栀子黄植物染料及其染色真丝面料的鉴别
桂祖文 徐昊宁 陈海相 余志成 王磊
摘 要:栀子黄植物染料因色光靓丽、性能优良而被广泛应用于纺织品的染色印花,但目前市场上还没有规范的检测方法及标准对其进行鉴别;为填补植物染标准体系的缺失,现需要建立对栀子黄植物染系列产品的鉴别方法和标准。文章通过紫外分光光度计对鉴别栀子黄植物染料的标志物进行了确定,并采用液质联用仪对栀子黄植物染料及其染色真丝面料上萃取的染料进行了鉴别。结果表明:藏红花素Ⅰ、藏红花酸可以作为鉴别栀子黄植物染料及其染色真丝面料的标志物。栀子黄植物染料的质谱中检测到分子离子峰m/z=975.3472和m/z=327.1553,保留时间分别为0.61 min和1.38 min;染色真丝面料萃取液的质谱中检测到分子离子峰m/z=975.396和m/z=327.1489,保留时间分别为0.61 min和1.38 min;两者均与藏红花素Ⅰ标准品0.61 min和藏红花酸标准品1.36 min的出峰时间相近,在标准允许的±2.5%偏差范围内,由此可确定该染料和染色真丝面料为栀子黄植物染料及其染色真丝面料。
关键词:栀子黄植物染料;真丝;藏红花素Ⅰ;藏红花酸;鉴别
中图分类号:TS193.6 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1009-265X(2023)06-0001-08
近年来,在人们追求健康生活、国家推动绿色可持续发展与践行“2030年实现碳达峰、2060年实现碳中和”目标的历史背景下,植物染凭借其无毒无害、环境友好、生物可降解和特殊的药用价值而备受瞩目,并且已被人们广泛应用于纺织品的染色和印花。随着植物染论证系统工程的正式启动,为了填补世界植物染标准体系的缺失,夯实中国引领全球植物染产业的发展基础,现需要完善对植物染系列产品的鉴别方法和标准。因此,对于植物染料及其印染纺织品的鉴别进行探究就显得尤为重要。
栀子黄,是从栀子的果实中提取分离出来的天然色素,其主要成分是类胡萝卜素类的藏红花素和藏红花酸[1-2],是赋予栀子黄色素以黄色的有效成分[3];其他成分还包括环烯醚萜苷类的栀子苷和绿原酸等[3]。栀子黄色泽鲜艳、稳定性较好[4]、染色能力强[5],并且有清热去火、凉血利胆和降低胆固醇等功效[6]。因此,栀子黄植物染料及其染色真丝面料在市场上深受消费者青睐,而目前对于栀子黄植物染料及其染色真丝面料上萃取染料的鉴别却少有报道。
