Advances in Chinese medicine treatment and research on endocrine diseases in 2021
Bao-Chao Pan,Hui Zhang,Han-Zhou Li,En-Ze Yuan,Jun-Yu Luo,Ting-Rui Zhang,Shu-Quan Lv,Wei-Bo Wen,Huan-Tian Cui
1Hebei University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Shijiazhuang 050091,China.2Chengde Medical College, Chengde 067000, China.3The First Clinical Medical College of Yunnan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Kunming 650500, China.4Cangzhou Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine Affiliated to Hebei University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Cangzhou 061001, China.5The First Affiliated Hospital of Yunnan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Kunming 650021,China.6School of Life Sciences,Shandong University,Qingdao 266000,China.
Abstract This paper reviews the progress in treatment regimens involving traditional Chinese medicine and research on common clinical endocrine diseases in 2021, to provide a reliable basis for the traditional Chinese medicine treatment of endocrine diseases.In 2021-2022, research on traditional Chinese medicine for endocrine diseases has been focused on pathogenesis.We have summarized the results of the use of traditional Chinese medicine and herbal extracts for treating common endocrine system diseases in 2021, focusing on the following aspects.(1) Chinese herbal extracts or active ingredients, such as echinatin, breviscapine, and puerarin, can treat metabolic-associated fatty liver disease by inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress,improving lipid metabolism, and regulating intestinal flora.(2) Chinese herbal extracts or active ingredients, such as Juglandis Semen extracts, Momordica charantia saponins, and Anemarrhenae Rhizoma extracts can treat type 2 diabetes by reducing insulin resistance, improving pancreatic beta cell function, and regulating intestinal microbial disorders.(3) Chinese herbal extracts or active ingredients, such as berberine, astragaloside IV, and Scutellariae Barbatae Herba polysaccharides, can treat diabetes-related complications by improving mitochondrial function,regulating autophagy,and inhibiting apoptosis and pyroptosis.(4)Chinese herbal medicines and herbal extracts or active ingredients, such as berberrubine and Resedaodorata, can treat hyperuricemia by activating the Janus kinase 2/signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 signaling pathway and inhibiting toll-like receptor 4/NOD-like receptor family, pyrin domain-containing protein 3 signaling to increase urate excretion.(5) Herbal extracts or active ingredients, such as ginsenoside Rb1, corylin, and Scutellariae Radix polysaccharides, can exert anti-obesity effects by promoting the browning of white adipocytes, activation of brown adipose tissue,and regulation of intestinal flora.(6)Chinese herbal extracts or active ingredients,such as diosgenin and Prunellae Spica extract, are able to treat thyroid-related diseases by inhibiting nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3 inflammatory vesicle activation, regulating the expression of proliferating cell nuclear antigen, and cadherin 1, and upregulating the ubiquitination of interferon regulatory factor 4.
Keywords:endocrine metabolic diseases;Chinese medicine;Chinese herbal extracts;therapeutic mechanisms; intestinal flora
Background
Endocrine diseases, including metabolism-related fatty liver disease,diabetes, and its complications, hyperuricemia, obesity, and thyroid disorders, are chronic, progressive, and seriously affect patients’health and quality of life.After reviewing the literature related to traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) and its extracts for endocrine diseases in 2021 in the PubMed database, we found that the research hotspots in 2021 were not limited to simply verifying the effectiveness of TCM in treating diseases but were more inclined to study the deeper therapeutic mechanisms.Intestinal microorganisms play an important role in regulating the human immune system and participating in nutrient metabolism [1].The development of endocrine diseases is closely dependent on the human immune system and the metabolism of the organism.The study of the effect of TCM intervention on the downstream signaling pathways of the intestinal flora has become a new hot topic in the ongoing research on metabolism-related fatty liver disease, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), obesity, and other endocrine diseases.For example, TCM and its extracts can promote the balance of intestinal flora and thus treat related diseases by modulating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) γ.
Toll-like receptor 4(TLR4),recombinant fibroblast growth factor 21(FGF21), and other signaling pathways to a certain extent [2-4].In vitro cell model experiments have become one of the tools to advance medical progress with their more refined and deeper mechanistic exploration.Although most studies on identifying the mechanism of TCM and its compound prescriptions have included animal models, in vitro experiments are now being increasingly used.Representative in vitro model experiments includes Schwann cell model experiments,L02 model experiments, and INS-1 cell model experiments [5-7].The use of drug-containing serum in Chinese medicine and its pure extracts as in vitro models for drug administration is promising for future development.
Although the efficacy of Chinese medicine and its compound formulas has been clinically tested as one of the traditional ways of treating diseases,the active substances and mechanisms of action have not been elucidated.The fundamental reason for this is that Chinese herbal medicine has multiple active ingredients that can play a part in the diagnosis, treatment, and regulation of human diseases through multi-component and multi-target synergistic effects.Therefore,describing the causative pathogenic substances and the action pathways of complex syndromes, to comprehensively and accurately evaluate the effects of TCM and their compound prescriptions, has become a major area of research in modern medicine.The emergence and development of new biotechnologies, such as network pharmacology, metabolomics, and protein blot analysis, help meet this need.In addition,based on this,some new mechanisms have been discovered;for example,through network pharmacology,multi-omics,and protein blotting analysis, we found that breviscapine can inhibit human transforming growth factor kinase 1 phosphorylation and downstream c-Jun N-terminal kinase/p38 activation,Bupleuri Radixextract can upregulate the expression of the FGF21 signaling pathway,and Fufang Zhenzhu Tiaozhi formula can increase PI3K/AKT phosphorylation and decrease hypoxia-inducible factor 1α expression[4, 8, 9].
In summary, TCM and its extracts have their advantages in the prevention and treatment of endocrine diseases; therefore, studying the underlying mechanism of action is advantageous as it will contribute to their better use in clinical treatment.In this paper, we review the treatment and research progress of TCM for common endocrine diseases in clinical practice from 2021 to 2022, with the aim of providing a reliable basis for the TCM treatment of endocrine diseases.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/metabolic associated fatty liver disease
We renamed nonalcoholic fatty liver disease to metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) in accordance with the top international expert consensus in 2020 [10].MAFLD is one of the leading causes of chronic liver disease worldwide [11].MAFLD can be classified as simple steatosis or nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, which is associated with insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome, though their pathogenesis is unclear.Inflammatory response and oxidative stress are one of the main pathological manifestations of MAFLD, and disorders of lipid metabolism are observed throughout the development of MAFLD.In the past year, a large number of studies have shown that TCM and its extracts can prevent and treat MAFLD by inhibiting inflammatory responses and oxidative stress and improving disorders of hepatic lipid metabolism (Table 1).
