慢性乙型肝炎患者外周血NKG2A+NK细胞与Treg的关系研究①
郑美娟 秦义组 张 敏 张振华 徐元宏
(安徽医科大学第一附属医院检验科,合肥230022)
慢性乙型肝炎患者外周血NKG2A+NK细胞与Treg的关系研究①
郑美娟秦义组②张敏张振华③徐元宏
(安徽医科大学第一附属医院检验科,合肥230022)
目的:探讨慢性乙型肝炎病毒(CHB)患者外周血NKG2A+NK细胞与调节性T细胞(Treg)的关系及临床意义。方法:收集46例CHB患者和17例健康对照者外周血,采用实时荧光定量PCR法检测血清HBV DNA;采用流式细胞术检测NKG2A+NK细胞及Treg的比例。结果:将CHB患者分为Low HBV DNA组(300~104U/ml)及High HBV DNA组(105~108U/ml)。我们发现High HBV DNA组ALT明显高于Low HBV DNA组(P<0.05)。High HBV DNA组CD56dimNK细胞及NKG2A+CD56dimNK细胞的比例均分别明显高于Low HBV DNA组(P<0.05)。且High HBV DNA组Treg明显高于Low HBV DNA组和对照组(P<0.05)。此外,NKG2A+CD56dimNK细胞的比例与High HBV DNA载量及Treg水平均呈正相关性(r=0.59,P<0.05;r=0.53,P<0.05)。结论:CHB患者的NKG2A+CD56dimNK细胞的水平与HBV的免疫逃逸及疾病的进展相关。
慢性乙型肝炎;HBV DNA;NK细胞;NKG2A;调节性T细胞
乙型肝炎病毒(Hpatitis B virus,HBV)是一种非细胞毒性的嗜肝DNA病毒,HBV感染机体可导致慢性乙型肝炎(Chronic hepatitis B,CHB),其进一步发展可导致肝硬化和肝癌的发生,严重威胁人类的健康[1]。目前CHB慢性化的发病机制尚不完全清楚,可能与宿主免疫应答状态及HBV诱导的免疫耐受有关[2,3]。
NK细胞是天然免疫系统的重要成员,在机体抵抗病毒感染中发挥重要作用。人类成熟NK细胞根据CD56的表达,可分为CD56brightNK细胞和CD56dimNK细胞,其中CD56dimNK细胞约占外周血NK细胞的90%,具有较强的细胞毒性[4]。近来有研究表明NK细胞在清除HBV过程中发挥至关重要的作用[5],且HBV持续感染导致NK细胞功能受损[6]。NK细胞的功能受到其表达的活化性受体和抑制性受体博弈后的平衡所调控,受体的多样性传递不同的活化信号和抑制信号,NK细胞通过上调抑制性受体的表达介导其功能的抑制[7]。CD4+CD25+Foxp3+调节性T细胞(regulatory T cells,Treg)具有免疫抑制功能,可抑制天然免疫及获得性免疫应答,并且在HBV的发病过程中具有重要作用[8]。因此,本研究根据CHB患者血清HBV DNA载量分为High HBV DNA组和Low HBV DNA组,探讨NK细胞及其表达的抑制性受体NKG2A与Treg的关系及其在HBV免疫逃逸中的作用。
1 材料与方法
1.1材料
1.1.1研究对象收集2014年11月至2015年12月在安徽医科大学第一附属医院感染科诊治的CHB患者46例。所有CHB患者符合《病毒性肝炎防治方案》诊断标准和《慢性乙型肝炎防治指南》的诊断标准。所有病例排除患有甲、丙、丁、戊型等肝炎及其他病毒感染、肿瘤及自身免疫性肝病。选取17例同期体检合格的健康人群为对照组,乙型肝炎标志物为阴性且无肝炎病史。
1.1.2主要试剂及仪器红细胞裂解液,FITC-CD4,PE-CD25,CD3-Percp-Cy5.5,APC-CD56,流式细胞仪FACS Calibur均购自美国BD公司;Foxp3内标染色试剂盒和Alexa-647-Foxp3均购自美国eBioscience公司;PE-NKG2A购自美国R&D公司;HBV DNA检测试剂盒购自上海之江生物科技股份有限公司; 荧光定量PCR检测仪SLAN-965为上海宏石医疗科技有限公司。
