G1-4A, an arabinogalactan polysaccharide derived from Tinospora cordifolia(Thunb.)Miers:a natural immunomodulator
Sarita Das
1Microbiology Laboratory,Department of Botany,Berhampur University,Berhampur 760007,India.
Abstract The whole world has been challenged by the COVID-19, where people with poor immune status became the target.It is high time for us to strengthen our immunity through some safe,efficient and cost-effective immune boosters. Tinospora cordifolia (Thunb.) Miers is a well-known medicinal plant as the whole plant (leaves, stems and roots) is used extensively for different ailments, since it is rich in many bioactive secondary metabolites.The immunomodulatory efficacy of Tinospora cordifolia was reported by several workers and this plant is considered to be a “Rasayana” herb in Ayurveda because of its potential cell renewal, health re-establishment and physical equilibrium maintenance capabilities.1,4-Linked arabinogalactan polysaccharide(G1-4A), an acidic polysaccharide and arabinogalactan polymer is reported to strengthen host innate immunity by multifactorial pathways.It induces immune cells (neutrophil, macrophage,T lymphocyte) proliferation and increases cytokine/chemokine production and reactive oxygen species generation thereby contributing to boost our immunity.G1-4A activates macrophages by a classical pathway in toll-like receptor 4 - myeloid differentiation primary response 88 dependent manner, natural killer cells and cytotoxic T cells to destroy pathogens, virus-infected cells, or tumor cells.Binding of G1-4A to the toll-like receptor or mannose receptor activates a cascade of events along with nuclear translocation of nuclear factor-kappa B leading to the synthesis of different cytokine/chemokine and reactive oxygen species generation.Natural immunomodulators like G1-4A are safer and cheaper, when extracted from botanical sources.Therefore, such phytocompounds can be taken as a daily supplement to enhance immunity,which might be beneficial to fight and survive in this ongoing pandemic health crisis.
Keywords: arabinogalactan polysaccharides; 1,4-linked arabinogalactan polysaccharide;immunomodulation; macrophage; Tinospora cordifolia
Background
Nature has countless treasures in the form of natural products to solve our health problems andTinospora cordifolia(Thunb.) Miers (T.cordifolia) is one such miraculous herb with numerous proven pharmacological activities.T.cordifoliahas been widely used by folks and tribals as a miraculous herb for the treatment of different diseases due to its excellent rejuvenating, immune-boosting, anti-rheumatic and detoxifying properties.T.cordifoliais also used in modern medicine for the treatment and prevention of cold and flu, skin disorders,liver disorders,immune-boosting,arthritis,gout,and also to overcome the adverse effects of chemotherapy [1].Though there are several reports on the antioxidant, antidiabetic, antihyperlipidemic,neuroprotective, cardioprotective, hepatoprotective, renoprotective,radioprotective, osteoprotective, anti-anxiety, adaptogenic,antipyretic, antidiarrheal, analgesic, antimicrobial, antiulcer,anti-inflammatory and anticancer properties ofT.cordifolia, the most significant activity is reported to be immunomodulatory, which is evident from multiple scientific reports and citations.This herb and its extracts are used as an immunity enhancer.They have been reported maximum times as an immune cell booster.1,4-Linked arabinogalactan polysaccharide (G1-4A), an arabinogalactan, acidic polysaccharide derived from the stem ofT.cordifoliais also reported by several researchers to be an excellent immune charger; however,till date, no review has been published on it.Therefore, the present review aims at providing insight and overall knowledge on the different activities of G1-4A and the mechanism by which it stimulates the immune system.
Immunity and host defense
Immunity is a phenomenon of self-defense found in almost all biological systems to protect themselves from potentially harmful agents like bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites or cells from other individuals or our own worn-out or transformed cells.The immune system comprises all the molecules, cells, organs associated with immunity and the immune response is the system's reaction or response to the potential threats.Immunity can be of two types:innate(always on) and adaptive (developed in response to an active infection).Both immunity types comprise two important components based on the key functional players: (1) cell-mediated (involve immune cells i.e.antigen-presenting cells, macrophages, neutrophils,eosinophils, basophils, dendritic cells, natural killer (NK) cells, T lymphocytes, etc.)); and (2) humoral (involve serum proteins i.e.complements and antibodies)immunity.Innate or natural immunity is non-specific as it lacks memory cells but, acquired or adaptive immunity is specific and involves memory cells.The innate cellular immunity comprises the monocytes macrophage system and acts via counteracting the harmful entities or pathogens, followed by activation of the acquired immune system to eradicate the pathogens,which includes T lymphocytes.On the contrary, innate humoral immunity is mediated through activation of the complement system and adaptive humoral immunity comprises antibodies.The antigen-presenting cells (macrophages, dendritic cells) process the antigens or foreign entities such as bacteria, fungi, viruses, or fungal/bacterial toxins into smaller fragments and present them on their cell surface to recruit and attract more immune cells.Similarly,phagocytic cells like neutrophils, basophils and eosinophil engulf and destroy the antigens and foreign substances [2, 3].The probable role of our immune system in protecting our body against different pathogenic agents and how natural immunomodulators likeT.cordifoliaplant/stem and G1-4A dervied from them can strengthen it further is diagrammatically represented in Figure 1.
