Identification and dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory activity verification of peptides from mouse lymphocytes
Jun Wng, Yuji Xie, Yunyun Lun, Tingting Guo, Shnshn Xio, Xingxing Zeng, Shohui Zhng,*
a School of Agriculture and Biology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
b Zhejiang Go Peptides Life Science and Healthcare Technology Co., Ltd., Wenzhou 325000, China
ABSTRACT
The objective of this study was to isolate and identify the intracellular bioactive peptides from mouse lymphocytes before and after lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulation, to explore novel peptides and to research the bioactive function. Mouse spleen lymphocytes were isolated and cultured with LPS stimulation(experimental group) or not (control group) to collect intracellular peptides. Totally 385 peptides were analyzed by nanoliter liquid phase-Q Exactive quadrupole ultra-high resolution orbitrap mass spectrometer(Nano LC-Q Exactive Plus) and identified by PEAKS X software. After compared with peptides reported,131 novel peptides were discovered, which then were predicted bioactivity by Peptide Ranker and 6 peptides with high bioactivity were predicted function by BIOPEP-UMW database. Prediction data showed that they may have dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory activity. Finally, two peptides showed better potent inhibition were verified with competitive and noncompetitive modes.
Keywords:
Lymphocytes
Peptides
Lipopolysaccharide
Dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory activity
1. Introduction
Bioactive peptides have been researched for many years as a kind of functional substance beneficial to human health. It can be produced by protein hydrolysis or fermentation [1]. After hydrolysis, peptide bonds are broken, resulting in the generation of peptides and amino acids [2]. Therefore, the size of bioactive peptides are small, they have better permeability and are easier to be absorbed by human body [3].
Nowadays, all kinds of beneficial effects of bioactive peptides have been well proved in many research, including the activities of anticancer [4], blood pressure lowering [5,6], antibacterial [7],cholesterol lowering [8], anti-diabetes [9] and so on. However, the current research about bioactive peptides mainly focuses on food derived peptides, only few studies and reports focus on the peptides derived from other substances. Regarding previous research, nonfood derived bioactive peptides have higher affinity and can play their bioactive functions more effectively [10].
Lymphocytes exist in animal central lymphoid organs and tissues, including tonsils, spleen and so on, they are the central regulatory cells in the immune system, cell lineage made up by lymphocytes is fundamentally important for the immune system [11].Most of their functions are mediated by a group of small molecular peptides called lymphokines, the expression and secretion of these small molecular peptides are induced by cell activation stimulated by antigen [10].
In our previous work, we studied and identified novel peptides derived from casein in milk. In this study, the peptide components in mouse spleen lymphocytes were isolated and identified. Then, these peptides were analyzed and compared with peptides reported. Finally,6 novel highly bioactive peptides were synthesized to verify potential dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory function.
2. Materials and methods
2.1 Materials and reagents
BALB/c mice (male, 8 weeks) strain were purchased from Jiesijie laboratory animal Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Roswell Park Memorial Institute (RPMI) 1 640 medium, Phosphate buffered saline(PBS) solution and trypsin-ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA)solution were purchased from Kaiji Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Jiangsu,China). 10 kDa ultrafiltration tube was purchased from Sedolis Co.,Ltd. (Gottingen, Germany). Caco-2 cell lines were purchased from Shanghai Cell Bank of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai,China). Dulbecco’s modified essential medium (DEME) was purchased from Gibco (California, USA). Peptides (purity ≥ 95%)in verification assay were synthesized by China Peptides Co., Ltd.(Shanghai, China). All other chemicals and reagents were of the highest grade.
2.2 Mouse feeding
The BALB/c mice were ordered from the animal experimental center of Shanghai Jiao Tong University and were fed adaptively in the specific pathogen free (SPF) animal room for one week. The feeding conditions were as follows: temperature 18–22 °C, relative humidity 50%–80%, light and dark environment 12 h a day. The number of mice in each cage should not be more than 3. During feeding, the bedding should be changed in time, and the supply of water and feed should be sufficient. After the adaptive feeding,the physical signs of the experimental mice were suitable for the subsequent experiment.
2.3 Preparation of mouse spleen single cell suspension
The mice were executed by cutting their necks, soaked in 75% alcohol for 5 min, and then transferred to the ultra-clean table. Then the spleen was isolated from mice and washed with PBS, chopped and placed in a 35 mm culture dish, added 5 mL mouse lymphocyte separation solution, and ground with syringe piston (the grinding operation is shown in Fig. 1). The tissue grinding fluid was aspirated by Pasteur’s pipette, passed through 100 mesh nylon mesh, 1 500 r/min,centrifuged for 3 min, then washed with Hank’s solution for 3 times,centrifuged at 500 r/min for 1 min, andfiltered with a 200 mesh cell sieve to prepare spleen tissue single cell suspension for standby.
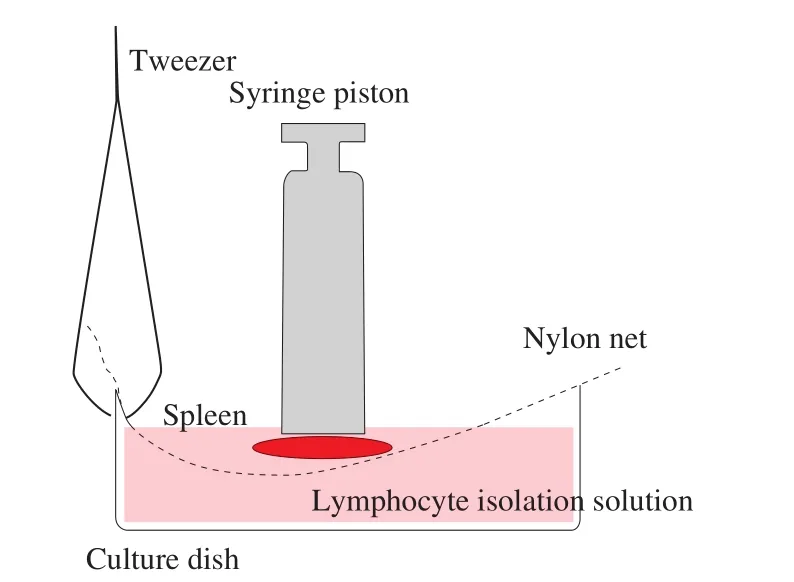
Fig. 1 Spleen grinding method. The syringe piston was used to grind the spleen, and the upward rebound force of nylon net was used to control the grinding force, so as to minimize the possible mechanical damage to cells.