1.2方法
1.2.1血浆HBV DNA定量检测采集患者的外周血并分离血清,血清HBV DNA检测采用荧光定量PCR法检测,操作严格按照试剂盒说明书进行。
1.2.2流式细胞术检测NK细胞和Treg①检测NK细胞表面受体:同时取2份肝素钠抗凝血各100 μl,分别加入PE-NKG2A/CD3-Percp-Cy5.5/APC-CD56及同型对照管,室温避光孵育15 min,每管加入红细胞裂解液室温避光10 min,PBS洗涤2次,300 μl PBS重悬细胞沉淀,FACSCalibur流式细胞仪检测,FlowJo软件分析CD56+CD3-NK细胞的比例及NKG2A的表达;②检测Treg:取肝素钠抗凝血100 μl,加入FITC-CD4/ PE-25,室温避光孵育15 min,每管加入红细胞裂解液室温避光10 min,PBS洗涤2次,加入固定液室温避光反应40 min,穿膜液洗涤2次,加入Alexa 647-Foxp3,同时设同型对照管,室温避光孵育1 h,穿膜液及PBS各洗涤1次,300 μl PBS重悬细胞沉淀,FACS Calibur流式细胞仪检测,FlowJo软件分析CD4+CD25+Foxp3+细胞的比例。

2 结果
2.1患者一般资料根据血清HBV DNA水平,将46例CHB患者分为Low HBV DNA组(300~104U/ml)及High HBV DNA组(105~108U/ml),其中男性38例,女性8例,HBeAg (+) 患者为24例;健康对照17例;对CHB患者组ALT水平检测,发现High HBV DNA组ALT明显高于Low HBV DNA组(P<0.05)。CHB患者组及对照组的一般资料见表1。
2.2CHB患者外周血NK细胞水平的比较检测Low HBV DNA组、High HBV DNA组及健康对照组外周血CD3-CD56dimNK细胞及CD3-CD56brightNK细胞百分比,我们发现CD56dimNK细胞在Low HBV DNA组(6.15%±0.82%)和 High HBV DNA组(8.99% ± 1.12%)均明显低于对照组(16.36% ± 1.90%),差异均具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。High HBV DNA组的CD56dimNK细胞比例明显高于Low HBV DNA组(P<0.05),见图1A、B。此外,Low HBV DNA组、High HBV DNA组CD56brightNK细胞的比例与对照组相比,均无明显差异(P>0.05),且Low HBV DNA组CD56brightNK细胞的比例与High HBV DNA组相比亦无明显差异(P>0.05),见图1A、C。
表1CHB患者组及健康对照组的一般资料
Tab.1Clinical characteristics of enrolled subjects
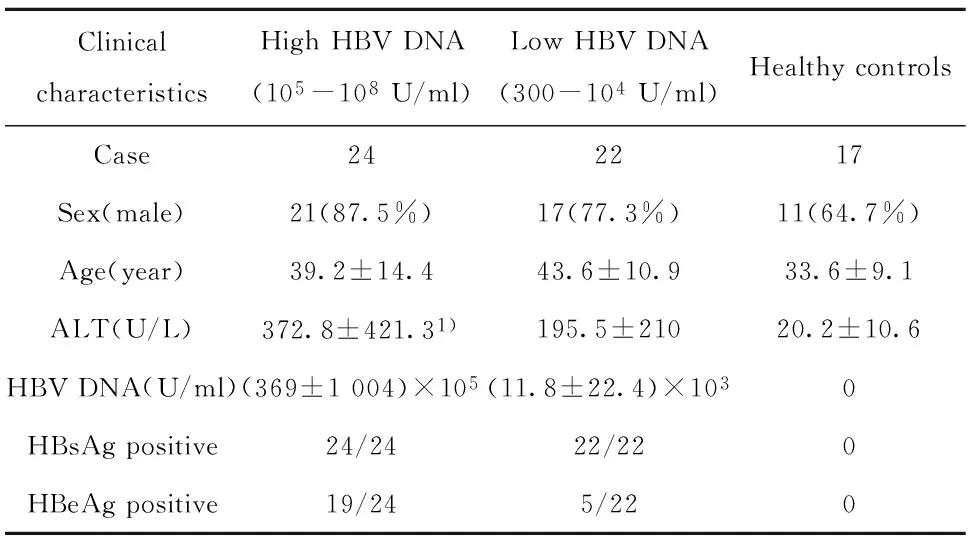
ClinicalcharacteristicsHighHBVDNA(105-108U/ml)LowHBVDNA(300-104U/ml)HealthycontrolsCase242217Sex(male)21(87.5%)17(77.3%)11(64.7%)Age(year)39.2±14.443.6±10.933.6±9.1ALT(U/L)372.8±421.31)195.5±21020.2±10.6HBVDNA(U/ml)(369±1004)×105(11.8±22.4)×1030HBsAgpositive24/2422/220HBeAgpositive19/245/220
Note:Compared with Low HBV DNA group,1)P<0.05.
