Synthesis,Crystal Structure and Luminescent Property of[CdCl(HL)(dpp)(H2O)]n·nH2O
GENG Xiao-Hong FENG Yun-Long
(Zhejiang Key Laboratory for Reactive Chemistry on Solid Surfaces,Institute of Physical Chemistry, Zhejiang Normal University,Jinhua,Zhejiang 321004)
Synthesis,Crystal Structure and Luminescent Property of[CdCl(HL)(dpp)(H2O)]n·nH2O
GENG Xiao-Hong FENG Yun-Long*
(Zhejiang Key Laboratory for Reactive Chemistry on Solid Surfaces,Institute of Physical Chemistry, Zhejiang Normal University,Jinhua,Zhejiang321004)
研究简报
Under hydrothermal condition,the reaction of 3-hydroxy-1-adamantaneacetic acid (H2L)with CdCl2and 1,3-di-4-pyridylpropane(dpp)has afforded a new Cd(Ⅱ) compound,[CdCl(HL)(dpp)(H2O)]n·nH2O(1),which was structurally characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis.The crystal is triclinic,space group P1 with a= 1.0910(1)nm,b=1.1318(1)nm,c=1.2464(1)nm,α=88.52(1)°,β=71.34(1)°,γ=68.11(1)°,V=1.3452(1)nm3,Z=2, Mr=591.40,F(000)=608,Dc=1.460 g·cm-3,μ=0.947 mm-1,the final R=0.0401 and wR=0.1040 for 4950 observed reflections(I>2σ(I)).Complex 1 consists of one-dimensional chains deriving from CdCl(HL)(H2O)units linked by dpp ligands,and lattice water molecules decorate between the chains.The O-H…O and O-H…Cl hydrogen bonds lead to the formation of a 2D layer structure.CCDC:756099.
Cd(Ⅱ)complex,3-hydroxy-1-adamantaneacetic acid,crystal structure,luminescent property
Since the discovery of adamantine in 1930[1],adamantane and its derivatives have been widely investigated.Some complexes with amantadine[2-3],adamantanethiol[4-5],and adamantanecarboxylic acids[6-11]have been prepared and studied.However,the complexes based on 3-hydroxy-1-adamantaneacetic acid (H2L)ligand have never been reported so far.The ligand might be utilized as a linker in the construction of coordination polymers.In addition,long flexible ligands have the ability to produce unique structural motifs[12-13],the 1,3-di-4-pyridylpropane(dpp)ligand has been proven to be a good candidate for the organization of polymeric because of its length and flexibility[14-16].We combined H2L and dpp as a mixed ligand system to react with CdCl2under hydrothermal condition,obtaining a new Cd(Ⅱ)compound,[CdCl(HL)(dpp)(H2O)]n·nH2O(1).Inthis paper,we report the synthesis,crystal structure and luminescent property of the title compound.

Scheme 1 3-hydroxy-1-adamantaneacetic acid(H2L)
1 Experimental
1.1 Reagents and measurements
All solvents and chemicals were used without further purification.Elemental analyses were carried out using a Perkin-Elmer 2400Ⅱelemental analyzer.The diffraction data were collected on a Bruker APEXⅡsingle-crystal X-ray diffractometer.IR spectra were measured in KBr pellets on a Nicolet 5DX FTIR spectrometer.The thermogravimetric measurements were performed on preweighed samples in an oxygen stream using a Netzsch STA449C apparatus with a heating rate of 10℃·min-1.The excitation and luminescence spectra were performed on a HITACHIF-2500 fluorescence spectrometer in solid state at room temperature.
1.2 Synthesis of the complex