本文以栀子黄植物染料及其染色真丝面料为研究对象,首先通过紫外分光光度计对栀子黄植物染料进行测试,从而确定鉴别栀子黄植物染料的标志物;然后采用液质联用仪在负离子模式下分别对标准品、栀子黄植物染料及其染色真丝面料的萃取液进行检测,通过比较染料、染色真丝面料萃取液与标准品的保留时间和质谱图,以此来鉴别该染料和面料是否为栀子黄植物染料及其染色真丝面料。同时也为植物染行业标准的制定提供参考。
1 实 验
1.1 材料及仪器
实验材料:60.3 g/m2(14姆米)真丝斜纹绸;栀子黄植物染料(河南中大恒源生物科技股份有限公司);藏红花素Ⅰ(上海同田生物技术有限公司)、藏红花酸(上海麦克林生化科技股份有限公司);冰醋酸、甲醇、中性皂片(杭州高晶精细化工有限公司);0.22 μm有机系针式样品过滤器(天津市领航实验设备股份有限公司)。
实验仪器:DYE-24型可调向式打色机(上海千立自动化设备有限公司);雷磁pH计(上海仪电科学仪器股份有限公司);RE-2000B旋转蒸发器(巩义瑞德仪器设备有限公司);赛多利斯BSA124S电子分析天平(济南欧莱博科学仪器有限公司);DR6000紫外-可见光分光光度计(美国哈希公司);ZQ2000液质联用仪(沃特世科技(上海)有限公司)。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 栀子黄植物染料染色真丝样品的制备
a)直接染色
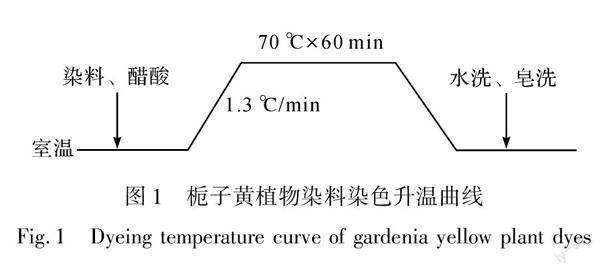
将真丝面料在浴比1∶50,染料用量2.5%(o.w.f),染液pH值4~5,70 ℃条件下染色60 min。其染色升温曲线如图1所示。
b)皂洗工艺
皂片2 g/L、浴比1∶50,50 ℃处理20 min。
1.2.2 标准品和栀子黄植物染料液质联用检测样品的制备
1.2.2.1 藏红花素Ⅰ与藏红花酸标准品液质联用检测样品的制备
准确称取1 mg的藏红花素Ⅰ与藏红花酸标准品,分别用甲醇溶液溶解,定容于10 mL的容量瓶中,得到0.1 mg/mL的标准品溶液,再用一次性0.22 μm有机系针式样品过滤器进行过滤,制得液质联用检测样品。
1.2.2.2 栀子黄植物染料液质联用检测样品的制备
准确称取1 mg的栀子黄植物染料,用甲醇溶液溶解,定容于10 mL的容量瓶中,得到0.1 mg/mL的栀子黄植物染料溶液,再用一次性0.22 μm有机系针式样品过滤器进行过滤,制得液质联用检测样品。
1.2.3 真丝面料上栀子黄植物染料萃取及液质联用检测样品的制备