2.3CHB患者外周血NKG2A+ NK细胞的检测我们进一步分析High HBV DNA组、Low HBV DNA组及健康对照组外周血CD56dimNK细胞上NKG2A的表达,我们发现High HBV DNA组(35.14% ± 2.22%)NKG2A+CD56dimNK细胞明显高于对照组(26.56% ± 2.01%),差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。而Low HBV DNA组(27.17% ± 2.70%)与对照组相比,无明显差异(P>0.05)。同时High HBV DNA组NKG2A+CD56dimNK细胞百分比明显高于Low HBV DNA组(P<0.05),见图2A、B。
2.4CHB患者外周血CD4+CD25+Foxp3+Treg的检测进一步比较Low HBV DNA组、High HBV DNA组及健康对照组外周血CD4+CD25+Foxp3+Treg占CD4+T细胞的百分比,我们发现Treg在Low HBV DNA组(3.94% ± 0.33%)和 High HBV DNA组(4.96% ± 0.26%)与对照组(2.42% ± 0.24%)相比均明显增高,差异均具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。且High HBV DNA组的Treg水平明显高于Low HBV DNA组(P<0.05),见图3A、B。
2.5CHB患者外周血NKG2A+CD56dimNK细胞与HBV DNA及Treg相关性分析进一步分析 NKG2A+CD56dimNK细胞与HBV DNA、Treg的相关性,结果表明NKG2A+CD56dimNK细胞比例与High HBV DNA组的HBV DNA载量呈正相关(r=0.59,P<0.05),见图4A;同时NKG2A+CD56dimNK细胞比例与Treg的比例亦呈正相关(r=0.53,P<0.05),见图4B。

图1 比较Low HBV DNA组、High HBV DNA组患者及正常对照者外周血CD56dim及CD56bright NK细胞Fig.1 Comparison of percentages of CD56dim and CD56bright NK cells in peripheral blood of CHB patients with Low HBV DNA and High HBV DNA and normal controlsNote: N.S.represented no significant differences in Fig.1C.
