超敏C反应蛋白及rs1205基因多态性与脑梗死的相关性研究
徐福平,薛 浩
(山东省淄博市中心医院,山东 淄博 255036)
超敏C反应蛋白及rs1205基因多态性与脑梗死的相关性研究
徐福平,薛 浩
(山东省淄博市中心医院,山东 淄博 255036)

目的 分析并评价超敏C反应蛋白(hs-CRP)及rs1205基因多态性与脑梗死的相关性。方法 将113例中老年脑梗死患者作为观察组,113例健康体检者作为对照组。通过免疫透射比浊法测定hs-CRP含量;同时以聚合酶链式反应(PCR)及限制性片段长度多态(RFLP)方法测定rs1205基因的多态性;采用美国国立卫生院神经功能缺损评分(NIHSS)量表评定神经功能。分析各指标的关系。结果 2组的基因型频率与等位基因的分布趋势差异无统计学意义(P均>0.05);重度患者的hs-CRP与log CRP含量均显著高于轻、中度患者(P均<0.05);rs1205基因型与脑梗死病情程度未见明显关联(P>0.05)。结论 hs-CRP含量与脑梗死患者病情密切相关,而rs1205基因多态性与脑梗死发病之间未见显著相关性。
脑梗死;超敏C反应蛋白;rs1205基因多态性;基因频率
C反应蛋白(CRP)是在机体受损、发生感染或出现炎症时引起血浆浓度急剧上升的重要急性期蛋白[1]。一直以来CRP被视为重要的非特异的炎症标志物,但近年来的研究显示,CRP与机体炎症与动脉粥样硬化等心血管疾病过程密切相关,炎症在缺血、动脉粥样硬化等疾病进展过程中发挥重要作用[2]。大量文献报道显示,单独测定血清CRP含量能够指示或预测首发与再发脑血管事件[3-5]。本研究对比观察了老年脑梗死患者与健康体检者的超敏C反应蛋白(hs-CRP)水平及rs1205基因多态性情况,旨在评价hs-CRP及rs1205基因多态性与脑梗死的相关性。
1 临床资料
1.1 一般资料 选择2012年1月—2013年8月我院神经内科收治113例中老年脑梗死患者作为观察组,均满足全国第四届脑血管病学术会议通过的临床诊断标准,同时经脑CT/MRI进一步确诊。其中男79例,女34例;年龄38~91(64.3±12.1)岁;病程均≤3 d;按照美国国立卫生研究院卒中量表(NIHSS)进行病情分级评定:轻度(NIHSS分<6分)63例,中度(NIHSS分6~13分)39例,重度(NIHSS分>14分)11例。体质量指数(BMI)为(24.32±6.38)kg/m2。伴有脑卒中家族史22例,伴有高血压病史94例,伴有糖尿病史24例,伴有冠心病史31例,有吸烟史49例,有饮酒史23例。另选同期我院门诊113例体检者作为对照组,其中男69例,女44例;年龄47~82(61.9±10.4)岁;BMI(23.92±8.31)kg/m2;有脑卒中家族史1例,有高血压病史27例,有冠心病史13例,有糖尿病史1例;有吸烟史17例,有饮酒史10例。2组均排除伴有严重肝肾功能不全者,脑出血、周围血管疾病、血液病、大动脉炎、结核、重症肺部感染、恶性肿瘤以及曾接受器官移植者。2组年龄、性别、BMI比较差异无统计学意义(P均>0.05),存在可比性;但在常见的危险因素,包括脑卒中家族史、高血压病史、糖尿病史、冠心病史、吸烟史以及饮酒史等,观察组显著高于对照组(P均<0.05)。
1.2 血清hs-CRP含量测定 全部受检者清晨空腹(脑梗死患者在发病24 h内,少数患者发病在3 d内)抽取2 mL静脉血,使用荷兰Vital全自动生化分析仪进行分析,通过免疫透射比浊法测定hs-CRP含量。
1.3 CRP基因型分析 抽取5 mL肘静脉血,选择低渗溶血及酚氯仿法提取外周血白细胞基因组DNA,TE缓冲液溶解保存;通过聚合酶链式反应(PCR)与限制性片段长度多态性(RFLP)分析rs1205基因多态性,引物由宝生物工程(大连)有限公司合成。引物序列:上游引物为5’-TCGAGGTTCCTGAAGTCACA-3’,下游引物为5’-AACAAAGGCCCAGAGACAGA-3’,内切酶CC型为149 bp和128 bp,CT型为275 bp,149 bp,128 bp,TT型为275 bp和128 bp。25 μL的反应体系包括:10×PCR缓冲液2.5 μL,1 μL 25 mmol/L Mg2+,25 nmol/L 4×dNTP 1 μL,10 μmol/L上、下游引物各1 μL,1 μL基因组DNA模板,0.5 μL Taq DNA聚合酶5 IU/μL,2.5 μL二甲基亚砜。扩增程序:95 ℃预变性5 min,95 ℃变性30 s,54 ℃退火50 s,72 ℃延伸55 s,共22个循环,最后72 ℃延伸10 min,4 ℃保存待用。限制性内切酶酶切反应体系总体积20 μL包括:10 μL PCR扩增产物,2 μL 10×Buffer,2 IU内切酶,在37 ℃条件下酶切14 h。将pUC19DNA/MspI酶解片段作为DNA片段的标准物,配置浓度为20%的聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳分离,结果见图1。
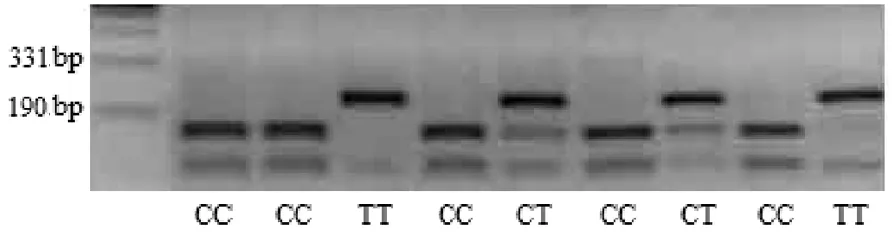
图1 rs 1205基因酶切片段20%的聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳分离结果
2 结 果
2.1 2组基因型结果对比 在全部受检者中,rs1205基因型的频率依次为CC型占12.7%,CT型占48.7%,TT型占34.1%;等位基因C频率为0.416,等位基因T频率为0.584,符合Hardy-Weinberg平衡(2=0.017,P=0.891)。2组受检者的基因型频率与等位基因的分布趋势差异无统计学意义(P均>0.05)。见表1。