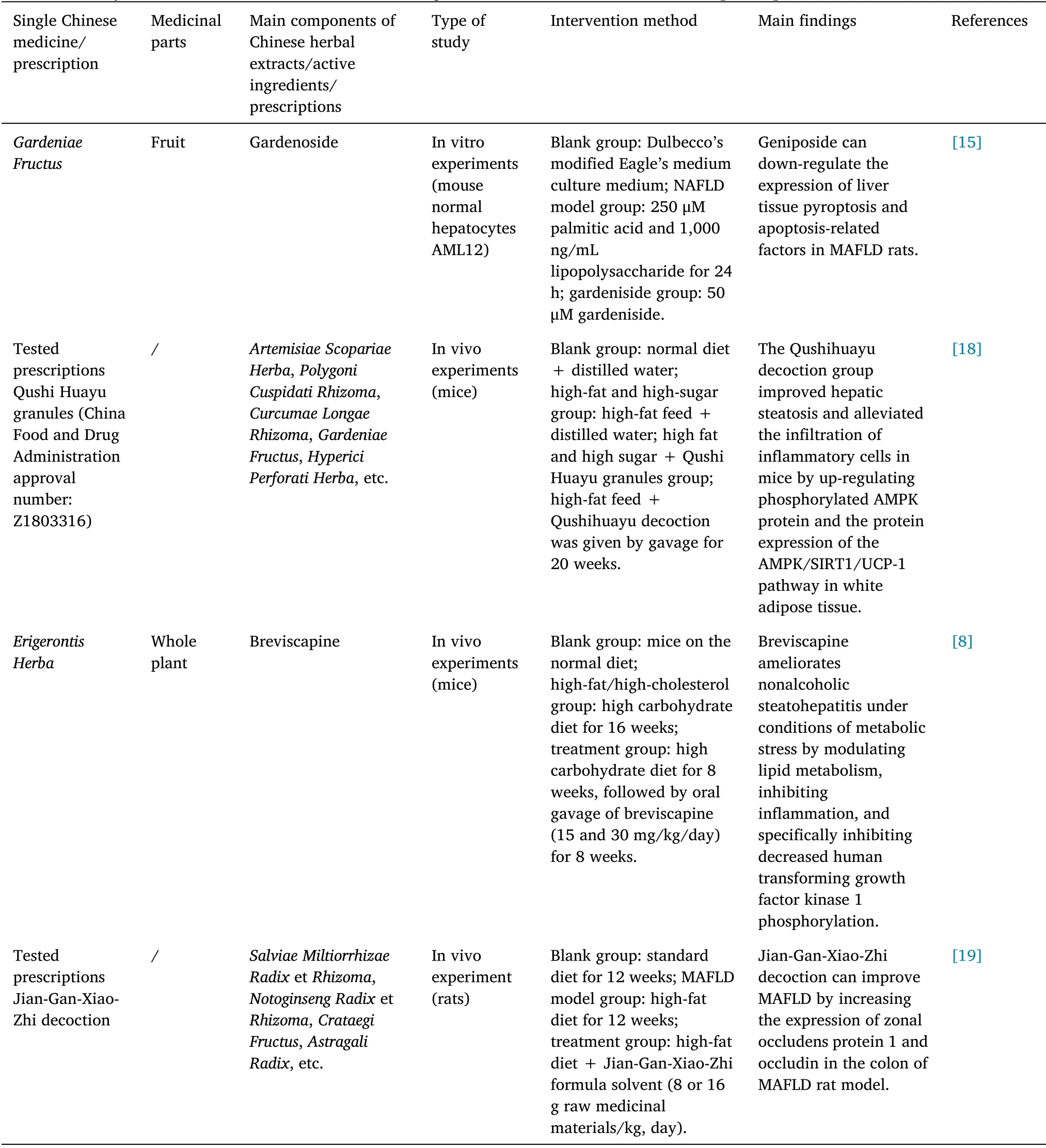
Table 1 Study on the mechanism of action of main single traditional Chinese medicine and prescriptions in the treatment of MAFLD
Inhibition of inflammatory response and oxidative stress
Chinese medicine monomers and extracts.Flavonoids: echinatin, a bioactive flavonoid ofGlycyrrhizae Radix, can inhibit hepatic recombinant NOD-like receptor family, pyrin domain-containing protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammatory vesicle activation in MAFLD in a mouse model by binding to the heat shock protein 90, thereby interfering with the interaction between the small glutamine-rich tetratricopeptide repeat-containing protein 1 and the heat shock protein 90-NLRP3 complex [12].Puerarin is an isoflavone derivative extracted from the Chinese medicinePuerariae Radix.Puerarin was shown to improve metabolic disorders and balance intestinal flora by inhibiting the production ofHelicobacterspp.and promoting the production ofRhodobacterspp.to reduce liver steatosis and inflammation in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis mice[13].
Glycosides: cordycepin (source:Puerariae Radix) was found to significantly downregulate the expression of inflammatory factors(tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin (IL)-6, and IL-1β) and macrophage markers (monocyte chemotactic protein-1, macrophage inflammatory protein 2, megakaryocyte, and vascular cell adhesion molecule 1) in MAFLD, while upregulating β-oxidation-related proteins[14].Gardenoside is one of the extracts of the TCM gardenia.
Gardenoside (source:Gardeniae Fructus) can downregulate the expression of scorch death and apoptosis-related factors in MAFLD rat liver tissues, and further in vitro studies have confirmed that the mechanism of gardenia glucoside-inhibiting cell scorch death is related to the downregulation of the CTCF/DPP4 signaling pathway[15].
Chinese herbal extracts.Defatted walnut powder extract is the main active ingredient of the Chinese herbal medicine walnut kernels.Defatted walnut powder extract (source:Juglandis Semen) could improve lipid metabolism disorders and reduce the expression of nuclear factor-kappa B and mitogen-activated protein kinases family proteins in the liver tissues of MAFLD mice, and its mechanism of action might be related to an increase in the relative abundance ofBacteroidesandClostridiumand a decrease in the relative abundance of thick-walled bacteria andActinomyces[16].
Chinese herbal compounds.Tested prescriptions: the Cigu Xiaozhi pill (composed ofIphigenia indicaKunth,Pinelliae Rhizoma Praeparatum,Bupleuri Radix,Poria,Salviae Miltiorrhizae RadixetRhizoma, and other herbal medicines) exerts therapeutic effects on nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by regulating the expression of p-JNK,p-c-Jun, caspase-8, Fas, and Fas-L to inhibit the occurrence of hepatocyte apoptosis [17].The Qushi Huayu granules (composed ofArtemisiae Scopariae Herba,Polygoni Cuspidati Rhizoma,Curcumae Longae Rhizoma,Gardeniae Fructus,Hyperici Perforati Herba, and other herbal medicines) improve hepatocyte steatosis and reduce inflammatory cell infiltration in mice by upregulating the expression of adenosine 5’-monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK)protein and AMPK/silent mating type information regulation 2 homolog-1/uncoupling protein 1 pathway protein in white adipose tissue [18].The Jian-Gan-Xiao-Zhi decoction (composed ofSalviae Miltiorrhizae RadixetRhizoma,Notoginseng RadixetRhizoma,Crataegi Fructus,Astragali Radix, and other herbal medicines) can improve MAFLD by increasing the expression of zonal occludens protein 1 and occludin in the colon of the MAFLD rat model [19].
Classic ancient formula: the ancient classic Chinese medicine formula Shenling Baizhu powder (Codonopsis Radix,Atractylodes macrocephala,Poria,Dioscoreae Rhizoma,Nelumbinis Semenand other medicinal components)can upregulate the expression of inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1b, IL-1ra, IL-2, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant-1, in the liver tissues of the MAFLD rat model by reducing the expression of the TLR4/NLRP3 signaling pathway-related proteins [3].
Improvement of lipid metabolism disorders
Chinese medicine monomers and extracts.Flavonoids:breviscapine is a natural flavonoid prescription drug isolated from the traditional Chinese herbErigerontis Herba[8].In an article published inHepatology,the use of multi-omics and protein blot analysis showed that breviscapine delayed the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by inhibiting human transforming growth factor kinase 1 phosphorylation and downstream c-Jun N-terminal kinase/p38 activation, and further studies revealed that breviscapine ameliorated nonalcoholic steatohepatitis under conditions of metabolic stress by regulating lipid metabolism, suppressing inflammation, and inhibiting human transforming growth factor kinase 1 phosphorylation.In a model of free fatty acid-induced hepatocyte steatosis, the anthocyanin malvidin-3-O-glucoside, extracted from blueberries, ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by modulating the transcription factor EB (TFEB) mediated lysosomal function and activating the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway[20].
Esters: crocetin is one of the active ingredients in the traditional Chinese herbCarthami Flos.It has been shown that crocetin can significantly improve lipid metabolism disorder in L02 cells and zebrafish, and its mechanism of action may be related to the regulation of mitochondrial dysfunction [6].
Chinese herbal extracts.The highland barleyMonascus PurpureusWent extract can improve abnormal lipid metabolism in MAFLD by regulating fatty acid metabolism (sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1/acetyl-CoA carboxylase/fatty acid synthase,PPARα/long-chain acyl-co A synthetase/carnitine palmitoyl transterase-1/acyl-coenzyme A oxidase 1) and factors related to cholesterol metabolism (recombinant 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase, low-density lipoprotein receptor, cholesterol 7a-hydroxylase) [21].In vitro studies revealed an increase in AMPK phosphorylation and a decrease in liver X receptor α activity in human hepatocellular liver carcinoma cell line cells treated with vine tea extracts (source:Ampelopsis Megalophylla DielsetGilg) in a model of steatosis[22].