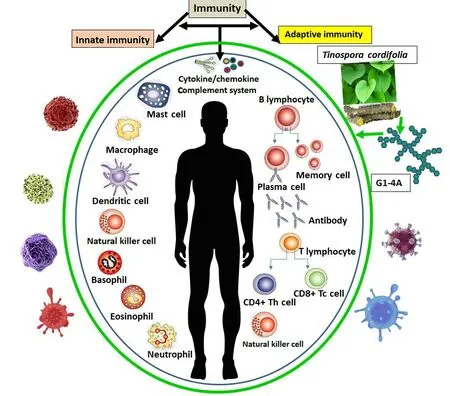
Figure 1 Role of our immune system in combating infections.Innate and adaptive immunity are mediated through different cells(cell-mediated) and molecules (humoral) and they are interconnected through the cytokine/chemokines and complement system.Our functional immune system protects us against invading pathogens and immunomodulators like G1-4A, derived from Tinospora cordifolia (Thunb.) Miers stem could strengthen our immune system.G1-4A, 1,4-linked arabinogalactan polysaccharide.
Innate immunity does not involve antigen-specific defense mechanisms and does not need rearrangement of certain immunoglobulin and receptor genes to produce specific antibodies to identify and counteract the antigens.Innate immunity is majorly responsible for acute and chronic inflammation as well as bacterial sepsis [4, 5].Our body’s defense mechanism comes into play immediately after any infection through various acute phase responses and prepares itself to combat and eradicate the assaulter, which is represented in Figure 2.Natural immunomodulators like G1-4A can activate the different immune cells and pro-inflammatory cytokines to protect us from such pathogenic attacks.
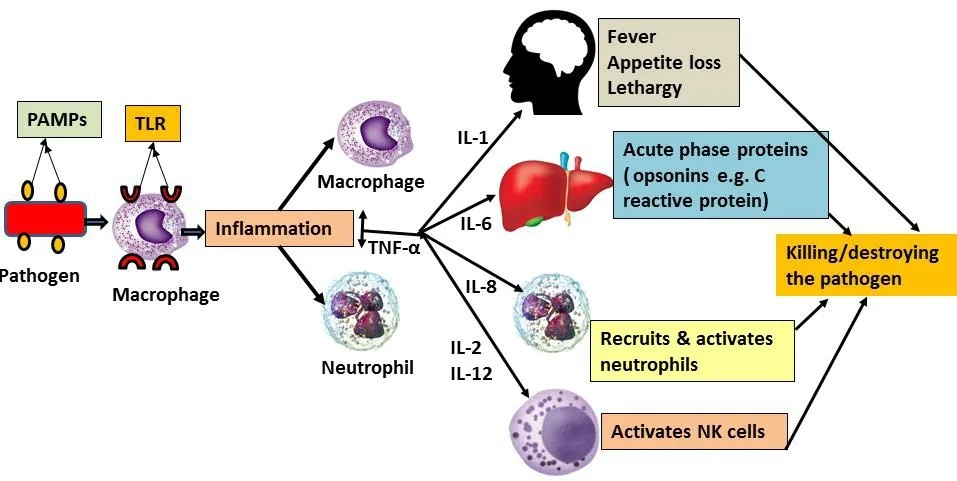
Figure 2 Acute phase responses of our immune system.Pathogens have their unique PAMPs which are identified by TLR present on macrophages.It helps in phagocytosis and killing/clearing of pathogens.If pathogen load is more, inflammation occurs with secretion of different cytokine/chemokines.Different proinflammatory cytokines have a differential role in activating different pathways of our immune system to destroy pathogens.PAMPs,pathogen-associated molecular patterns;TLR, toll-like receptor; IL, interleukin; NK, natural killer.
Importance of natural immunomodulators
Immunodeficiency is a physical condition of an inactive or impaired immune system.Many factors are responsible for changing the immune competency like sex, age, genetic variability, lifestyle, stress,malnutrition, alcohol/drug abuse or any immunodeficiency diseases.Immunomodulation is broadly described as any change in the immune system through amplification or inhibition, induction or expression of any part or point in the immune response by either strengthening or weakening cellular or humoral immunity.Recently, the rate of deadly infections has increased vividly among acquired immune deficiency syndrome patients, transplant recipients, cancer patients and in those receiving cytotoxic drugs like corticosteroids and broad-spectrum antibiotics [6] and moreover, antibiotics are losing their impact after decades of reckless prescription,incorrect use and unavoidable spread of multidrug-resistant bacterial genes [7].Therefore,immunomodulation through some specific and non-specific methods is gaining popularity.Immune stimulation is desired for immune-compromised patients to improve their resistance to allergy,autoimmunity, infections and even cancer by strengthening both innate and adaptive immunity, whereas immune suppression is preferred for patient with inflammatory or autoimmune diseases or graft/transplant receivers[8,9].Clinically,immunomodulators can be divided into two groups: immunostimulants and immunosuppressants[10].
