转录因子Twist及其相关因子N-cadherin在胰腺癌中的表达及意义
张喆 陈少夫
·论著·
转录因子Twist及其相关因子N-cadherin在胰腺癌中的表达及意义
张喆 陈少夫
目的探讨转录因子Twist及其下游相关因子N-cadherin在人胰腺癌组织中的表达及与肿瘤临床病理特征、患者预后的关系。方法采用免疫组化MaxVision两步法分别检测62例胰腺癌组织和10例正常胰腺组织中Twist及N-cadherin的表达,分析二者表达与临床病理特征及患者预后的相关性。结果Twist在胰腺癌组织的阳性表达率明显高于正常胰腺组织(96.8%比30.0%,P<0.01),N-cadherin在胰腺癌组织的阳性表达率也明显高于正常胰腺组织(75.8%比0,P<0.01),但两者的表达无明显相关性(r=0.100,P=0.441)。Twist及N-cadherin表达与胰腺癌TNM分期、淋巴结转移、门静脉或神经浸润、肿瘤部位均密切相关(P值均<0.05),与患者年龄、性别及肿瘤分化程度均无明显相关性(P值均>0.05)。胰腺癌患者术后生存期随Twist表达的增强而缩短,但与N-cadherin表达强度无明显相关性。TNM分期、Twist表达强度是影响胰腺癌患者预后的独立因素。结论胰腺癌组织Twist及N-cadherin均高表达,其表达与胰腺癌的恶性生物学行为相关,Twist的异常表达可能是评估胰腺癌患者预后的潜在指标。
胰腺肿瘤; Twist转录因子; N-cadherin
上皮-间质间转化(epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, EMT)和癌细胞脱离原发灶是恶性肿瘤完成转移的关键步骤[1-2]。EMT过程中所表现出的细胞极性紊乱、细胞间黏附力降低以及细胞迁徙能力增强等特征与N-cadherin表达增加相关[3]。N-cadherin的异常表达还与调节肿瘤的抗凋亡信号转导有关[4]。近年来研究表明,转录因子Twist参与了肿瘤的形成、侵袭及转移的过程[5],还与恶性肿瘤的耐药密切相关[6]。本研究检测胰腺癌组织Twist、N-cadherin的表达,探讨其与胰腺癌临床病理特征及患者预后的关系。
材料与方法
一、研究对象