Chinese herbal compound.Tested prescriptions: based on network pharmacology validation and experimental studies, it was shown that the TCM formula compound Fufang Zhenzhu Tiaozhi formula (Ligustri Lucidi Fructus,Coptidis Rhizoma,Salviae Miltiorrhizae RadixetRhizoma,Notoginseng RadixetRhizoma,Citri Sarcodactylis Fructusand other drugs) could improve lipid metabolism by increasing the phosphorylation of PI3K/AKT and decreasing the expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α [9].
Classic ancient formula: the classic ancient Chinese medicine formula Sini powder (composed ofBupleuri Radix,Paeoniae Alba Radix,Aurantii Immaturus FructusandGlycyrrhizae Radix) ameliorates MAFLD lipid metabolism disorders by inhibiting the Janus kinase 2/signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 (STAT3)signaling pathway[23].
T2DM
With the improving living standards, the incidence of T2DM is increasing annually.The International Diabetes Federation predicts that the number of people with diabetes globally will reach 700 million by 2,045[24].After cardiovascular diseases and cancer,T2DM has become the third most prevalent chronic disease that seriously endangers human health, and its complications can cause disability or even death [25].The pathogenesis of T2DM is not clear, and its main features include different degrees of insulin resistance and pancreatic β-cell dysfunction.A large number of studies in the last year have confirmed that TCM and herbal extracts can prevent and treat T2DM by reducing insulin resistance and improving pancreatic β-cell function (Table 2).
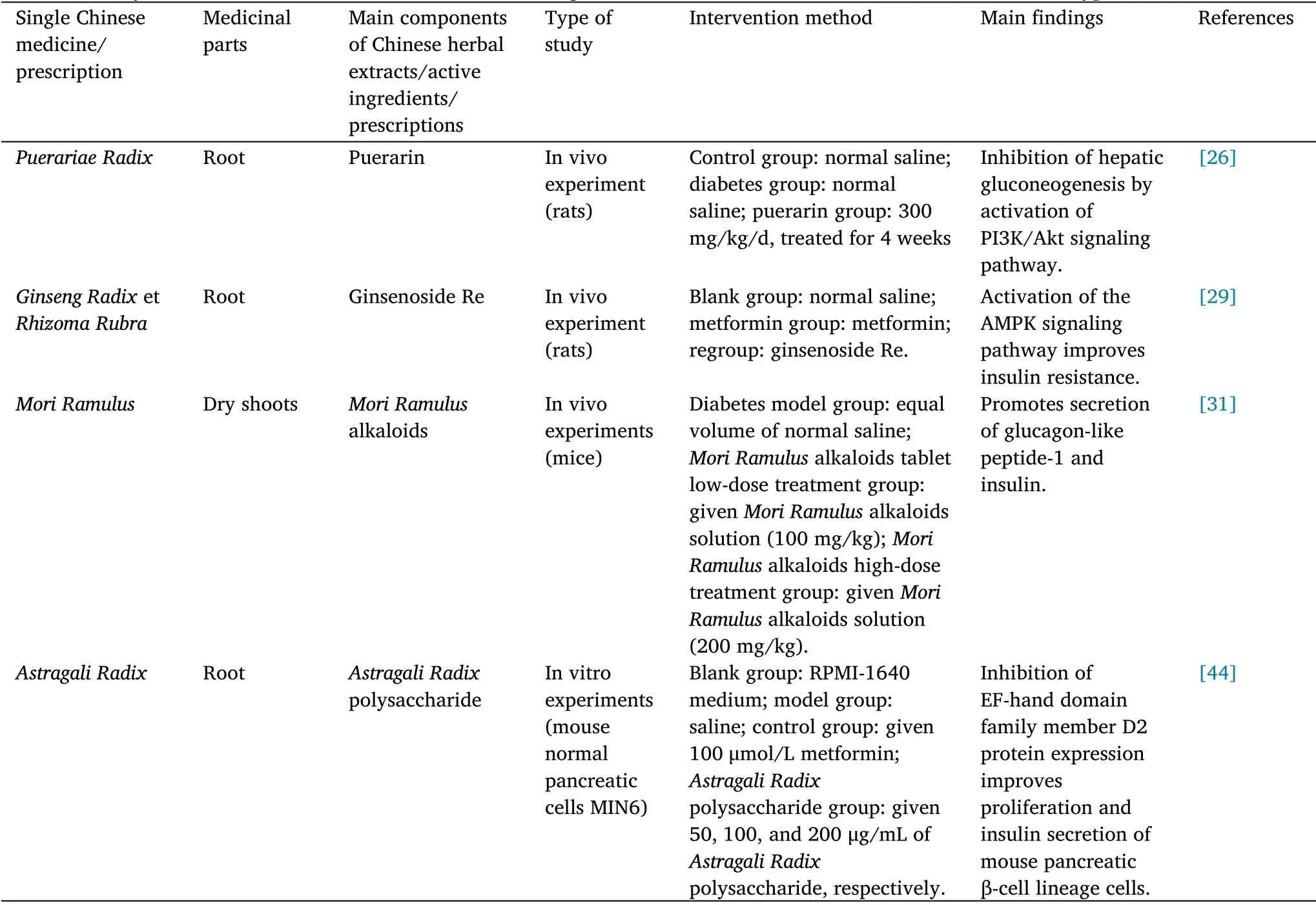
Table 2 Study on the mechanism of action of the main single traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Reduction of insulin resistance
Chinese medicine monomers and extracts.Flavonoids: puerarin,extracted fromPuerariae Radix,can inhibit hepatic gluconeogenesis by activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, thus effectively reducing fasting glucose, glycated hemoglobin, and triglyceride levels in diabetic rats [26].
Glycosides: cistanche tubulosa total glycosides (source:Cistanches Herba) improved oral glucose tolerance test and insulin sensitivity while reducing fasting glucose and glycated hemoglobin levels in rats by inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation [27].Hesperidin(source:Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium) can reduce insulin resistance in diabetic rats, and its mechanism of action may be identified by enhancing the expression of miR-149, thus improving oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction [28].It was found that ginsenoside Re(source:Ginseng RadixetRhizoma Rubra) activated the AMPK signaling pathway to improve insulin resistance by stimulating cannabinoid receptor 1 and calmodulin-dependent protein kinase β[29].The study confirmed that astragaloside IV (source:Astragali Radix) significantly improved the disorders of glucolipid metabolism,insulin resistance, and abnormal levels of oxidative stress in T2DM mice, and its mechanism of action may be related to the regulation of the AMPK and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways[30].
Alkaloids:Mori Ramulusalkaloid are natural water-soluble alkaloids isolated and purified fromMori Ramulusthat promote the secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1 and insulin and improve insulin resistance in mice by increasing the relative abundance ofBacillariophyceaeandWartybacteriaand decreasing the abundance ofRikeniaceaeandDesulfovibrio[31].
Polysaccharides:Puerariae Radixpolysaccharide, derived from the TCMPuerariae Radixcan improve insulin resistance and glucose and lipid metabolism in db/db mice by activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway [32].TheCoicis Semenpolysaccharide (source:Coicis Semen)improves blood glucose levels in mice by promoting the growth of bacteria rich in short-chain fatty acids, thereby activating the GF1/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway[33].
Chinese herbal extracts.Scutellariae Radixextract is a general term used to refer to the effective substances extracted from the Chinese herbScutellariae Radix, which can induce the autophagy of macrophages in pancreatic islets by activating the AMPK signaling pathway, increase insulin secretion, and alleviate clinical symptoms[34].Sophorae Flavescentis Radixextract (source:Sophorae Flavescentis Radix) ameliorated hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia, and insulin resistance in mice by activating the protein kinase C/glucose transporter 4 signaling pathway and regulating the expression of PPARα and PPARγ [2].The administration of piperine powder significantly improved clinical symptoms in diabetic rats, and the mechanism of action was related to the regulation of glucose transporter-2/4 and AKT signaling pathways [35].In a study on theJuglandis Semenextracts (source:Juglandis Semen), it was confirmed that it could improve intestinal microbial disorders by modulatingLactobacillusspp.,Rikensspp.,Bigeliaspp.,Treponemaspp., andKlebsiellaspp., which in turn improved oxidative stress and inflammatory response and reduced insulin resistance in rats [36].Anemarrhenae Rhizomaextract (source:Anemarrhenae Rhizoma)ultimately improved blood glucose, lipid levels, and inflammatory status and reduced insulin resistance in diabetic rats by promoting the proliferation ofBlastocystisglobosa and expression of peroxidase 4[37].