2.4 Extraction and culture of mouse lymphocytes
Six milliliter lymphocyte isolation solution was added into the centrifuge tube (recovered to room temperature and shaken before use), and 5 mL spleen tissue single cell suspension was slowly added along the tube wall, covered with 400 μL RPMI-1640 complete culture medium, and centrifuged at 2 000 r/min for 30 min at room temperature. Obvious stratification can be seen after centrifugation(Fig. 2). According to Fig. 2, discard the upper cell culture medium,suck out the middle white lymphocyte layer, then add 10 mL RPMI-1640 complete medium, wash the cells upside down, make them fully mixed, centrifugation at 700 r/min for 10 min at room temperature,then use 5 mL RPMI-1640 incomplete culture medium to resuspend cells and count cells. 10 μL cell suspension was taken and trypan blue staining was used to determine the cell survival rate. The survival rate was more than 90%, indicating that the cell culture was successful,and the next step of experiment could be carried out.
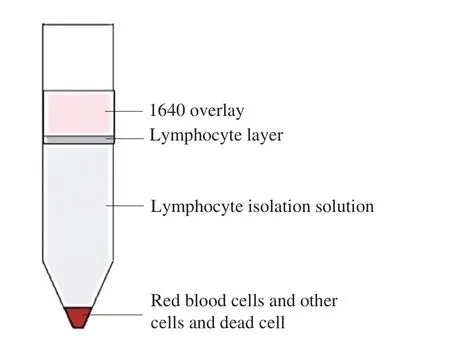
Fig. 2 Cell stratification. The upper layer was covered by 1640 culture medium, and the lower layer was precipitated with red blood cells, other cells and dead cell fragments, and the middle was lymphocyte layer.
The cell concentration was adjusted to 1 × 106cells/mL and inoculated into 6-well plates. 2 mL cell suspension was added to each well plate and cultured for 6 h under the conditions of 37 °C, 95% O2and 5% CO2. During the culture, the 6-well plate was slightly shaken every 2 h to make the cells evenly distributed and suspended in the culture medium.
