基于STQ系统的一个四比特簇态制备方案
陈 娟,郭琰博,姜年权
基于STQ系统的一个四比特簇态制备方案
*陈 娟,郭琰博,姜年权
(温州大学物理与电子信息工程学院,浙江,温州 325035)
Transmon 比特通过电容与一个超导TLR(transmission line resonator)耦合。本文采用Transmon 比特与TLR之间有更强的耦合常量,提出了一个在STQ(superconducting transmon qubit)系统中制备四比特纠缠簇态(cluster state)的简单方案。与已有的方案相比,此方案有更长的消相干时间。又由于Transmon 比特和TLR有以上的属性,此方案在实验上更可行。
cluster态;超导Transmon比特;传输线型谐振腔
量子纠缠因其独特的性质而成为量子信息处理的重要资源[1]。其中,三体或多体纠缠不仅可以用于检验量子力学非局域理论[2],而且被用于许多量子信息处理方案中。比如:量子隐形传态[3-4],量子纠缠交换[5]和量子稠密编码等[6-7]。因此, 探究和制备多体纠缠态具有重要意义。在近年来的研究中,已有多种不同的多体纠缠态被提出,如:Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger (GHZ)态[8-9]、W 态[10]和cluster 态[11]等。其中,Briegel 和 Raussendor[11]提出的cluster 态比GHZ 态对消相干更不敏感[12-13],而且量子计算机能通过cluster 态来实现[12],正因为如此,cluster 态备受人们的关注。其在不同的物理系统(如:腔量子电动力学系统(QED))中的制备方案已经被提出[14-21]。在文献[20]中,Yang 等人提出了一个在热腔QED中制备四原子cluster 态的方案,此方案包括两个单比特操作和四个两比特操作;在文献[14-19,21]中,提出了需要三步来制备一个四比特cluster态的方案;郑晓娟等提出了一个在腔QED中通过两个三比特操作制备四比特cluster态的方案[22]。


(a)
(b)
图 1 (a)Transmon量子比特基本的线路图;(b)N个Transmon量子比特与TLR耦合的电路图,其中频率为d的微波输入到TLR
Fig. 1 (a) The basic circuit of transmon qubit; (b) The circuit of N transmon qubits coupled with the TLR, in which a microwave field of frequencydis applied to the input wire of the TRL
本文将基于STQ系统提出了一个有效地制备四比特纠缠cluster态的方案,与上述已有方案相比,该方案仅包括两个三比特操作,方案中超导TLR被选为量子数据总线(QDB)[25],并且Transmon量子位和QDB之间的耦合常数非常大[26]。因此,方案具有更长的消相干时间和更短的操作时间。本文将在第二部分给出系统的模型和它的哈密顿量,在第三部分介绍如何制备四比特纠缠cluster态,最后讨论此方案在实验中的可行性。
1 模型和哈密顿量

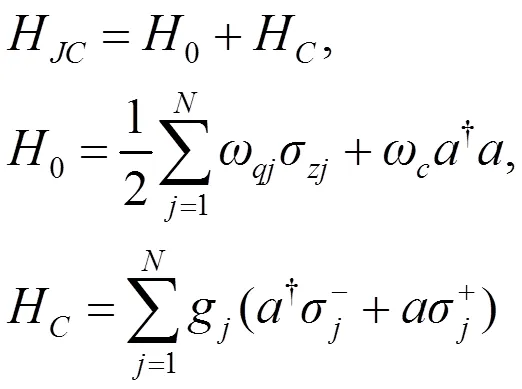


因此,总系统的哈密顿量为
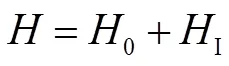
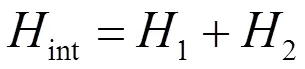