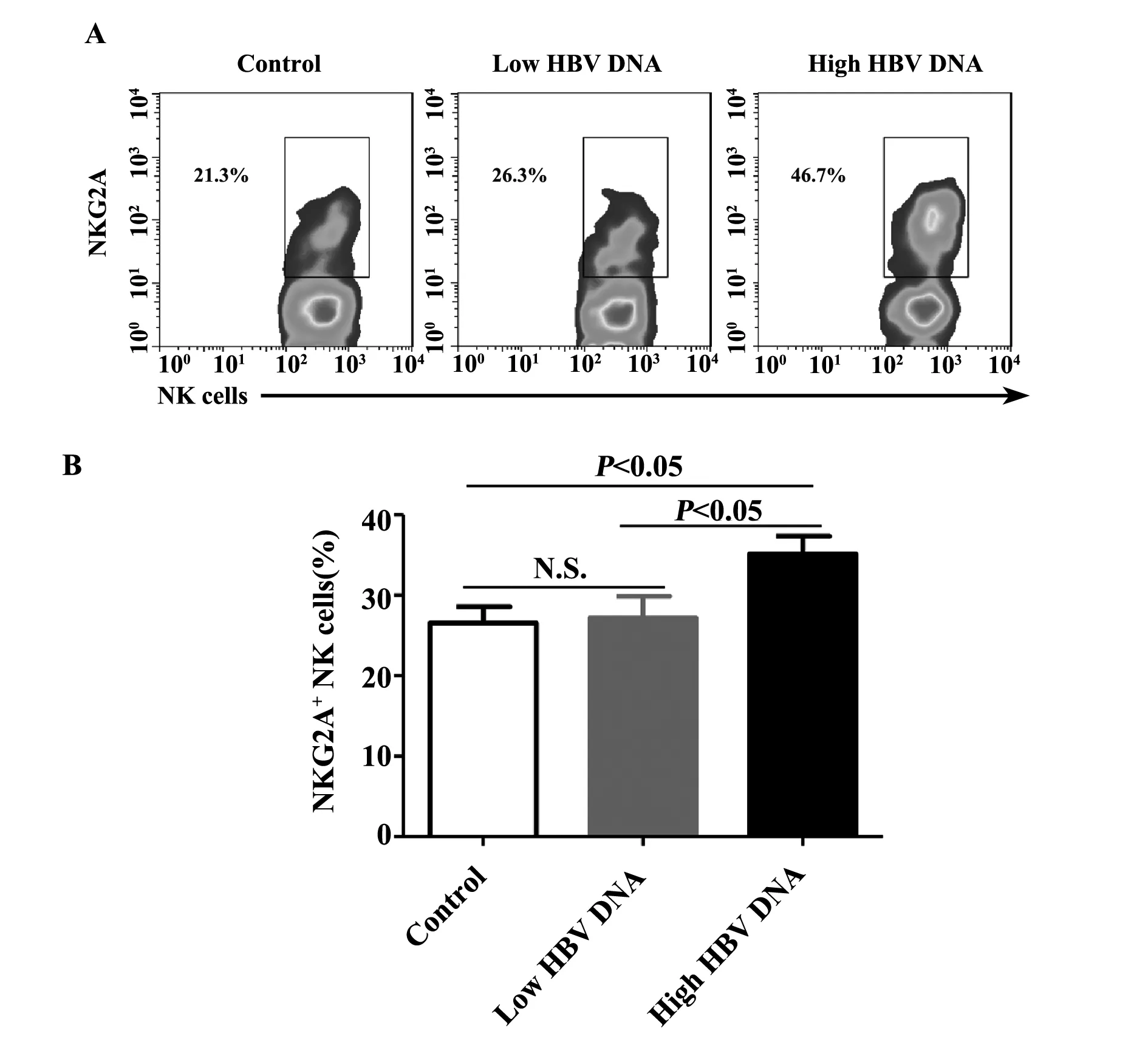
图2 比较Low HBV DNA组、High HBV DNA组及正常对照组外周血CD56dim NK细胞上NKG2A的表达Fig.2 Comparison of proportions of NKG2A+CD56dim NK cells in peripheral blood of CHB patients with Low HBV DNA and High HBV DNA and normal controlsNote: NK cells represented CD56dim NK cells in Fig.2A;N.S.represented no significant differences in Fig.2B.