a)真丝面料上栀子黄植物染料萃取
準确称取0.5 g栀子黄植物染料染色真丝面料剪碎置于染杯中,加入70%甲醇水溶液,用醋酸调节溶液pH至6,浴比1∶30,在60 ℃下加热萃取100 min。取出真丝面料得到萃取液,采用旋转蒸发器浓缩至5 mL,得到浓缩后萃取液。
b)液质联用检测样品的制备
采用甲醇溶液将浓缩后萃取液稀释一定倍数,再用一次性0.22 μm有机系针式样品过滤器进行过滤,制得液质联用检测样品。
1.3 测试方法
1.3.1 吸收光谱
采用DR6000紫外-可见光分光光度计测其波长200~760 nm范围的吸光度,绘制紫外-可见光吸收光谱图。
1.3.2 液质联用测试
采用ZQ2000液质联用仪对栀子黄植物染料及其染色真丝面料萃取液进行测试,并绘制总离子流图与质谱图。
a)色谱条件
色谱柱:C18反相色谱柱(250 mm×4.60 mm I.D,5μm);流动相:30% A+70% B(A为0.1%甲酸水溶液、B为乙腈);流速:0.3 mL/min;进样量:100 μL;柱温:30 ℃;检测波长:200~500 nm。
b)质谱条件
进样方式:LC-MS;离子源:ESI;离子源温度:320 ℃;检测模式:负离子;扫描范围(m/z):50~1200 nm;毛细管电压(V):3500;毛细口出口电压(V):109.7。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 栀子黄植物染料的紫外-可见光吸收光谱及标志物确定
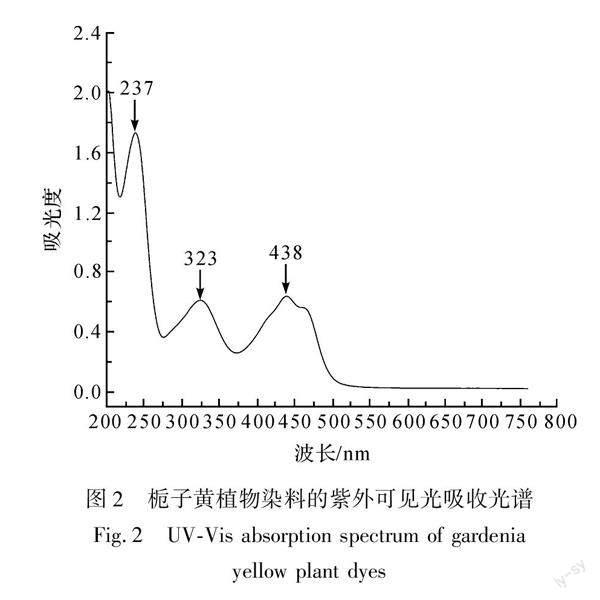
以50%甲醇水溶液为溶剂,配置1 g/L的栀子黄植物染料溶液,用紫外分光光度计测试其在一定稀释倍数下的吸收光谱,其结果如图2所示。
如图2所示,栀子黄植物染料的紫外可见光吸收光谱中出现了3个吸收峰,其中,438 nm处的吸收峰为藏红花素的特征峰、323 nm处的吸收峰为绿原酸的特征峰、237 nm处的吸收峰为栀子苷的特征峰[7]。
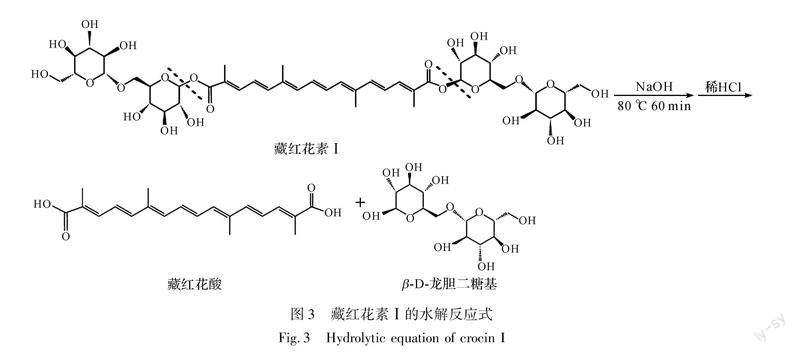
已有研究表明[2],栀子黄植物染料主要成分为藏红花素和藏红花酸;藏红花素是藏红花酸与龙胆二糖或葡萄糖形成的糖苷,包括藏红花素Ⅰ、藏红花素Ⅱ、藏红花素Ⅲ、藏红花素Ⅳ和藏红花素Ⅴ等5种组成,其中藏红花素Ⅰ占70%以上[8];而藏红花酸是由藏红花素先在碱性条件下水解脱去二分子龙胆双糖,再用稀盐酸将溶液pH调回酸性而转化生成的,其中藏红花素Ⅰ的水解反应过程如图3所示[9-10],因此,提取方法及工艺参数不同,藏红花素、藏红花酸含量不同。