单次扫描检测大表面痕量赖氨酸和黑索今的质谱分析方法
李 毅,朱腾高,王国凤,陈焕文
(东华理工大学,江西省质谱科学与仪器重点实验室,江西 南昌 330013)
单次扫描检测大表面痕量赖氨酸和黑索今的质谱分析方法
李 毅,朱腾高,王国凤,陈焕文
(东华理工大学,江西省质谱科学与仪器重点实验室,江西 南昌 330013)
为了进一步提高大表面样品的分析速度,减少给定样品表面的扫描次数,建立了一种单次扫描即可检测分布于大表面样品上任意位置痕量待测物的质谱分析方法。以人造革表面(4 cm×4 cm)添加的赖氨酸和黑索今为代表性检测对象,用一块无毛刺等边三角形金属铜电极(边长为8.6 cm)紧贴在样品表面,将甲醇-水(3∶7,V/V)电离试剂涂洒在金属电极表面,让其与样品表面保持湿润接触,并使三角形电极尖端对准质谱仪的离子入口;然后在金属电极上施加+5.8 kV高压,在电场的驱动下,湿润表面的待测物朝着质谱入口移动,并在三角形电极尖端形成待测物离子进入质谱仪检测。结果表明,该方法可单次扫描检测随机分布在皮革样品表面上任意位置的非均匀分布的赖氨酸和黑索今,检测限可达6.2×10-7μg/cm2,分析单个样品表面的时间不到2 s;与采用电喷雾解吸电离质谱等顺次扫描检测(采样面积不到1 mm2)的方法相比,本方法的分析速度提高了1 000倍。
单次扫描;大表面样品;非均匀分布;常压质谱;赖氨酸;黑索今
Abstract: Ambient ionization mass spectrometry has significantly improved the efficiency of analysis complex matrix sample due to its high sensitivity, selectivity and throughput. At present, direct ionization sources coupled with mass spectrometer including desorption electrospray ionization (DESI), real time online (DART), matrix assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI), laser ablation electrospray ionization (LAESI), desorption atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (DAPCI), extractive electrospray ionization (EESI) etc. are applied for the direct ionization targeting molecular followed by mass spectrometer characterization. A famous ionization technique namely DESI is the most representative ambient source, which can ionization the polar compounds with bulk solid surface focused on a large number of studies on the detection methods of explosives. However, DESI in the ionization of solid explosives is needed continuous scanning and a single sampling area can not exceeding 1 cm2, resulting in time-consuming and inaccurate enough results. In order to further improve the analysis rate of the large surface sample and decrease the number of scanning for a given sample surface, a novel mass spectrometry method with a single scan was established for detecting trace substance distributed in large sample surface of any position. Using artificial leather surface (length of a side: 4 cm×4 cm) added lysine and royal demolition explosive (RDX) as representative detection object, the triangular metal copper electrode (length of a side: 8.6 cm) which was applied the ionization regent with methanol-water (3∶7,V/V) was closed to the sample surface, making the tip of the triangle metal copper electrode on the mass spectrometer entrance. The trace substance form into ions in triangle electrode tip towards mass spectrometry when applying +5.8 kV high voltage on the metal copper electrode. This experimental results show that the novel method with a single scan can detect randomly and non-uniform distributed on the surface of the leather sample of lysine and/or RDX at any position, providing the speed for a single sample analysis within 2 s, the limit of detection (LOD) of 6.2×10-7μg/cm2. compared with analyzing speeding on desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (single sampling area less than 1 cm2), the analyzing speed of the established method is 1 000 times than DESI. Overall, this method can provide a promising analytical tool for advanced studies on monitoring of trace explosive, the identification of the food quality and the products in the import and export trade, and the pharmacokinetics of drug metabolism in vivo.