2 制备四比特纠缠cluster态
现将介绍如何在一个由四个STQ和一个TLR组成的系统中制备四比特纠缠cluster态。利用前面已经写出的系统的哈密顿量,选取

这些条件在实验上能很容易实现。因此,哈密顿量 (4) 变为

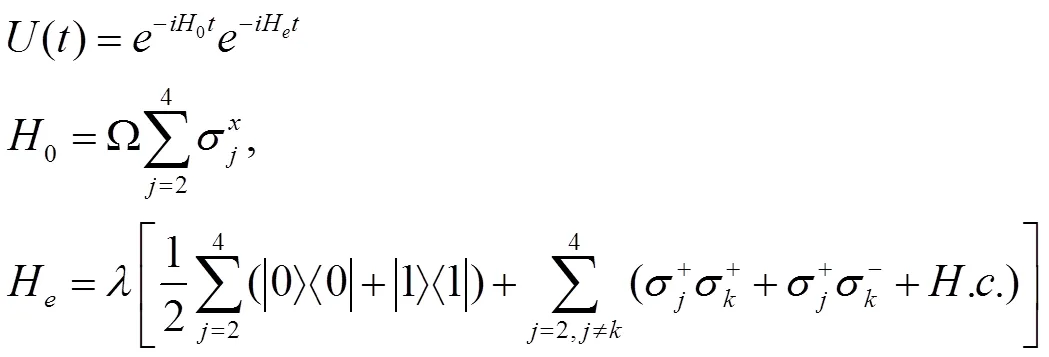
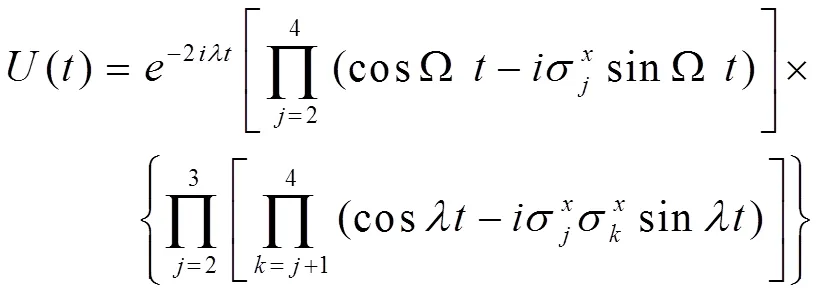
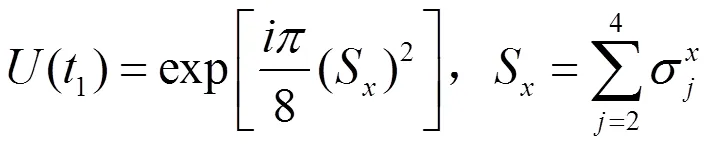
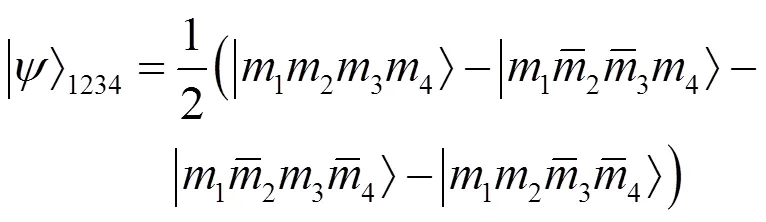
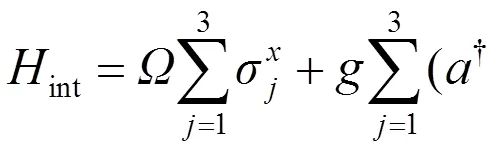
应用上面相同的理论,得到演化算符为

