Research hotspots and trends in Chinese minority traditional medicine during 2021:a visual bibliometrics analysis
Shao-Hui Wang,Jing Qin,Xian-Li Meng,Yi Zhang*
1School of Ethnic Medicine,Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Chengdu 611137,China.2Medical College of Qingdao Binhai University,Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao Binhai University/Qingdao Military-Civilian Integration Hospital,Qingdao 266555,China.3State Key Laboratory of Southwestern Chinese Medicine Resources,Innovative Institute of Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy,Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Chengdu 611137,China.
Abstract Background:Chinese minority traditional medicine(CMTM)is an important component of Chinese traditional culture and medicine that has contributed to the health and prosperity of Chinese people of all ethnic groups.Although this type of medicine has attracted interest,its developmental trends and research status remain unclear.Therefore,we used literature metrology to evaluate the publications on CMTM during 2021 and explore hotspots and frontier areas.Methods:Reports associated with CMTM published between January 1,2021,and December 31,2021,were downloaded from the Web of Science database.The authors,institutions,countries,journals,keywords,and other standard bibliometric indicators were analyzed and visualized using CiteSpace,and research hotspots and trends were identified.Results:We retrieved 152 CMTM-related publications,among which Tibetan medicine attracted the most interest.Journals covering alternative and complementary medicine topics were the most prevalent sources of reports about CMTM,particularly the Journal of Ethnopharmacology.Most research in this field was conducted in China and frequently published by traditional Chinese medicine colleges and universities.One author,Yi Zhang,has extensively investigated Tibetan and Korean medicine.The keyword co-occurrence network revealed that investigations into ethnic groups mainly focused on the pharmacological activities and phytochemical components of ethnic medicines.The keywords of gut microbiota and autophagy in some publications reflect the direction of future CMTM investigations.Conclusion:Our findings showed the current status and trends in CMTM investigations.This information will help identify new research directions and hotspots in this field.
Keywords:Chinese minority traditional medicine;bibliometrics;CiteSpace;Web of Science;Tibetan medicine;Mongolian medicine
Background
China is a multi-ethnic country,and the medicines of various ethnic groups have also developed over thousands of years of civilization.In addition to traditional Han Chinese medicine,other ethnic minorities such as Tibetan,Mongolian,Miao,and Uyghur have also developed unique medical cultures[1].In the Inner Mongolia region of China,Mongolian medicine is recognized as a significant part of the health care system and has formed a systematic theoretical system with rich resources of drugs and unique therapies.Additionally,it is a crucial part of the Chinese healthcare system and has contributed to the wealth of global traditional medicine[2,3].Tibetan medicine also developed during 2,000 years into a complete theoretical system that plays an important role in preventing and treating various diseases[4].The Tibetan medicinal bath therapy was listed in theRepresentative List of Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanityin 2018 due to its curative effects and gradually became recognized worldwide[5,6].Several other ethnic medicines have been preserved and developed through state and civil protection.Chinese minority traditional medicine(CMTM)mainly comprises Tibetan,Mongolian,Miao,Uyghur,and traditional Korean medicine.Among them,Tibetan and Mongolian medicines have developed at an industrial scale that is expanding[7].The Chinese government recently attached great importance to CMTM,leading to significant progression.Moreover,various ethnic therapies have been gradually promoted and documented[3,8,9].Therefore,identifying the research status and trends of CMTM from various literature sources is particularly important for analyzing developmental hotspots and the future direction of CMTM research.
Bibliometrics is a statistical analysis tool that can be used to quantify and explore research hotspots and developmental trends[10].It can be used to quickly identify the characteristics of various types of literature and analyze research hotspots and developmental processes[11].CiteSpace is the most popular software used in bibliometrics analysis.It can be used to measure,analyze,and visualize literature in a specific field,mine valuable information,and display research hotspots,frontiers,and future evolution trends as an atlas[12,13].Bibliometrics analysis relies on literature databases in the English language such as the Web of Science,Scopus,and PubMed and academic databases in other languages such as the China National Knowledge Infrastructure[14].Among these,the Web of Science database is the most popular,mainly because it contains large-scale international,comprehensive,and high-impact multidisciplinary academic journals.In addition,considerable evidence supports the notion that the Web of Science database can provide better knowledge network maps when using CiteSpace for literature visualization analysis[11,15-17].
Therefore,we selected the Web of Science database as the research literature source and used the CiteSpace software to analyze the bibliometrics of reports describing different aspects of CMTM published during 2021.In addition,the literature characteristics,research direction,depth,future hotspots,and trends in investigations of different ethnic medicines were systematically summarized and evaluated to provide a reference for further CMTM development.
Methods
Data acquisition
All publications were downloaded from the Web of Science database using the keywords “Tibetan medicine”,“Mongolian medicine”,“Zhuang medicine”,“traditional Korean medicine”,“Uyghur medicine”,and “Miao medicine”.The literature types comprised articles,reviews,and online publications,and the language was limited to English.The period was from January 1 to December 31,2021,and publications were retrieved until January 15,2022.We identified 152 publications,saved them as full records and exported them in plain text format.