绿原酸和栀子苷在染料中均不赋予染料以任何颜色[3],并且当其与藏红花素共存时,若其含量较多,则会产生色变、褪色等问题[11],所以不能选择绿原酸与栀子苷作为鉴别的标志物。综上所述,可以考虑选择藏红花素Ⅰ与藏红花酸作为鉴别栀子黄植物染料的标志物。
2.2 藏红花素Ⅰ与藏红花酸标准品的液质联用检测
2.2.1 藏红花素Ⅰ标准品的液质联用检测
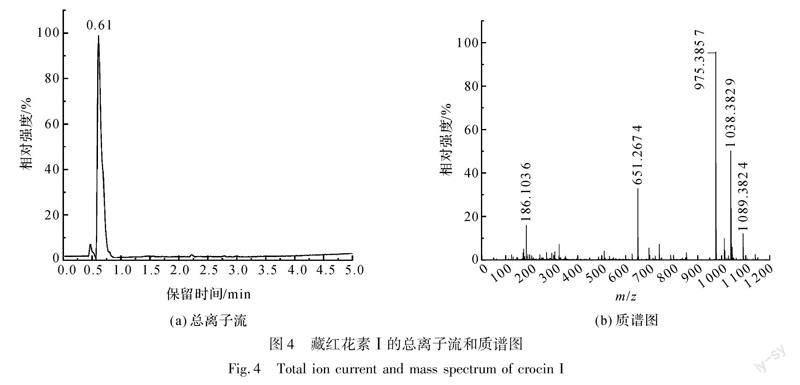
采用液质联用仪对藏红花素Ⅰ标准品溶液进行检测,其结果如图4所示。
由图4可知,在负离子模式下检测,藏红花素Ⅰ标准品(C44H64O24,M=976.972)的保留時间为0.61 min;m/z=975.3857([M-H]-)为藏红花素Ⅰ失去一个氢离子产生的分子离子峰[12]。
2.2.2 藏红花酸标准品的液质联用检测
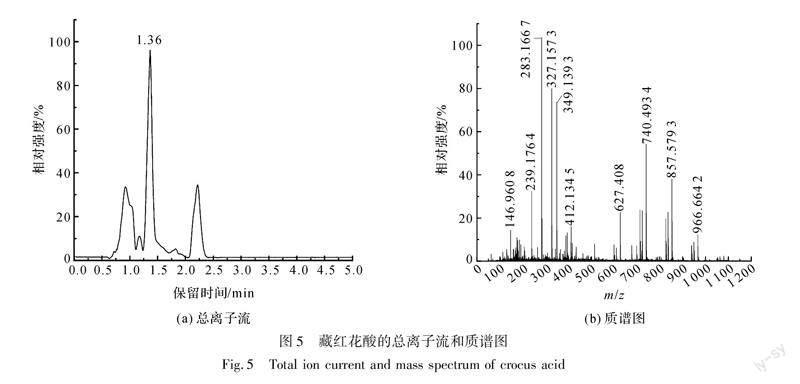
采用液质联用仪对藏红花酸标准品溶液进行检测,其结果如图5所示。
由图5可知,在负离子模式下检测,藏红花酸标准品(C20H24O4,M=328.408)的保留时间为1.36 min;m/z=327.1573([M-H]-)为藏红花酸失去一个氢离子产生的分子离子峰;m/z=283.1667([M-H]-)分子离子峰与藏红花酸的分子离子峰正好相差一个羧酸根离子的相对分子质量(44 Da),为藏红花酸失去一个羧基所形成的分子离子峰[13]。
2.3 栀子黄植物染料的液质联用检测
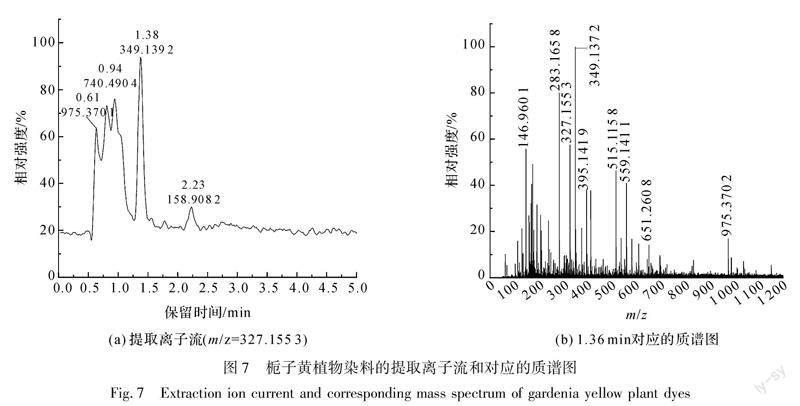
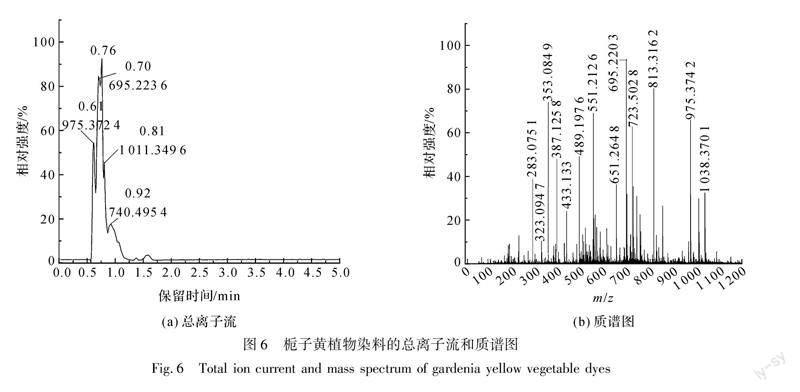
以甲醇溶液为溶剂,配置0.1 mg/mL的栀子黄植物染料溶液,采用液质联用仪对其进行检测,其结果如图6、图7所示。
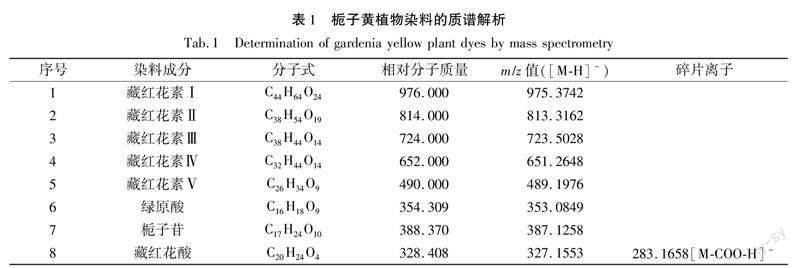
图6(b)可知,在负离子模式下检测,发现栀子黄植物染料中含有藏红花素(Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ、Ⅴ)、藏红花酸、绿原酸、栀子苷的分子离子峰,其各成分对应的质谱解析如表1所示。