A variety of natural, synthetic and recombinant compounds is available with the regulatory, stimulatory or suppressive activity that has some pros and cons.Pentoxifilline, isoprinosine, levamisole and thalidomide are some of the most important synthetic immunomodulators [11].Strong immunosuppressant drugs like cyclophosphamide and cyclosporine prevent graft rejection and used in autoimmune diseases [12].Although these synthetic drugs have several benefits, their antagonistic side effects and generalized influence on the whole immune system restrict their use and allow the quest for better and safer immunomodulatory agents.Therefore,natural compounds with prospective immunostimulating activity are preferred,which can be classified into two categories i.e.high and low molecular weight compounds.Phenolic compounds, alkaloids and terpenoids are some important low molecular weight compounds,while polysaccharides are among the high molecular weight immunomodulatory compounds [9].
Therapeutic botanicals (plants and plant products) are used as nutraceuticals for ages for their low cost, low toxicity and easy acceptability.They can easily be used as food supplements and in culinary provisions [13].In recent years, the use of natural products for making medicines, dietary supplements and immune boosters has increased rapidly.Different nutraceutical, pharmaceutical and food industries are now focusing more towards designing, producing and delivering such products.Herbal drugs are trusted to endorse good health and immunity against microbial infection by body tissue renewal and rejuvenation [14],possibly due to their pro-action on the immune system,which protect the human body from foreign elements and help in maintaining the physiological homeostasis [15].Plant-based (lichens, algae, mushrooms, and higher plants)immunomodulators are more popular among the biomedical scientists because of their extensive therapeutic properties and comparatively low toxicity.Therefore, they are gaining popularity in recent years as alternatives to conventional synthetic drug treatments for improving immunity.Mostly these natural immunomodulators are associated with the induction of innate immunity [16, 17].
The glycosides or polysaccharides derived from higher plants are comparatively safe and do not cause any significant side effects [18],whereas immunomodulatory synthetic compounds and bacterial polysaccharides have more toxicity.Therefore, plant polysaccharides are preferred as ideal immunomodulatory, anti-tumor, bactericidal and wound-healing therapeutics agents [19].They are reported to activate macrophage and modulate the complement system [20].Emergence and reemergence of deadly pathogens always surge for novel and better preventive strategies to resist or protect against diseases, which could be possible only by developing alternative therapeutics to augment our innate immunity nonspecifically to combat the existing and emerging infectious diseases.In the last two years, the COVID-19 has brought the world into a standstill condition and we are desperately looking for immunity boosters and plant polysaccharides can be prescribed to improve immunity.
Botanical description, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of T.cordifolia:a miraculous herb
T.cordifolia(vernacular name - Guduchi, Amrita, Giloy), (family -Menispermaceae) is a large climbing shrub or lianas and extensively spreading with long twining branches with pulvinate base and heart-shaped leaves of 5-10 cm or longer [21].It is mainly found in India, Sri Lanka, and Myanmar [22].
Different alkaloids derived fromT.cordifoliaexhibited promising pharmacological activities such as anti-inflammatory, anticancer,antidiabetic, antiviral and immunomodulatory, which include berberine, tinosporin, tinosporic acid, choline, magnoflorine,palmetine, isocolumbine, tembetarine, jatrorrhizine,tetrahydropalmatine and aporphine alkaloids.T.cordifoliawas also reported to have glycosides (tinocordiside, tinocordifoliside,cordioside, cordifolioside A, B, C, D, E, 18- nonderodane glycoside,syringin, syringinapiosylglycoside, palmatosides C and P, furanoid diterpene glycoside), sterols (β- and δ-sitosterol, ecdysterone,hydroxyecdysone, makisterone A and giloinsterol), lactones(tinosporon, tinosporisides, tinosporal, tinosporide, columbin,tinosporon columbin, diterpenoid lactone, furanolactone and clerodane derivatives) and others including cordifol, cordifelone,tinosporidin, tinocordifolin, giloin, giloinin, arabinogalactan etc.[23,24].