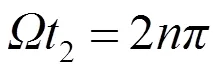

因此,任意初态演化为
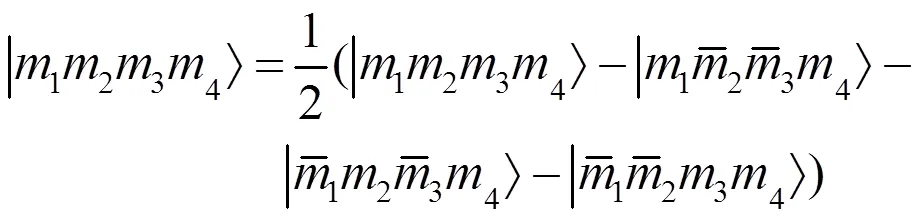


这是一个四比特纠缠cluster态。
3 讨论和结论

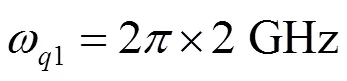

很明显非常小。所以说,在第一步中只有三个Transmon比特演化。第一个Transmon比特一直处于基态。同理可得第二步中Transmon比特被激发的可能性

所以方案是可行的。
总之,本文提出了一个在STQ系统中制备四比特纠缠cluster态的方案。因为所用的量子比特有更长的消相干时间和更大的耦合量,所以该方案在实验上更加可行。同时也计算了无关Transmon比特被激发的可能性,发现对于态的制备来说,影响非常小。
[1] Einstein A, Podolsky B, Rosen N. Can quantum-mechanical description of physical reality be considered complete?[J]. Physical review, 1935, 47(10): 777-780.
[2] Zheng S B. One-step synthesis of multiatom Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger states[J]. Physical review letters, 2001, 87(23): 230404-1.
[3] Vitali D, Fortunato M, Tombesi P. Complete quantum teleportation with a Kerr nonlinearity[J]. arXiv preprint quant-ph/0003082, 2000.
[4] Zheng X J, Fang M F, Cai J W, et al. Teleportation of atomic entangled states with a thermal cavity[J]. Chinese Physics, 2006, 15(12): 2840-2846.
[5] Yang M, Zhao Y, Song W, et al. Entanglement concentration for unknown atomic entangled states via entanglement swapping[J]. arXiv preprint quant-ph/0411157, 2004.
[6] Bennett C H, Wiesner S J. Communication via one-and two-particle operators on Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen states[J]. Physical review letters, 1992, 69(20): 2881.
[7] Xiao-Juan Z, Shuai C, Mao-Fa F, et al. Scheme for implementing quantum dense coding with four-particle decoherence-free states in an ion trap[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2008, 17(2): 431.
[8] Greenberger D M, Horne M A, Zeilinger A. Going beyond Bell’s theorem[M]//Bell’s theorem, quantum theory and conceptions of the universe. Springer Netherlands, 1989: 69-72.
[9] Greenberger D M, Horne M A, Shimony A, et al. Bell’s theorem without inequalities[J]. Am. J. Phys, 1990, 58(12): 1131-1143.
[10] Dür W, Vidal G, Cirac J I. Three qubits can be entangled in two inequivalent ways[J]. Physical Review A, 2000, 62(6): 062314.
[11] Briegel H J, Raussendorf R. Persistent entanglement in arrays of interacting particles[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2001, 86(5): 910.
[12] Walther P, Aspelmeyer M, Resch K J, et al. Experimental violation of a cluster state Bell inequality[J]. Physical review letters, 2005, 95(2): 020403.
[13] Scarani V, Acín A, Schenck E, et al. Nonlocality of cluster states of qubits[J]. Physical Review A, 2005, 71(4): 042325.
[14] Zou X B, Mathis W. Generating a four-photon polarization-entangled cluster state[J]. Physical Review A, 2005, 71(3): 032308.
[15] Zheng S B. Generation of cluster states in ion-trap systems[J]. Physical Review A, 2006, 73(6): 65802.
[16] Yang W X, Zhan Z M, Li J H. Efficient scheme for multipartite entanglement and quantum information processing with trapped ions[J]. Physical Review A, 2005, 72(6): 062108.
[17] Zhang X L, Gao K L, Feng M. Preparation of cluster states and W states with superconducting quantum-interference-device qubits in cavity QED[J]. Physical Review A, 2006, 74(2): 024303.
[18] Zou X B, Mathis W. Schemes for generating the cluster states in microwave cavity QED[J]. Physical Review A, 2005, 72(1): 013809.
[19] Ye L, Yu L B, Guo G C. Generation of entangled states in cavity QED[J]. Physical review a, 2005, 72(3): 034304.
[20] Rong-Can Y, Hong-Cai L, Mei-Xiang C, et al. Generation of four-atom cluster states in thermal cavity and implementing remote controlled not gate[J]. Chinese Physics, 2006, 15(10): 2315.