表1 2组rs 1205基因型及等位基因频率比较 例(%)
2.2 不同CRP基因型患者hs-CRP含量情况 rs1205的CC、CT、TT 3种基因型log CRP含量为(0.355±0.599)lg mg/L、(0.249±0.601)lg mg/L及(0.168±0.641)lg mg/L,三者基因型的血清lg CRP含量依次递降,但三者比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。
2.3 观察组不同病情患者CRP含量比较 观察组重度患者的hs-CRP与lg CRP含量均显著高于轻、中度患者(P均<0.05)。见表2。
表2 不同病情脑梗死患者hs-CRP含量比较±s)
注:①与重度比较,P<0.05。

表3 hs-CRP基因型与脑梗死病情关系 例
3 讨 论
目前已证实动脉粥样硬化是脑梗死的基本病因,而且脑梗死是一个慢性炎性过程[6]。Nozue等[7]的研究显示,性别、年龄及体质量等指标能够影响血清CRP含量。CRP能够激活补体同时增强吞噬细胞的吞噬能力进而发挥调理功能,有效清除入侵机体的病原菌,修复并清理损伤、坏死以及程序化死亡的组织细胞,在天然免疫过程中起保护作用。CRP已被认为是心血管疾病最敏感的预示因子或危险因子[8]。rs1205单核苷酸多态性(SNP)是CRP最为常见的多态性之一,其位于CRP基因的3’端非翻译区[9]。不同研究机构关于rs1205影响hs-CRP含量的研究结果各不相同[10]。本研究结果显示带有rs1205T等位基因的受检者血清hs-CRP含量低,但与CRP含量之间无明显的相关性,分析这可能是由于CRP的含量变化由诸多因素决定的,而且遗传方面的影响不大[11]。不同种族、不同地区人群的rs1205的分布各不相同[12]。通过对NCBI中SNP数据库查询显示,欧洲人rs1205T等位基因频率为0.33,而非洲人rs1205T等位基因频率为0.15;黄种人(北京地区)则为0.56。在本研究中,rs1205T单核苷酸多态性位点共有CC、CT及TT 3种基因型,其中等位基因T的频率为0.584[13-14]。本研究所得等位基因T的分布频率显著高于欧洲人,且与中国北京黄种人的分布频率基本相似[15]。这表明T等位基因频率在不同人种的分布是不同的。CRP含量与缺血性脑梗死的发病密切相关, 而关于CRP基因多态性与缺血性脑梗死的相关性却并无定论[16-18]。Di Napoli等[19]分析了4个人类CRP 基因单核苷酸多态性基因型rs1341662,rs1130864,rs1800947以及rs1205后发现,仅rs1800947与缺血性脑梗死有明显的相关性。Tanno等[20]对4个单核苷酸多态性位点(rs1205,rs3093075,rs1800947以及rs1130864)进行分析,结果显示无相关的SNP位点或SNP单体型与缺血性脑梗死具有关联,但3个SNP位点(rs1130864、rs1800947以及rs3093075)与微血管闭室密切相关。Park等[21]的研究亦未见rs1205与缺血性脑梗死具有相关性,但单体型H3与缺血性脑梗死密切相关。本研究未对脑梗死类型进行细致划分及构建单体型,结果显示重度脑梗死患者的hs-CRP含量明显高于轻度与中度患者,rs1205基因型与脑梗死及脑梗死病情的严重程度均无明显相关性,与以往报道的结果相符。总之,本研究结果显示hs-CRP含量与脑梗死患者病情密切相关,rs1205基因多态性与脑梗死发病之间未见明显相关性。
[1] Tu WJ,Zhao SJ,Liu TG,et al. Combination of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and homocysteine predicts the short-term outcomes of Chinese patients with acute ischemic stroke[J]. Neurol Res,2013,35(9):912-921
[2] Arikanoglu A,Yucel Y,Acar A,et al. The relationship of the mean platelet volume and C-reactive protein levels with mortality in ischemic stroke patients[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci,2013,17(13):1774-1777
[3] Ahmadi-Abhari S,Luben RN,Wareham NJ,et al. Seventeen year risk of all-cause and cause-specific mortality associated with C-reactive protein,fibrinogen and leukocyte count in men and women:the EPIC-Norfolk study[J]. Eur J Epidemiol,2013,28(7):541-550
[4] 邓可,肖志杰,赵水平,等. 血清超敏C-反应蛋白水平及CRP 1059G/C基因多态性与脑梗死的相关性[J]. 临床神经病学杂志,2009,22(6): 413-415
[5] 钱铁镛. 高敏C反应蛋白、脂联素、同型半胱氨酸与2型糖尿病大血管病变的相关性研究[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志,2010,19(4):403-404