收集中国医科大学附属盛京医院2008年1月至2010年6月胰腺癌手术切除后石蜡包埋标本62例,均经病理证实为胰腺导管腺癌。患者术前未接受任何抗癌治疗。另选取十二指肠肿物切除术所获得的10例正常胰腺组织作为对照。随访至2011年12月31日,至截止随访日期,共病死57例,存活5例,无失随访者,生存期从术后算起。
二、Twist、N-cadherin蛋白检测
采用快捷免疫组化MaxVision两步法检测,试剂盒购自福州迈新生物技术开发有限公司,按说明书操作。兔抗人SC-15393 Twist(H-81)多抗购自美国SantaCruz生物技术公司,鼠抗人N-cadherin(ZM-0094)单抗购自北京中杉金桥生物技术公司。工作浓度均为1∶100。
Twist阳性表达于细胞质或细胞核,呈浅黄到棕褐色。N-cadherin阳性表达于细胞质或细胞膜,呈棕黄色到棕褐色。每张切片随机选取10个400倍视野,每个视野计数100个细胞,计算阳性细胞比例,阳性细胞占0、1%~49%、50%~70%、>70%分别计为0~3分,即-、+、++、+++。
三、统计学处理
数据采用SPSS13.0统计软件分析。计数资料采用χ2检验和Fisher精确概率法,阳性表达与肿瘤临床病理特征间的相关性分析采用Spearman等级相关分析。单因素生存分析采用Kaplan-Meier法和Log-rank检验。多因素生存分析采用Cox比例风险模型。P<0.05为差异具有统计学意义。
结 果
一、Twist、N-cadherin在胰腺癌及正常胰腺组织的表达
Twist在胰腺癌组织的阳性表达率为96.8%(60/62),其中表达+、++、+++者分别为30、26、4例;在正常胰腺组织的阳性表达率为30%(3/10),其中表达+、++、+++者分别为2、1、0例,二者差异具有统计学意义(χ2=35.265,P<0.01,图1)。N-cadherin在胰腺癌组织的阳性表达率为75.8%(47/62),其中表达+、++、+++者分别为25、16、6例;在正常胰腺组织中均为阴性表达(0/10),二者差异具有统计学意义(χ2=21.832,P<0.01,图1)。
胰腺癌组织Twist与N-cadherin的表达无明显相关性(r=0.100,P=0.441,表1)。
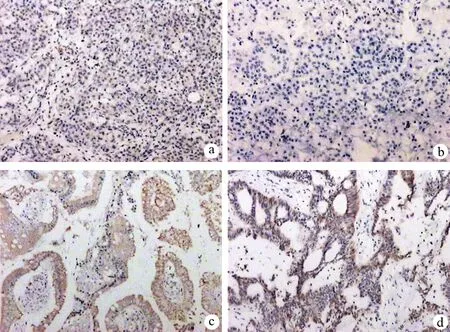
图1Twist、N-cadherin在正常胰腺组织(a、b)及胰腺癌组织(c、d)的表达(×100、200)