2.5 Cell purity detection by flow cytometry
The cells in the 6-well plate were collected into a 15 mL centrifuge tube. After being centrifuged at 1 000 r/min for 5 min at room temperature. The supernatant being discarded and the cells were resuspended with 5 mL RPMI-1640 complete culture medium to be counted by blood cell counting plate.
Two milliliter single cell suspension was centrifuged at 1 000 r/min for 5 min. The cell density was adjusted to 1 × 106cells /mL by PBS and centrifuged at 1 000 r/min for 5 min, then washed 2 times by PBS. 100 μL cell suspension was drawn into 4 flow cytometry tubes(experimental tube 1, 2, 3 and blank control tube 4). According to the antibody instructions and Table 1, 1 μL of fluorescent labeled mouse antibodies cluster of differentiation- fluorescein isothiocyanate (CD3-FITC) and cluster of differentiation-Phycoerythrin (CD19 PE) were added into the flow cytometry tubes, incubated for 20 min at room temperature and detected by flow cytometry.

Table 1Staining tube layout for detection by flow cytometry.
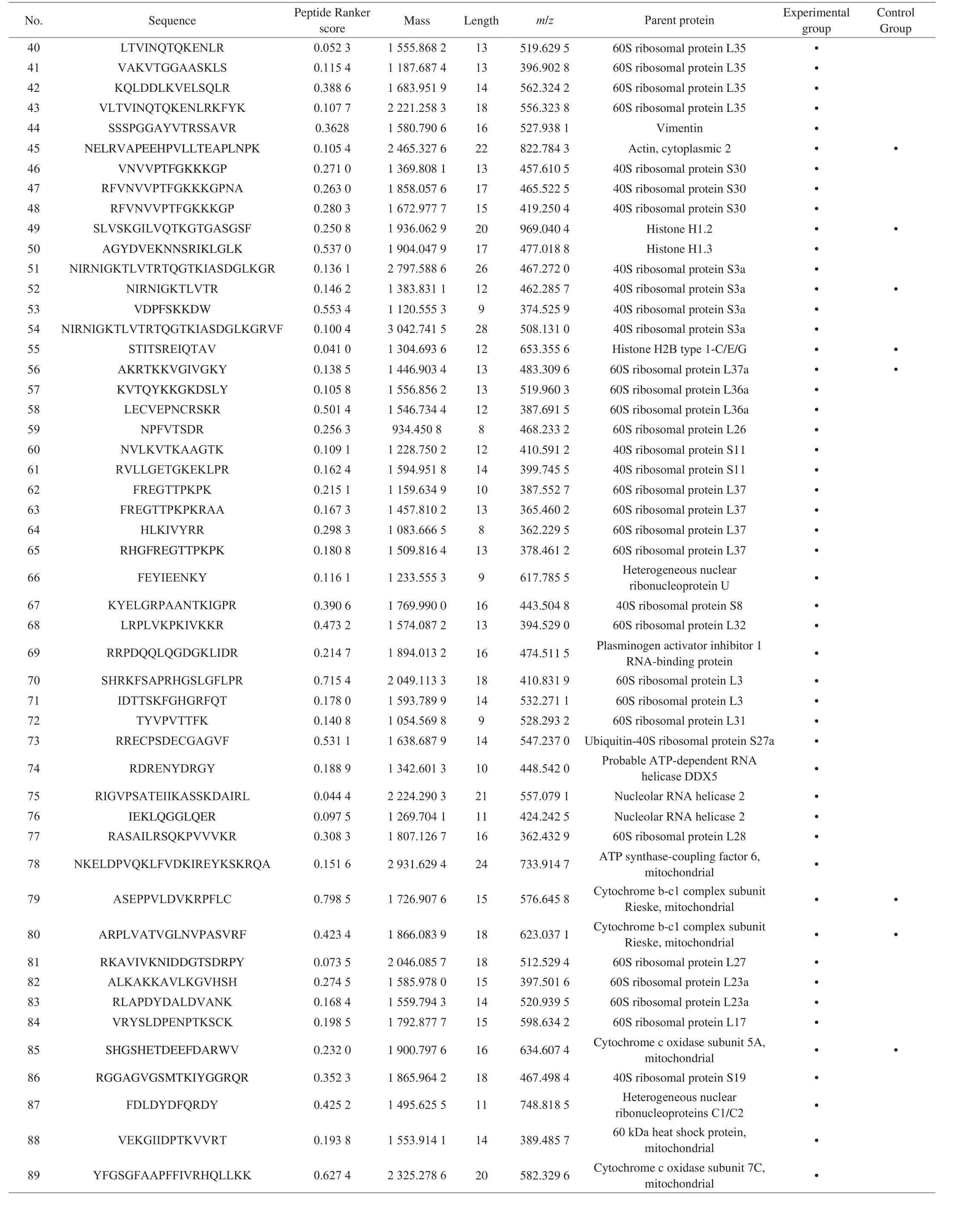
Table 2 (Continued)
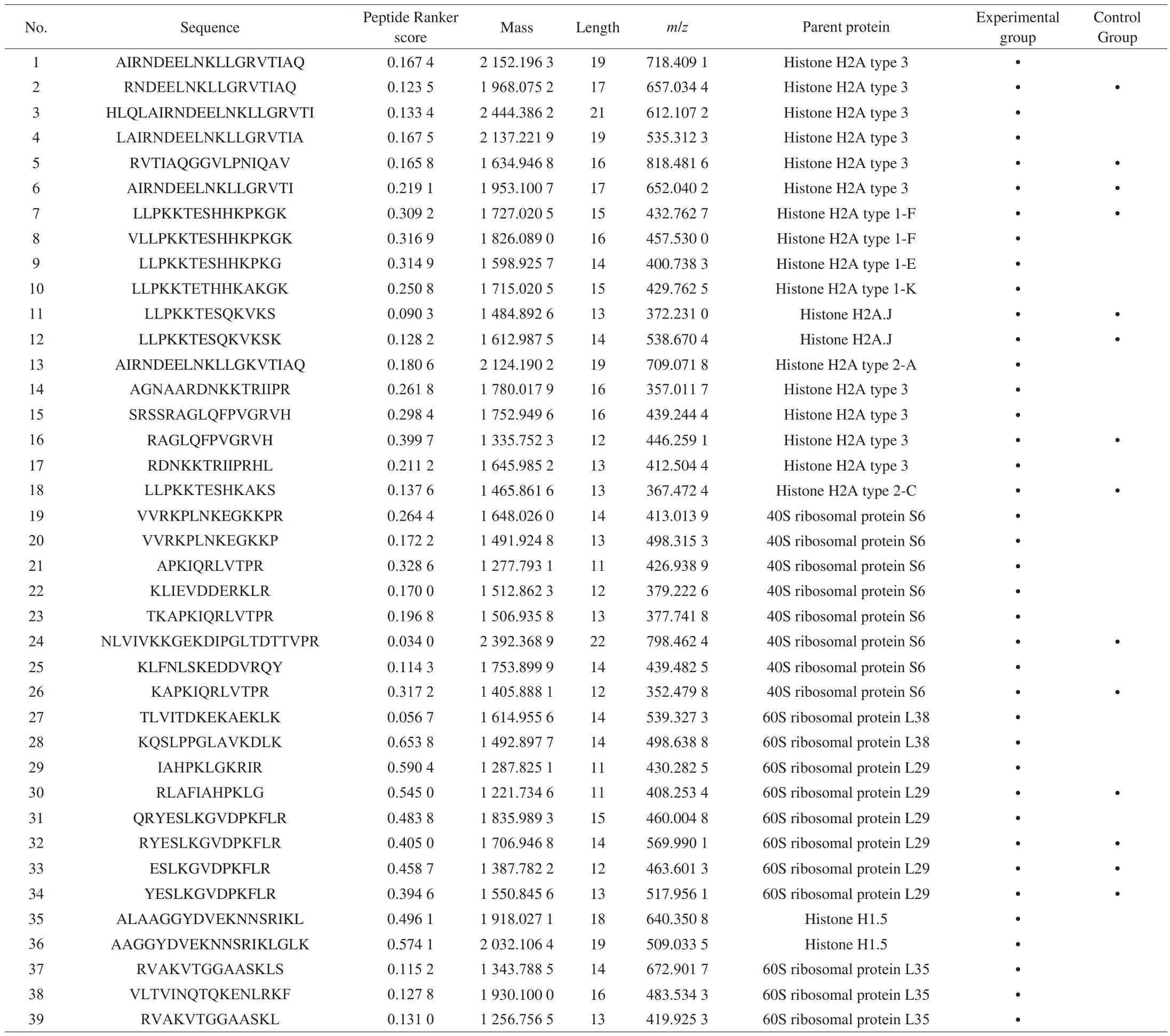
Table 2Novel peptides identified in mouse spleen lymphocytes.

Table 2 (Continued)
2.6 Construction of in flammatory cells
After flow cytometry detection, the cells were recovered and cultured for 48 h. The cells in the experimental group and the control group were added with 10 μg/mL lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and 10 μg/mL PBS, respectively. Thefinal concentration was 500 ng/mL.At 8 h after culture, the cells were collected to be counted numbers.
