介电弹性体材料致动器的非线性动态行为研究*
盛俊杰 李树勇 张玉庆 陈花铃
(1.中国工程物理研究院总体工程研究所, 绵阳 621900) (2.西安交通大学机械工程学院, 西安 710049)(3.西安交通大学机械结构强度与振动国家重点实验室, 西安 710049)
介电弹性体材料致动器的非线性动态行为研究*
盛俊杰1†李树勇1张玉庆1陈花铃2,3
(1.中国工程物理研究院总体工程研究所, 绵阳 621900) (2.西安交通大学机械工程学院, 西安 710049)(3.西安交通大学机械结构强度与振动国家重点实验室, 西安 710049)
介电弹性体材料(Dielectric Elastomer,简称DE),是制造柔性智能致动器最有潜力的电活性聚合物(Electroactive polymer,缩写EAP)材料之一,可在电压驱动下产生大幅度的厚度与面积变形,最大面积应变高达1600%.由于DE材料的固有阻尼特性,从而使其变形具有时间依赖性,因此动态变形中,其能量转换、宏观变形等特性也必然受到阻尼的影响.借助热力学自由能理论,考虑DE材料致动器面内动态变形过程中的惯性力和阻尼力,构建平面DE材料致动器的非线性动力学模型.研究了交变电载荷下DE系统的非线性动态特性,包括其幅频曲线、位移响应和相平面图.研究表明,存在阻尼的时候,DE系统的振动会随着时间的增加出现锁频现象,最后变成一种具有恒定振幅的振动.相平面图和Poincaré映射图研究表明,考虑阻尼后DE系统的稳态相平面图是一条闭合的曲线,其Poincaré映射点集是有限的,代表其产生周期性运动.研究成果为DE材料致动器在各种动态驱动器或传感器中的应用提供理论依据.
介电弹性体材料, 动态, 阻尼, 相平面, Poincaré映射
引言
介电弹性材料(Dielectric Elastomer,简称DE)是一种新型的智能电活性聚合物(Electroactive Polymer,简称EAP).相比于其他EAP材料,DE材料独有的特点是变形大,最大面积应变高达1600%[1],且弹性模量低,机电耦合效率高,工作温度范围宽和频率范围广(0.1~20KHz).DE致动器指的是在DE材料上下表面涂有柔性电极的三明治结构,在电极上施加电压后,DE材料上产生的Maxwell电场力和电致伸缩电应力的共同作用挤压材料,结果使其面积增大,厚度减小,并逐渐成为近几年国内外的研究热点之一[2-4].近年来,研究学者设计出很多种基于DE材料的致动器和换能器结构,并尝试将DE应用于智能机器人[5]、微机电系统[6]、扬声器[7]和能量回收[8-9]等领域.
在理论建模研究中,最具代表性的研究当属Harvard大学的Suo[10]小组,他们基于热力学的自由能理论,构建了一套非线性本构方程,从而能够从理论角度分析DE材料的力电耦合过程以及失稳产生的临界条件.由于该理论物理意义明确,扩展性好,在国内外得到了广泛的应用和推广,基于该理论的研究也层出不穷,如:UT Austin大学的Huang[11]研究了力电耦合下的相变问题;Harvard大学的Bertoldi[12]研究了多层DE材料中的不稳定性的传播问题;新加坡A-star研究中心的Koh[13]等人研究了预拉伸下的稳定性机理问题;奥地利Johannes Kepler大学的Bauer[14]等人研究了变形失稳的能量转换效率问题;哈尔滨工业大学的刘立武[15]应用两个材料常数的Mooney-Rivlin弹性应变能函数,分析了介电弹性体稳定性行为,盛俊杰[16]在自由能模型基础上研究了温度对介电弹性体材料力电耦合变形的影响等.