Chinese herbal compound.Tested prescriptions: the Chinese medicine formula Sanye tablet (Mori Folium,Nelumbinis Folium,Crataegi Fructus,Salviae Miltiorrhizae RadixetRhizoma,Paeoniae Alba Radix and other medicinal compositions) can inhibit hepatic adipogenesis through the downregulation of sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1/acetyl-CoA carboxylase and JAK/STAT signaling pathways, thus improving diabetic lipid metabolism and insulin resistance [38].The Chinese medicine formula Dangua recipe(Salviae Miltiorrhizae RadixetRhizoma,Trichosanthis Fructus,Curcumae Radix,Paeoniae Rubra Radix,Chuanxiong Rhizomaand other medicinal compositions) regulates glycolipid metabolism in rats by activating the Nampt signaling pathway[39].
Classic ancient formula: the classic ancient Chinese medicine formula Gegen Qinlian decoction (composed ofPuerariae Radix,Scutellariae Radix,Coptidis RhizomaandGlycyrrhizae Radix) can improve glycolipid metabolism disorders by activating the PPARα/recombinant retinoid X receptor-alpha and SIRT1 signaling pathways, promoting brown adipose tissue differentiation and maturation, and increasing energy expenditure [40].
Improvement of the function of pancreatic islet beta cells
Chinese medicine monomers and extracts.Glycosides: in a high-concentration glucose-induced INS-1 cell model,Momordica Charantiasaponins (source:Momordica Charantia) overactivated the PI3K/AKT/FoxO signaling pathway, which in turn improved INS-1 pancreatic β-cell function [7].Diosgenin (source:Dioscoreae Rhizoma)significantly inhibited phosphodiesterase 3B expression in a dose-dependent manner, thereby reducing oxidative stress levels in INS-1 cells, inhibiting β-cell apoptosis, and improving pancreatic β-cell function [41].
Alkaloids:oxyberberine(source:Coptidis Rhizoma),derived from the Chinese medicineCoptidis Rhizoma, can exert good hypoglycemic and pancreatic β-cell protective effects by activating the pancreatic PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and upregulating mRNA expression in the Nrf2 signaling pathway[42].As one of the main active substances in the Chinese herbSophorae Flavescentis Radix,sophocarpine can prevent oxidative stress-mediated pancreatic β-cell damage by increasing vitamin E, L-glutathione,and C-peptide levels [43].
Polysaccharides:Astragali Radixpolysaccharide is a polysaccharide compound extracted from the rhizome ofAstragali Radix.Astragali Radixpolysaccharide inhibited EF-hand domain family member D2 protein expression by promoting miR-136-5p and miR-149-5p expression, which improved cell proliferation and increased insulin secretion in the mouse pancreatic β-cell lineage to some extent [44].
Chinese herbal extracts.The pomegranate metabolite urolithin A(source: pomegranate) restored cell viability, morphology, and mitochondrial membrane potential by downregulating the autophagy protein sequestosome-1 and upregulating microtubule-associated proteins light chain 3 II,thereby avoiding mouse pancreatic islet β cell apoptosis[45].
Common complications of diabetes
Diabetic patients developed a series of complications over time, such as diabetic nephropathy, diabetic peripheral neuropathy, diabetic retinopathy, diabetic foot, and diabetic cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease.These complications seriously affected the quality of life of patients and posed a huge economic burden to society.Numerous studies have shown that TCM and its extracts are effective in preventing and treating diabetic complications(Table 3).
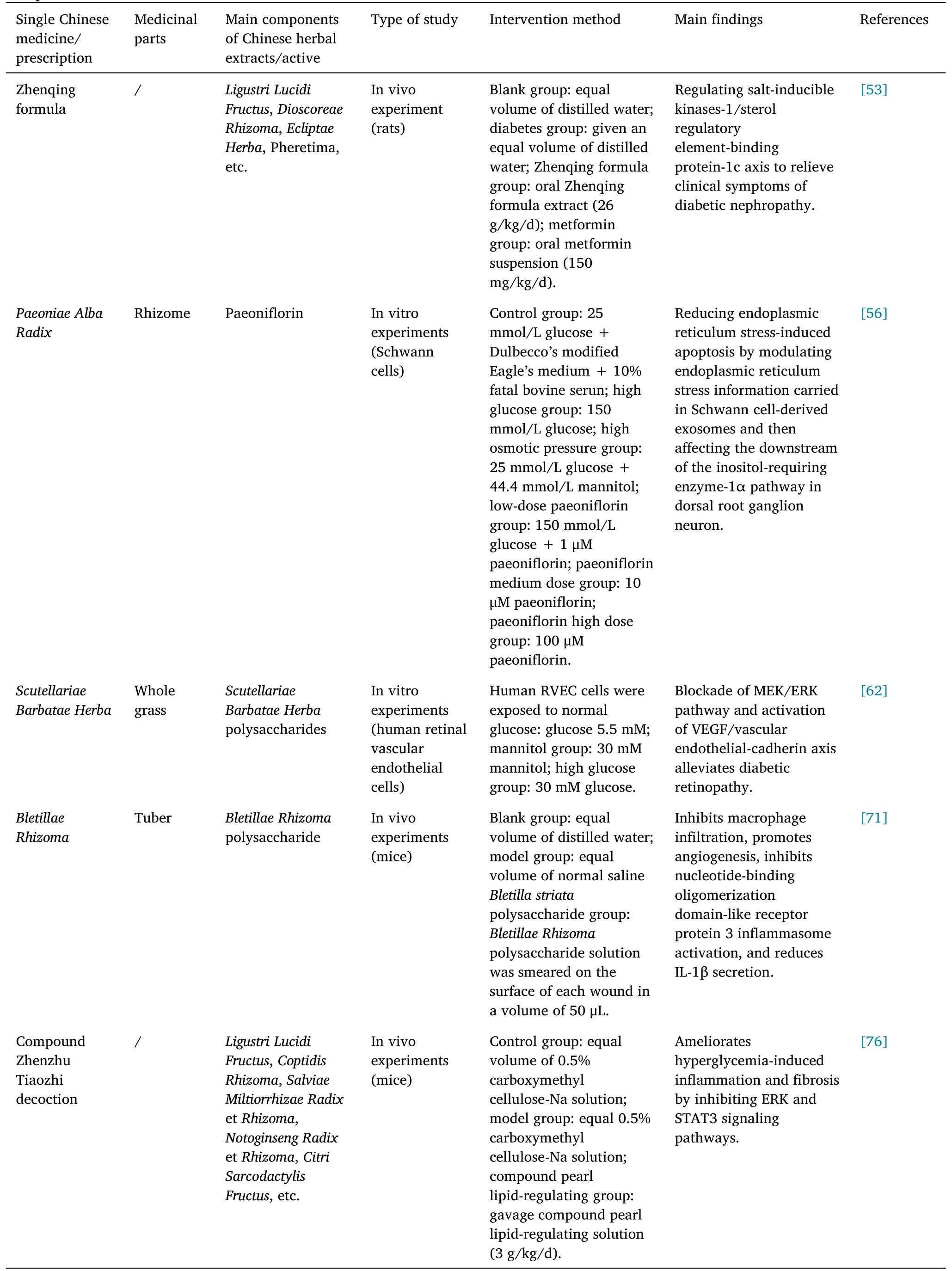
Table 3 Study on the mechanism of action of main single traditional Chinese medicines and prescriptions in the treatment of diabetic complications
Diabetic nephropathy (DN)
DN is a major complication of diabetes mellitus.Its early clinical manifestations are mainly microproteinuria, followed by a gradual decrease in the glomerular filtration rate and progressive symptoms,such as massive proteinuria, edema, hypertension, and high blood creatinine.If not treated in time, it can evolve into end-stage renal failure[46].