表1 胰腺癌组织Twist表达与N-cadherin表达的相关性
二、Twist、N-cadherin表达与临床病理特征的关系
Twist蛋白表达与胰腺癌TNM分期、淋巴结转移、门静脉或神经浸润、肿瘤发生部位密切相关(P值均<0.05)。N-cadherin蛋白表达也与TNM分期、淋巴结转移、门静脉或神经浸润、肿瘤发生部位密切相关(P值均<0.05)。两种表达与患者年龄、性别及肿瘤分化程度均无明显相关性(P值均>0.05,表2)。
三、Twist、N-cadherin表达与患者术后生存期的关系
Twist-、+、++、+++表达组患者的术后平均生存期分别为24、13.6、4.1、3.3个月,中位生存期分别为24、14、4.3、3.7个月,患者生存期随Twist表达的增强而缩短(P<0.05)。N-cadherin表达-、+、++、+++患者的平均生存期分别为10.2、9.6、7.9、8.0个月,中位生存期分别为8.5、10.3、6.3、11.0个月,患者术后生存期与N-cadherin表达强度无明显相关性(P>0.05)。
经单因素分析,胰腺癌肿瘤部位、TNM分期、淋巴结转移、远处脏器转移、门静脉或神经浸润、Twist表达强度、切缘阳性与胰腺癌患者术后生存率均显著相关(P值均<0.05)。将以上7个指标纳入Cox比例风险模型进行多因素回归分析,影响胰腺癌患者预后的独立因素是TNM分期、Twist表达强度(P值均<0.05,图2,表3)。
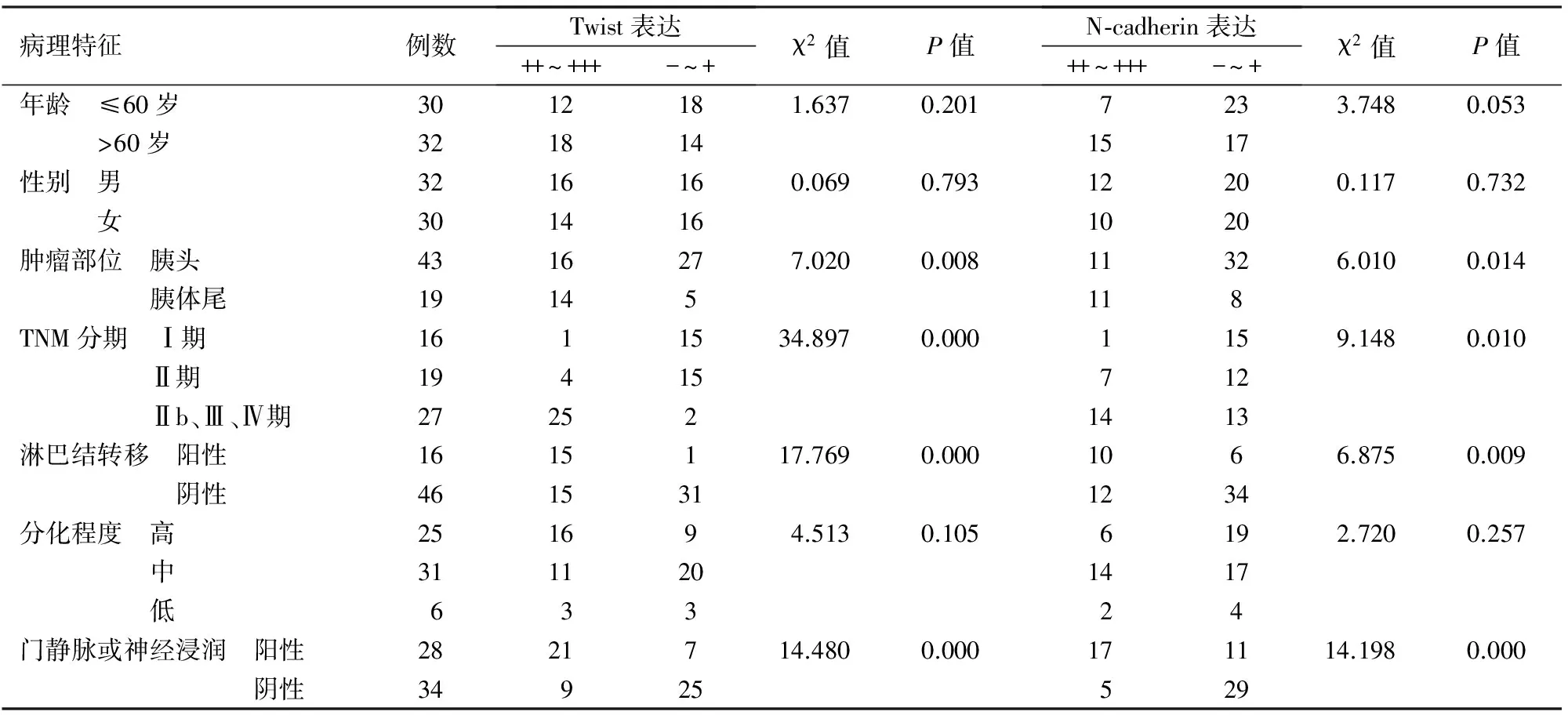
表2 胰腺癌Twist、N-cadherin表达与临床病理特征的关系
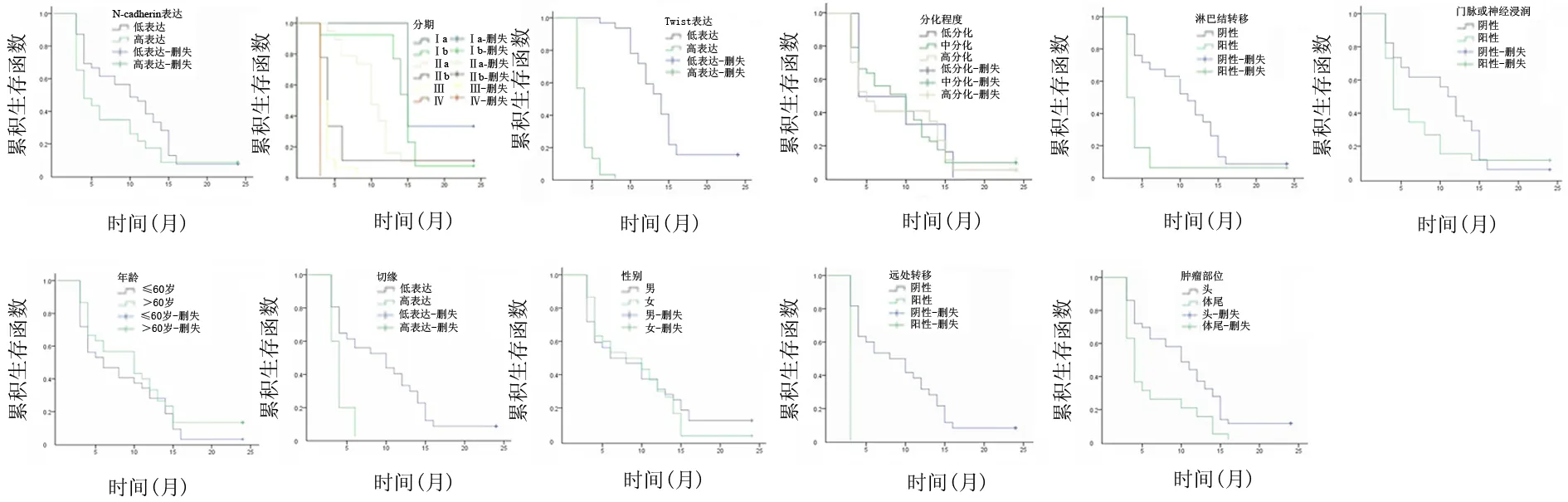
图2 各病理参数对患者术后生存期的影响
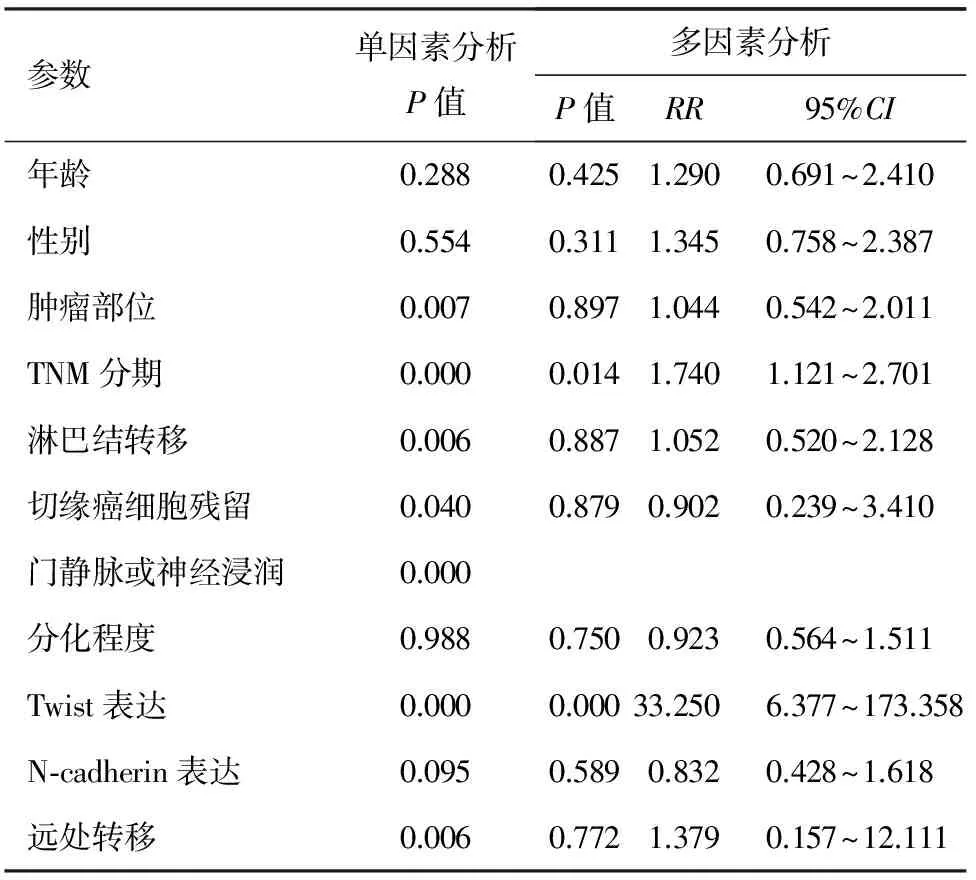
参数单因素分析P值多因素分析P值RR95%CI年龄0.2880.4251.2900.691~2.410性别0.5540.3111.3450.758~2.387肿瘤部位0.0070.8971.0440.542~2.011TNM分期0.0000.0141.7401.121~2.701淋巴结转移0.0060.8871.0520.520~2.128切缘癌细胞残留0.0400.8790