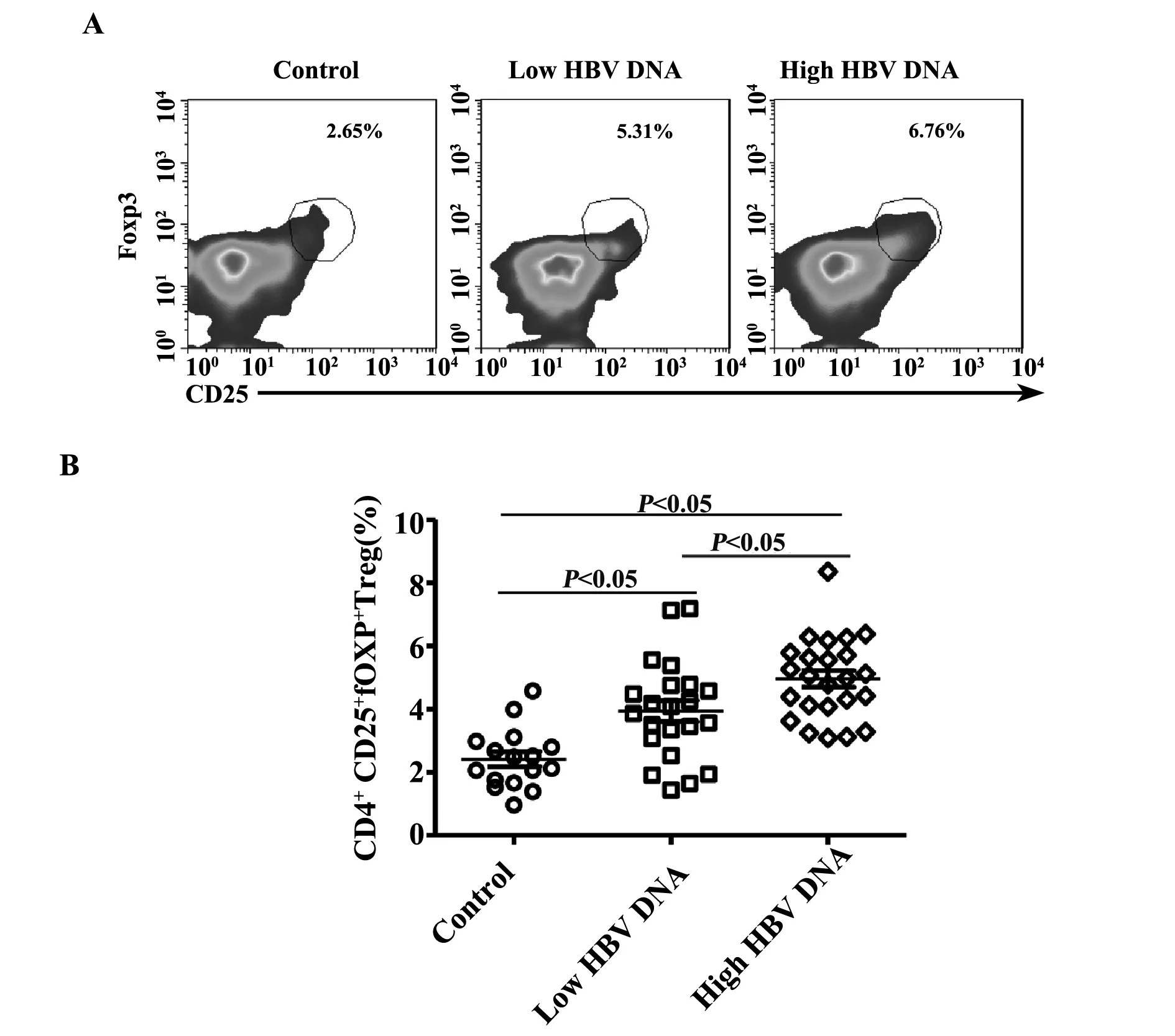
图3 Low HBV DNA组、High HBV DNA组及正常对照组Treg水平的比较Fig.3 Comparison of frequency of Treg in peripheral blood of CHB patients with Low HBV DNA,High HBV DNA and normal controlsNote: The smooth dot plots were gated from CD4+ T cells in Fig.3A.