Chinese medicine monomers and extracts
Glycosides:catalpol is a cyclic enol ether glycoside compound isolated from the root ofRehmanniae Radix, which improves endothelial dysfunction and inflammation by inhibiting the receptor for advanced glycation end product/RhoA/ROCK pathway, thereby slowing the progression of DN [47].In vivo experiments have shown that Rg3, an active saponin isolated from ginseng, can alleviate DN by increasing antioxidant activity and reducing kidney inflammation [48].Glomerular podocytes, as important injury targets in DN, are inextricably linked to DN.In a high glucose-induced mouse podocyte injury model, ginsenoside Rb1 (source:Ginseng RadixetRhizomaRubra) inhibited apoptosis and mitochondrial damage by inhibiting aldose reductase-mediated overproduction of the reactive oxygen species[49].
Alkaloids: berberine, extracted from the Chinese medicineCoptidis Rhizoma, can enhance the nephroprotective effect of metformin by effectively promoting the expression of tribbles homotog 1 through the mechanism of tribbles homotog 1 downregulation of increased enhancer-binding protein α protein levels and the eventual inhibition of adiponectin and nuclear factor-kappa B signaling.The combination of the two drugs can jointly promote lipolysis and inhibit inflammation to improve anti-diabetic nephropathy activity [50].The combination of these two drugs can jointly promote lipolysis and inhibit inflammation to improve anti-diabetic nephropathy activity.
Polysaccharides:Moutan Cortexpolysaccharide, a novel heteropolysaccharide obtained from theMoutan Cortex, ameliorates DN.In vivo experiments revealed that it could reduce thylakoid dilatation and renal tubular interstitial fibrosis in rats with DN,as well as significantly reduce serum advanced glycation end products and receptors for advanced glycation end products levels [51].Further in vitro studies showed that the drug could inhibit advanced glycation end product-induced reactive oxygen species production in a human umbilical vein endothelial cell model.
Chinese herbal extracts.The study found, through network pharmacology and molecular docking methods, that the active ingredients in cicada can participate in the R-HSA-450341,157.14-3-3 cell cycle, and platelet-derived growth factor pathway through mitogen-activated protein kinases 8, tumor protein 53, and other targets and then act on DN [52].
Chinese herbal compound.The TCM prescription Zhenqing formula(composed ofLigustri Lucidi Fructus,Dioscoreae Rhizoma,Ecliptae Herba,Lonicera JaponicaThunb and other medicinal compositions)can effectively reduce blood sugar and blood lipid levels in rats with DN and improve renal function when applied to a DN rat model [53].Further research found that it could alleviate DN by regulating the salt-inducible kinases-1/sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c axis.Zheng et al.found that Fuxin granules, a TCM prescription(composed of drugs such asScrophulariae Radix,Rhei RadixetRhizoma,Astragali Radix,Alismatis Rhizoma,Anemarrhenae Rhizoma),caused significant improvement in clinical indicators related to DN in mice through the TGF-β1/Smad and VEGF/VEGFR-2 signaling pathways to treat DN [54].
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN)
DPN is a common chronic complication of diabetes and is characterized by symmetrical sensory and motor neuron damage.Its pathogenesis is complex and has not yet been fully elucidated.Studies have shown that TCM and its extracts can prevent and treat DPN by improving mitochondrial function, regulating autophagy, inhibiting apoptosis and pyroptosis, and reducing neuroinflammation and oxidative stress.
Chinese medicine monomers and extracts.Glycosides:astragaloside,extracted fromAstragali Radix,can act as an antioxidant to protect mitochondrial morphology and maintain membrane potential by inhibiting the excessive activation of autophagy in Schwann cells and reducing the level of reactive oxygen species under hyperglycemic conditions, thus downregulating the expression of autophagy-related proteins: LC3, PINK, and Parkin [5].Astragaloside is effective in treating DPN, and its mechanism of action is partly the regulation of the miR-155-mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway to promote autophagy and reduce apoptosis in RSC96 cells[55].Endoplasmic reticulum stress is associated with the development of DPN, and exosomes derived from Schwann cells can carry inositol-requiring enzyme-1α signaling factors from the endoplasmic reticulum to dorsal root ganglia neural and damage it.Paeoniflorin(source:Paeoniae Alba Radix) can modulate endoplasmic reticulum stress information carried in exosomes derived from Schwann cells and thus affect the inositol-requiring enzyme-1α pathway in dorsal root ganglia neural downstream, reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis[56].
Phenolic:one of the active components ofSalviae Miltiorrhizae RadixetRhizoma, salvianolic acid B, can downregulate the expression of poly ADP-ribose polymerase, cleaved-caspase 3, cleaved-caspase 9,IL-1 β, and other related proteins in rat Schwann RSC96 cells, and its mechanism of action may involve the inhibition of reactive oxygen species-activated apoptosis and cell scorching [57].
Chinese herbal extracts.Extracts ofRhodiola Roseasignificantly reduced diabetic neuropathic pain by inhibiting the AMPK/NLRP3 inflammatory body axis in dorsal root ganglion [58].
Chinese herbal compound.The test formula of the compound XiongShao formula (Paeoniae Alba Radix,Glehniae Radix,Chuanxiong Rhizoma,Lycii Fructus,Cassiae Semenand other medicinal compositions) demonstrated neuroprotective effects in rats with DPN by inhibiting the expression of B-cell lymphoma-2, B-cell lymphoma-2-associated X and caspase-3 apoptosis-related proteins in the sciatic nerve and downregulating the levels of serum nitric oxide synthase, superoxide dismutase and advanced glycation end products through a multidimensional pharmacological mechanism [59].Studies have shown that the administration of the TCM prescription Jingmaitong (composed ofCuscutae Semen,Ligustri Lucidi Fructus,Ecliptae Herba,Prunellae Spica,Litchi Semen, etc.) can significantly improve the myelin protein zero level in DPN rats, possibly through the activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway[60].
Diabetic retinopathy (DR)
DR refers to local microvascular pathological changes in the retina of diabetic patients due to long-term high sugar intake, and it is one of the main causes of blindness in adults.Some studies have shown that Chinese medicine and its extracts have a positive effect in the treatment of DR.
Chinese medicine monomers and extracts.Glycosides: it was shown that arbutin (source:Arctostaphylos uva-ursi) significantly enhanced the viability of adult retinal pigment epithelial cells exposed to hyperglycemia and autophagic mediators by increasing SIRT1 protein levels, while reducing pro-inflammatory proteins and apoptosis[61].
Polysaccharides: studies have confirmed the ability ofScutellariae Barbatae Herbapolysaccharides(source:Scutellariae Barbatae Herba)to attenuate DR by inhibiting the proliferation, migration, and neovascularization of human retinal vascular endothelial cells induced by high glucose, which may be mediated by blocking the activation of the MEK/ERK pathway and VEGF/vascular endothelial-cadherin axis[62].Lycii Fructuspolysaccharides (source:Lycii Fructus) can reduce the expression of VEGFA, VEGFR-2, angiopoietin-2, and recombinant acid sphingomyelinase mRNA proteins by activating the expression of miR-15a-5p in macaque choroids-retinal endothelial (RF/6A) cells,which can ultimately reduce diabetic retinal angiogenesis[63].
Chinese herbal extracts.Euonymus JaponicusThunb extract (source:Euonymus JaponicusThunb) inhibits angiogenesis-related factors in RF/6A cells, thereby reducing cell migration and tube formation and improving diabetic retinopathy [64].
Proprietary Chinese medicines and Chinese medicine compounds.Chinese patent medicine: in a rat model of DR, the administration of Fufang Xueshuantong capsules (Chinese patent medicine, China Food and Drug Administration approval number:Z20030017) significantly improved the hemodynamics and morphology of the retina, and its mechanism of action may be mediated by the complement and coagulation cascades and the PPAR signaling pathway[65].
Tested prescriptions:the experimental formula Hu-Zhang-Qing-Mai-Yin (composed ofPolygoni Cuspidati Rhizoma,Forsythiae Fructus,Rhodiolae Crenulatae RadixetRhizoma,Platycladi Cacumen,Glycyrrhizae Radixand other medicinal compositions) can inhibit the proliferation of human retinal capillary endothelial cells under high glucose exposure and promote mitochondria-associated apoptosis[66].Its mechanism of action is to increase the expression of proteins related to the P38 signaling pathway,as well as to inhibit.
