Study on hardware-in-the-loop simulation of beer fermentation system
YAO Chao-xiu, ZHENG Juan-juan, JIANG Yu-long, ZHAO You-bo
(College of Information and Electrical Engineering, Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao 266590, China)
In the past, workers used the traditional manual operation method to control beer fermentation process.This method has the characteristics of intensive labor, low productivity, more beer wine loss, low yield and poor quality[1].Using computer to automatically control beer fermentation process can solve these problems, and the quality of the beer has also been greatly improved.In this article, we use VB program and Kingview software to simulate the beer fermentation process in laboratory, which also has great significance to experimental teaching.
1 Fermentation process
The main equipment of beer fermentation is beer fermentation tank.The cylindrical conical tank has become the mainstream in recent years gradually.The beer fermentation tank consists of outer layer and inner layers with insulation materials filled between the two layers.There are also three cooling areas between the two layers, which are connected with three valves.The controller adjusts the opening size of the valve to control the refrigerant’s flow rate into the cooling area, and then controls the temperature in the tank to make it comply with the beer fermentation temperature curve.The schematic diagram of beer fermenation tank with three temperature areas and pipelines is shown in Fig.1.
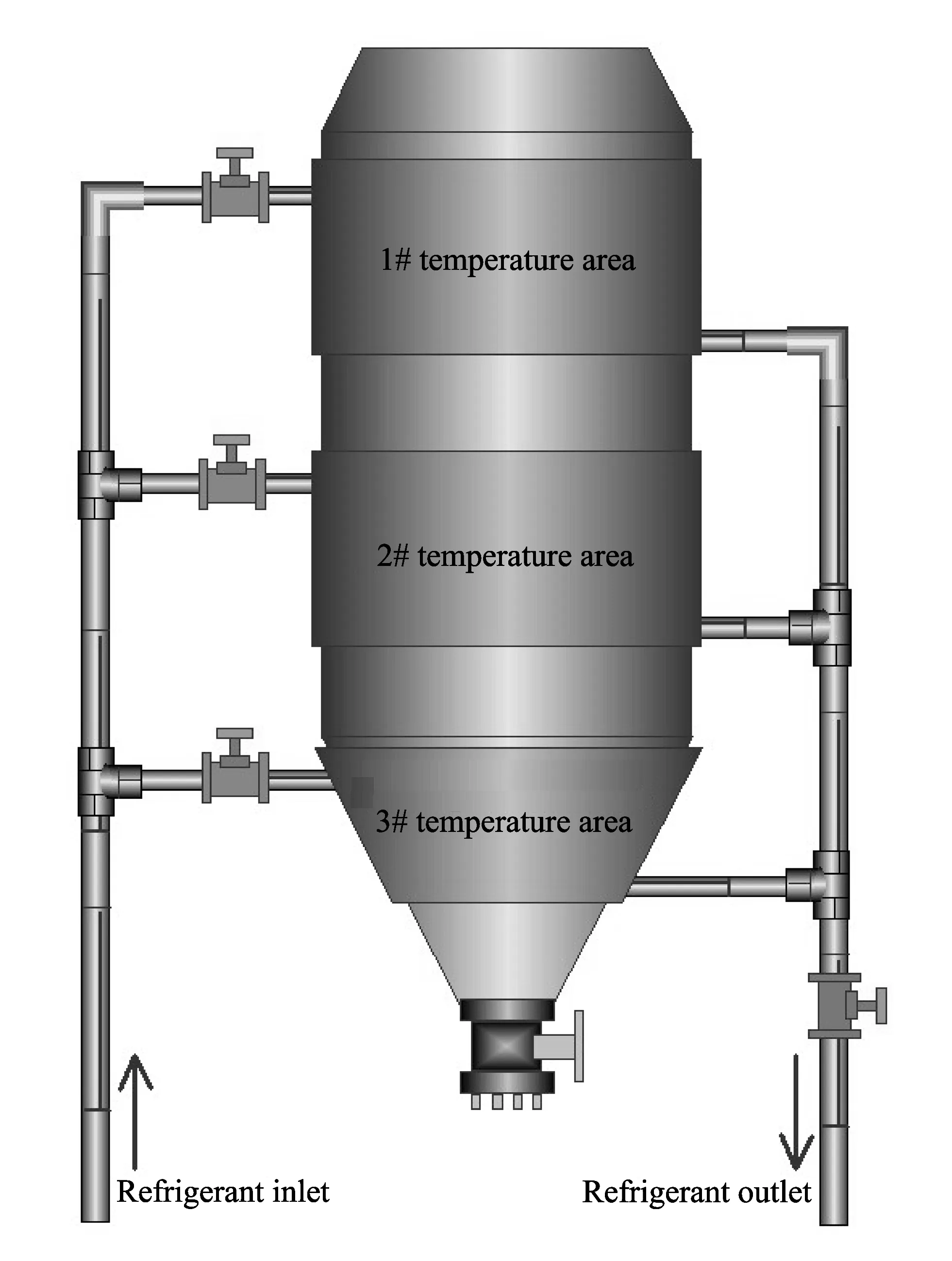
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of beer fermentation tank with three temperature areas and pipelines
The control accuracy of fermentation temperature in the entire process determines success or failure of the beer fermentation.Therefore, the temperature must be strictly controlled in the whole fermentation cycle.The typical temperature control curve of fermentation process is shown in Fig.2.