[21] Shao-Hua X, Ke-Hui S. Generation of two-atom cluster state via cavity QED[J]. Chinese Physics Letters, 2006, 23(6): 1466.
[22] Xiao-Juan Z, Hui X, Mao-Fa F, et al. Preparation of the four-qubit cluster states in cavity QED and the trapped-ion system[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2010, 19(3): 034207.
[23] Koch J, Terri M Y, Gambetta J, et al. Charge-insensitive qubit design derived from the Cooper pair box[J]. Physical Review A, 2007, 76(4): 042319.
[24] Schreier J A, Houck A A, Koch J, et al. Suppressing charge noise decoherence in superconducting charge qubits[J]. Physical Review B, 2008, 77(18): 180502.
[25] Blais A, Huang R S, Wallraff A, et al. Cavity quantum electrodynamics for superconducting electrical circuits: An architecture for quantum computation[J]. Physical Review A, 2004, 69(6): 062320.
[26] You-Bang Z, Qun-Yong Z, Yu-Wu W. Schemes for splitting quantum information with four-particle genuine entangled states[J]. Communications in Theoretical Physics, 2010, 53(5): 847.
[27] Blais A, Gambetta J, Wallraff A, et al. Quantum-information processing with circuit quantum electrodynamics[J]. Physical Review A, 2007, 75(3): 032329.
[28] Astafiev O, Pashkin Y A, Nakamura Y, et al. Quantum noise in the Josephson charge qubit[J]. arXiv preprint cond-mat/0411216, 2004.
[29] Kowal M, Jachimowicz P, Sobiczewski A. Fission barriers for even-even superheavy nuclei[J]. Physical Review C, 2010, 82(1): 014303.
[30] Makhlin Y, Schön G, Shnirman A. Quantum-state engineering with Josephson-junction devices[J]. Reviews of modern physics, 2001, 73(2): 357.
[31] Clarke J, Wilhelm F K. Superconducting quantum bits[J]. Nature, 2008, 453(7198): 1031-1042.
[32] S. Haroche, Fundamental Systems in Qunantum Optics, edited by J. Dalibard and J.Zinn-Just in (Elsevier, New York, 1992), p. 767.
[33] Zheng S B. Generation of entangled states for many multilevel atoms in a thermal cavity and ions in thermal motion[J]. Physical Review A, 2003, 68(3): 035801.
[34] Yang C P, Liu Y, Nori F. Phase gate of one qubit simultaneously controlling n qubits in a cavity[J]. Physical Review A, 2010, 81(6): 062323.
[35] DiCarlo L, Reed M D, Sun L, et al. Preparation and measurement of three-qubit entanglement in a superconducting circuit[J]. Nature, 2010, 467(7315): 574-578.
[36] Yang C P. Quantum information transfer with superconducting flux qubits coupled to a resonator[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1012.2030, 2010.
Scheme To PreparE four-qubit cluster states Based On STQ sYstem
*CHEN Juan,GUO Yan-bo,JIANG Nian-quan
( College of Physics and Electronic Information Engineering of Wenzhou University, Wenzhou, Zhejiang 325035,China)
Transmon qubits capacitively coupled to a superconducting transmission line resonator (TLR). We adopt transmon qubits which have much stronger coupling constant with TLR and propose a simple scheme to prepare a four-qubit entangled cluster state in superconducting transmon qubit (STQ) system. Compared with the scheme firstly introduced by Zheng Xiao-Juan et al, our schemes have longer dephasing time. Based on the favorable properties of transmons and TLR, our method is more feasible in experiment.
cluster states; superconducting Transmon qubit; transmission line resonator
O413.1
A
10.3969/j.issn.1674-8085.2014.03.006
1674-8085(2014)03-0027-05
2013-12-09;
2014-01-11
国家自然科学基金项目(10947017/A05)
*陈 娟(1989-),女,江西抚州人,硕士生,主要从事量子信息研究(E-mail: 214386945@qq.com);
郭琰博(1990-),男,甘肃天水人,硕士生,主要从事量子信息研究(E-mail:344516047@qq.com);
姜年权(1966-),男,安徽安庆人,教授,博士,主要从事量子信息和太阳能电池研究(E-mail:jiangnq@wzu.edu.cn).