在工程实际应用中,对DE材料施加的载荷常常是周期性的电压或者应力,如微泵结构、各种运动驱动器、能量循环收集器等等[4].然而现有研究对DE材料在交变载荷下的动力学变形行为以及力电耦合特性尚没有得到足够的重视.近两年来,学者们才开始对DE材料动态特性进行研究.哈佛大学的Zhu从热动力学出发,通过扰动方法分别研究了DE气球[17]的非线性振动特性;兰州大学的Yong等人[18]建立了一套DE动态分析模型,研究了厚球壳的稳定性;浙江大学的Li[19]研究了纯剪切共振器的力电耦合性能及其动态性能;Federal University of Goiás的Soares等[20]利用打靶法对预拉伸后的超弹性平面薄膜的动态方程进行了求解,并与有限元求解方法进行了对比;最近TU Darmstadt的Xu[21]利用朗格朗日方程得到了平面DE的动态运动方程,并研究了动态载荷下的位移响应和稳定性,但是没有考虑预应力的影响;西安交通大学的Li[22]研究了DE材料共振器在纯剪切工作模式下的动态性能;西安交通大学的zhang[23]利用欧拉拉格朗日方法研究了三种外力边界条件下DE致动器的动态性能.
研究发现阻尼是DE材料的固有特性[24],可以用来减振.最近两年虽然一些研究机构开始关注DE材料的动态性能,但是却忽略了阻尼等的影响,几乎没有学者研究经典的DE材料平面变形的振动特性,不能全面反映DE材料的动态力电耦合特征.由于平面致动结构是DE致动器的最常用结构,通过热力学自由能理论,在考虑DE材料致动器面内动态变形过程中的惯性力和阻尼力的基础上,构建平面DE材料致动器的非线性动力学模型.基于所建立的模型,研究了交变电载荷下DE系统的非线性动态特性.
1 DE致动器的动态运动方程
在静力学问题的研究中,DE材料的变形与时间无关,问题相对简单;在动力学问题研究中,DE材料的运动将会随时间的变化而变化,由于需要考虑其惯性力及阻尼力的作用,且由于DE材料的变形是典型的力电耦合作用下的变形,属于典型的非线性问题.
通过自由能方法[17,19]来建立DE材料致动器的面内振动模型能够为DE材料面内应用提供理论指导.本文主要研究的是如图1所示的DE材料致动器的面内变形动态性能,认为DE材料是一种理想的电介质,其变形λ1=l1/L1,λ2=l2/L2和λ3=l3/L3是时间的函数.

图1 平面DE致动器的振动示意图Fig. 1 Vibration schematics of an in-plane dielectric elastomer actuator
由于研究的是在平衡位置附近的小幅振动特性,忽略变形及温度对极化率的影响.这种理想的DE材料的介电性能与聚合物熔融体一样,其真实电位移D和真实电场强度E的关系可以表示为D=εE(ε是DE材料的介电常数,典型代表值为ε=4×10-11F/m[10,25]),那么可以得到DE致动器的电荷量和电压的关系为:
(1)
在时间t时刻,当有少量的电荷流过DE材料的两侧电极的时候,电压做功为ΦδQ,当DE的尺寸发生微小的δλ1和δλ2变化时,外力做的功分别为P1L1δλ1和P2L2δλ2.此时,x和y方向上微小单元的惯性力分别为ρL2L3x2(d2λ1/dt2)和ρL1L3y2(d2λ2/dt2)[19],阻尼力分别为cxdλ1/dt和cydλ2/dt.分别对微小单元上δλ1dx和δλ2dy的惯性力和阻尼力在x和y方向进行积分,可求得惯性力和阻尼力所做的功.在任意热力学系统中,自由能的改变量等于外力、电压、惯性力和阻尼力所做功的总和,即:
L1L2L3δW=ΦδQ+P1L1δλ1+P2L2δλ2-

(2)
DE致动器的自由能包括弹性应变能和静电能.应变能仍用Gent模型描述[26],那么DE的自由能为:

(3)
式中Jm为DE材料的变形极限,Jm=100[26-28];μ是DE材料的剪切模量,μ=1×106N/m2[10,25].