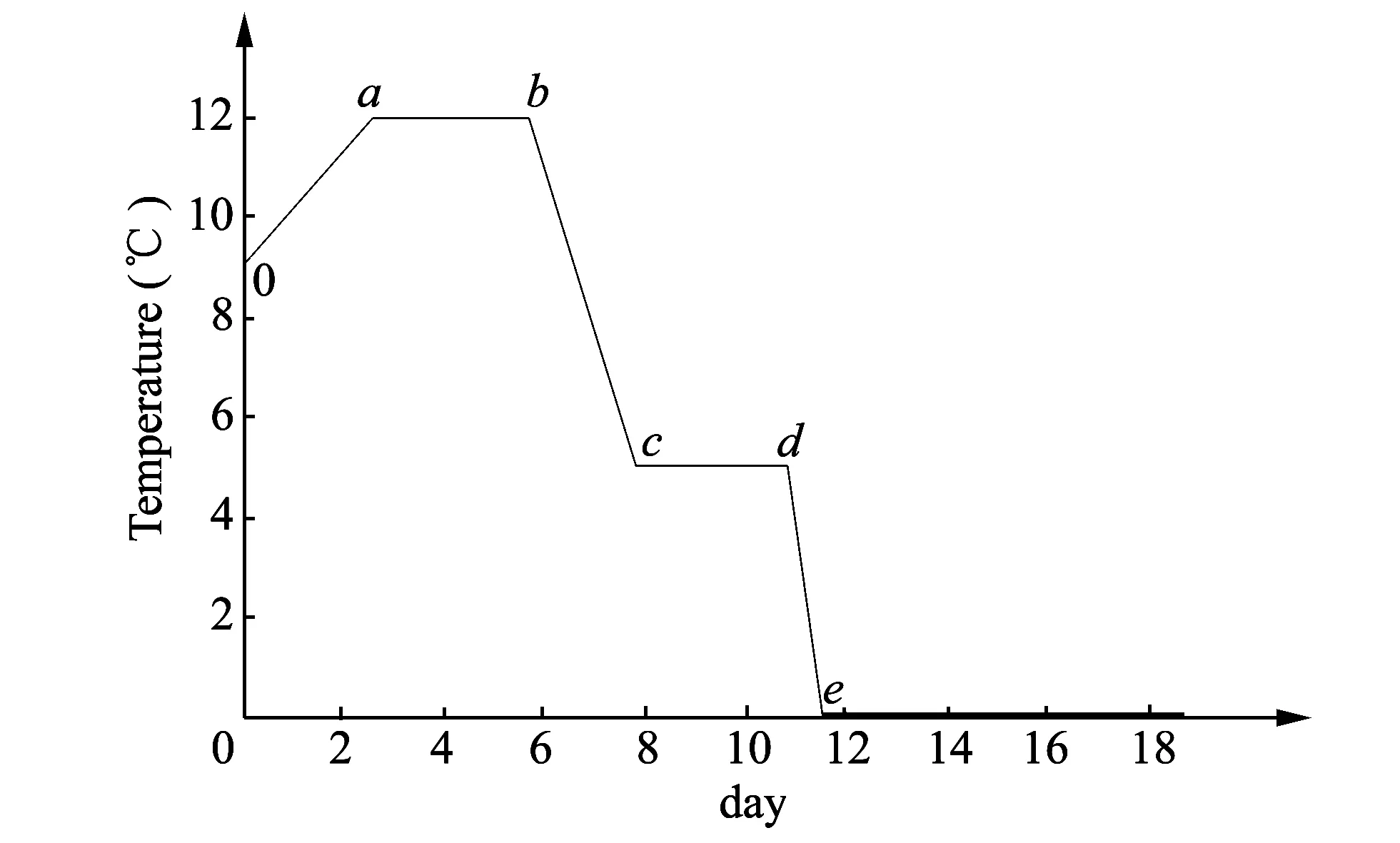
Fig.2 Typical temperature curve of fermentation process
2 Realization of the system
The principle diagram of beer fermentation control system is shown in Fig.3.D(z) is pulse transfer function of the controller,F(z) is the transfer function of decoupling compensation matrix,H(s) is the zero-order hold andG(s) is the mathematical model of control object.