藏红花素Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ、Ⅴ的分子离子峰在质谱图中均能找到,由表1可知,其各自对应的相对分子质量分别为976(C44H64O24)、814(C38H54O19)、724(C38H44O14)、652(C32H44O14)、490(C26H34O9),其中藏红花素Ⅰ和藏红花素Ⅳ的分子离子峰强度较高,m/z=975.3742([M-H]-)为藏红花素Ⅰ(C44H64O24,M=976.965)失去一个氢离子产生的分子离子峰,m/z=651.2648([M-H]-)为藏红花素Ⅳ(C32H44O14,M=652)失去一个氢离子产生的分子离子峰;而质谱图中绿原酸和栀子苷的分子离子峰强度较低,其中m/z=353.0849([M-H]-)为绿原酸(C16H18O9,M=354.309)失去一个氢离子产生的分子离子峰,m/z=387.1258([M-H]-)为栀子苷(C17H24O10,M=388.37)失去一个氢离子产生的分子离子峰[14]。由图6(a)可知,栀子黄植物染料中藏红花素Ⅰ的保留时间为0.61 min,与图4(a)中藏红花素Ⅰ标准品0.61 min的出峰时间一致,由此可确定为栀子黄植物染料。
在负离子模式下对栀子黄植物染料进行液质联用检测,首先从栀子黄植物染料总离子流(见图6(a))中调出1.36 min左右对应的质谱图(见图7(b)),可以看到分子离子峰m/z=327.1553,该离子峰为栀子黄植物染料中的藏红花酸失去一个氢离子产生的分子离子峰,m/z=283.1658([M-H]-)为栀子黄植物染料中藏红花酸失去一个羧基所形成的分子离子峰,其各成分对应的质谱解析如表1所示。
其次,从图7(b)中m/z=327.1553分子离子峰处调出栀子黄植物染料的提取离子流(见图7(a)),可知栀子黄植物染料中藏红花酸的保留时间为1.38 min,与图5(a)中藏红花酸标准品1.36 min的出峰时间相近,在标准GB/Z 35959—2018《液相色谱-质谱联用分析方法通则》中允许的±2.5%偏差范围内,由此可确定为栀子黄植物染料。
2.4 栀子黄植物染料染色真丝面料的液质联用检测
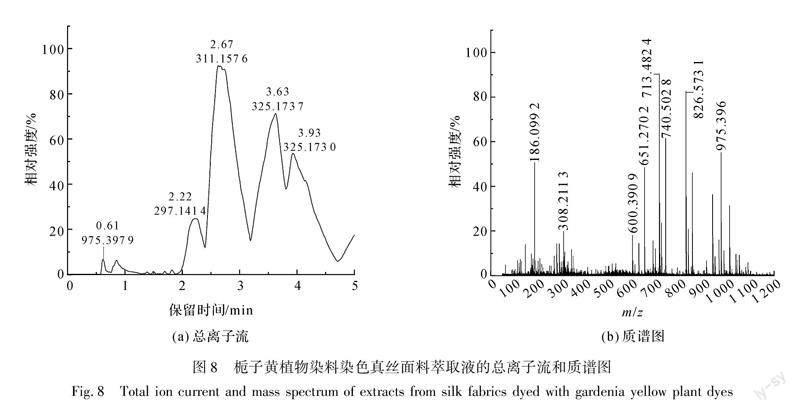
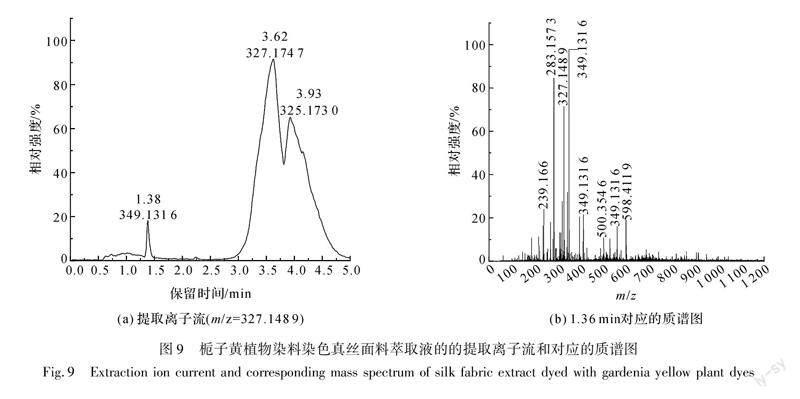
采用液质联用仪对栀子黄植物染料染色真丝面料萃取液进行检测,其结果如图8、图9所示。
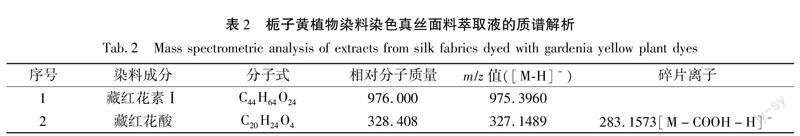