A mixture of H2L (0.210 g,1.0 mmol),CdCl2· 2.5H2O (0.228 g,1.0 mmol),dpp(0.099 g,0.5 mmol) and Na2CO3(0.053 g,0.5 mmol)were dissolved in 18 mL distilled water.The solution was heated to 433 K for 72 h and then cooled to room temperature over 3 days.Colorless single crystals of 1 were obtained by slow evaporation of the filtrate over a few days(yield 48.1% based on HL).Anal.Calcd.(%)for C25H35CdClN2O5:C, 50.66;H,5.96;N,4.73.Found(%):C,50.60;H,5.98; N,4.76.IR (KBr,cm-1):3283s,2932s,1613s,1540s, 1432s,1339m,1311m,1247m,1227m,1147m,1047 m,1015m,807m,603m,519m.
1.3 X-ray crystallography
A colorless single crystal with dimensions of 0.37 mm×0.20 mm×0.04 mm was mounted on a diffractometer equipped with a graphite-monochromatic Mo Kα radiation(λ=0.071073 nm)for data collection at 296(2) K in the range of 1.73°≤θ≤27.58°.The total 22831 reflections with 6 167 independent ones(Rint=0.034 7) were obtained,of which 4 950 observed reflections with I>2σ(I)were used to solve the structure.The data intensity was corrected by Lorentz-polarization factor and empirical absorption on the SADABS program[17].
The structure was solved by direct methods and refined by full-matrix least-squares on F2with the SHELX-97 program[18].The non-hydrogen atoms were refined anisotropically.The hydrogen atoms attached to carbon were located by geometrical calculations,while those to oxygen were located from difference Fourier maps.The final cycle of full-matrix least-squares refinement based on 313 variable parameters gave R=0.040 1,wR=0.104 0 (w=1/[σ2(Fo2)+(0.052 6P)2+ 0.4667P],where P=(Fo2+2Fc2)/3),(Δ/σ)max=0.000 and S= 1.111.The maximum and minimum peaks on the final difference Fourier map are 1 054 and-405 e·nm-3, respectively.The guest H2O molecule is disordered over two positions and the site occupancy factors refined to 0.83∶0.17.Further details for crystallographic date and refinement conditions are summarized in Table 1.The selected bond lengths and bond angles are given in Table 2.The hydrogen bond lengths and bond angles are shown in Table 3.
CCDC:756099.
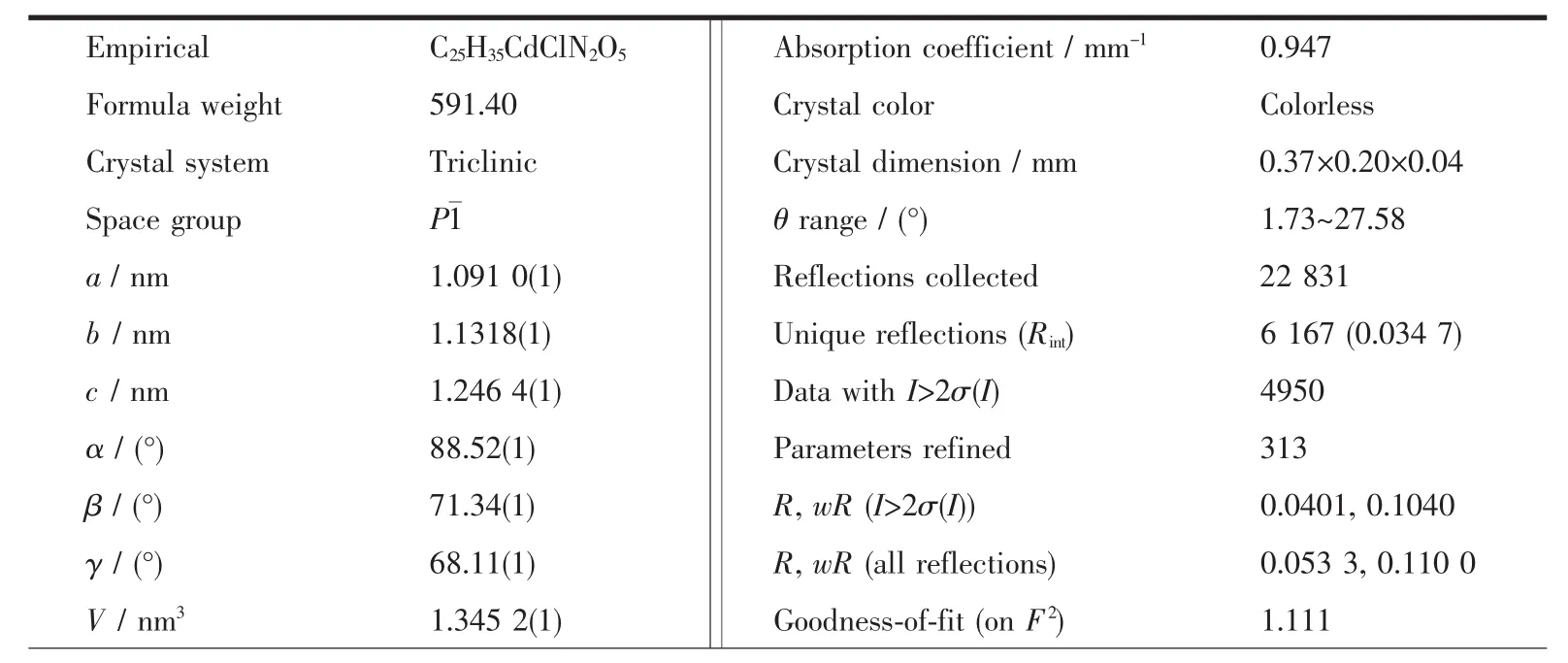
Table 1 Crystal date and structure parameters for the title complex
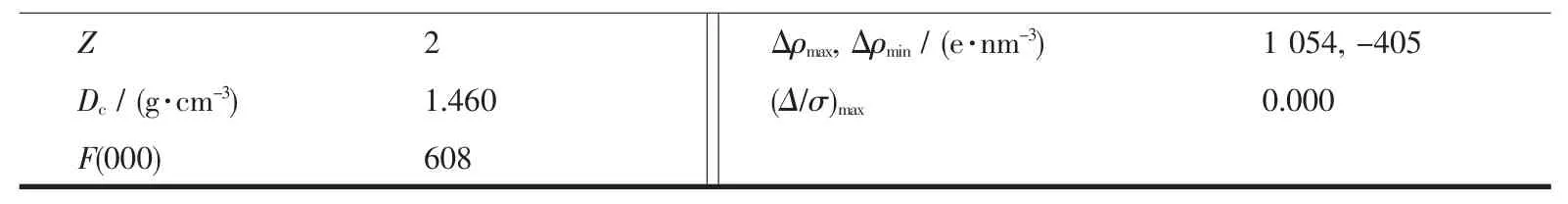
Continued Table 1