T.cordifoliais a mystic herb with profuse health benefits and used extensively by tribal and folks for the treatment of various diseases due to its excellent detoxifying, immune-boosting, anti-rheumatic and rejuvenating properties.T.cordifoliais reported to be useful as appetizer,analgesic,astringent,carminative,anthelmintic,antiemetic,galacto-purifier and health-tonic.It is also reported to have anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, cardiotonic, depurative, aphrodisiac,haematinic, expectorant and rejuvenating properties [25].Several common ailments like chronic and intermittent fevers, asthma,anemia, dyspepsia, hyperdipsia, gout, jaundice, cardiac debility,erysipelas, splenopathy, uropathy, seminal weakness, etc.were also improved by this multi-functional herb [26].It is a major constituent of different Ayurvedic formulations i.e.Amrita Guggulu,Amritashtaka Churna, Sanjivani Vati, Guduchi Satva, Guduchu Ghrita, Guduchi Taila, Kanta-Kari Avaleha, Chyavnaprasha, Guduchyadi Churna,Brihat Guduchi Taila, and used for the treatment of several diseases such as fever, dyspepsia, debility, and urinary disorders [1].
There are several scientific reports on the diverse pharmacological activities ofT.cordifolia.Among all pharmacological activities,T.cordifoliais exclusively known as an immune booster due to its immunomodulatory and cytoprotective activities through some non-specific mechanisms [27].The alcoholic extract ofT.cordifoliastem was reported to enhance immunity by amplifying antibody production [28] andT.cordifoliaplants growing on neem trees had better immunomodulatory functions than otherT.cordifoliaplants growing on non-neem trees [29].Aqueous extract ofT.cordifoliastem was reported to have excellent immunosuppressive,anti-inflammatory and other pharmacological activities [30].
Isolation, purification and composition of polysaccharides (1,4)-α-D-glucan, (α-D-glucan) or G1-4A derived from T. cordifolia stem
T.cordifoliastems were dried and powdered, then subjected to boiling water extraction followed by precipitation with excess acetone after cooling the aqueous extract.The precipitate gave positive Molisch test for existence of carbohydrates/polysaccharides that exhibited immunogenic potency with murine splenocytes (stimulation index 11.0).Further purification ensued improvement of mitogenic property.Fraction T with more mitogenic potency with a stimulation index of 17.4 has resulted after elimination of proteinous material from the precipitate.Further purification resulted in a product T1 with a substantially greater stimulation index of 66.8.It was effective only against B cells,since T cells remained unaffected.The mean molecular weight of T1 was determined to be about 2.2 × 106.Thorough acid hydrolysis of T1 furnished a mixture of monosaccharide derivatives,those were recognized and assessed by gas chromatography.The main constituents were galacturonic acid(35%),galactose(32%),arabinose(31%) and rhamnose (1.4%).The molecular weight continued in the range of 106even after partial hydrolysis,which indicates that most of the arabinose were liberated as monosaccharides and present in the side chains.About 65% of galacturonic acid was released after partial hydrolysis, indicating their presence in the side chains, linked to the main backbone of T1, through arabinose residues.About 80% of galactose endured partial hydrolysis, indicating their presence in the linear/main chain.Isolated polysaccharides exhibited polyclonal mitogenic potential against B-cells without involvement of macrophages [31, 32].The structure of G1-4A is presented in Figure 3.
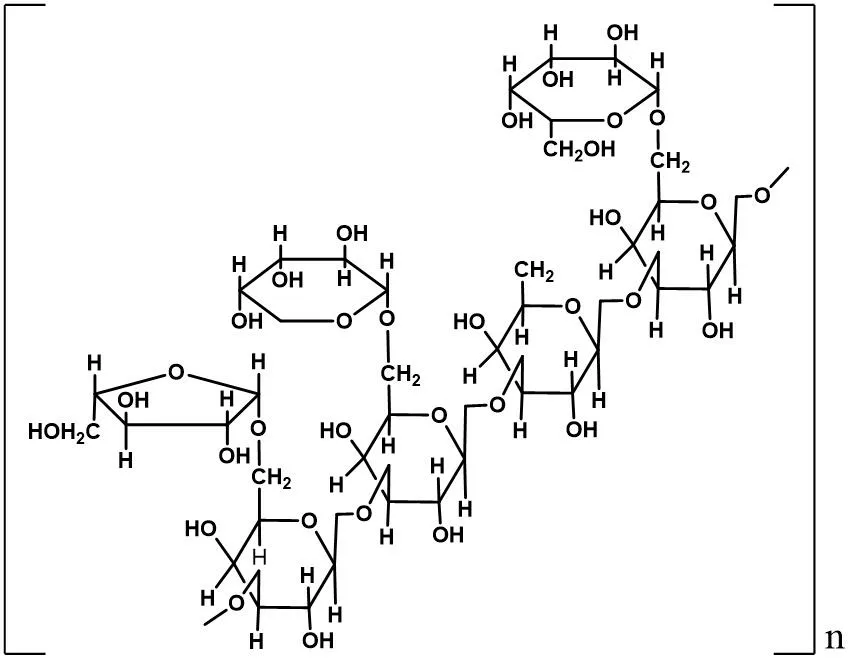
Figure 3 Structure of G1-4A.G1-4A, 1,4-linked arabinogalactan polysaccharide.