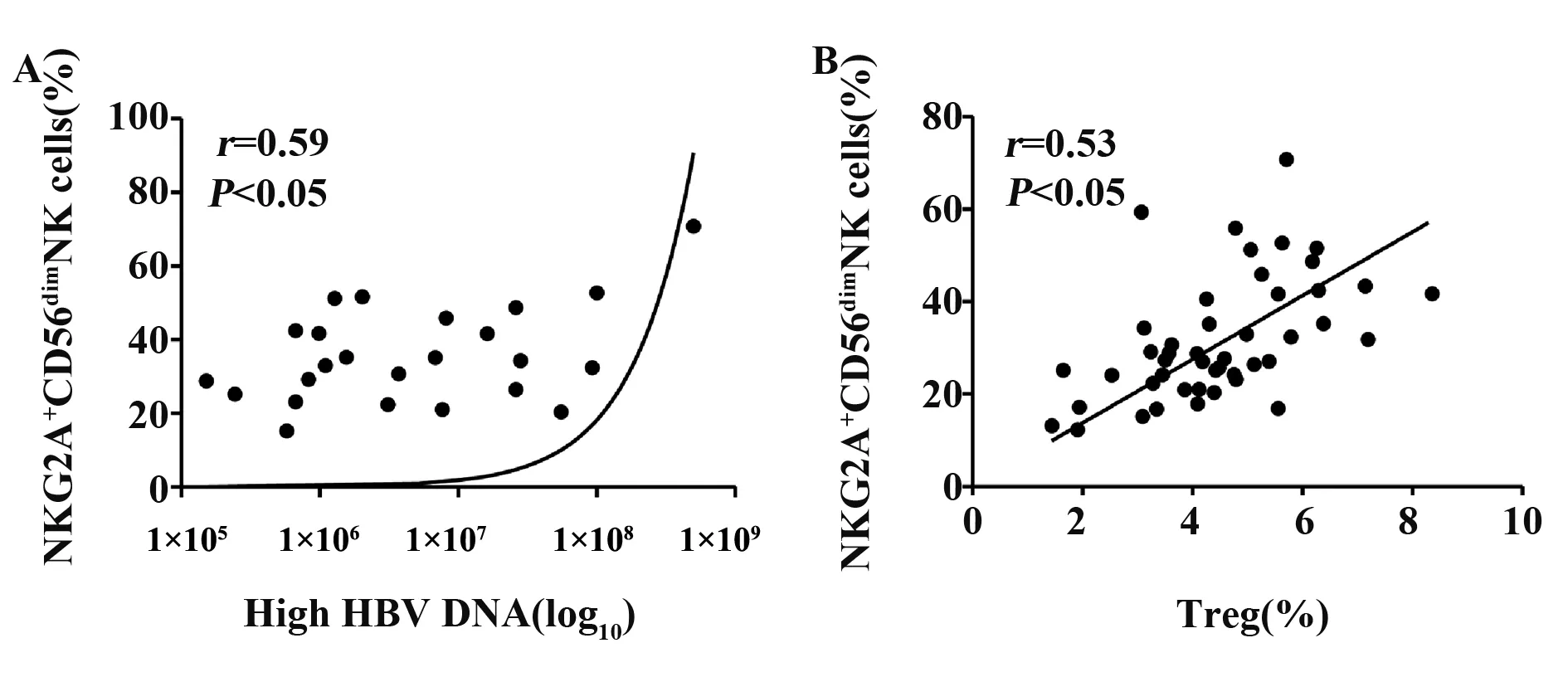
图4 CHB患者NKG2A+CD56dimNK细胞比例与HBV DNA、Treg的相关性分析Fig.4 Correlations between percentage of NKG2A+CD56dim NK cell with serum High HBV DNA levels and percentage of Treg in peripheral blood from patients with chronic hepatitis
3 讨论
我国CHB患者约有3 000万例,且这些CHB患者是肝硬化、肝癌等终末期肝病发生的重要诱因。目前CHB的临床治疗主要依赖于干扰素和核苷类似物,然而这些药物仅能抑制HBV在体内的复制,不能从根本上有效激发宿主免疫应答来清除HBV。固有免疫系统是机体抵御病原体入侵的第一道防线,无需抗原刺激即可发挥快速的免疫效应[9]。然而HBV的研究较多的研究集中在HBV-特异性CD8+T细胞的研究[10],值得关注的是机体抵抗病毒感染需要固有免疫和获得性免疫的协同作用,因此固有免疫在HBV清除中的作用不容忽视。我们之前对小鼠尾静脉高压注射HBV质粒构建HBV转染模型发现NK细胞是促进CD8+T细胞活化并介导HBV清除的重要细胞[5],表明NK细胞在HBV清除中发挥重要作用。此外,也有文献表明在HBV持续感染者体内NK细胞抑制性受体表达增高,提示CHB的发生与NK细胞功能受到抑制有关[11,12]。
NK细胞表达的抑制性受体通过传递抑制性信号介导NK细胞的功能抑制,已有研究表明NKG2A可下调NK细胞的功能,而阻断NKG2A的配体识别可恢复NK细胞的功能[13]。HBV持续感染者体内NKG2A在细胞的表达明显升高,利用HBV转染小鼠模型发现阻断NKG2A的信号显著增强NK细胞的抗HBV功能[11]。我们的结果表明High HBV DNA组患者NKG2A+CD56dimNK细胞比例明显高于Low HBV DNA组和健康对照组,差异具有统计学意义,提示随着HBV DNA水平增加,CHB患者NKG2A+CD56dimNK细胞比例亦随之明显升高,此外,我们也发现High HBV DNA组ALT明显高于Low HBV DNA组,且High HBV DNA组患者HBeAg阳性率亦明显高于Low HBV DNA组。上述结果表明CHB患者NK细胞高表达NKG2A导致NK细胞的功能受到抑制可能与HBV的复制及疾病进展有关。
我们亦发现High HBV DNA组患者外周血Treg比例明显高于Low HBV DNA组和健康对照组,差异具有统计学意义,且High HBV DNA组患者的Treg亦明显高于Low HBV DNA组。此外,NKG2A+CD56dimNK细胞与Treg细胞的比例呈正相关性,表明CHB患者的NKG2A+CD56dimNK细胞可能也发挥免疫抑制效应,或与后续的获得性免疫应答受到抑制相关。进一步的研究表明,NKG2A+CD56dimNK细胞与HBV DNA高病毒载量呈正相关,提示随着HBV DNA载量升高,CD56dimNK细胞表达NKG2A增加。虽然有研究分别表明CHB患者NKG2A+ NK细胞的比例与HBV DNA载量升高相一致[11],以及CHB患者中Treg比例与HBV DNA呈正相关[14]。而我们通过对CHB患者同时检测三者之间的关系,发现NKG2A+CD56dimNK细胞与High HBV DNA组HBV DNA载量和Treg均存在正相关性,表明NKG2A结果与HBV的复制相关,可能也介导HBV的免疫逃逸。