Table 2 Selected bond lengths(nm)and bond angles(°)

Table 3 Hydrogen bond lengths and bond angles
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Crystal structure
The crystal structure of complex 1 is composed of a one-dimensional chain[CdCl(HL)(dpp)(H2O)]nand lattice water molecules.As shown in Fig.1,the Cd(Ⅱ)is six coordinated by two oxygen atoms from one chelate carboxyl group of HL,one aqua molecule,one chlorine atom,and two nitrogen atoms from two dpp molecules, giving a distorted octahedral coordination geometry, where Cl(1),N(2)#1,O(1)and O(2)locate at the equator positions,while N(1)and O(1W)occupy the axial positions.Here,bond angles of N(2)#1-Cd(1)-Cl(1),N(2)#1-Cd(1)-O(1),O(2)-Cd(1)-O(1)and O(2)-Cd(1)-Cl(1)are 106.24(5)°,89.28(7)°,53.63(9)°and 111.28(7)°,respectively.The sum of these angles is 360.43°(close to 360°),suggesting a planar nature of Cl(1),N(2)#1,O(1), O(2)and Cd(1)(plane equation 0.077 0x+0.862 5y-0.500 1z=3.453 7)with their corresponding deviations from the base plane to be 0.005 4,0.001 2,0.021 7, -0.009 5 and-0.000 4 nm.N(1)and O(1W)are away from the mean plane by-0.238 21 and 0.232 72 nm, respectively.The bond angle defined by the axial atoms of N(1)and O(1W)is 174.67(7)°.

Fig.1 OPTEP view of complex 1 with 30%probability displacement ellipsoids,showing the atomlabeling scheme
As shown in Fig.2,dpp acts as a bridge ligand to link two Cd(Ⅱ) atoms to generate a one-dimensional chain,with Cd…Cd separation of 1.245 1(1)nm.Two pyridyl rings in dpp molecule are close to vertical and thedihedralanglebetweenthemis82.46(11)°.Hydrogen -bonding interactions are usually important in the supramolecular architectures.As shown in Fig.3,it should be noted that there are persistent intermolecular hydrogen bonds involving lattice water molecules and chlorine atoms in the neighboring chains.The O-H…O and O-H…Cl hydrogen bonds link the neighboring chains to yield 2D layer.

Fig.2 View of one-dimensional chain down the b axis in 1

Fig.3 Packing diagram for complex 1,showing the hydrogen-bonding interactions
2.2 IR spectrum
IR spectrum of complex 1 shows the characteristic bands of the carboxyl group at 1613 cm-1for the antisymmetric stretching and at 1 540 cm-1for the symmetric stretching.The separation(Δ)between νasym(CO2)and νsym(CO2)of 73 cm-1indicates the presence of chelating coordination mode[19],which is consistent with the crystal structure.The absence of the expected characteristic bands at 1 730~1 690 cm-1attributed to the protonated carboxylate groups accounts for the deprotonation of carboxyl group.The wide absorption peak at about 3 283 cm-1characterizes the peak of OH group of H2O and and 3-hydroxy group of HL.
2.3 Thermal property
The sample of complex 1 was heated at a rate of 10℃·min-1under O2atmosphere.As shown in Fig.4,the TG diagram reveals decomposition of 1 begins from 83℃,the first weight loss of 5.5%from 83 to 122℃corresponds to the loss of the lattice and coordination watermolecules.Then the structure appearsto decompose with a total weight loss of 75.9%between 203 and 664℃,mainly corresponding to loss of the organic ligands and chlorine atom.The final residuals may be CdO(calcd.21.7%).