Hot water-soluble polysaccharides and cold water-soluble polysaccharides fromT.cordifoliastems were secluded and purified with a mean yield of 1.99% and 2.99%, separately.Thorough hydrolysis followed by paper chromatography and gas-liquid chromatography analysis indicated the presence of monosaccharides in the ratio of D-glucose:D-xylose:D-mannose:D-galactose:L-rhamnose:L-arabinose (95.763:0.727:0.526:0.708:0.857:1.106) in cold water-soluble polysaccharides and D-glucose:D-xylose:D-mannose:D-galactose:L-rhamnose:L-arabinose (95.408:2.048:0.777:0.292:0.697:0.777) in hot water-soluble polysaccharides.Galacturonic acid contents were 5.16% and 3.06% in hot water-soluble polysaccharides and cold water-soluble polysaccharides respectively as indicated by gas-liquid chromatography analyses [33].
Mechanism of action of G1-4A
G1-4A is reported to enhance and/or activate macrophage immune responses, including increasing reactive oxygen species (ROS)production, and increasing secretion of cytokines and chemokines.It is reported to augment the host innate immunity.The probable outcomes of G1-4A treatment on our immune system are presented in Figure 4.
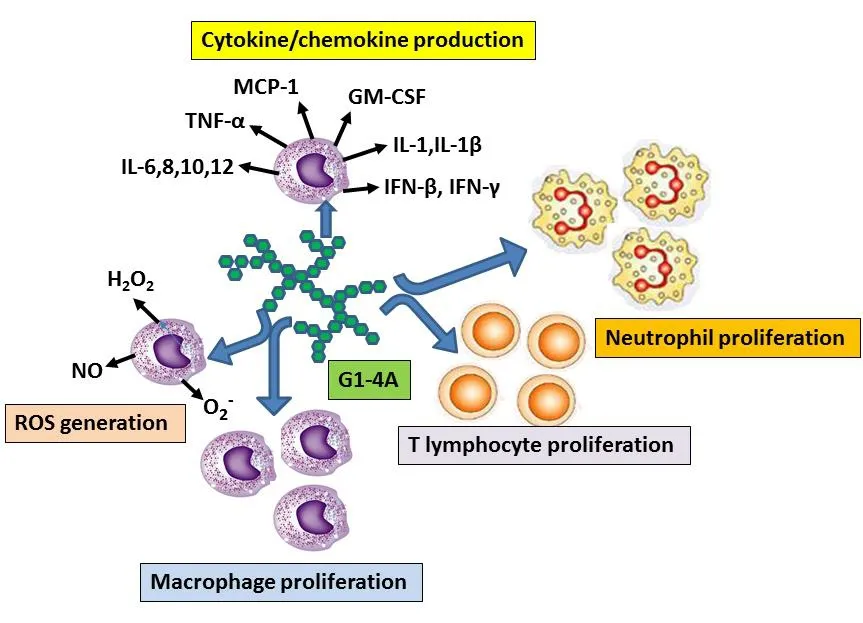
Figure 4 The possible roles of G1-4A in augmenting different cells and molecules involved with immune response.G1-4A induces immune cells(neutrophil,macrophage,T lymphocyte proliferation and increases cytokine/chemokine production and ROS generation)thereby contributing to strengthening our immune system.G1-4A, 1,4-linked arabinogalactan polysaccharide; ROS, reactive oxygen species; IFN, interferon, IL,interleukin; TNF,tumor necrosis factor; MCP-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor.
Immunomodulatory activities of G1-4A
G1-4A, an arabinogalactan polysaccharide activates both cell-mediated and humoral immunity by multiple pathways, which is reported by different researchers.The different immunomodulatory activities of G1-4A were summarized in the following paragraphs.
Anticancer activity.Treatment of polysaccharide fraction derived fromT.cordifoliastem reduced the metastatic potential of B16F-10 cancer cells (72%) in the lungs of syngeneic C57BL/6 mice, when given concurrently with tumor initiation.The biochemical markers of neoplastic development (hexosamines, uronic acids and lung collagen hydroxyproline) were decreased considerably in the treated mice as compared to the untreated.Serum sialic acid and γ-glutamyl transpeptidase levels have remained unchanged in the treated group[34].
Dendritic cell immunogenicity.The dendritic cells mediated immunity is known to rise with their maturation state and is induced by microbial toxins like lipopolysaccharide.The effect of G1-4A was investigated on the morphological and functional maturation of mouse bone marrow derived dendritic cells (BMDC) along with its role as adjuvant in immunotherapy.G1-4A, enhanced surface expression of major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-II, CD40, CD80, and CD86 by BMDC in vitro and in vivo in splenic dendritic cells.Allostimulatory activity of T cells and secretion of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and IL-12 by BMDC were also amplified by G1-4A.G1-4A treatment resulted in reduced phagocytosis and better antigen processing as shown by mature dendritic cells.G1-4A treated dendritic cells, activated cytotoxic T cells by cross-presenting exogenous antigens on an MHC-I background and caused in vitro lysis of target tumor cells.G1-4A treated dendritic cells gave rise to decreased tumor liability in prophylactic and therapeutic tumor challenge research in a mouse lymphoma model.These findings endorsed that G1-4A could be used as a potent nontoxic maturation mediator in dendritic cells based immune therapy of tumors[35].