假设DE材料致动器的初始尺寸相等L1=L2=L,由于我们主要研究的是等双轴的变形,令λ1=λ2=λ,P1/(L2L3)=P2/(L1L3)=s,对式(1)~(3)求解进行化简后就得到了DE材料致动器的非线性动力学方程:
(4)


(5)
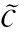
2 考虑阻尼时致动器的动态特性
以正弦电压作为激励电压,即
Φ(t)=Φdc+Φacsin(Ωt)
(6)
式中Φdc为直流电压,单位:V;Φac为交流电压幅值,单位:V;Ω为正弦电压的频率,单位:rad/s.
把公式(6)代入方程(4)中,化简后得到
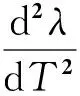
(7)

图2 阻尼对DE致动器幅频特性的影响Fig. 2 Effect of different damping on amplitude-frequency characteristic for DE actuator
虽然有阻尼的时候,DE致动器系统的非线性振动包含着阻尼引起的衰减振动,但由于在其振动的过程中一直存在的外加交变电压的力电耦合效果,其中电能和变形能会抵消振动过程中的能量耗散,随着时间的增加,其最后会达到一个恒定振幅的振动状态.如图3中的变形响应曲线所示,这种非线性振动出现了锁频现象,表明承受着周期性的阻尼振动,这和相关文献报道类似[21-23].
图4给出了阻尼为0.05时,DE系统响应的相平面图(a、b、c)和Poincaré映射图(d、e、f).图4(a)是激励频率为1.62时的相平面图,此时稳态的相平面图上形成闭合的曲线,代表着周期性的运动[29],这同样反映在其Poincaré映射图4(d)上,其点集是有限的,存在着周期吸引子.频率为3.24和0.82的时候,也出现了类似的情况.表明此条件下DE致动器在固有频率、2倍固有频率和二分之一固有频率下的振动均是周期振动.

图3 阻尼为0.05时DE致动器在三种激励频率下的振动响应Fig. 3 Vibration response of DE actuator system for three excitation frequencies with a dimensionless damping effect of 0.05
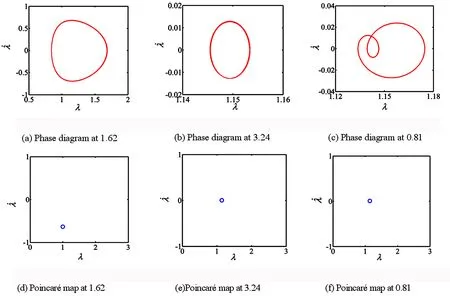
图4 阻尼为0.05时DE致动器的相平面图和Poincaré映射图Fig. 4 Phase diagrams and poincaré of DE actuator system with a dimensionless damping effect of 0.05
3 结论
通过热动力学方程,考虑了惯性力和阻尼力的共同作用,建立了DE致动器非线性力电耦合系统的动态行为方程.研究发现,存在阻尼的时候,DE系统的振动会随着时间的增加出现锁频现象,最后变成一种具有恒定振幅的振动.这是因为尽管存在着阻尼的耗能作用,但是由于DE致动器的振动是由外加交变电场产生的Maxwell应力引起的,静电能和变形能补偿了阻尼的能耗,这种力电耦合效果最后使得DE系统变成具有恒定振幅的振动.相平面图和Poincaré映射图研究表明,考虑阻尼后DE系统的稳态相平面图是一条闭合的曲线,其Poincaré映射点集是有限的,代表其产生周期性运动.
通过对平面运动DE致动器系统非线性动态力电耦合性能的研究,可以预测DE材料在动态载荷下的非线性动态变形规律,能为DE材料在各种动态驱动器或传感器中的应用提供理论依据.