2.7 Obtaining peptides from lymphocytes
The collected cells were washed by PBS and centrifuged at 4 000 r/min for 5 min. After centrifugation, the supernatant was discarded. This process was repeated twice. The cells were resuspended with PBS, and broken by ultrasonic wave for 50 min with 5 s ultrasonic time, and 5 s intervals. After the completion of ultrasonic cell crushing operation, 2.5 mL 100% acetonitrile was added into the crushed mixture, shaked for 15–30 min and centrifugated at 12 000 r/min for 20 min at 4 °C, take out the supernatant and dry it with centrifugal concentrator. The dried precipitate was dissolved in 5 mL 5 mmol/L NH4HCO3, then mixed with 5 mL 1 mol/L dithiothreitol solution (DTT) before the incubation in 60 °C water bath for 60 min. After incubation, 5 mL 1 mol/L iodoacetamide solution (IAA) was added and the mixture was left in room temperature for 40 min. The above solution was centrifuged at 12 000 r/min for 10 min. The supernatant was transferred to a 10 kDa ultrafiltration tube, and centrifuged at 12 000 r/min for 40 min. Then 50 μL 50 mmol/L NH4HCO3was added before being centrifuged at 12 000 r/min for 20 min. Finally, thefiltrate was collected and dried by centrifugal concentrator. Half of dried samples were desalted with C18desalination column and tested by Nano LC-Q Exactive plus mass spectrometer.
2.8 Identification of peptides in lymphocytes
The samples in lymphocytes were analyzed by Nano LC-Q Exactive plus mass spectrometer (Thermofisher, USA). The analytical column was C18(75 μm × 50 cm, 1.9 μm). The mobile phase A was water phase containing 0.1% (V/V) formic acid, and the mobile phase B was acetonitrile containing 0.1% (V/V) formic acid. The liquid gradient: 0–1 min, 2%–6% B; 1–38 min, 6%–22% B; 38–46 min,22%–32% B; 46–48 min, 32%–100% B; 48–60 min, 100% B. The flow rate of mobile phase was 300 nL/min. In electrospray ionization(ESI)+ mode, full scan acquisition (m/z350–1 800) was performed in an orbit well with a resolution of 70 000 (AGC 3e6). Thefirst 20 peptide signals isolated (charge state ≥ + 2) were broken by high energy collision (HCD), and the normalized collision energy (NCE)was 28.0. The capillary temperature was 275 °C and the spray voltage was 1 800 V. The sub ions were measured at a resolution of 17 500(AGC 1E5). The maximum fill time of full scan and MS-MS scan were set up to 50 and 45 ms, respectively, and the dynamic exclusion time was set to 30 s.
2.9 Data processing
The peptide samples were analyzed by Nano LC-Q Exactive plus mass spectrometer, and were identified by PEAKS X software(version 2.4, Matrix Science). MS raw data were refined by PEAKS X software to match corresponding sequence in protein database, and the highest score of peptide spectrum matches will be the best match.The protein database was downloaded from the UniProt [12] website(http://www.uniprot.org/) as the peptide retrieval database for this study. This database searching was proceeded with target-decoy analysis,decoy protein sequence database was mixed with target protein sequence database and searched together helping to screen out false positive peptide sequences under given false discovery rate (FDR = 1%). Besides,de novosequencing was subject to identify novel peptide.
The parent protein of peptide was determined, when peptide coverage reached 50% or higher, and the score reached 40 points or higher, it could be considered that the protein source had a high credibility. The parameters analyzed were as following: parent ion mass tolerance was 10 × 10-6U, mass tolerance of secondary spectrum was 0.020 U,fixed modification was carbamide methyl (c),variable modification was Deacidation (NQ), Oxidation (m), and nonenzymatic digestion.
2.10 Prediction of peptides bioactivity
The process of peptide separationin vitroincludes protein selection, hydrolysis, separation and purification. The last step is to determine peptide sequences, structure and corresponding functional properties [13]. Studies had shown that the functional activity of polypeptide was largely determined by the amino acid sequence [14].
After spectrum matching and protein identification, in order to further determine the peptides with potential bioactivity, Peptide Ranker (http://distilldeep.ucd.ie/PeptideRanker/) [15] was used to analyze the bioactive possibility of newly discovered peptides at a threshold of 0.8. Peptides predicted over a 0.8 threshold represent higher bioactivity with lower possibility of false positive. And then,BIOPEP database (http://www.uwm.edu.pl/Biochemia/biopep/start_biopep.php) [16] was used to predict their potential bioactivity. This database is continuously updated and is a powerful tool to explore the functional activity of peptides [17].
2.11 Verification of bioactive peptides function
2.11.1 Cell culture
Caco-2 cells were cultured in DEME with 10% fetal bovine serum(FBS), glucose,L-glutamine, sodium pyruvate. Cells were kept in 37 °C incubator with 5% CO2and 90% relative humidity. They were subcultured when up to 80%–90% con fluence with washed 2–3 times by 2–3 mL PBS and released by 0.25% trypsin-EDTA.
Caco-2 cells were seeded in a 6-well plate (1 mL/well) at density of 1.5 × 105cells/mL and cultured in 37 °C humidified CO2incubator for 15 days. Fresh media were changed every 48 h and changed into 24 h at 90% con fluence of cells.
2.11.2 DPP-IV extraction and enzyme activity measurement
DPP- IV extraction: after 15 days’ culture, cells were washed by PBS for 2–3 times, and then collected in a sterilized centrifuge tube.The collected cells were broken with an ultrasonic cell disruptor in ice bath, and ultrasonication was performed with time of 3 s,interval of 6 s, totally 90 times, and ultrasonic power of 250 kW. Part of fragmentized liquid was kept in 90 °C water bath for 20 min to inactivate. Then the fragmentized liquid was centrifuged at 800 r/min for 10 min, the supernatant was reserved as the DPP-IV extract.
Establishment of p-nitroaniline (pNA) standard curve: GLy-PropNA (GLy-Pro-pNA) can be hydrolyzed by DPP-IV enzyme as a substrate under alkaline condition to form pNA, which has a strong absorption peak at 405 nm [18]. The serially diluted pNA solution(0–0.48 mmol/L) with Tris-HCl (pH 8.3) were added into a 96-well plate. Each concentration was set 6 replicate wells. The 96-well plate was incubated at 37 °C for 30 min and the optical density (OD) was measured at 450 nm.