由图8(b)可知,在负离子模式下检测,发现栀子黄植物染料染色真丝面料萃取液的质谱图中存在藏红花素Ⅰ和藏红花酸的分子离子峰,未发现栀子
苷和绿原酸的分子离子峰,其各成分对应的质谱解析如表2所示。其中m/z=975.396([M-H]-)为藏红花素Ⅰ(C44H64O24)失去一个氢离子产生的分子离子峰。由图8(a)可知,萃取液中藏红花素Ⅰ的保留时间为0.61 min,与图4(a)中藏红花素Ⅰ标准品0.61 min的出峰时间一致,由此可确定该真丝面料为栀子黄植物染料染色。
在负离子模式下对栀子黄植物染料染色真丝面料萃取液进行液质联用检测,首先从萃取液的总离子流(见图8(a))中调出1.36 min左右对应的质谱图(见图9(b)),可以看到分子离子峰m/z=327.1489,该离子峰为栀子黄植物染料中的藏红花酸失去一个氢离子产生的分子离子峰,m/z=283.1573([M-H]-)为栀子黄植物染料中藏红花酸失去一个羧基所形成的分子离子峰,其各成分对应的质谱解析如表2所示。其次,从图9(b)中m/z=327.1489分子离子峰处调出栀子黄植物染料染色真丝面料萃取液的提取离子流(见图9(a)),可知萃取液中藏红花酸的保留时间为1.38 min,与图5(a)中藏红花酸标准品1.36 min的出峰时间相近,在标准允许的±2.5%偏差范围内,由此可确定该真丝面料为栀子黄植物染料染色。
3 结 论
本文以栀子黄植物染料及其染色真丝面料为研究对象,选用藏红花素Ⅰ与藏红花酸为标志物,采用液质联用仪在负离子模式下分别对标准品、栀子黄植物染料及其染色真丝面料的萃取液进行检测。得到如下结论:
a)在栀子黄植物染料的质谱中检测到分子离子峰m/z=975.3472和m/z=327.1553,且保留时间分别为0.61 min和1.38 min,与藏红花素Ⅰ标准品0.61 min和藏红花酸标准品1.36 min的出峰时间相近,在标准允许的±2.5%偏差范围内,由此可确定该染料为栀子黄植物染料。
b)在栀子黄植物染料染色真丝面料萃取液的质谱中检测到分子离子峰m/z=975.396和m/z=327.1489,且保留时间分别为0.61 min和1.38 min,与藏红花素Ⅰ标准品0.61 min和藏红花酸标准品1.36 min的出峰时间相近,在标準允许的±2.5%偏差范围内,由此可确定该面料为栀子黄植物染料染色。
参考文献:
[1]高丽,邓青云,姜益泉,等.超声波法提取栀子黄色素的工艺研究[J].安徽农业科学,2012,40(22):11445-11446,11531.