2.1 Mathematical model of controlled object
Based on practical experience and system identification, the author of Ref.[2] regarded one of temperature areas' mathematical models as a first-order inertial system with delay, which is defined as
(1)
whereGij(s) is the transfer function of valvejto temperature areai;Tijis the inertial time constant;Kijis the ratio of coefficient; andτijis the delay time constant.
Transfer function of zero-order hold is
(2)
According to Fig.2 and Eq.(1) and Eq.(2), it can be got as
(3)
The differential equation can be obtained as[3]
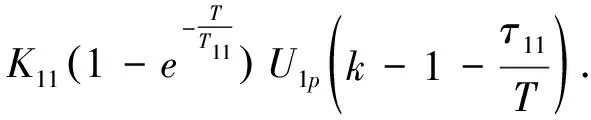
(4)
Using the same method, other differential equations are obtained and then the total output equations are
(5)
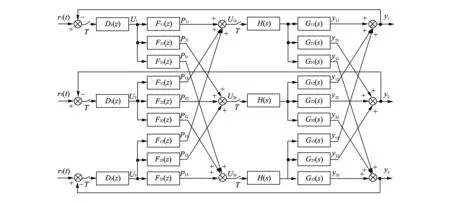
Fig.3 Principle diagram of beer fermentation control system
2.2 Decoupling control algorithm
Due to the mutual coupling between different temperature areas, the temperature of one area can not only be directly affected by its own control variable, but also indirectly influenced by the other two control variables[4].Therefore, using control algorithm, output should be decoupled[5].In this paper, diagonal matrix decoupling algorithm is used[6]based on the fact that the product of controlled object’s characteristic matrix and decoupling matrix is a diagonal matrix as
(6)
According to Eq.(6),F(z) can be written and calculated as
The calculation process is very cumbersome, so it can be completed by Matlab[7].
2.3 Temperature control algorithm
Temperature control algorithms for temperature areas 1,2 and 3 of virtual beer fermentation system are the same, where taking temperature area 1 as an example.
In this paper, digital incremental proportion integration differentiation (PID) control algorithm is used, and it is described as[1].
Δu1(k)=q0e1(k)+q1e1(k-1)+q2e1(k-2),
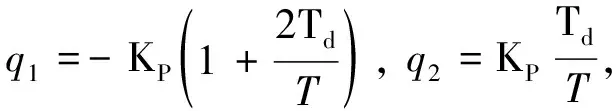
(8)
where KPis proportionality constant, Tiis integration time constant, Tdis differential time constant,e1(k) is temperature deviation value of current time,e1(k-1) is temperature deviation value of last sampling time ande1(k-2) is temperature deviation value of last two sampling times.The final output controlled variable at current time is
u1(k)=u1(k-1)+Δu1(k).
(9)
P11(k) is got by putting Eq.(9) intoF11(z);P21(k),F21(z);P31(k),F31(z).The others can be got using the same method.Finally, the total output equations are
(10)
3 Simulation result
The simulation program is completed by VB[8]with appropriate constants.The simulation results are displayed by Kingview software[9]via dynamic data exchange (DDE) connection, including animation interface, real-time temperature curve and historical temperature curve.
Fig.4 is the historical temperature curve.It can be seen that the error of temperature curve is within the allowance, so the basic requirements of the system are met.