Enzyme activity measurement: 5 different volume (10–50 μL) of 4 °C DPP-IV extract were added into a 96-well plate in ice bath, each concentration was set 6 replicate wells. Each well was added with 500 μmol/L GLy-Pro-pNA solution (4 °C, 50 μL) and supplemented to 125 μL by Tris-HCl. The DPP-IV extract was replaced by inactivated DPP-IV extract in blank control. The 96-well plate was incubated in a 37 °C incubator for 30 min and then the OD value was measured at 405 nm. The enzyme activity was calculated according to the pNA standard curve.
2.11.3 Model evaluation
DPP-IV extract, Ile-Pro-Ile (IPI) solution, 6 peptides solution and Tris-HCl were kept in ice bath for 30 min.
Inhibitory group: IPI peptide was positive control to evaluate model in this assay. Each well in the 96-well plate contained 50 μL DPPIV extract, 25 μL IPI solution and 50 μL 500 μmol/L GLy-Pro-pNA solution. The concentration of IPI solution were at 0.5, 5.0, 10.0, 15.0,20.0, 25.0 and 30.0 mg/L, and each concentration was set 6 replicate wells. IPI solution was replaced by Tris-HCl in the blank control.
Negative group: DPP-IV extract was replaced by inactivated DPPIV extract. Other conditions were the same as the inhibitory group.
The 96-well plate was incubated in a 37 °C incubator for 30 min and then the OD value was measured at 405 nm. the DPP-IV inhibition rate was calculated by formula as follows:
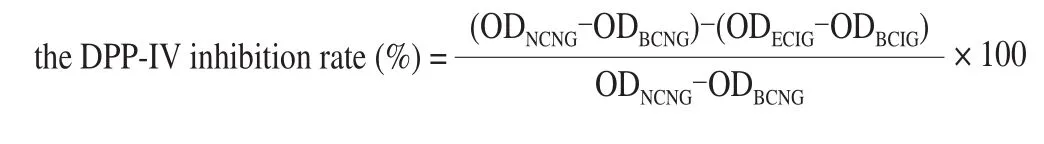
where NCNG represented negative control in negative group;BCNG represented blank control in negative group; ECIG represented experimental control in inhibitory group; BCIG represented blank control in inhibitory group.
2.11.4 Determination of the DPP-IV inhibition rate
Inhibitory group: each well in the 96-well plate contained 50 μL DPP-IV extract, 50 μL 500 μmol/L GLy-Pro-pNA solution and 25 μL peptide solution with six different concentration serially diluted(0.5–100 mg/L). Each concentration was set 6 replicate wells. Peptide solution was replaced by Tris-HCl in the blank control.
Negative group: DPP-IV extract was replaced by inactivated DPPIV extract. Other conditions were the same as the inhibitory control.
The 96-well plate was incubated in a 37 °C incubator for 30 min and then the OD value was measured at 405 nm. the DPP-IV inhibition rate was calculated by formula mentioned before.
2.11.5 Determination of the DPP-IV inhibition mechanism
The GLy-Pro-pNA solution (25–1 000 μmol/L) and peptides(0, IC50/4 mg/mL, IC50/8 mg/mL) were kept in ice bath for 30 min and measured absorbance at 405 nm for 30 min (37 °C). Each concentration was set 4 replicate wells. Then, regression equations(y = Km/Vmax× x + 1/Vmax) werefitted and DPP-IV inhibition modes were assessed by the Lineweaver-Burk plots.
2.12 Data statistics
The experimental results were presented as the form of mean ±standard deviation (SD), and the DPP-IV inhibition rate and modes were analyzed by Origin 2019 software.
3. Results and discussion
3.1 Cell purity detection by flow cytometry
The purity of lymphocytes was detected by flow cytometry. The results showed that CD3 and CD19 were positive. The number of lymphocytes in mouse spleen was 6 × 106cells, and the purity reached 98.3% (Fig. 3). Therefore, it was considered that mouse spleen lymphocyte culture was successful, and it was suitable for the analysis of intracellular peptides, next step experiments can be proceeded.
3.2 Identification of peptides
The UniProt database whose sequences were mainly from genome sequencing offered the proteome identifier to identify the unique sequence and track the parent protein, in which an annotation score was provided to identify the best characterized protein [19].All detailed annotations about peptides supported by literature and database are always updating as new proteins were characterized [12].The UniProt Knowledgebase (UniProtKB) is combination of database of UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot and UniProtKB/TrEMBL, which has the largest number and the most complete information [20].
The mass spectrum results were shown in Fig. 4. According to the mass spectrum data analysis by PEAKS X software, 385 peptides were identified from mouse spleen lymphocytes in this study. 309 peptides were identified from 116 parent proteins in the experimental group and 149 peptides were identified from 51 parent proteins in the control group (Fig. 5). There were 73 peptides both in the experimental group and control group. These results indicated that the type and number of peptides in mouse spleen lymphocytes have changed greatly after being stimulated by the external source.

Fig. 3 Determination of purity of mouse spleen lymphocytes by flow cytometry. A-D. unlabelled, CD3, CD19, CD3 + CD19.