Fig.4 TG diagram for complex 1
2.4 Luminescent property
The solid-state luminescent property of complex 1 was investigated at room temperature,and the emission spectra are given in Fig.5.Complex 1 exhibit an intense photoluminescence,and the maximum emission wavelength is at 443 nm (λex=353 nm).At room temperature, the free H2L ligand shows no detectable luminescence and the free dpp ligand display fluorescent properties in the solid state at room temperature with the emission maximum being located at 523 nm[20].Therefore,the emission band of 1 may be mainly ascribed to π-π* electronic transition of the ligands[21-22].

Fig.5 Solid-state luminescent emission spectra of complex 1 at room temperature
[1]Seidel S R,Stang P J.Acc.Chem.Res.,2002,35:972-983
[2]ZHAO Guo-Liang(赵国良),FENG Yun-Long(冯云龙),HU Xiao-Chun(胡晓春),et al.Chinese J.Struct.Chem.(Jiegou Huaxue),2003,22:321-323
[3]Westerhausen M,Bollwein T,Pfitzner A,et al.Inorg.Chem. Acta,2001,312:239-244
[4]Agapie T,Odom A L,Cummins C C.Inorg.Chem.,2000,39: 174-179
[5]Fujisawa K,Imai S,Kitajima N,et al.Inorg.Chem.,1998,37: 168-169
[6]Xu D J,Pan L,Emge T J,et al.Acta Cryst.,2006,C62:m150-m152
[7]Rosi N L,Kim J,Eddaoudi M,et al.J.Am.Chem.Soc.,2005, 127:1504-1518
[8]Kim J,Chen B,Reineke T M,et al.J.Am.Chem.Soc.,2001, 123:8239-8247
[9]Chen B,Eddaoudi M,Reineke T M,et al.J.Am.Chem.Soc., 2000,122:11559-11560
[10]Millange F,Serre C,Marrot J,et al.J.Mater.Chem.,2004,14: 642-645
[11]Bruce S,Hibbs D E,Jones C,et al.New J.Chem.,2003,27: 466-474
[12]Hong X L,Li Y Z,Hu H M,et al.Cryst.Growth Des.,2006, 6:1221-1226
[13]Wang S N,Bai J F,Li Y Z,et al.CrystEngComm,2007,9:228-235
[14]Wang R H,Han L,Sun Y Q,et al.J.Mol.Struct.,2004,694: 79-83
[15]Yin P X,Zhang J,Cheng J K,et al.Inorg.Chem.Commun., 2006,9:541-543
[16]Chen P K,Che Y X,Xue L,et al.Cryst.Growth Des.,2006,6: 2517-2522
[17]Sheldrick G M.SADABS,Absorption Correction Program, University of Göttingen,Germany,1996.
[18]Sheldrick G M.SHELXS-97 and SHELXL-97,Program for X-ray Crystal Structure Solution and Refinement,University of Göttingen,Germany,1997.
[19]Nakamoto K.Infrared and Raman Spectra of Inorganic and Coordination Compounds.3rd Edn.New York:John Wiley and Sons,1978.
[20]Wang X Q,Cheng J K,Wen Y H,et al.Inorg.Chem.Commun., 2005,8:897-899
[21]Yang F,Ren Y X,Li D S,et al.J.Mol.Struct.,2008,892:283-288
[22]Roy P,Manassero M,Dhara K,et al.Polyhedron,2009,28: 1133-1137
配合物[CdCl(HL)(dpp)(H2O)]n·nH2O的合成、晶体结构与荧光性能研究
耿晓红 冯云龙*
(浙江师范大学物理化学研究所,浙江省固体表面反应化学重点实验室,金华 321004)
Cd(Ⅱ)配合物;3-羟基-1-金刚烷乙酸;晶体结构;荧光
O614.24+2
A
1001-4861(2010)02-0360-05
2009-05-12。收修改稿日期:2009-11-15。
耿晓红,女,26岁,硕士研究生;研究方向:配位化学。
浙江省自然科学基金(No.Y406355)资助项目。
*通讯联系人。E-mail:sky37@zjnu.cn
——以塔里木盆地塔中地区凝析油为例