GAO Li, DENG Qingyun, JIANG Yiquan, et al. Study on the ultrasonic extraction of yellow pigment from Gardenia jasminoides Ellis[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 40(22): 11445-11446, 11531.
[2]刘晓棠,赵伯涛,张玖,等.栀子的综合开发与利用[J].中国野生植物资源,2008(1):19-23.
LIU Xiaotang, ZHAO Botao, ZHANG Jiu, et al. Compre-hensive development and utilization of Gardenia jasminoides Ellis[J]. China Wild Plant Resources, 2008, 27(1): 19-23.
[3]叶楠,陈峰,王喜萍,等.栀子黄色素提取工艺的研究进展2[J].化学工程与装备,2011(9):181-184,176.
YE Nan, CHEN Feng, WANG Xiping, et al. Research progress on extraction of gardenia yellow pigment[J]. Chemical Engineering & Equipment, 2011(9): 181-184, 176.
[4]常锋,薛毅.天然栀子黄色素稳定性研究[J].郑州工程学院学报,2004(2):81-84.
CHANG Feng, XUE Yi. The stability of natural gardenia yellow pigment[J]. Journal of Zhengzhou Institute of Technology, 2004, 25(2): 81-84.
[5]李崇瑛,王安,杨涛,等.食用天然色素的纯化与研究进展[J].中国调味品,2007,32(9):18-22,38.
LI Chongying, WANG An, YANG Tao, et al. Purification and research progress on the natural pigment[J]. Chinese Condiment, 2007, 32(9): 18-22, 38.
[6]KOO H J, SONG Y S, KIM H J, et al. Antiinflammatory effects of genipin, an active principle of gardenia[J]. European Journal of Pharmacology, 2004,495(2/3): 201-208.
[7]高麗,邓青云,姜益泉,等.栀子黄色素提取工艺的研究[J].农业机械,2011(26):132-134.
GAO Li, DENG Qingyun, JIANG Yiquan, et al. Study on extraction process of gardenia yellow pigment[J]. Farm Machinery, 2011(26): 132-134.
[8]齐雅静,顾军强,王立,等.栀子果功能性成分研究进展[J].食品工业科技,2013,34(14):363-369.
QI Yajing, GU Junqiang, WANG Li, et al. Research progress in functional ingredients in the fruit of Gardenia jasminoides Ellis[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2013, 34(14): 363-369.
[9]王吉宇,李成文,徐彦靖,等.响应面法优化藏红花素碱水解制备反式藏红花酸工艺[J].食品工业科技,2021,42(23):176-183.
WANG Jiyu, LI Chengwen, XU Yanjing, et al. Optimi-zation of the preparation of Trans-crocetin from crocin by alkaline hydrolysis via response surface methodology[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 201, 42(23): 176-183.
[10]陈志慧,王文彩,郭微,等.栀子源藏红花素的生物合成研究进展[J/OL].分子植物育种:2023:1-13[2023-03-29].http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20220325.1803.005.html.
CHEN Zhihui, WANG Wencai, GUO Wei, et al. Research progress on the crocin biosynthesis of Gardenia jasminodies[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding:2023:1-13[2023-03-29].http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20220325.1803.005.html.
[11]刘慧璐,冯建勇,王增尚,等.高色价栀子黄的精制工艺研究[J].中国现代应用药学,2013,30(12):1315-1319.
LIU Huilu, FENG Jianyong, WANG Zengshang, et al. Preparative separation of crocins with high color value from gardenia fruits[J]. Chinese Journal of Modern Applied Pharmacy, 2013, 30(12): 1315-1319.
[12]张莹,夏炎,陈莹,等.栀子黄色素标准品藏红花素的制备[J].食品与发酵工业,2009,35(2):100-103.
ZHANG Ying, XIA Yan, CHEN Ying, et al. Preparation of pure gardenia yellow pigment[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2009, 35(2): 100-103.
