血清总胆汁酸水平与老年人冠心病的相关性
王观华, 胡增敏, 向海霞, 方 鹏
(柞水县人民医院 内一科, 陕西 柞水 711400)
血清总胆汁酸水平与老年人冠心病的相关性
王观华, 胡增敏, 向海霞, 方鹏
(柞水县人民医院 内一科, 陕西 柞水711400)
目的: 检测血清总胆汁酸(TBA)水平与老年人冠心病(CHD)的相关性。方法: 40例(稳定性心绞痛)老年CHD患者作为观察组(用Gensini评分评价CHD的严重程度),42例同期老年健康体检者作为对照组,取观察组入院时或对照组体检当日的血清,采用全自动生化仪检测总胆固醇(TC)、高密度脂蛋白(HDL-c)、低密度脂蛋白(LDL-c)及甘油三脂(TG)等血脂指标,白介素-6(IL-6)、肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)等炎症因子及TBA的表达,比较2组受检者血清血脂指标、炎症因子和TBA水平;采用Spearman法分析冠心病患者TBA与血脂指标、炎症因子及Gensini评分的相关性。结果: 与对照组比较,观察组除TC、TNF-α及TBA水平显著升高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);Spearman法分析结果显示,老年CHD患者血清TBA水平与TC、TNF-α及Gensini评分均呈现显著正相关(r=0.787、0.924、0.837,P<0.01)。 结论: 老年CHD患者TBA水平显著升高,且与疾病严重程度密切相关。
冠状动脉硬化; 心脏病; 老年人; 总胆汁酸; 炎症趋化因子类; 血脂
[Abstract]Objective: To analyze the correlation between serum total bile acid level(TBA) and coronary heart disease of aged patients. Methods: 40 cases of patients with (stable angina) CHD were collected as observation group (with the Gensini score evaluating the severity of coronary heart disease) and 42 cases of healthy old people in the same period as control group. Serum was collected from observation group at admission and control group at examination day. The automatic biochemical analyzer was adopted to detect blood lipid indexes including serum total cholesterol(TC), high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and triglyceride (TG), and inflammatory factors including interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF alpha) and other inflammatory cytokines and TBA, all of which were compared between observation group and control group.Spearmanmethod was used to analyze the correlation between TBA and serum lipid, inflammatory factors and Gensini score in patients with CHD. Results: The patients in observation group had higher levels of TBA, TC and TNF-α than those of control group, and the difference were statistically significant (P<0.05). The result ofSpearmananalysis showed that in observation group, the levels of TBA was significantly positive correlated with TC and TNF-α and Gensini score(r=0.787、0.924、0.837,P<0.01). Conclusion: TBA level was significantly elevated in elderly patients with coronary heart disease, and is closely related to the severity of the disease.
[Key words]coronary artery sclerosis; heart disease;the aged; total bile acid; chemokines; blood lipid