Keywords: single scan; large surface sample; non-uniform distribution; atmospheric pressure mass spectrometry; lysine; royal demolition explosive (RDX)
直接质谱分析技术能够提高分析效率,拓展应用领域,是质谱学研究的前沿和热点[1]。目前,常见的直接离子化技术,如电喷雾解吸电离(DESI)[2-4]、实时在线分析(DART)[5-7]、基质辅助激光解吸电离(MALDI)[8-9]、激光消融电喷雾电离(LAESI)[10]、电喷雾辅助激光解吸电离(ELDI)[11]、表面解吸常压化学电离(DAPCI)[12-14]和电喷雾萃取电离(EESI)[15-17]等越来越多地应用于复杂基体样品的直接分析,这些方法具有样品预处理简单、消耗量少、响应速度快、灵敏度高等特点。在诸多的直接离子化技术中,Cooks教授发明的DESI是该领域最具代表性的方法,其优点是能够直接检测块状固体表面的极性物质,在爆炸物检测方面有大量的研究报道。然而,DESI在检测固体表面分布不均的爆炸物时,需要多次连续地扫描固体表面的多个位点,且单次采样面积不大于1 cm2,检测范围有限,对整个样品进行分析不仅耗时长,还可能存在漏检、检测结果不够准确的情况。
本研究拟建立一种单次扫描即可检测分布于大表面样品上任意位置痕量待测物的质谱分析方法,单次扫描检测随机分布在皮革样品表面任意位置非均匀分布的赖氨酸和黑索今。希望该方法能够解决其他常压电离技术单次检测面积小、漏检、检测效率较低等问题,同时为行李包上痕量爆炸物的监测、食品的品质鉴定、进出口贸易中商品的鉴定等提供新的研究思路。
1 实验部分
1.1 主要仪器与装置
LTQ-XL型线性离子阱质谱仪:美国Finnigan公司产品,配有Xcalibur2.0数据处理系统。
1.2 主要材料与试剂
赖氨酸标准品:上海蓝季科技发展有限公司产品;黑索今(RDX):由公安部第三研究所提供;甲醇(色谱纯):美国Tedia公司产品;超纯水(电阻率18.2 MΩ·cm):美国Thermo Scientific公司产品。
1.3 实验方法
设置LTQ-MS正离子检测模式,放电电压+5.8 kV,离子传输管温度200 ℃,质量扫描范围m/z50~400。单次扫描金属电极离子源装置示于图1。离子的选择窗口为1.0 u,碰撞能量为13%~25%,其他参数由LTQ-MS系统自动优化得到,实验过程无需对任何样品进行预处理,以人造革表面(4 cm×4 cm)添加的赖氨酸和黑索今为代表性检测对象,将一块无毛刺等边三角形金属铜电极(边长为8.6 cm)紧贴在赖氨酸或黑索今表面,将甲醇-水(3∶7,V/V)电离试剂涂洒在金属电极表面,让其与样品表面保持湿润接触,并使三角形电极尖端对准质谱仪离子入口,然后在金属电极上施加+5.8 kV高压。在电场的驱动下,使样品表面的待测物朝着质谱入口移动,形成待测物离子进入质谱仪检测。所得质谱数据扣除背景后导出,质荷比精确到整数位。

图1 实验装置原理示意图Fig.1 Schematic diagrams of the metal electrode ion source
2 结果与讨论
2.1 人造革表面痕量赖氨酸和黑索今的常压金属电极-质谱分析
检测以黑索今为代表的痕量爆炸物对保障国土安全具有重要意义。黑索今不但影响人类的中枢神经系统,还显示出对肾、胃肠的毒性,被视为具有一定的致癌性,是重要的工业污染物之一[18-21]。赖氨酸是控制人体生长的抑长素中的重要成分,对人的中枢神经和周围的神经系统起着重要的调节作用;如果缺乏赖氨酸,会造成胃液分泌不足而出现厌食、营养性贫血,致使中枢神经受阻、发育不良[22-26]。本研究以人造革表面(4 cm×4 cm)添加的黑索今和赖氨酸为代表性检测对象,按1.3节方法对其进行直接质谱分析,实验结果示于图2。在正离子检测模式下可形成质子化准分子离子[M+H]+,质子化黑索今和赖氨酸的准分子离子信号峰分别为m/z233和m/z147。

注:a.RDX(m/z 223)一级质谱图,插图为MS/MS图;b.Lys(m/z 147)一级质谱图,插图为MS/MS图图2 正离子模式下,金属电极-质谱检测人造革表面RDX和Lys的串联质谱图 Fig.2 Metal electrode-mass spectrometry of leather surface of RDX and Lys samples in positive ion mode