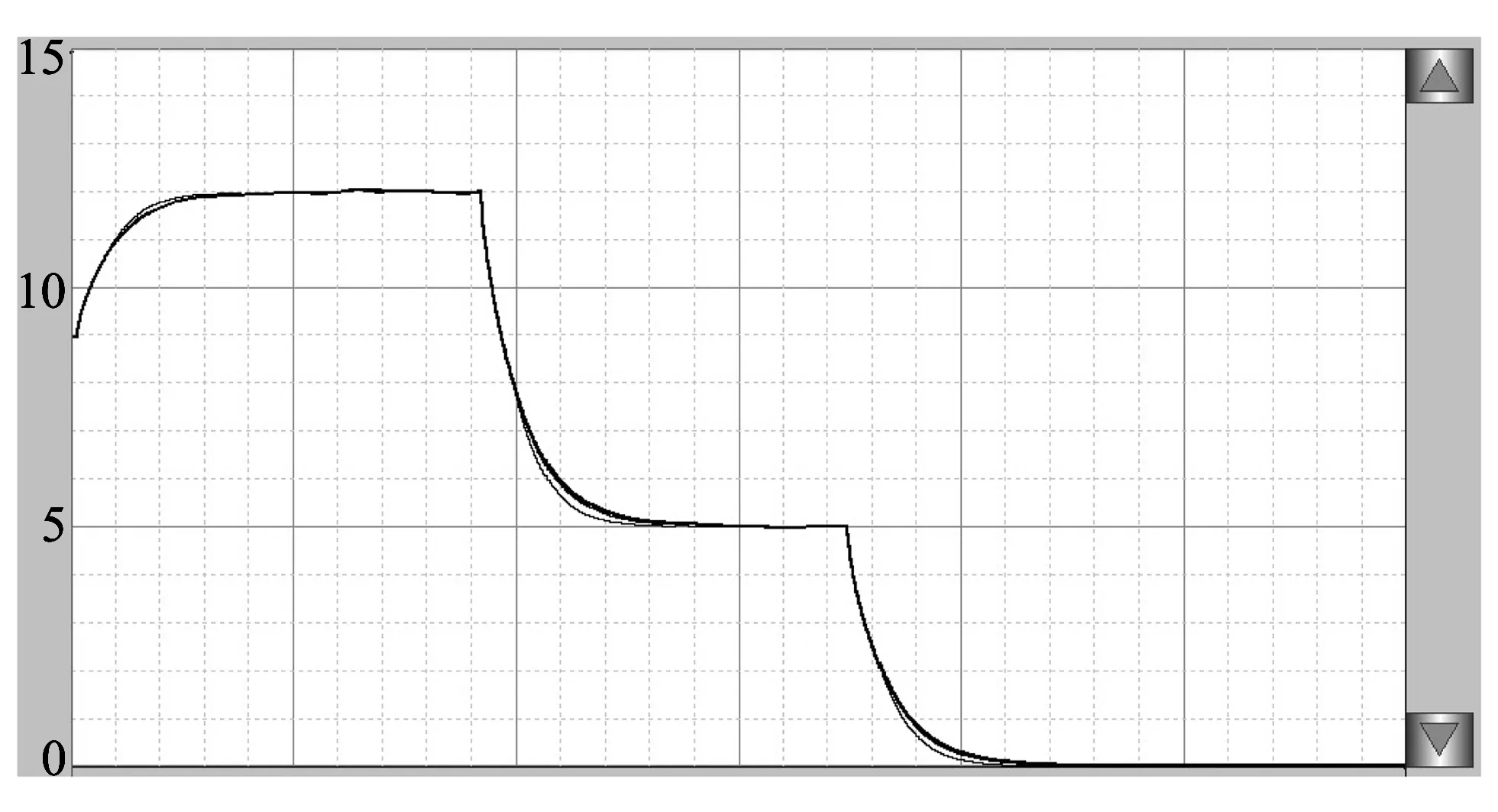
Fig.4 Historical temperature curve
4 Conclusion
In this paper, a temperature control method for beer fermentation system is presented.Based on digital incremental PID control algorithm which controls transmission quantity to controlled object after diagonal matrix decoupling.The simulation system is completed by VB and Kingview software.The simulation results show that the in the laboratory.So it has the features of good security and low cost, and is very suitable for experimental teaching.
[1] YU Hai-sheng.Computer control technology.Beijing: Machinery Industry Press, 2007: 105-106, 298-299.
[2] DOU Xiu-hua.Study of Smith compensation distributed for predictive control in beer fermentation temperature.Masteer thesis.Qingdao: Qingdao University of Science and Technology, 2009.
[3] DING Yu-mei, GAO Xi-quan.Digital signal processing.Xi’an: Xidian University Press, 2003: 175.
[4] WANG Ming, QING Xiao-zhen.Automatic control principle.Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2005: 16-17.
[5] LI Yun-zhou, TAO An-li.Study on hardwre-in-loop simulation of twin-screw extruder system.Journal of Measurement Science and Instrumentation, 2010, 1(S1): 90-94.
[6] FANG Kang-ling.Process control system.Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology Press, 2002: 195-197.
[7] WANG Zheng-lin, WANG Sheng-kai.Matlab/Simulink control system simulation.Beijing: Electronic Industry Press, 2011.
[8] LIU Pei-zeng, LU Wei-min, YANG Zhi-qing.Visual basic program design brief tutorial.Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2004: 22-34.
[9] Kingview version 6.0 use manual.Beijing Wellin Control Technology Developmen Co., Ltd, 2001.
 Journal of Measurement Science and Instrumentation2014年1期
Journal of Measurement Science and Instrumentation2014年1期
- Journal of Measurement Science and Instrumentation的其它文章
- Error separation in CMM coordinate metrology
- Design and theoretical analysis of test system for propellants’ gas pressure in warhead
- A new probe for atmospheric electric field mill
- Experimental analysis of high temperature capacitance variance of MLCC
- Application of RLS adaptive filtering in signal de-noising
- QIM digital watermarking based on LDPC code and message passing under scaling attacks