1 Keplinger C, Li T, Baumgartner R, et al. Harnessing snap-through instability in soft dielectrics to achieve giant voltage-triggered deformation.SoftMatter, 2011,8(2):285~288
2 Pelrine R, Kornbluh R, Pei Q, Joseph J. High-speed electrically actuated elastomers with strain greater than 100%.Science, 2000,287(5454):836~839
3 Carpi F, Rossi D. D, Kornbluh R, Pelrine R, Sommer-Lasen P. Dielectric Elastomers as Electromechanical Transducers. Amsterdam: Elsevier Press, 2008
4 Brochu P, Pei Q. Advances in dielectric elastomers for actuators and artificial muscle.MacromolecularRapidCommunication, 2010,31(1):10~36
5 Pei Q, Rosenthal M, Stanford S, Prahlad H and Pelrin R. Multiple-degrees-of-freedom electroelastomer roll actuators.SmartMaterialsandStructures, 2004,13(5): N86
6 Kovacs G, Düring L, Michel S, and Terrasi G. Stacked dielectric elastomer actuator for tensile force transmission.SensorsandActuatorsA:Physical, 2009,155(2):299~307.
7 Keplinger C, Sun J Y, Foo C C, Rothemund P, Whitesides G M, and Suo Z. Stretchable, Transparent, Ionic Conductors.Science, 2013,341(6149): 984~987.
8 Huang J, Shian S, Suo Z. and Clarke D R. Maximizing the energy density of dielectric elastomer generators using equi-biaxial loading.AdvancedFunctionalMaterials, 2013,23(40):5056~5061
9 陈宝鸿,周进雄. 离子导体驱动的介电弹性体软机器研究进展. 固体力学学报, 2015,36(6):481~492 (Chen B H, Zhou J X. Dielectric elastomers based soft machines actuated by ionic conductors: progress and perspectives.ChineseJournalofSolidMechanics, 2015,36(6):481~492 (in Chinese))
10 Suo Z. Theory of dielectric elastomer.ActaMechanicaSolidaSinica, 2010,23(6):549~578
11 Huang R, Suo Z G. Electromechanical phase transition of dielectric elastomer.ProceedingsoftheRoyalSocietyAMathematicalPhysical&EngineeringSciences, 2012,468(2140):1014~1040
12 Bertoldi K, Gei M. Instability in multilayered soft dielectircs.JournaloftheMechanics&PhysicsofSolids, 2011,59(1):18~42
13 Koh SJA, Li T F, Zhou J X, et al. Mechanisms of large actuation strain in dielectric elastomer.JournalofPolymerSciencePartBPolymerPhysics, 2011,49(7):504~515
14 Kaltseis R, Keplinger C, Baumgartner R, et al. Method for measuring energy generation and efficiency of dielectric elastomer generators.AppliedPhysicsLetters, 2011,99(16):162904.
15 盛俊杰,张玉庆,李树勇,刘磊,陈花玲. 温度对介电弹性体材料力电耦合变形的影响. 固体力学学报, 2015,36(2):129~136 (Sheng J J, Zhang Y Q, Li S Y, Liu L, Chen H L. Effect of temperature on the electromechanical deformation of dielectric elastomer.ChineseJournalofSolidMechanics, 2015,36(2):129~136 (in Chinese))
16 刘立武,孙寿华,刘彦菊,冷劲松. 具有线性介电常数的Ogden型介电弹性体的本构关系和机电稳定性. 固体力学学报, 2010,31(2):181~192 (Liu L W, Sun S H, Liu Y J, Leng J S. Constibutive relation electromechanical stability analysis of Ogden type dielectirc elastomer with linear permittivity.ChineseJournalofSolidMechanics, 2010,31(2):181~192 (in Chinese))
17 Zhu J, Cai S, Suo Z. Nonlinear oscillation of a dielectric elastomer balloon.PolymerInternational, 2010,59(3):378~383
18 Yong H, He X, Zhou Y. Dynamics of a thick-walled dielectric elastomer spherical shell.InternationalJournalofEngineeringScience, 2011,49(8):792~800
19 Li T, Qu S, Yang W. Electromechanical and dynamic analyses of tunable dielectric elastomer resonator.InternationalJournalofSolidsandStructures, 2012,49(26):3754~3761
20 Soares R M, Gonc-alves P B. Nonlinear vibrations and instabilities of a stretched hyperelastic annular membrane.InternationalJournalofSolidsandStructures, 2012,49(3-4):514~526
21 Xu B, Mueller R, Theis A, Klassen M, Gross D. Dynamic analysis of dielectric elastomer actuators.AppliedPhysicsLetters, 2012,100(11):112903