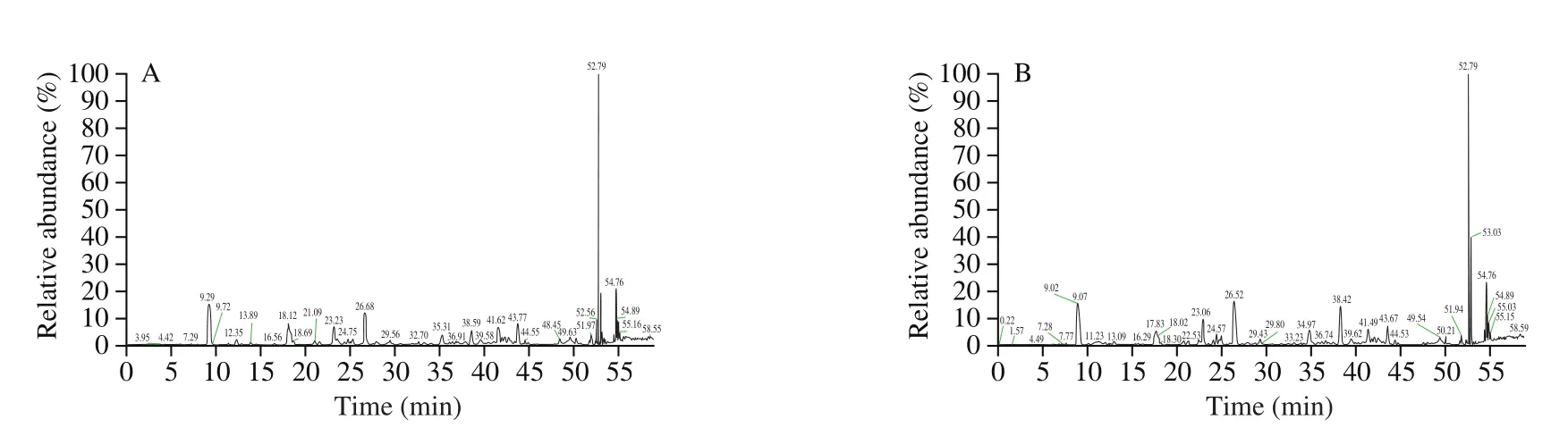
Fig. 4 Mass spectra of intracellular peptides in control group (A) and experimental group (B) stimulated by LPS.
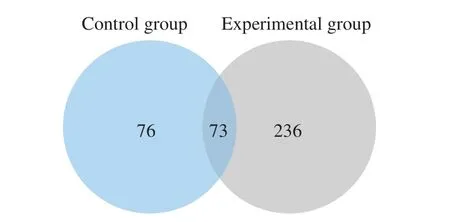
Fig. 5 Comparison of the intracellular peptides number in control group and experimental group before and after LPS stimulation.
The source of peptide can be divided into exogenous peptide and endogenous peptide. At present, the research of peptide mainly focuses on exogenous peptide, and generally comes from animal and plant protein directly or indirectly. For example, the peptide spectrum of milk and goat milk was analyzed by NANO-LC-QTOF, and identified 159 and 187 peptides respectively [21,22]. After purification by gelfiltration chromatography and reversed-phase HPLC, Brondani et al. [23] detected 104 peptides in enzymatic soybean hydrolysates.Endogenous peptides mainly came from living organs, tissues, cells and body fluids. Previous studies have used ultrafiltration to separate natural peptides from urine of diabetic patients and analyzed them by LC-MS/MS. After searching MS/MS data in UniProt human protein database for peptide and protein identification, 1 080 peptides were identified, corresponding to a total of 100 proteins [24]. In addition,researchers conducted peptideomics analysis on three different human cell lines (SH-SY5Y, MCF7 and HEK293), and identified 272 peptides, and some peptides existed in different cell lines at the same time [25]. Therefore, a large number of peptide components could be obtained from tissues and cells of organisms. The results of this study were basically consistent with these reports.
The experimental results also showed that the number and type of peptides in lymphocytes stimulated by LPS are significantly more than those in the control group. The reason might be that lymphocytes secreted a variety of cytokines stimulated by LPS. In the process of immune response, immune cells played a key role in immune response by acting on target cells by cytokines. And these cytokines were natural peptides. Therefore, lymphocytes stimulated by LPS might produce many new peptides with immunoregulatory activity.
Most peptides are products of protein after hydrolysis or ubiquitin proteasome degradation. Peptides are generally located in the functional regions (protein binding or active regions) of the parent protein, so the peptides located in these two regions can retain certain functions of the parent protein, and even play similar roles [26].Therefore, the potential functional properties of peptide fragments could be predicted based on the function of the parent protein [27].The peptides identified in this study mainly come from two kinds of proteins: histone (H2A and H2B) and ribosomal proteins (40S and 60S). Histones were positively charged nucleoproteins that help to package DNA into nucleosomes common to all eukaryotes. In the process of cell injury or cell signal transmission, histone was released passively through cell necrosis or released actively from immune cells as an extracellular part. The function of extracellular histone was bactericidal protein, which could limit the spread of infection or isolated the damaged area by promoting intravascular thrombosis,so as to allowed immune cell infiltration, eliminate infection, and initiate tissue regeneration and repair [28,29]. Therefore, according to the related immune mechanism of histone, it could provide a new therapeutic strategy for histone targeted therapy of acute in flammatory diseases [30]. Ribosomal protein was the main component of ribosome, and it was also the key substance for protein synthesis in cells. Ribosomal protein was mainly processed and assembled by 4 rRNA and 80 ribosomal proteins to form large (60S) and small (40S)ribosomal subunits, and each of which had a specific function of translating mRNA into protein. Studies have shown that ribosomal proteins had tissue-specific functions in addition to ribosome structure and mRNA translation [31]. Some researchers isolated and purified a peptide substance RPS3 from 40S/60S ribosome, which could participate in the regulation of apoptosis signal pathway and geneexpression, and had positive effects on the immune system [32]. It could induce the maturation and activation of dendritic cells, acted as a new ligand for Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) in the innate immune system, and significantly increased the production of CD8+T cells in the presence of tumor specific antigen in the adaptive immune system.Therefore, RPS3 was a new and potentially important substance for the development of cancer vaccine for treatment and prevention [33,34].It could be found that these two types of proteins played important roles in the immune system, so the peptide fragments derived from these two types of proteins were likely to have high immunoregulatory activity.
In this study, we searched through Google (http://www.google.cn/), Bing database (https://cn.bing.com), domestic patent websites(http://pss-system), foreign patent websites (https://www.wipo.int/pct/en/, https://www.epo.org/)and some other websites to search and compare the peptide sequences identified in this study to determine whether they have been reported or not. The results were shown in Table 2. The results showed that 108 peptides were found in the experimental group and 45 peptides were found in the control group.Among them, 22 peptides were found in both of them.