Classic ancient formula: in network-based pharmacology and experimental validation study, it was shown that the classic ancient Chinese medicine formula Si-Miao-Yong-An decoction (composed ofLonicerae Japonicae Flos,Scrophulariae Radix,Angelicae Sinensis RadixandGlycyrrhizae Radix) can slow down the development of DR by inhibiting retinal inflammation and angiogenesis by eliminating the nuclear factor-kappa B/tumor necrosis factor-α and hypoxia-inducible factor-1a/VEGF signaling pathways[67].
Diabetic foot ulcer (DFU)
DFU is one of the most common complications of diabetes and is defined by the International Diabetes Working Group as, “infection,ulceration, or destruction of foot tissue in patients with current or previously diagnosed diabetes, usually with lower extremity neuropathy and/or peripheral arterial disease”.Severe cases are at risk of disability or even death.Studies have found that TCM and its extracts have benefited patients with diabetic foot.
Chinese medicine monomers and extracts.Glycosides: in vivo studies have shown that paeoniflorin (source:Paeoniae Alba Radix)can reduce the levels of IL-1β, IL-18, and tumor necrosis factor-α and downregulate the activities of chemokine receptors CXC chemokine receptor 2,nuclear factor-kappa B,and tumor necrosis factor-α in DFU rats [68].In addition, it also reduced phosphorylation inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B levels and increased IκB levels; further in vitro studies found that paeoniflorin effectively inhibited inflammation mediated by NLRP3 and nuclear factor-kappa B, and its mechanism was related to the inhibition of CXC chemokine receptor 2.Ginsenoside Rg1 (source:Ginseng RadixetRhizoma Rubra) can effectively alleviate DFU, and its mechanism is to increase SIRT1 expression and promote PI3K/AKT/eNOS signaling by downregulating miR-489-3p expression [69].The study found that baicalin (source:Scutellariae Radix) inhibited wound healing in DFU rats by regulating the VEGF-c, TGF-β and Smad2/3 mRNA expression [70].
Polysaccharides: in DFU model mice, the topical application ofBletillae Rhizomapolysaccharide (source:Bletillae Rhizoma) to the wound surface inhibited macrophage infiltration and NLRP3 inflammatory vesicle activation, promoted angiogenesis, and decreased IL-1β secretion, accelerating wound healing[71].
Diabetic cardiovascular disease abbreviation
Cardiovascular disease caused by diabetes has a complicated pathology and is one of the major causes of death in patients with diabetes; however, its pathogenesis is not yet fully understood.In recent years, several studies have shown that Chinese medicine can effectively treat this disease, and this warrants further investigation.
Chinese medicine monomers and extracts.Flavonoids: baicalein is a flavonoid extracted from the Chinese herbScutellariae Radixthat has shown anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic, and antioxidant pharmacological activities.Studies have shown that baicalin alleviates T2DM-induced cardiac injury by modulating oxidative stress,inflammation,apoptosis,and fibrosis in mice through the Nrf2/Keap1,TLR4/MyD88/nuclear factor-kappa B-mediated inflammatory and intrinsic (mitochondrial) apoptotic pathways[72].
Glycosides: ophiopogonin D (source:Ophiopogonis Radix) is a steroidal saponin, and the results of a previous study confirmed that ophiopogonin D alleviates cardiac injury in a mouse model and ameliorates palmitic acid-stimulated lipid accumulation and mitochondrial damage in cardiomyocytes through a mechanism that is linked to regulating mitochondrial dynamics [73].
Proprietary Chinese medicines and Chinese medicine compounds.Chinese patent medicine: in a diabetic cardiomyopathy mouse model, a gavage of Qili Qiangxin capsules (Chinese patent medicine, China Food and Drug Administration approval number:Z20040141) improved cardiac dysfunction [74].In vitro studies have shown that Qili Qiangxin capsule activates PPARγ and attenuates hyperglycemia-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis.
Tested prescriptions: in a diabetes mellitus-coronary heart disease piglet model, gavage with the TCM compound Zhenzhu Tiaozhi decoction (prescribed, composed ofLigustri Lucidi Fructus,Coptidis Rhizoma,Salviae Miltiorrhizae RadixetRhizoma,Notoginseng RadixetRhizoma,Citri Sarcodactylis Fructusand other drugs) effectively improved coronary artery impaction and protected the myocardium of diabetes mellitus-coronary heart disease piglets from injury; the mechanism is related to downregulation in the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and upregulation of the protein expression in the PI3K/Akt pathway [75].Another study showed that the compound Zhenzhu Tiaozhi decoction can improve hyperglycemia-induced inflammation and fibrosis by inhibiting ERK and STAT3 signaling pathways, thereby playing a role in the treatment of diabetic cardiomyopathy [76].
Classic ancient formula: the classic TCM Shengmai powder(composed ofGinseng RadixetRhizoma Rubra,Ophiopogonis RadixandSchisandrae Chinensis Fructus) is often used to treat cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases [77].Studies have found that Shengmai powder can attenuate myocardial oxidative damage in diabetic cardiomyopathy, and its mechanism is related to the activation of AMPKα and the inhibition of NOX signaling.
Other common endocrine system diseases
In addition to the aforementioned diseases, hyperuricemia, obesity,and thyroid diseases are common and frequently-occurring diseases of the endocrine system, and TCM has certain advantages over other treatments (Table 4).
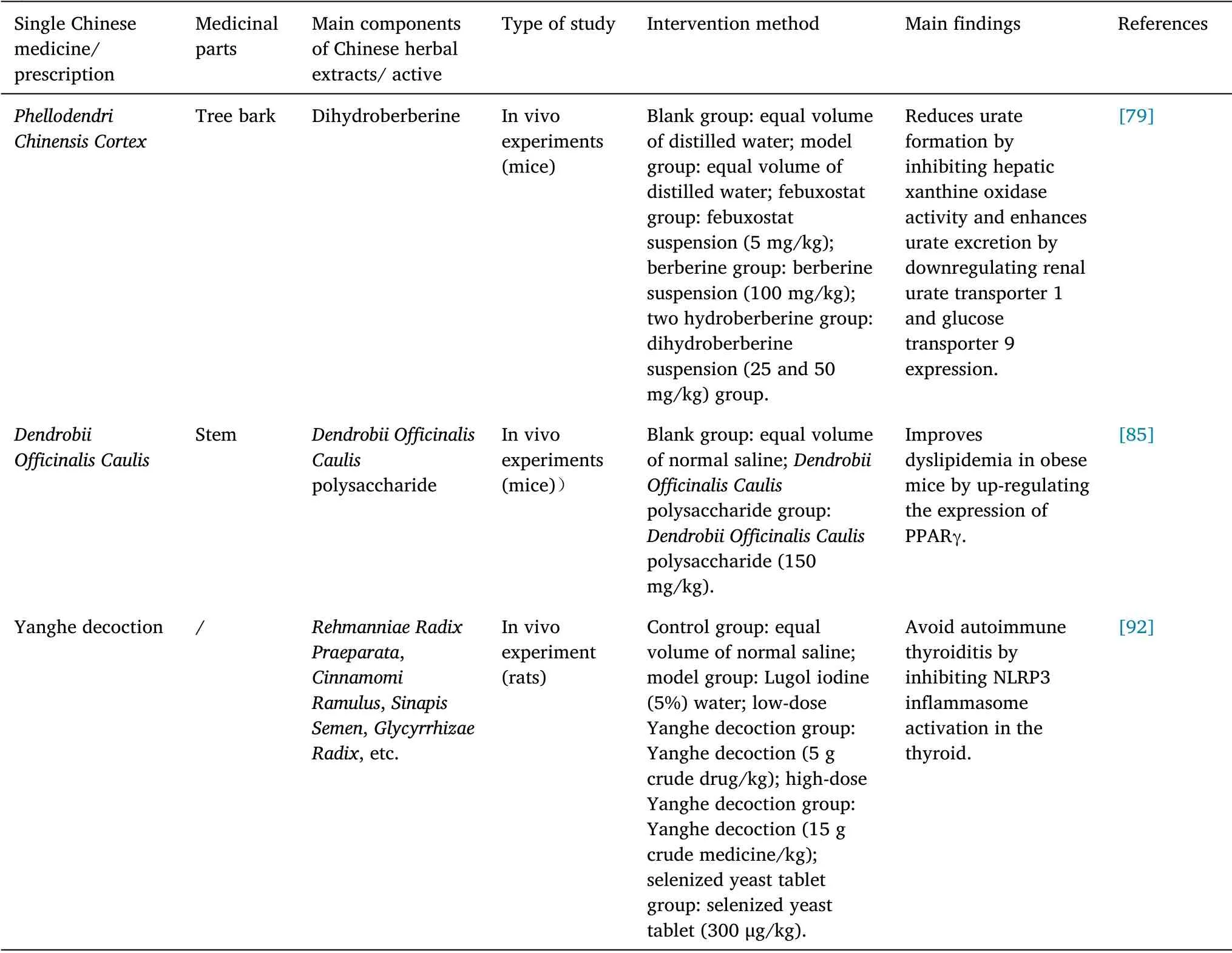
Table 4 Action mechanism of main single traditional Chinese medicines and prescriptions in the treatment of hyperuricemia,obesity and thyroid diseases
Hyperuricemia
Hyperuricemia is a metabolic disease caused by the increased production or decreased excretion of serum uric acid,and it is also the main cause of gout.