.9020.239~3.410门静脉或神经浸润0.000分化程度0.9880.7500.9230.564~1.511Twist表达0.0000.00033.2506.377~173.358N⁃cadherin表达0.0950.5890.8320.428~1.618远处转移0.0060.7721.3790.157~12.111
讨 论
EMT与乳腺癌、胃癌、大肠癌等多种恶性肿瘤的侵袭、转移及预后密切相关[7-9]。EMT的重要特征之一是作为间质标志的N-cadherin表达上调[10]。本研究结果显示,胰腺癌组织N-cadherin阳性表达率较正常胰腺组织明显升高,其高表达与胰腺癌的TNM分期、淋巴结转移、门静脉或神经浸润等密切相关,提示N-cadherin不仅与胰腺癌的发生有关,而且在胰腺癌侵袭转移过程中起重要作用。但N-cadherin的表达与胰腺癌患者术后生存率无关,提示N-cadherin在胰腺癌的浸润转移过程中可能并非起主导作用。
Twist在恶性肿瘤的侵袭转移过程中起重要作用[11]。有研究表明,胃癌组织中Twist的阳性表达率较正常胃黏膜组织明显升高[8]。本研究结果显示,Twist在胰腺癌组织的阳性表达率较正常胰腺组织明显升高,其表达与胰腺癌TNM分期、淋巴结转移、门静脉或神经浸润等密切相关,其阳性表达强度与胰腺癌患者术后生存期密切相关,提示Twist表达的上调不仅与胰腺癌的发生密切相关,还可以使胰腺癌细胞获得更为恶性的生物学行为,促进肿瘤的播散和转移。
N-cadherin是Twist的下游相关因子,Twist的过量表达可上调N-cadherin的表达[7]。但有研究报道,浸润性乳腺癌组织中Twist与N-cadherin表达呈显著负相关[12]。本研究结果显示,胰腺癌组织Twist与N-cadherin的表达无显著相关性,说明Twist与N-cadherin表达的相关性在不同组织中是不一致的,其原因有待于进一步探讨。
[1] Gotzmann J, Mikula M, Eger A,et al.Molecular aspects of epithelial cell plasticity:implications for local for local tumor invasion and metastasis.Mutat Res,2004,566:9-20.