[13]雷磊,王玉,霍志鹏,等.LCMS-IT-TOF分析栀子炒焦前后化学成分的变化[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2019,25(17):88-97.
LEI Lei, WANG Yu, HUO Zhipeng, et al. Variations of chemical constituents in Gardeniae Fructus before and after stir-frying by LCMS-IT-TOF[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 2019, 25(17): 88-97.
[14]崔悦,张葆祺,李乐乐,等.UFLC-MS/MS法同时测定栀子中5种有效成分的含量[J].中国兽医杂志,2022,58(9):80-87.
CUI Yue, ZHANG Baoqi, LI Lele, et al. Simultaneous determination of five active components in Fructus Gardeniae by UFLC-MS/MS[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 2002, 58(9): 80-87.
Identification of gardenia yellow plant dyes and their dyed silk fabrics
GUI Zuwen XU Haoning CHEN Haixiang YU Zhicheng WANG Leia,b
Abstract: In recent years, with the improvement of people's awareness of environmental protection, ecological textiles have been increasingly favored by people. Because of their non-toxic, biodegradable and other characteristics, plant dyes are widely used to study the dyeing and printing of textiles. Dyeing and printing with plant dyes can not only reduce the harm of dyes to the human body and make full use of natural renewable resources, but also greatly reduce the toxicity of printing and dyeing wastewater, playing a role in protecting the environment indirectly. At present, the development and utilization of plant dyes is under the active exploration and research, and the plant dye demonstration system engineering has been launched officially. In order to fill the deficiency of the world plant dye standard system, and lay a solid foundation for China to lead the development of the global plant dye industry, it is necessary to establish the identification methods and standards of plant dye series of products. In order to ensure the quality of plant dyeing products on the market, crack down on fake and shoddy products, and standardize market operation, so that consumers can rest assured and buy satisfactory plant dyeing products, it is very important to identify the corresponding vegetable dyes and dyeing textiles.
In order to identify plant dyes and their dyed textiles, this paper takes gardenia yellow plant dyes and dyed silk fabrics as the research objects. Firstly, the gardenia yellow plant dyes were tested by ultraviolet spectrophotometer, and the markers of gardenia yellow plant dyes were indentified by combining with the descriptions in the literature. Then the markers, gardenia yellow plant dyes and their dyed silk fabric extract were detected by using liquid mass combination instrument under negative ion mode. By comparing the retention time and mass spectrometry of the dyes, dyed silk fabric extract and the dyed silk fabric, whether the dye and fabric were gardenia yellow plant dye and its dyed silk fabric was determined.
The results showed that crocin Ⅰ and crocin acid could be used as markers to distinguish gardenia yellow plant dyes and their dyed silk fabrics. The molecular ion peaks m/z=975.3472 and m/z=327.1553 were detected in the mass spectrum of gardenia yellow plant dyes, and the retention times were 0.61 min and 1.38 min, respectively. The molecular ion peaks m/z=975.396 and m/z=327.1489 were detected in the mass spectrum of dyed silk fabric extract, and the retention times were 0.61 min and 1.38 min, respectively. The retention times were similar to the peak time of the crocin Ⅰ standard substance (0.61 min) and crocin acid standard substance (1.36 min), and the deviations were within the allowable deviation range of ±2.5%. Therefore, it was determined that the dye and the dyed silk fabric are respectively the gardenia yellow plant dye and its dyed silk fabric.
At present, many textile colleges and universities have established relatively complete database of vegetable dyes and comprehensive vegetable dye color cards. However, there are certain deficiencies in the relevant standards of plant dyeing in every link in the current market, and consumers have insufficient awareness of them and cannot verify the conformity of products. Therefore, identifying the corresponding plant dyes and their dyed fabrics is a priority in the development of plant dyeing.
Keywords: gardenia yellow vegetable dye; real silk; crocinⅠ; croctin acid; identification
收稿日期:20230116 網络出版日期:20230321
基金项目:浙江理工大学柯桥研究院项目(KYY2021002C)
作者简介:桂祖文(1995—),男,安徽池州人,硕士研究生,主要从事新型染整技术方面的研究。
通信作者:余志成,E-mail:yuzhicheng8@aliyun.com