Dendritic cells play pivotal role in the development of acquired immune response against tumor.Along with antigen presentation,dendritic cells also owns cytotoxicity against tumor cells.The killer phenotype of BMDC matured in the presence of G1-4A, (mouse BMDC(G1-4A)) had several fold increased capacity to destroy tumor cells.Nitric oxide (NO) released by mouse BMDC (G1-4A) produced peroxynitrite in tumor cells and killed them that was completely abolished by NADPH oxidase inhibitor apocyanin and inducible nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitor 1400W.The slaughtered target cells are phagocytosed by BMDC, which further activated syngeneic cytotoxic T cells.These outcomes prove that G1-4A treated mouse BMDC acquired killing attributes and also activated cytotoxic T cells[36].Therefore, it could be suggested that G1-4A supplement might augment tumor prevention and cancer therapy.
Cytokine modulating activity.G1-4A treatment blocked the bacterial lipopolysaccharide-binding sites to macrophages and also activated the macrophages.Serum levels of TNF-α and IL-1β slightly elevated after G1-4A treatment.But, when they were challenged with lipopolysaccharide, levels of TNF-α and TNF receptor elicited significantly in G1-4A pretreated mice in comparison to control.Serum IL-6, IL-1β and IFN-γ levels were increased and IL-10 was decreased after lipopolysaccharide challenge in mice pretreated with G1-4A in comparison to control.Moreover, G1-4A also modified the release of NO by murine macrophages.Concurrent results were also witnessed in a human monocytic cell line (U937).Therefore, G1-4A seemed to induce endotoxic shock tolerance in macrophages by changing the cytokine production and NO release[37].
The effects of G1-4A on the expression of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, IFN-γ and IL-10)were studied in the spleen and lungs of endotoxin-intoxicated juvenile rats at a non-lethal dose ofEscherichia coliendotoxin (10 mg/kg).The intoxicated rats were treated intraperitoneally with two doses of G1-4A (10 mg/kg) after 2 and 4 h of endotoxin injection.After 24 h,rats were euthanized, the spleen and lungs were separated for estimation of lung injury and cytokines production.Endotoxaemia resulted a five-fold increase in IL-1β concentration in both organs with moderate pulmonary hypercellularity (11% more alveolar-septal thickening and 11% less alveolar-interstitial space ratio).G1-4A treatment reduced concentrations of pro- inflammatory cytokines i.e.IL-6 (43%), IL-1β (30%), IFN-γ (46%) and the anti-inflammatory cytokine i.e.IL-10 (31%) in the treated lungs as compared to untreated.G1-4A treatment reduced the ratio of IL-1β to IL-10 by 55%,which indicated its anti-inflammatory potency.So, G1-4A is reported to modify the pro- and anti-inflammatory equilibrium during the period of endotoxaemia in juvenile rats by altering cytokines differentially in the lungs and spleen [38].
G1-4A stimulated human lymphocytes with pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines production, in vitro.The immunological and physiological effects of a low and high dose of G1-4A (0.5 and 10 mg/kg) was studied in normal rats.Differential cell count, plasma concentration of IL-4,IL-6, IL-1β,TNF-α,and IFN-γ,gaseous exchange and average arterial blood pressure remained within the physiological range.Intravenous administration of high dose of G1-4A induced tachycardia allied to hyperventilation with substantial decline in hematocrit ratio and blood hemoglobin [39].Infections with pathogens generally give rise to different acute phase responses mediated by different immune cells and varied pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines as depicted in Figure 2 and G1-4A can enhance host immune defense significantly.
Immunostimulatory activity.G1-4A was nonproliferating and noncytotoxic to normal lymphocytes as well as tumor cell lines at 0-1,000 μg/mL.But, at 100 μg/mL concentration, it triggered different subclasses of lymphocytes like B cells (39%), T cells (102%)and NK cells (331%).The substantial stimulation of NK cells is connected to the dose-dependent killing of tumor cells.G1-4A at 100 μg/mL concentration stimulated the synthesis of monocyte chemoattractant protein(MCP)-1(2,307 pg/mL),IL-6(21,833 pg/mL),IL-12 (50.19 pg/mL), IL-12 (918.23 pg/mL), IL-18 (27.47 pg/mL),IL-1β(1,080 pg/mL),TNF-α(2,225 pg/mL) and IFN-γ(90.16 pg/mL),without affecting the production of IL-2, IL-4,IL-10, IFN-α and TNF-β.G1-4A did not induce any oxidative stress or inducible NOS in the lymphocytes or NO production.All these properties were responsible for the potent immunoprotective role of G1-4A [40].