总之,我们根据血清HBV DNA的水平,将CHB患者分为High HBV DNA组和Low HBV DNA组,发现NKG2A+CD56dimNK细胞随着HBV DNA水平、Treg细胞的比例的增加而明显增加,且与High HBV DNA载量和Treg均存在正相关性,提示CHB患者的NK细胞高表达NKG2A,与HBV的免疫逃逸及CHB的疾病进展有密切联系,提示对NKG2A的干预可能成为CHB免疫治疗的靶点,为CHB免疫治疗提供新的治疗提供新策略。
[1]Ganem D,Prince AM.Hepatitis B virus infection--natural history and clinical consequences[J].N Engl J Med,2004,350(11):1118-1129.
[2]Rehermann B,Nascimbeni M.Immunology of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infection[J].Nat Rev Immunol,2005,5(3):215-229.
[3]Zeng Z,Kong X,Li F,etal.IL-12-based vaccination therapy reverses liver-induced systemic tolerance in a mouse model of hepatitis B virus carrier[J].J Immunol,2013,191(8):4184-4193.
[4]Cooper MA,Fehniger TA,Caligiuri MA.The biology of human natural killer-cell subsets[J].Trends Immunol,2001,22(11):633-640.
[5]Zheng M,Sun R,Wei H,etal.NK cells help induce anti-hepatitis B virus CD8+T cell immunity in mice[J].J Immunol,2016,196(10):4122-4131.
[6]Sun C,Sun H,Zhang C,etal.NK cell receptor imbalance and NK cell dysfunction in HBV infection and hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Cell Mol Immunol,2015,12(3):292-302.
[7]Parham P,Moffett A.Variable NK cell receptors and their MHC classⅠ ligands in immunity,reproduction and human evolution[J].Nat Rev Immunol,2013,13(2):133-144.