Chinese medicine monomers and extracts
Alkaloids.In a hyperuricemia mouse model, a gavage of berberine(source:Phellodendri Chinensis Cortex)can effectively reduce the levels of serum uric acid, blood urea nitrogen, serum creatinine, and inflammatory mediators (IL-1β, IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α) and at the same time reduce liver xanthine oxidase activity;its mechanism is related to the regulation of the urate transporter and Janus kinase 2/STAT3 signaling pathway [78].Dihydroberberine, a hydrogenated derivative of berberine,has dual anti-hyperuric acid effects:it reduces urate formation by inhibiting xanthine oxidase activity in the liver and downregulates the expression of urate transporter 1 and glucose transporter 9 in the kidney to enhance urine acid excretion [79].
Chinese herbal extracts.Luteolin is a herb derived from traditional Tibetan medicine [80].Its extracts (luteolin and apigenin) can effectively improve hyperuricemia, and the mechanism is related to the inhibition of TLR4/NLRP3 signaling in the kidneys of hyperuricemia mice.
Chinese medicine compound
The classical ancient recipe Gegen Qinlian decoction (composed ofPuerariae Radix,Coptidis Rhizoma,Glycyrrhizae RadixandScutellariae Radix) promoted renal uric acid excretion by inhibiting gasdermin D-dependent pyroptosis, induced by the NLRP3 inflammasome, and the mitochondrial apoptosis-signaling pathway to reduce apoptosis[81].
Obesity
Obesity, a chronic metabolic disease, has a high incidence and global trend and is often complicated by hypertension, hyperlipidemia,coronary heart disease, diabetes, and infertility, which endanger patients’ health and life.
Chinese medicine monomers and extracts
Flavonoids.Corylin, a flavonoid extract fromPsoraleae Fructus, can exert anti-obesity effects by activating SIRT1- or β3-adrenergic receptor-dependent pathways, resulting in the browning of white adipocytes, activation of brown adipose tissue, and promotion of lipid metabolism [82].
Glycosides.The ginsenoside Rb1 (source:Ginseng RadixetRhizoma Rubra) can promote adipocyte browning by inhibiting Wnt/ß-catenin signaling and can reduce lipid accumulation in a dose-dependent manner [83].
Alkaloids.Studies have demonstrated that berberine (source:Coptidis Rhizoma)can reduce inflammation in adipose tissue of obesity models by binding directly to and activating the deacetylase Sirtuin 3 and inhibiting mitogen-activated protein kinase and nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathways, thereby inhibiting macrophage infiltration in adipose tissue and reducing abnormal extracellular matrix deposition[84].
Polysaccharides.Dendrobii Officinalis Caulispolysaccharide was extracted from a valuable Chinese herb,Dendrobii Officinalis Caulis[85].It was found that theDendrobiumpolysaccharide could improve dyslipidemia in obese mice by upregulating PPARγ expression.
Phenolic.Paeonol, derived from the Chinese herbal medicineMoutan Cortex,can improve lipid metabolism and obesity by promoting lipid degradation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes, increasing the expression levels of PPARγ and apetala 2, and inhibiting the synthesis of triglycerides in these cells[86].The compound 6-gingerol,extracted from ginger,was effective in suppressing high-fat diet-induced obesity, and its mechanism of action may be related to the regulation of PPARγ,CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein α, fatty acid-binding protein 4, and lipocalin in adipose tissue and the TLR3/IL-6/JAK1/STAT3 axis[87].
Chinese herbal extracts
Bupleuri radix extract reduced obesity, hepatic steatosis, and dyslipidemia in HFD-fed mice by upregulating the expression of FGF21 and proteins downstream of the FGF21 signaling pathway in the liver and white adipose tissue and modulated the relative abundance of acidophilus and ruminal cocci in the intestinal microflora [4].
Thyroid disease
The common clinical types of thyroid diseases include hyperthyroidism, thyroid nodules, thyroid adenoma, thyroid cancer,chronic thyroiditis(Hashimoto’s thyroiditis),subacute thyroiditis, and hypothyroidism.
Chinese medicine monomers and extracts
Glycosides.In a lipopolysaccharide-induced Hashimoto’s thyroiditis rat model, diosgenin (source:Trigonellae Semen) can promote Treg differentiation and relieve inflammation by upregulating the ubiquitination of interferon regulatory factor 4 (sumoylation) [88].
Chinese herbal extracts
In a hypothyroid model rat, Han et al.found that the volatile oil,triterpene, and crude polysaccharide components inPoria Cocosalleviated the disease through the tricarboxylic acid cycle,glycolysis/glycoisomerization, amino acid biosynthesis, fatty acid biosynthesis,pentose phosphate,and PPAR pathways by metabolomic and proteomic analysis [89].Prunellae Spicais a TCM.Its extract(PVE) inhibits the proliferation and migration of thyroid cancer cells by regulating the expression of proliferating cell nuclear antigen and cadherin 1, to influence the occurrence and development of diseases[90].Zhang et al.used ultra-high pressure liquidchroma/quadrupole-time of flight-mass spectrometry metabolomics and found that in a hyperthyroidism rat model, the use ofScrophulariae Radixextracts significantly reduced the levels of metabolites related to linoleic acid metabolism and sphingolipid metabolism in the serum of the model [91].In addition, comprehensive network pharmacological validation indicated that the extract might play a role in the treatment of hyperthyroidism by modulating the “IL6-APOA1-cholesterol” and hypoxia-inducible factor signaling pathways.
Chinese medicine compound
Inflammation is a significant trigger for autoimmune thyroiditis.In a rat model of autoimmune thyroiditis established by thyroglobulin injection and excessive iodine intake, Yanghe decoction (a classical ancient formula composed ofRehmanniae Radix Praeparata,Cinnamomi Ramulus,Sinapis Semen,Glycyrrhizae Radixand other medicinal compositions) can inhibit NLRP3 inflammatory vesicle activation in the thyroid gland [92].
In summary,research on TCM and its extracts has revealed the good material basis and broad development prospects of TCM in the treatment of diseases of the endocrine system.The above research demonstrates that studies on the prevention and treatment of endocrine diseases using TCM can be divided into two categories.The first is research on TCM compound prescriptions,which attaches great importance to the integrity and coordination of drug collocation, and the second is research on the combination of TCM.Research on monomers of TCM focuses on the mechanism of action of TCM extracts or compounds.Since the compound formula is a combination of multiple components,it is difficult to study it predominantly (Table 5).