Immune boosting potency of G1-4A was evaluated in vitro and in aerosol mouse models ofMycobacterium tuberculosisinfection.Treatment ofMycobacterium tuberculosis-infected macrophages(RAW264.7) with G1-4A considerably incited the surface expression of CD86 and MHC-II molecules, secretion of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-12, IL-β, TNF-α, IFN-γ) and NO release that led to reduced intracellular survival of both drug-sensitive (H37Rv) and multidrug-resistant strains ofMycobacterium tuberculosisby toll-like receptor (TLR) 4 - myeloid differentiation primary response 88(MyD88) dependent method.Likewise, bacillary load was considerably decreased in theMycobacterium tuberculosis-infected lungs of BALB/c mice administered with G1-4A, with concurrent rise in the levels of Th1 cytokines IL-12, INF-γ, TNF-α and NOS2 and low levels of Th2 cytokine-like IL-4 in the serum.Moreover,amalgamation of G1-4A with isoniazid displayed better protection againstMycobacterium tuberculosisin comparison to either isoniazid or G1-4A singly,thereby proving its potency in adjunct therapy.So G1-4A might be beneficial in providing alternative therapies to control tuberculosis and also supplement the healing capacity of the present anti-tubercular drugs [41].Emergence and re-emergence of multidrug-resistant strains had forced the biomedical scientists and pharma companies to look for safe and easily available nutraceuticals to prevent or treat these ailments effectively with bioactive phytocompounds like G1-4A.
Activation of macrophages.G1-4A treatment increased CD69 expression in lymphocytes.G1-4A-mediated B cell multiplication was completely inhibited by phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase inhibitor(Ly294002), nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) inhibitor (plumbagin)and mTOR inhibitor (rapamycin).Extracellular signal-regulated kinase,n-Jun N-teminal kinase and protein kinase B were triggered by G1-4A, which finally ensued activation of I kappa B kinase, break down of inhibitor kappa B-alpha and translocation of NF-κB to the nucleus.G1-4A exhibits its effect probably by modulating the NF-κB signaling pathway.G1-4A treatment in mice led to splenomegaly and augmented the numbers of phagocytic macrophages, B cells and T cells.Similarly, G1-4A-induced B cell production and degradation of inhibitor kappa B-alpha were also repressed by the anti-TLR4-myeloid differentiation 2 complex antibody.G1-4A activated the RAW 264.7 macrophages and the phagocytosis index in peritoneal exudate cells sequestered from G1-4A-treated mice was found to be significantly higher than the peritoneal exudate cells isolated from controlled mice[42].
Incubation of RAW264.7 macrophages with G1-4A at 4°C,inhibited the phagocytosis of unopsonized zymosan A biomolecules in a dose-dependent manner and reduced the binding and internalization of opsonized zymosan A biomolecules,although to a lower extent than laminarin.Incubation of macrophages with anti-CD11b mAb succeeded by G1-4A aborted the effects of G1-4A-induced TNF-α synthesis, which confirmed that complement receptor 3 is not associated with opsonic binding and internalization of G1-4A in macrophages unlike zymosan A.The anti-CD11b mAb has substantial inhibitory effect on the zymosan A-prompted TNF-α synthesis.G1-4A stimulated TNF-α synthesis in macrophages dose-dependently, which can be entirely subdued by the NF-κB inhibitors i.e.caffeic acid phenethyl ester or curcumin.G1-4A stimulated NF-κB that is associated with the degradation of inhibitor kappa B-alpha and facilitates the nuclear translocation of NF-κB.G1-4A activated NF-κB through TLR6 signaling as supported by the synthesis of IL-8 in TLR6-transfected HEK293 cells.These observations proved that G1-4A stimulates immune system via activation of macrophages through TLR6 signaling pathway, translocation of NF-κB and production of different cytokines [43].
G1-4A treatment led to elevated levels of IL-6, IL-12, IL-10, IL-β,TNF-α and IFN-γ in peritoneal macrophages and RAW 264.7 cell line.NO levels were also raised with NOS2 expression in murine macrophages and surface expression of CD86 and MHC-II in macrophages were also augmented.G1-4A stimulated the macrophages by a classical pathway in TLR4-MyD88 dependent manner.This was proven by using siRNA against TLR4, MyD88 and anti-TLR4 blocking antibodies.G1-4A treatment also activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase, n-Jun N-teminal kinase, protein kinase 38 and mitogen-activated protein kinases in macrophages,which was established by using therapeutic inhibitors of the above mitogen-activated protein kinases.This suggests that treatment of G1-4A stimulated macrophages by classical pathway [44].The probable signaling pathway and mechanism of macrophage activation was depicted in Figure 5.