为了排除假阳性,对黑索今m/z223进行串联质谱分析,得到m/z209、207、195和177碎片离子。其中,碎片离子m/z209比m/z223少了14 u,推测为中性丢失一分子CH2;m/z207比m/z223少了16 u,推测为中性丢失一分子O;m/z177比m/z223少了46 u,推测为中性丢失一分子NO2;m/z149比m/z223少了74 u,推测为失去CH2+N+NO2。该结果与胡燕等[18]报道的一致。
本实验进一步研究了赖氨酸在碰撞诱导解离(CID)中的裂解规律,选择质子化的赖氨酸m/z147进行多级串联质谱分析。在二级质谱中,母离子m/z147主要产生m/z129和m/z101碎片离子,以及响应较弱的m/z130、119和105碎片离子。其中,m/z129比m/z147少了18 u,推测是由于电荷诱导羧基中C—O单键发生断裂,中性丢失一分子H2O形成的;m/z101比m/z129少了28 u,推测为分子内重排后中性丢失一分子CO形成的。由实验原理可知,单次扫描大表面金属电极-质谱法能使待测物与溶剂形成溶剂化分子,在电场作用下形成极化团簇,待测物在电场及电渗流的作用下朝着质谱入口移动,在质谱入口形成离子进行检测,极大地提高了不均匀大表面单个样品的分析速度。单次扫描大表面金属电极-质谱法能够对人造革表面(4 cm×4 cm)的黑索今和赖氨酸进行定性分析,检测限可达6.2×10-7~6.2×10-3μg/cm2,分析单个样品表面的时间不到2 s,同时可对黑索今和赖氨酸的结构进行鉴定。
2.2 条件优化
为了获得稳定的信号和较好的重现性,本实验对电极的材质、电极尖端的角度、电压和人造革表面湿润情况进行了优化,并选取赖氨酸的二级碎片离子m/z101作为研究对象。不同电极材质与信号强度的关系示于图3a,可见,当电极材料为铜金属时,m/z101信号强度高,这可能是因为铜电极的导电性优于锌电极和铝电极。图3b显示,电极尖端的角度为60°时,信号强度最佳,这可能是由于施加在等边三角形电极的高压在等边三角形表面产生的梯度电场能够使待测物朝着电极尖端移动,极大地提高了目标化合物的质子化效率。图3c显示,施加电压为5~5.8 kV时,m/z101信号强度逐渐增大,当电压大于5.8 kV时,信号强度反而下降,这是由于在电压大于5.8 kV时,铜金属电极尖端容易放电。图3d表明,当人造革表面涂撒250 μL电离试剂时,m/z101信号强度最佳,其他参数由系统自动优化。

a.不同金属材质;b.施加电压;c.电极尖端角度;d.电离试剂体积图3 金属电极-质谱法对赖氨酸检测的工作参数优化 Fig.3 Optimization working parameters of metal electrode-mass spectrometry for Lys detection
2.3 金属电极-质谱法与DESI-MS法检测RDX和Lys的结果对比
将待测物RDX和Lys均匀或非均匀的涂撒在人造革表面,分别以串联质谱中m/z207、101为特征离子,采用单次扫描大表面金属电极-质谱法和DESI-MS法检测RDX和Lys。对比结果可知,本方法比DESI-MS法的分析速度提高了52 倍,其特征离子强度、检测时间和RSD列于表1。
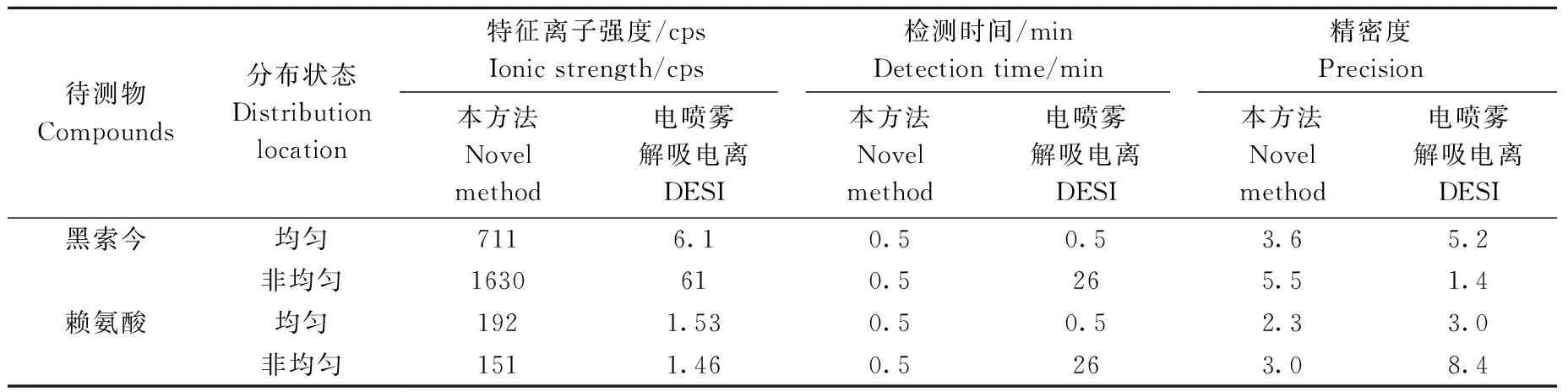
表1 本方法与DESI-MS法检测黑索今和赖氨酸的结果对比Table 1 Comparison of novel method and DESI-MS for detecting RDX and Lys
3 结论
本研究建立了一种单次扫描即可检测分布于大表面样品上任意位置痕量黑索今和赖氨酸的质谱分析方法。该方法无需对任何样品进行预处理,每个样品在30 s时内即可完成质谱分析,分析速度快,可检测样品表面均匀、非均匀分布的待测物,获得的二级离子信号强度和检测效率均优于DESI法。
[1] 陈焕文,张华,王海东,等. 常压下能量与电荷在分子间的传递机制[J]. 中国科学:化学,2014,44(5):789-794.
CHEN Huanwen, ZHANG Hua, WANG Haidong, et al. The molecular view of energy and charge transfer among the ambient molecules[J]. Science China, 2014, 44(5): 789-794(in Chinese).
[2] OETJEN J, VESELKOV K, WATROUS J, et al. Benchmark datasets for 3D MALDI-and DESI-imaging mass spectrometry[J]. Gigascience, 2015, 4(1): 1-8.
