2997(2017)05-0551-08
10.7538/zpxb.youxian.2016.0063
2016-06-16;
2016-08-23
中央高校基本科研业务费实验室基金项目(201551012)资助
宋 妮(1975—),女(汉族),山东青岛人,工程师,从事有机质谱分析研究。E-mail: nisong1975@ouc.edu.cn
任素梅(1963—),女(汉族),山东青岛人,教授级高级工程师,从事有机质谱分析研究。E-mail: rensumei@ouc.edu.cn
时间:2016-12-28;网络出版地址:http:∥www.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2979.TH.20161228.0935.020.html