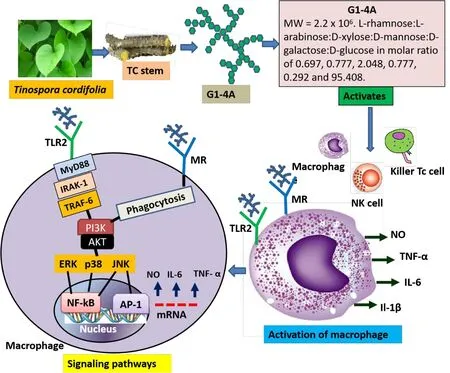
Figure 5 An overview of the mechanism of action of G1-4A in immunostimulation.G1-4A activates macrophages, NK cells and cytotoxic T cells to destroy pathogens, virus-infected cells or tumor cells.Binding of G1-4A to TLR or MR activates a cascade of events along with nuclear translocation of NF-κB leading to synthesis of different cytokine/chemokine and reactive oxygen species generation.G1-4A, 1,4-linked arabinogalactan polysaccharide; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; IL, interleukin; NK, natural killer; NO, nitric oxide; TLR, toll-like receptor; NF-κB,nuclear factor-kappa B; MR, mannose receptor; MW, molecular weight; TC, Tinospora cordifolia (Thunb.) Miers; MyD88, myeloid differentiation primary response 88; IRAK-1, interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-1; TRAF-6, tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor-6; PI3K,phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; AKT, protein kinase B; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; p38, protein kinase 38; JNK, n-Jun N-teminal kinase; AP-1, activator protein-1.
Repeated dose treatment of purified polysaccharide G1-4A and polysaccharide-rich extract ofT.cordifoliain BALB/c mice exhibited significant increase in the number of splenic macrophages and activated antigen-presenting cells without any increase in phagocytosis.Expression of phenotypic maturation markers was increased in splenic dendritic cells and but not in BMDC of polysaccharide-rich extract-treated mice.Polysaccharide-rich extract treatment resulted normal biochemical parameters similar to control without any organ toxicity as evident from histopathological analyses.Therefore polysaccharide-rich extract can be used instead of G1-4A as a promising immunotherapeutic adjuvant [45].
Clinical trials and toxicity studies
Till date, there is no report on the clinical trials undertaken on G1-4A.But, there are few reports on the toxicity study of arbinogalactan polysaccharides in rat and mouse models.Arbinogalactan was reported to be safe up to 5 g/kg and did not cause mortality in either rats or mice injected intravenously with different doses of arbinogalactan,nor showed any signs or symptoms of toxicity.Repeat dose toxicity was also evaluated after the injection of 31-500 mg/kg/day of arbinogalactan to rats.No signs or symptoms of toxicity were observed after arbinogalactan administration and the animals gained weight during the 90 days dosing period [46].
Conclusion
G1-4A, an arabinogalactan polysaccharide is reported to reinforce the host defense by multiple pathways by either inducing immune cell proliferation or upregulating cytokine/chemokine production or ROS generation, thus modulating our immunity.Binding of G1-4A to TLR or mannose receptor activates a cascade of events along with nuclear translocation of NF-κB leading to synthesis of different cytokine/chemokine and ROS generation.G1-4A activates different immune cells like macrophages, NK cells and cytotoxic T cells to eliminate pathogens, virus infected cells or tumor cells.
T.cordifoliais used extensively since ancient times to elicit the overall immune status of human beings.Moreover, COVID-19 pandemic had opened new vistas to exploreT.cordifoliaand other herbs to improve immunity.Till date, many bioactive compounds fromT.cordifoliawere isolated and testified in various experimental models for different pharmacological activities, but so far, only a few compounds were screened for immunomodulatory or immunostimulatory properties.Therefore, more number ofT.cordifoliacompounds should be verified scientifically by both in vitro and in vivo studies in several experimental models to decipher their mode of action.Few clinical studies were previously reported, but they were poorly planned due to absence of appropriate supportive preclinical information and the phytoextracts used were not consistent with active biochemical indicators.Therefore, more appropriate and functional trials should be conducted with ample and rational scientific aptitude.Potential generalized and pharmacokinetic study succeeded by sufficient clinical trials can produce conclusive evidences on its effective role in modulating the immune system.
 Traditional Medicine Research2022年5期
Traditional Medicine Research2022年5期
- Traditional Medicine Research的其它文章
- Pseudotargeted metabolomics for exploring the changes of neurotransmitters profile in aging rat brain and the potential neuroprotective effect of alkaloids from Uncaria rhynchophylla
- Antioxidant, hepatoprotective and nephroprotective activities of Gazania rigens against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity in rats
- Traditional medicines and experimental analysis methods for Alzheimer’s disease
- Effect of Terminalia chebula Retz.extraction with water on Staphylococcus epidermidis activity and its biofilm formation
- Update on the preclinical and clinical assessment of Withania somnifera: from ancient Rasayana to modern perspectives
- Valerian(Valeriana officinalis)extract inhibits TNF-α and iNOS gene expression in mouse LPS-activated microglial cells