[3] DONG Y, GUELLA G, MATTIVI F, et al. High production of small organic dicarboxylate dianions by DESI and ESI[J]. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry, 2015, 26(3): 386-389.
[4] ZHANG T, ZHOU W, JIN W, et al. Direct detection of aromatic amines and observation of intermediates of Schiff-base reactions by reactive desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrom-etry[J]. Microchemical Journal, 2013, 108(108): 18-23.
[5] KIM H J, SEO Y T, PARK S I, et al. DART-TOF-MS based metabolomics study for the discrimination analysis of geographical origin of Angelica gigas roots collected from Korea and China[J]. Metabolomics, 2015, 11(1): 64-70.
[6] AVULA B, SMILLIE T J, WANG Y H, et al. Authentication of true cinnamon (Cinnamonverum) utilising direct analysis in real time (DART)-QToF-MS[J]. Food Additives & Contaminants: Part A, 2015, 32(1): 1-8.
[7] XU B, ZHANG D Y, LIU Z Y, et al. Rapid determination of 1-deoxynojirimycin inMorusalbaL. leaves by direct analysis in real time (DART) mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 2015, 114: 447-454.
[8] HANDBERG E, CHINGIN K, WANG N, et al. Mass spectrometry imaging for visualizing organic analytes in food[J]. Mass Spectrometry Reviews, 2015, 34(6): 641-658.
[9] YSSOUF A, ALMERAS L, TERRAS J, et al. Detection of rickettsia spp in ticks by MALDI-TOF MS[J]. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 2015, 9(2): 1-16.
[10] SHRESTHA B, SRIPADI P, RESCHKE B R, et al. Subcellular metabolite and lipid analysis of Xenopus laevis eggs by LAESI mass spectrometry[J]. PloS One, 2014, 9(12): e115173.
[11] 夏树华,王璋. 反相高效液相色谱/基质辅助激光解吸电离飞行时间质谱分离鉴定螺蛳血管紧张素转换酶抑制肽[J]. 色谱,2007,25(1):58-65.
XIA Shuhua, WANG Zhang. Purification and identification of a novel ACE inhibitory peptide derived from the mud snail bellamya purification by RP-HPLC/MALDI-TOF MS[J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 2007, 25(1): 58-65(in Chinese).