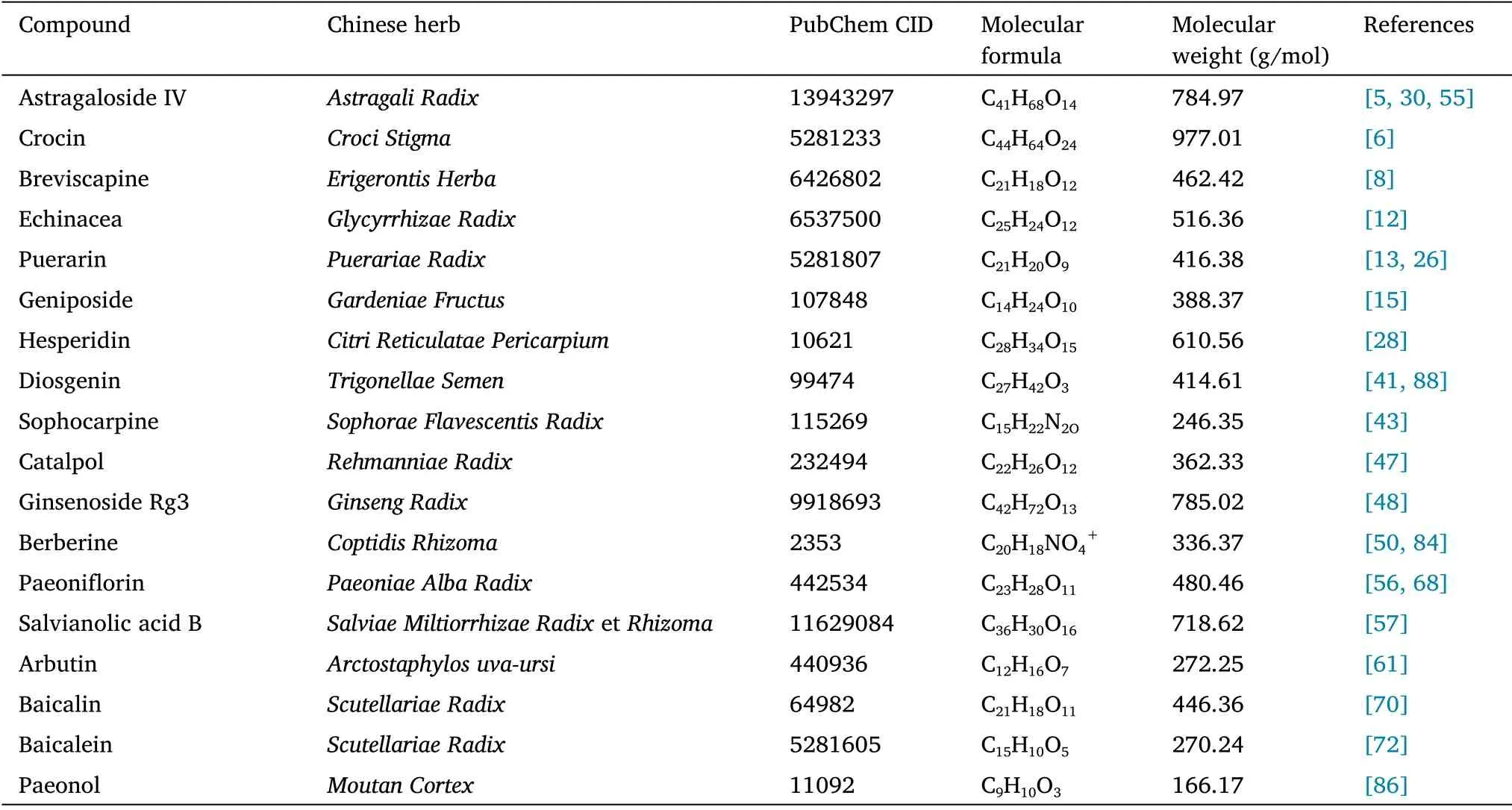
Table 5 Characteristics of important chemical components separated from traditional Chinese medicine
Summary and outlook
In recent years, great progress has been made in the treatment of endocrine diseases using TCM monomers, extracts, and compound formulations.In recent years,the study of various components of TCM for endocrine diseases has become a hot topic, and new biotechnologies, such as histological studies and network pharmacology,have become tools that can more comprehensively and systematically elucidate the mechanism of action of TCM with multiple pathways and targets.Network pharmacology is an important tool for studying the mechanism of TCM, and nowadays,compared with earlier studies, research is more inclined toward experimental validation based on network pharmacology and more in-depth interpretation and validation.However, the disadvantages of network pharmacology are obvious.First, network pharmacology turns herbal medicine into an accumulation of components, which is more conducive to experiments or results.However, it is important to point out that herbal medicine is a complex system of chemical components, and its material basis is multi-component, and these components are not simple accumulations.The application of Chinese medicine is based on the application of the physician’s theory,method, and prescription, as well as the application of the principles of “four gases and five tastes” and the “elevation and sinking” of Chinese medicine.In particular, some researchers have corresponded targets, pathways,protein expression, blood vessels, and nerves to the Qi (Qi refers both to the refined nutritive substance that flows within the human body as well as to its functional activities.), blood, Yin (in Chinese philosophy, the female, latent, passive principle,characterized by dark, cold, wetness, passivity, disintegration, etc.),Yang (in Chinese philosophy, the masculine, active and positive principle, characterized by light, warmth, dryness, activity, etc.),meridians, and acupoints in Chinese medicine, which is inconsistent with the objective basis.Second, the database on which network pharmacology relies is slowly updated and incomplete,and many drug databases of classic ancient prescriptions are not included; this seriously affects and restricts the continued exploration and progress of TCM in this area.In the subsequent development of network pharmacology research, it is necessary to make arguments in many aspects to ensure that the research does not have major deviations.Although there are drawbacks of network pharmacology, it is still one of the means to explore the mechanisms of TCM at this stage.In the study of most TCM and TCM compounds, we were able to determine which mechanism the TCM compound or extract acted through, but most of the mechanisms were found to be correlated without sufficient evidence on their targets.This requires that we delve deeper in our future studies and strive to study the disease mechanisms of specific pathways or targets.Although the efficacy of Chinese medicine and its compound formulas has been clinically tested as one of the traditional ways of treating diseases in Chinese medicine, the mechanism cannotbe adequately studied, and neither can a control group be effectively designed for scientific analysis.The fundamental reason for this is that TCM compounds have multiple active ingredients, which act synergistically through multiple components and targets to achieve the diagnosis,treatment,and regulation of human diseases.Therefore,explaining the pathogenic substances and pathways of action of complex syndromes to comprehensively and accurately evaluate the effects of prescriptions has become the focus of research in the field of modern Chinese medicine.Recent studies have shown that metabolomics can provide a scientific interpretation of the effecting substances and mechanisms of action of TCM prescriptions.The main reason for this is that it can reveal the metabolic pathways related to the action of Chinese medicine by detecting the dynamic changes of the compounding substances in the organism and screening and identifying specific biomarkers with panoramic, holistic, and comprehensive technical characteristics.At the same time, the understanding and control of TCM compounding as a whole are strengthened, which is more conducive to the research and clinical application of compounding.
The treatment of metabolism-related diseases from the perspective of intestinal flora has been a hot research topic, and in recent years,most of the research on intestinal flora has focused on the change in flora abundance.However, the simple study of the change in flora is not enough to explain the mechanism of flora treatment-related diseases; therefore, the study of flora and its downstream pathway related to the mechanism of action can improve the research on intestinal flora.In the future, the combination of intestinal flora with metabolomics, molecular docking, and other biotechnologies can be used to explore the specific mechanism of action of intestinal flora in the treatment of endocrine diseases, which can provide direction for the treatment of diseases.In the past, most of the studies on the mechanism of action of TCM compounds were usually performed at the animal level, but as research progresses, it is evident that in 2021 many in vitro models have been used to study the mechanism of action TCM compounds, and TCM-containing serum and its pure extracts can be used as in vitro models for drug delivery protocols.In vitro models can be used to study the targets and mechanisms of action of TCM monomers and compounds at the cellular level and are promising and important tools for future studies of TCM in the treatment of endocrine diseases.
 Traditional Medicine Research2022年5期
Traditional Medicine Research2022年5期
- Traditional Medicine Research的其它文章
- G1-4A, an arabinogalactan polysaccharide derived from Tinospora cordifolia(Thunb.)Miers:a natural immunomodulator
- Pseudotargeted metabolomics for exploring the changes of neurotransmitters profile in aging rat brain and the potential neuroprotective effect of alkaloids from Uncaria rhynchophylla
- Antioxidant, hepatoprotective and nephroprotective activities of Gazania rigens against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity in rats
- Traditional medicines and experimental analysis methods for Alzheimer’s disease
- Effect of Terminalia chebula Retz.extraction with water on Staphylococcus epidermidis activity and its biofilm formation
- Update on the preclinical and clinical assessment of Withania somnifera: from ancient Rasayana to modern perspectives