[8]Xu D,Fu J,Jin L,etal.Circulating and liver resident CD4+CD25+regulatory T cells actively influence the antiviral immune response and disease progression in patients with hepatitis B[J].J Immunol,2006,177(1):739-747.
[9]Vivier E,Raulet DH,Moretta A,etal.Innate or adaptive immunity? The example of natural killer cells[J].Science,2011,331(6013):44-49.
[10]Chisari FV,Isogawa M,Wieland SF.Pathogenesis of hepatitis B virus infection[J].Pathol Biol (Paris),2010,58(4):258-266.
[11]Li F,Wei H,Gao Y,etal.Blocking the natural killer cell inhibitory receptor NKG2A increases activity of human natural killer cells and clears hepatitis B virus infection in mice[J].Gastroenterology,2013,144(2):392-401.
[12]Ju Y,Hou N,Meng J,etal.T cell immunoglobulin- and mucin-domain-containing molecule-3 (Tim-3) mediates natural killer cell suppression in chronic hepatitis B[J].J Hepatol,2010,52(3):322-329.
[13]Jinushi M,Takehara T,Tatsumi T,etal.Negative regulation of NK cell activities by inhibitory receptor CD94/NKG2A leads to altered NK cell-induced modulation of dendritic cell functions in chronic hepatitis C virus infection[J].J Immunol,2004,173(10):6072-6081.
[14]Stoop JN,van der Molen RG,Baan CC,etal.Regulatory T cells contribute to the impaired immune response in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection[J].Hepatology,2005,41(4):771-778.
[收稿2016-06-02]
(编辑许四平)
Clinical correlation between NKG2A+NK cells and regulatory T cells in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection
ZHENG Mei-Juan,QIN Yi-Zu,ZHANG Min,ZHANG Zhen-Hua,XU Yuan-Hong.
Department of Clinicial Laboratory,the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University,Hefei 230022,China
Objective:To investigate the correlation between NKG2A+NK cells and regulatory T cells in peripheral blood of patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection,and explore the clinical significances.Methods: Forty-six patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection and 17 health individuals were included in this study.HBV DNA levels were measured by Real-time quantitative PCR (FQ-PCR).NKG2A+ NK cells and Treg in PBMC were quantitatively analyzed by flow cytometry.Results: According to HBV DNA levels,the CHB patients were divided into two groups:Low HBV DNA group(Low viral load group,300-104U/ml)and High HBV DNA group(High viral load group,105-108U/ml).We found that ALT levels of High HBV DNA group were obviously higher than Low HBV DNA group(P<0.05).The frequenies of CD56dimNK cells of High HBV DNA group were obviously higher than low HBV DNA group (P<0.05),and similarly the percentages of NKG2A+CD56dimNK cells of High HBV DNA group were significantly higher than Low HBV DNA and control groups (P<0.05).We also found that the percentages of regulatory T cells (Treg) of High HBV DNA group were significantly higher than Low HBV DNA and control groups (P<0.05).In addition,the proportions of NKG2A+CD56dimNK cells were positively correlated with High HBV DNA levels (r=0.59,P<0.05) and the percentages of Treg(r=0.53,P<0.05) in CHB patients.Conclusion: NKG2A+CD56dimNK cells may closely relate to the HBV-related immune escape and the progress of CHB.
Chronic hepatitis B virus;HBV DNA;NK cells;NKG2A;Regulatory T cells
10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2016.09.021
郑美娟(1983年-),女,博士,主管技师,硕士生导师,主要从事HBV的致病机制研究, E-mail:meijzheng@hotmail.com。
及指导教师:徐元宏(1964年-),男,硕士,教授,主任技师,博士生导师,主要从事感染免疫方面的研究,E-mail:xyhong1964@163.com。
R392.12
A
1000-484X(2016)09-1342-05
①本文为国家自然科学基金(81302525)资助项目。
②安徽省疾病预防控制中心艾滋病防治科,合肥230601。
③安徽医科大学第一附属医院感染科,合肥230022。