冠状动脉粥样硬化性心脏病(coronary heart disease,CHD)是我国最为常见的心血管系统疾病之一,目前认为血脂代谢紊乱与血管内皮细胞受损的交互作用在该病的发生和发展中起着重要作用[1-4]。高脂血症是公认的CHD危险因素,新近的研究显示血清总胆汁酸(total bile acid,TBA)水平升高与CHD的发生发展有关[5]。本研究以老年CHD患者作为研究对象,观察其外周血清TBA水平的改变。
1 对象与方法
1.1对象
2013年1月~2015年1月收治的40例CHD(稳定性心绞痛)患者作为观察组,年龄≥60岁,CHD的诊断符合《冠状动脉粥样硬化性心脏病诊断标准》[6],参考文献[7]采用Gensini评分评估CHD的病变严重程度;排除有合并心脏手术史、其它心脏器质性病变、活动性感染及恶性肿瘤等终末期疾病患者。另选取42例同期老年健康体检者作为对照组。2组研究对象的性别、年龄等基础资料比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),具有可比性,见表1。
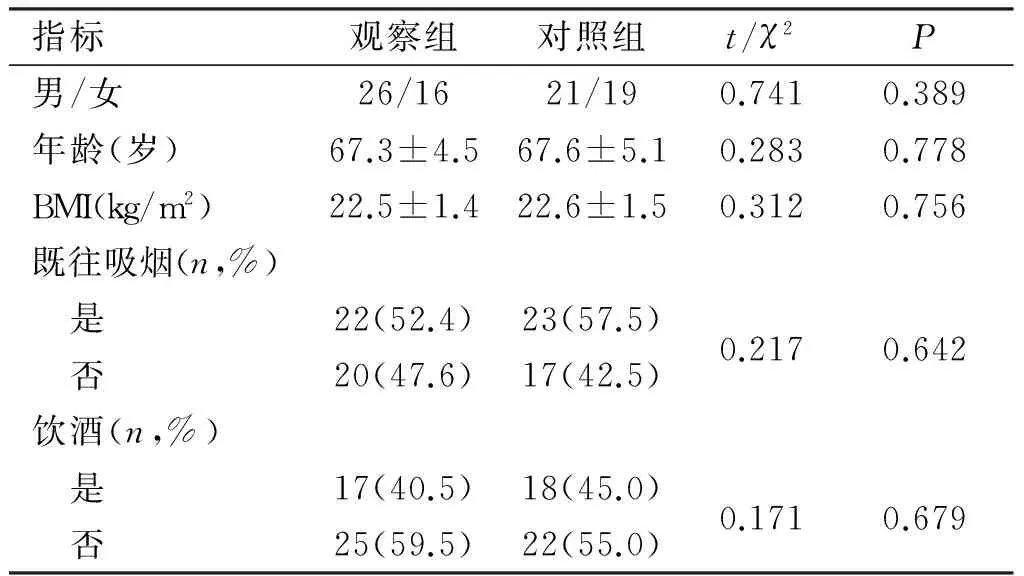
表1 两组被检者一般资料比较
1.2方法
分别抽取观察组入院时或对照组体检当日的空腹外周静脉血5 mL,分离血清。采用全自动生化仪检测:(1)总胆固醇(total cholesterol,TC)、高密度脂蛋白(high-density lipoprotein,HDL-c)、低密度脂蛋白(low-density lipoprotein,LDL-c)及甘油三脂(triglyceride,TG)等血脂指标;(2)白介素-6(interleukin-6,IL-6)、肿瘤坏死因子-α(tumor necrosis factor-α,TNF-α)等炎症因子;(3)TBA。
1.3统计学方法

2 结果
2.1血脂指标、炎症因子及TBA
与对照组比较,观察组除TC、TNF-α及TBA水平显著高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)外,其余指标比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表2。
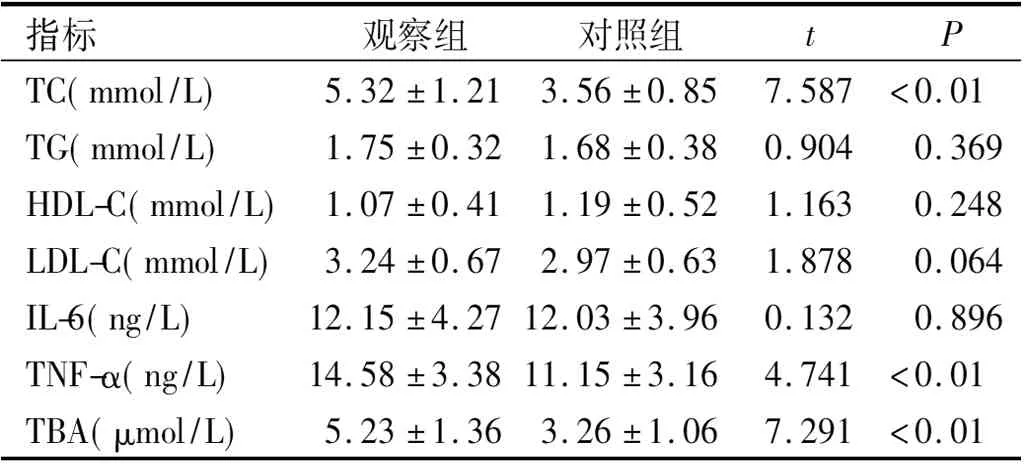
表2 两组被检者血脂指标、炎性因子及TBA比较
2.2老年CHD患者TBA与TC及TNF-α的相关性
如图1所示,老年CHD患者血清TBA水平与TC及TNF-α均呈现显著正相关(r=0.787、0.924,P<0.01)。2.3老年CHD患者TBA与Gensini评分的相关性
如图2所示,老年CHD患者TBA水平与Gensini评分呈现显著正相关(r=0.837,P<0.01)。
3 讨论
我国心血管疾病的发病率逐年攀升,这可能与我国人口老龄化、西方化的生活饮食方式及食品安全恶化等因素有关[8]。目前认为脂质代谢紊乱是CHD发病的主要推动力量[9-10]。并发高血脂在CHD人群中十分常见,内、外源性胆固醇的代谢异常导致的血清总胆固醇及低密度脂蛋白水平升高在冠状动脉粥样硬化的形成过程中起到了重要作用[11]。胆固醇的代谢主要在肝脏,肝脏可以将胆固醇转化为胆汁酸进入肠道。正常人体具有将过多摄入的胆固醇转化为胆汁酸排出体外的内力,而如果无法排出过多的胆汁酸将会导致血清TBA水平升高[12]。TBA具有细胞毒性作用,可以损伤血管内皮细胞,这种细胞毒性作用且具有剂量依赖性[5, 13]。鉴于此,本研究从分析老年CHD患者血清TBA着手,探讨TBA与血脂及血清炎症因子间的相关性,分析TBA与CHD的关系,以期为CHD的临床诊疗提供一定数据支持和参考。

图1 老年CHD患者血清TBA与TC及TNF-α的相关性Fig.1 Correlation of serum TBA with TC and TNF-α in patients with coronary heart disease
本研究结果显示,老年CHD患者血清TC、TNF-α及TBA水平显著高于老年健康体检者。提示TBA可能与CHD有一定关联,同时再次证实血清TC、TNF-α水平与CHD发病有关。TNF-α是经典的促炎因子,在慢性炎症的维持及急性炎症的级联放大中均发挥关键作用[14-15]。血管内皮受损及全身性慢性炎症是CHD的主要发病机制假说之一。本研究的相关性分析结果显示,CHD患者血清TBA与TNF-α及TC均呈现显著正相关。这提示TBA可能同时与血脂代谢及系统性炎症反应相关,推测TBA可能与CHD的严重程度亦相关,Gensini评分可直接反映冠心病的严重程度,本研究结果显示老年CHD患者TBA与Gensini评分呈现显著正相关关系,佐证上述推断。提示检测老年CHD患者血清TBA可推断疾病进展情况。
综上,老年CHD患者TBA水平显著升高,且与疾病严重程度密切相关,提示其在该病的发生或发展中发挥一定作用。
[1]Farooq V, Di MC, Serruys PW. Balancing idealism with realism to safeguard the welfare of patients: The importance of Heart Team led decision-making in patients with complex coronary artery disease[J]. Indian Heart J, 2016 (1):1-5.