[12] HUANG X Y, GUO X L, LUO H L, et al. Fast differential analysis of propolis using surface desorption atmospheric pressure chemical ionization mass spectrometry[J]. International Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 2 015(9/10): 1-9.
[13] ZHU L, YAN J, ZHU Z, et al. Differential analysis of camphor wood products by desorption atmospheric pressure chemical ionization mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2013, 61(3): 547-552.
[14] COTTE-RODRGUEZ I, TAKTS Z, TALATY N, et al. Desorption electrospray ionization of explosives on ssurfaces: sensitivity and selectivity enhancement by reactive desorption electrospray ionization[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2005, 77(21): 6 755-6 764.
[15] LUO M, HU B, ZHANG X, et al. Extractive electrospray ionization mass spectrometry for sensitive detection of uranyl species in natural water samples[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2010, 82(1): 282-289.
[16] DING J, YANG S, LIANG D, et al. Development of extractive electrospray ionization ion trap mass spectrometry for in vivo breath analysis[J]. Analyst, 2009, 134(10): 2 040-2 050.
[17] LI M, HU B, LI J, et al. Extractive electrospray ionization mass spectrometry toward in situ analysis without sample pretreatment[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2009, 81(18): 7 724-7 731.
[18] 胡燕,陈焕文,花榕,等. 电喷雾解吸电离质谱法检测多种物质表面黑索今[J]. 理化检验-化学分册,2009,45(5):504-507.
HU Yan, CHEN Huanwen, HUA Rong, et al. MS rapid detection of RDX on the surface of various materials with desorption elextrospray ionization[J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis Part B, 2009, 45(5): 504-507(in Chinese).
[19] ACHUTHAN C, MULLICK G. Hazards in the Manufacture of RDX and HMX[J]. Defence Science Journal, 2014, 33(1): 91-95.
[20] KAPLAN A S, BERGHOUT C F, PECZENIK A. Human intoxication from RDX[J]. Archives of Environmental Health: An International Journal, 1965, 10(6): 877-883.
[21] ETNIER E L. Water quality criteria for hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine (RDX)[J]. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology, 1989, 9(2): 147-157.
[22] LEE M, BAEK I, CHOI H, et al. Effects of lysine residues on structural characteristics and stability of tau proteins[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2015, 466(3): 486-492.
[23] WANG S, LV Q, YANG Y, et al. Cellular target recognition of perfluoroalkyl acids: in vitro evaluation of inhibitory effects on lysine decarboxylase[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 496(1): 381-388.
[24] 许柠,朱志强,杨水平,等. 新型电喷雾萃取电离质谱法快速标靶分析氨基酸[J]. 分析化学,2013,41(4):523-528.
XU Ning, ZHU Zhiqiang, YANG Shuiping, et al. Direct detection of amino acids using extractive electrospray ionization tandem mass spec-trometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 41(4): 523-528(in Chinese).
[25] 许国旺. 代谢组学及其研究进展[J]. 色谱,2003,21(4):316-320.
XU Guowang. Metabonomics and its research progress[J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 2003, 21(4): 316-320(in Chinese).
[26] CHACE D H, KALAS T A. A biochemical perspective on the use of tandem mass spectrometry for newborn screening and clinical testing[J]. Clinical Biochemistry, 2005, 38(4): 296-309.
Mass Spectrometric Detection of Lysine and Royal Demolition Explosive on Large Surfaces
LI Yi, ZHU Teng-gao, WANG Guo-feng, CHEN Huan-wen
(JiangxiKeyLaboratoryforMassSpectrometryandInstrumentation,EastChinaInstituteofTechnology,Nanchang330013,China)
O657.63
A
1004-2997(2017)05-0515-06
10.7538/zpxb.youxian.2016.0067
2016-07-04;
2016-09-23
国家自然科学基金(21520102007);长江学者和创新团队发展计划项目(IRT13054);江西省科技计划项目(20152ACB21021)资助
李 毅(1988—),男(汉族),江西九江人,硕士研究生,从事质谱技术的应用研究。E-mail: liyi_jiujiang@sina.com
陈焕文(1973—),男(汉族),江西兴国人,教授,从事质谱分析研究。E-mail: chw8868@gmail.com
时间:2016-12-28;网络出版地址:http:∥www.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2979.TH.20161228.0937.028.html