3.3 Prediction results of peptide bioactivity
Peptide Ranker is a useful tool for selecting the most likely bioactive peptides, and it uses different calculation methods for amino acid numbers greater than 20 and less than 20. Peptide Ranker scores the peptide sequence through the built-in N to 1 neural network. The algorithm can predict the biological activity of peptides based on the general characteristics shared by different functional classes of bioactive peptides [35]. The software will score peptides as a standard to predict bioactive possibility of peptides. The peptide with score higher than 0.5 will be considered to have bioactivity. In order to reduce false positive results, the threshold value was set to 0.8 [36].The peptide score was shown in Table 2.
Research showed that peptides with scores higher than 0.8 were considered to have high bioactivity [36]. In the peptide score row in Table 2, there were 6 peptides scored more than 0.8. Then, the“profiles of potential biological activity” in BIOPEP was used to search for the possible bioactive segments of six peptide. The result was shown in Table 3.
DPP-IV inhibitory activity was the main potential activity of these 6 peptides (Table 3). DPP-IV inhibitors are a class of commonly used in drugs for the treatment of type II diabetes. They can reduce blood glucose level by inhibiting DPP-IV enzyme activity, prolonging the action time of glucagon peptide I and promoting insulin secretion [37].Recent studies showed that several food-derived proteins in milk,eggs and fish, contained peptides inhibiting the activity of DPP-IV enzyme in their sequence [38]. Bioactive peptides in this study showed similar activity, so peptides in this study were synthesized to verify the function of DPP-IV inhibitor.

Table 3Retrieve the active peptides sequence using BIOPEP.
3.4 Verification of bioactive peptides
3.4.1 Enzyme activity measurement
GLy-Pro-pNA substrate were hydrolyzed by DPP-IV enzyme to generate pNA [39]. The pNA standard curve was shown in Fig. 6. The enzyme activity was calculated according to the pNA standard curve.As shown in Fig. 7, enzyme activity will be changed as increase of the amount of DPP-IV extract, two variables are in positively correlation.According to the result, the DPP-IV extract of different batches were diluted with Tris-HCl to 0.001 5 U/mL for the subsequent assay.
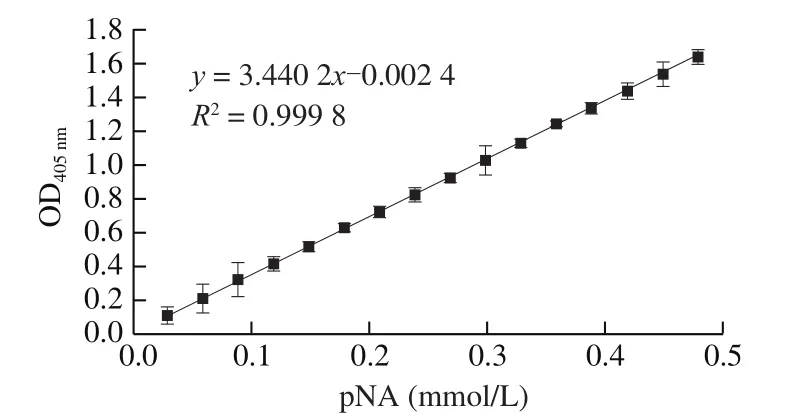
Fig. 6 The standard curve of pNA.
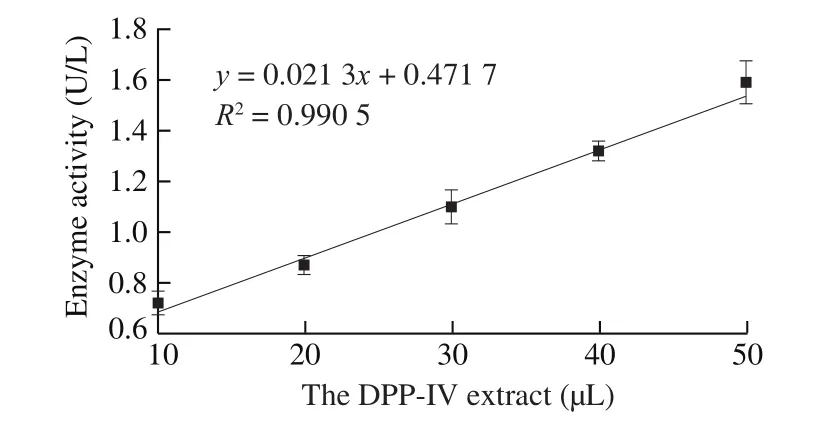
Fig. 7 Correlation curve of the DPP-IV extract and enzyme activity.
3.4.2 Model verification
The IPI is the best peptide in inhibiting DPP-IV enzyme reported to date [40]. In this study, IPI was used as the positive control to verify the selected DPP-IV inhibitor model. A regression curve was drawn and the regression equation wasfitted. As shown in Fig. 8, the DPP-IV inhibition rate increases with the increase of IPI concentration.IC50value of IPI was (11.406 6 ± 0.480 0) μg/mL, which was consistent with the previous report [41]. Therefore, the model in this study can be applied to the screening of DPP-IV inhibitors.

Fig. 8 Regression curve of the DPP-IV inhibition rate of IPI.
3.4.3 Determination of the DPP-IV inhibition rate
Six novel peptides were synthesized and the DPP-IV inhibition rate was determined by established mode. Regression curves were drawn and regression equations were fitted. As shown in Fig. 9,the IC50value of 6 peptides were calculated according to the regression equation and were shown in Table 4. The results indicated that SAPRHGSLGFLPRK (IC50(23.443 7 ± 1.040 0) mg/L) and SGVSLAALKKALAAAGYDVEK (IC50(84.193 9 ± 2.870 0) mg/L)showed better potential of DPP-IV inhibitor (< 100 μmol/L).
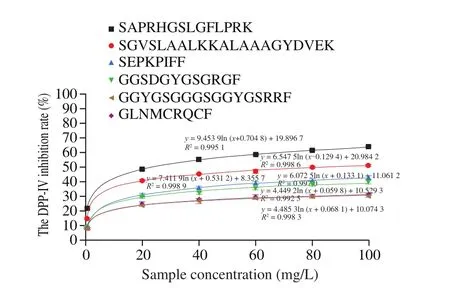
Fig. 9 Regression curve of the DPP-IV inhibition rate of 6 peptides.