[2]武海滨, 胡如英, 龚巍巍, 等. 2010至2012年浙江省25岁及以上居民急性冠心病事件监测[J]. 中华心血管病杂志, 2015 (2):179-183.
[3]Das UN. Heart-type fatty acid-binding protein (H-FABP) and coronary heart disease[J]. Indian Heart J, 2016 (1):16-18.
[4]Mehta V, Sukhija R, Mehra P,et al. Multimarker risk stratification approach and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with stable coronary artery disease undergoing elective percutaneous coronary intervention[J]. Indian Heart J, 2016 (1):57-62.
[5]Ross S, D'Mello M, Anand SS,et al. Effect of bile acid sequestrants on the risk of cardiovascular events: a mendelian randomization analysis[J]. Circ Cardiovasc Genet, 2015 (4):618-627.
[6]周玉杰, 贾德安. 批阅三载增删十次——《冠状动脉粥样硬化性心脏病诊断标准》诞生记[J]. 中国卫生标准管理, 2010 (4):20-21.
[7]高灵.冠状动脉评分方法的研究进展[J]. 医学综述, 2013 (9):1601-1603,1609.
[8]王波, 王临池, 赵翼洪, 等. 2009-2013年苏州20岁及以上居民冠心病发病率变化趋势及类型分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2015 (24):2952-2956.
[9]Simonsen JA, Johansen A, Gerke O,et al. Outcome with invasive versus medical treatment of stable coronary artery disease: influence of perfusion defect size, ischaemia, and ejection fraction[J]. EuroIntervention, 2016 (10):1118-1124.
[10]Liu JJ, Ren CW, Wu WH,et al.One-stage hybrid procedure for patients with valvular pulmonary stenosis and coronary artery disease[J]. Chin Med J (Engl), 2016 (5):624-625.
[11]Burgess S, Harshfield E. Mendelian randomization to assess causal effects of blood lipids on coronary heart disease: lessons from the past and applications to the future[J]. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes, 2016 (2):124-130.
[12]Charach G, Grosskopf I, Rabinovich A, et al.The association of bile acid excretion and atherosclerotic coronary artery disease[J]. Therap Adv Gastroenterol, 2011 (2):95-101.
[13]Wójcik OP, Koenig KL, Zeleniuch-Jacquotte A,et al. Serum taurine and risk of coronary heart disease: a prospective, nested case-control study[J]. Eur J Nutr, 2013 (1):169-178.
[14]Qiu HN, Liu B, Liu W,et al. Interleukin-27 enhances TNF-α-mediated activation of human coronary artery endothelial cells[J]. Mol Cell Biochem, 2016 (1-2):1-10.
[15]Vrselja Z,ram, Andrijevic D,et al. Transcardial gradient of adiponectin, interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α in overweight coronary artery disease patients[J]. Cytokine, 2015 (2):321-327.
(2016-02-01收稿,2016-07-01修回)
中文编辑: 吴昌学; 英文编辑: 刘华
Correlation between Serum Total Bile Acid Level and Coronary Heart Disease in the Elderly
WANG Guanhua, HU Zengmin, XIANG Haixia, FANG Peng
(ThePeople'sHospitalofZhashuiCounty,Zhashui711400,Shanxi,China)
R541.4
A
1000-2707(2016)08-0980-04
10.19367/j.cnki.1000-2707.2016.08.029
网络出版时间:2016-08-23网络出版地址:http://www.cnki.net/kcms/detail/52.5012.R.20160823.1343.034.html