[6] Abubakar SA,Okubadejo NU,Ojo OO,et al. Relationship between admission serum C-reactive protein and short term outcome following acute ischaemic stroke at a tertiary health institution in Nigeria[J]. Niger J Clin Pract,2013,16(3):320-324
[7] Nozue T,Fukui K,Yamamoto S,et al. C-Reactive protein and future cardiovascular events in statin-treated patients with angina pectoris:the extended TRUTH study[J]. J Atheroscler Thromb,2013,20(9):717-725
[8] Dahan E,Dichtwald S,Amar E,et al. Low plasma C-reactive protein level as an early diagnostic tool for heatstroke vs central nervous system-associated infection in the ED[J]. Am J Emerg Med,2013,31(8):1176-1180
[9] Oda E. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein and white blood cell c-ount equally predict development of the metabolic syndrome in a Japanese health screening population[J]. Acta Diabetol,2013,50(4):633-638
[10] Rallidis LS,Tellis CC,Lekakis J,et al. Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A(2) bound on high-density lipoprotein is associated with lower risk for cardiac death in stable coronary artery disease patients:a 3-year follow-up[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol,2012,60(20):2053-2060
[11] Kral M,Skoloudik D,Sanak D,et al. Assessment of relationship between acute ischemic stroke and heart disease-protocol of a prospective observational trial[J]. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub,2012,156(3):284-289
[12] Tang WH,Hartiala J,Fan Y,et al. Clinical and genetic association of serum paraoxonase and arylesterase activities with cardiovascular risk[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol,2012,32(11):2803-2812
[13] Elliott P,Chambers JC,Zhang W,et al. Genetic loci associated with C-reactive protein levels and risk of coronary heart disease[J]. JAMA,2009,302(1):37-48
[14] Crawford DC,Sanders CL,Qin X,et al. Genetic variation is associated with C-reactive protein levels in the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey[J]. Circulation,2006,114(23):2458-2465
[15] Shen C,Sun X,Wang H,et al. Association study of CRP gene and ischemic stroke in a Chinese Han population[J]. J Mol Neurosci,2013,49(3):559-566
[17] Tsai NW,Lee LH,Huang CR,et al. The association of statin therapy and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein level for predicting clinical outcome in acute non-cardioembolic ischemic stroke[J]. Clin Chim Acta,2012,413(23/24):1861-1865