[2] Thiery JP.Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in tumor progression.Nat Rev Cancer, 2002,2:442-454.
[3] Martin TA, Goyal A, Watkins G, et al.Expression of the transcription factors snail,slug,and twist and their clinical significance in human breast. Cancer, 2005,12:488-496.
[4] Tran NL, Adams DG, Vaillancourt RR, et al.Signal transduction from N-cadherin increases Bcl-2.Regulation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway by homophilic adhesion and actin cytoskeletal organization. J Biol Chem,2002,277:32905-32914.
[5] Kang Y,Massagué J.Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions:twist in development and metastasis.Cell, 2004,118:277-279.
[6] Zhou WL,Wang Y,Zhou XL,et al.Short interfering RNA directed against TWIST,a novel zinc finger transcription factor,increases A549 cell sensitivity to via MAPK/mitochondrial pathway.Biochem Biophys Res Commum,2008,369:1098-1102.
[7] Kasimir-Bauer S,Hoffmann O,Wallwiener D,et al.Expression of stem cell and epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers in primary breast cancerpatients with circulating tumor cells. Breast Cancer Res, 2012,14:R15.
[8] Rosivatz E, Becker I, Specht K, et al. Differential expression of the eithelial-mesenchymal transitions regulators snail,SIP1,and twist in gastric cancer.Am J Pathol, 2002,161:1881-1891.
[9] Loboda A, Nebozhyn MV,Watters JW,et al. EMT is the dominant program in human colon cancer.BMC Med Genomics,2011,4:9.
[10] De Wever O,Pauwels P,De Craene B,et al.Molecular and pathological signatures of epithelial-mesenchymal transitions at the cancer invasion front.Histochem Cell Biol,2008,130:481-494.
[11] Karreth F,Tuveson DA.Twist induces an eithelial-mesenchymal transition to facilitate tumor metastasis.Cancer Biol Ther,2004,3:1058-1059.
[12] Hazan RB,Qiao R,Keren R,et al.Cadherin switch in tumor progression.Ann N Y Acad Sci,2004,1014:155-163.
ExpressionandroleofTwistandN-cadherininpancreaticcancer
ZHANGZhe,CHENShao-fu.
TheSecondDepartmentofGastroenterology,ShengjingHospital,ChinaMedicalUniversity,Shenyang110004,China
Correspondingauthor:CHENShao-fu,Email:csf196211@yahoo.com.cn
ObjectiveTo investigate the expression of Twist and N-cadherin in pancreatic cancer, and to study its relationship with clinicopathological parameters and patients′ prognosis.MethodsThe expression of the Twist and N-cadherin in 62 tissue samples from patients with pancreatic ductal adencocarcinoma and 10 normal pancreatic tissue samples was determined by using immunohistochemistry MaxVision two step method,and the relationship with clinicopathological parameters and patients′ prognosis was analyzed.ResultsThe positive expression rate of Twist in pancreatic cancer was higher than that of normal pancreatic tissues (96.8%vs. 30%,P<0.01), and the positive expression rate of N-cadherin was higher than that of normal pancreatic tissues (75.8%vs. 0,P<0.01), but there was no correlation between them (r=0.100,P=0.441). The expressions of Twist and N-cadherin was significantly correlated with TNM stage, lymph node metastasis, infiltration of portal vein or nerves and tumor location (P<0.05), but not with age, gender and degree of differentiation (P>0.05). The post-operative survival of patients decreased with the increasing Twist expression, but the survival was not associated with the expression of N-cadherin. TNM stage, the expression of Twist was independent predictive factors of prognosis for pancreatic cancer patients.ConclusionsTwist and N-cadherin are highly expressed in pancreatic cancer, and the expression was associated malignant behavior of pancreatic cancer. The abnormal expression of Twist may be a potential marker for prognosis evaluation of pancreatic cancer patients.
Pancertic neoplasms; Twist transcription factor; N-cadherin
10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-1935.2012.04.007
110004 沈阳,中国医科大学附属盛京医院第二消化内科
陈少夫,Email:csf196211@yahoo.com.cn
2012-03-23)
(本文编辑:屠振兴)