22 Li B, Zhang J, Liu L, Chen H, Jia S, and Li D. Modeling of dielectric elastomer as electromechanical resonator.JournalofAppliedPhysics, 2014,116(12):124509
23 Zhang J S, Tang L L, Li B, Wang Y J, Chen H L. Modeling of the dynamic characteristic of viscoelastic dielectric elastomer actuators subject to different conditions of mechanical load.JournalofAppliedPhysics, 2015,117(8):084902
24 Wolf K, Röglin T, Haase F, Finnberg T, Steinhoff B. An electroactive polymer based concept for vibration reduction via adaptive supports. Proc SPIE, 2008, 6927: 69271F
25 Zhao X, Suo Z. Method to analyze electromechanical stability of dielectric elastomers.AppliedPhysicsLetters, 2007,91(6):061921-061921-3
26 Sheng J, Chen H, Li B, Wang Y. Nonlinear dynamic characteristics of a dielectric elastomer membrane undergoing in-plane deformation.SmartMaterialsandStructures, 2014,23(4):045010
27 Foo C C, Cai S, Koh S J A, et al. Model of dissipative dielectric elastomers.JournalofAppliedPhysics, 2012,111(3):034102-13
28 Sheng J, Chen H, Li B. Effect of temperature on the stability of dielectric elastomers.JournalofPhysicsDAppliedPhysics, 2011,44(36):365406-365414
29 闻邦椿,李以农,徐培民. 工程非线性振动. 北京: 科学出版社,2007 (Wen B C, Li Y N, Xu P M. Nonlinear Engineering Vibration. Beijing: Publication of Science Press, 2007(in Chinese))
*The project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11402246) and the Key Subject “Computational Solid Mechanics” of the China Academy of Engineering Physics
† Corresponding author E-mail: scu2005sjj@163.com
17 May 2016, revised 18 June 2016.
NONLINEAR DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE OF A DIELECTRIC ELASTOMER ACTUATOR*
Sheng Junjie1†Li Shuyong1Zhang Yuqing1Chen Hualing2,3
(1.InstituteofSystemsEngineering,ChinaAcademyofEngineeringPhysics,Mianyang621900,China)(2.SchoolofMechanicalEngineering,Xi′anJiaotongUniversity,Xi′an710049,China)(3.StateKeyLaboratoryforStrengthandVibrationofMechanicalStructures,Xi’anJiaotongUniversity,Xi′an710049,China)
Dielectric elastomers (DE) are one of the most potential electro-active polymer (EAP) used as high-performance actuators. A DE subjected to a voltage can generate large thickness and area expansion with a maximum area strain of 1600%. As DE has natural damping properties and its deformation is then dependent to time, its dynamic performance, energy conversion and large deformation are definitely influenced by damping. A free energy model is developed to study the dynamic characteristics of a dielectric elastomer actuator undergoing in-plane deformation subjected to the combined loadings of a mechanical press and an electriceld. The numerical results including the oscillation, phase diagrams and Poincaré maps are presented to show the inuence of the damping on the nonlinear dynamic characteristics of the dielectric elastomer. The numerical results indicate that the damping effect could cause the dynamic responses to constant vibration and decrease the amplitude. The phase paths are all presented in closed regions and the points of Poincaré map are finite, indicating that the DE system experiences a nonlinear periodic oscillation, and the dynamic oscillation of the DE system is stable. These conclusions provide the basis for the exploration of high-performance dielectric elastomers under dynamic mechanical and electrical loads.
dielectric elastomer, dynamic,damping, phase diagram, Poincaré map
*国家自然科学基金资助项目(11402246)、中国工程物理研究院重点学科项目“计算固体力学”资助
10.6052/1672-6553-2016-049
2016-05-17收到第1稿,2016-06-18收到修改稿.
† 通讯作者 E-mail: scu2005sjj@163.com