Table 4The DPP-IV inhibition rate (IC50 values) of 6 peptides (n = 6).
Enzyme inhibition mechanisms have 4 types including competitive, uncompetitive, noncompetitive and mixed modes [42]. Two peptides (SAPRHGSLGFLPRK and SGVSLAALKKALAAAGYDVEK) showed better potential of DPP-IV inhibitor were tested to confirm the inhibition mechanism.According to Lineweaver-Burk plots showed in Fig. 10 and Fig. 11, the DPP-IV inhibition modes of SAPRHGSLGFLPRK was competitive and SGVSLAALKKALAAAGYDVEK was noncompetitive. The result indicated that SAPRHGSLGFLPRK inhibited DPP-IV enzyme by binding enzyme at the active site and preventing binding of the substrate. And SGVSLAALKKALAAAGYDVEK inhibited the DPP-IV enzyme at a site other than enzyme-substrate binding site, which meant SGVSLAALKKALAAAGYDVEK will not obstruct the enzymesubstrate binding. SGVSLAALKKALAAAGYDVEK can not only bind to the enzyme-substrate complex, but also just bind to the enzyme. As for the competitive mode of SAPRHGSLGFLPRK, this might be related to the strong specificity of the second N-terminal site(P1) of the peptide [43].

Fig. 10 The Lineweaver-Burk plot of different concentrations of the peptide(SAPRHGSLGFLPRK) (n = 4).
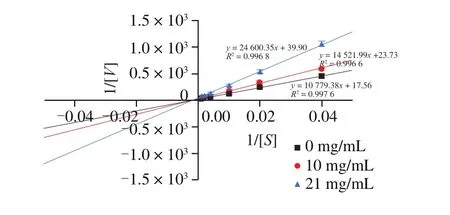
Fig. 11 The Lineweaver-Burk plot of different concentrations of the peptide(SGVSLAALKKALAAAGYDVEK) (n = 4).
The result of SAPRHGSLGFLPRK as potent DPP-IV inhibitor was consistent with the research, which mentioned that DPP-IV inhibitory activity will be better on condition thatP1position is Pro or Ala [43,44]. Gly atP1position was also deemed to be helpful to inhibit the DPP-IV enzyme, although affinity was not so splendid as Pro and Ala amino acids [45,46]. This also accounted for the higher IC50of SGVSLAALKKALAAAGYDVEK.
Hydrophobic amino acids lead to the superior DPP-IV inhibitory activity as well [47], and peptide SGVSLAALKKALAAAGYDVEK with better inhibitory activity may be related to the large number of hydrophobic amino acids, even including 6 consecutive amino acids(Ala, Leu, Ala, Ala, Ala, Gly) among the fragment. Similarly, vast majority of amino acids in SAPRHGSLGFLPRK were hydrophobic.The second (P1) and third (P1’) N-terminal site of two peptides were both hydrophobic amino acids.
At the same time, the difference of amino acids at the N-terminal and C-terminal will in fluence the inhibitory activity, the Lys residue can remarkably increase the DPP-IV inhibitory activity [48]. Two peptides all have the Lys residue at C-terminal, which may be one of the reasons of superior inhibitory activity. Besides, length of peptides may have effect on the inhibitory activity. The peptide with shorter sequence was more effective in inhibiting DPP-IV enzyme in this study, which meant shorter peptides may be more likely to be the potent DPP-IV inhibitor under certain cases. But there was no significant inhibitory effect observed on peptide SEPKPIFF,which indicated that the DPP-IV inhibitory activity was the result of numerous factors.
Significantly, peptide SAPRHGSLGFLPRK was found in the experimental group, so that SAPRHGSLGFLPRK as the most effective inhibitor in this study was the product stimulated by LPS.This revealed that more effective functional peptides might be secreted by lymphocytes after external stimulus.
4. Conclusion
A method of isolating and identifying peptides in mouse spleen lymphocytes was established through this study, of which 131 novel peptides (totally 385 peptides) were discovered. The length of peptide chains ranged from 8 to 30 amino acids. The parent protein of each peptide was determined as well. At the same time, a model of researching the DPP-IV inhibitory function was established.The result by this model showed that SAPRHGSLGFLPRK (IC50(23.443 7 ± 1.040 0) mg/L) and SGVSLAALKKALAAAGYDVEK(IC50(84.193 9 ± 2.870 0) mg/L) peptides can be selected as candidates of DPP-IV inhibitor by competitive mode and noncompetitive mode, respectively. Two non-food derived bioactive peptides with effective DPP-IV inhibitory activity were found in this study. Besides, this study showed that lymphocytes might secret more novel bioactive peptides after external stimulus, which might be more effective in certain aspects of function.
Different modes of two peptides indicated that they have different binding sites for the enzyme. So, stronger inhibitory effects may be found by the compound peptide. Further studies are required to develop difference effects of the single peptide and the compound peptide. Besides, exploring molecular structures fit and predicting interaction of ligand and receptor from the molecular structure by the molecular docking simulation are also a necessity, which will contribute to the development of bioactive peptide-based health products and formula food for special medical purposes.
Con flict of interest
The authors declared there is no con flict of interest.
- 食品科学与人类健康(英文)的其它文章
- A review on mechanisms of action of bioactive peptides against glucose intolerance and insulin resistance
- Adropin as an indicator of T2DM and its complications
- Isolation and characterization of novel peptides from fermented products of Lactobacillus for ulcerative colitis prevention and treatment
- The immunity-promoting activity of porcine placenta in mice as an immunomodulator for functional foods
- Nutritional properties of Europen eel (Anguilla anguilla) bone peptide-calcium and its apoptosis effect on Caco-2 cells
- A comprehensive method to explore inhibitory kinetics and mechanisms of an anticoagulant peptide derived from Crassostrea gigas