[18] Leonards CO,Ipsen N,Malzahn U,et al. White matter lesion severity in mild acute ischemic stroke patients and functional outcome after 1 year[J]. Stroke,2012,43(11):3046-3051
[19] Di Napoli M,Godoy DA,Campi V,et al. C-reactive protein in intracerebral hemorrhage:time course, tissue localization, and prognosis[J]. Neurology,2012,79(7):690-699[20] Tanno K,Ohsawa M,Onoda T,et al. Poor self-rated health is significantly associated with elevated C-reactive protein levels in women,but not in men,in the Japanese general population[J]. J Psychosom Res,2012,73(3):225-231
[21] Park HE,Cho GY,Chun EJ,et al. Can C-reactive protein predict cardiovascular events in asymptomatic patients Analysis based on plaque characterization[J]. Atherosclerosis,2012,224(1):201-207
The relevance study of hyper-sensitive C-reactive protein genes & rs1205 gene polymorphism and cerebral infarction
Xu Fuping,Xue Hao
(The Center Hospital of Zibo,Zibo 255036,Shandong China)
Objective: It is to analyze and evaluate the relevance of hyper-sensitive C-reactive protein(hs-CRP) & rs1205 gene polymorphism and cerebral infarction.Methods 113 patients with elderly cerebral infarction were selected as observation group, and 113 healthy controls were used as control group.The content of hs-CRP levels was determined by immune transmission turbidimetry; At the same time,rs1205 gene polymorphism was examined by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) methods;Nerve function was evaluated by neurological deficit score of the National Institutes of Health of USA. The relationships among every indexes were analyzed. Results Genotype frequency and the distribution trend of alleles of the patients with cerebral infarction of observation group and the subjects of control group were the same, the differences were not significant(P>0.05);hs-CRP and log CRP levels of severe patients were significantly higher than those of mild and moderate patients(P<0.05);There was no obvious correlation between rs1205 gene type and cerebral infarction disease degree. Conclusion The content of hs-CRP is closely related with states of patients with brain infarction, while rs1205 gene polymorphism had no significant relationship with the occurrence of cerebral infarction.
cerebral infarction;hyper-sensitive C-reactive protein genes; gene polymorphism;gene frequency
徐福平,女,副主任医师,主要从事神经内科工作。
10.3969/j.issn.1008-8849.2014.35.007
R743.3
A
1008-8849(2014)35-3898-04
2014-06-01