Parameter setting and data visualization analysis
The exported literature for each type of ethnic medicine was in download_***.txt format was recognized by CiteSpace(version 5.7.R2),where *** represents the number.We then used CiteSpace to convert the format,deduplicate,and visualize the data.The threshold parameters were:reports published from January 1 to December 31,2021,time-slicing of 0 years per slice,text processing selected all term sources,and node types including author,institute,keyword,and other nodes,one of which was selected for each analysis.The selection criteria were set in the top 50.We then analyzed co-occurrence among authors,institutions,countries,journal sources,and the keywords of each ethnic medicine-related literature according to the above parameters.Furthermore,we analyzed the network atlas information in depth based on software prompts combined with manual literature reads and information integration.
Results
Publications associated with CMTM during 2021
We conducted retrieval and visual analysis of CMTM related literature according to the flow chart shown in Figure 1.And We identified 152 publications associated with CMTM in the Web of Science database that comprised 77(50.66%),27(17.76%),13(8.55%),10(6.58%),17(11.18%),and 8(5.26%)associated with Tibetan,Mongolian,traditional Korean,Uyghur,Miao,and Zhuang medicines,respectively.Supplementary Figure 1 shows the numbers and percentages of ethnic medicine-related publications in 2021.Most publications focused on Tibetan medicine,followed by Mongolian medicine.
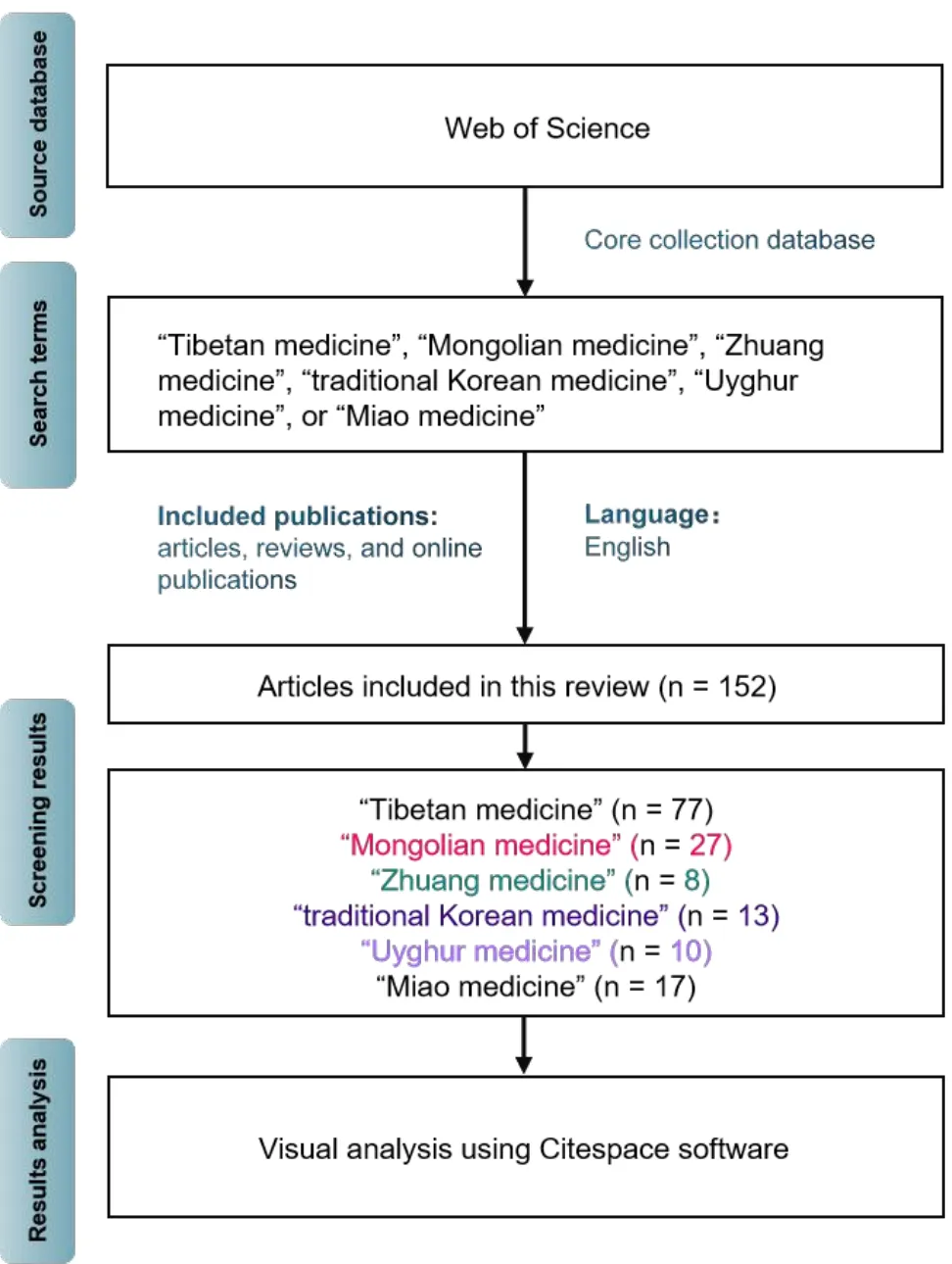
Figure 1 Flow diagram of the literature search process and visual analysis
Tibetan medicine
Tibetan medicine is a complete theoretical system with unique therapeutic methods and ethnic characteristics formed over 2,300 years of practice.We analyzed the literature associated with Tibetan medicine,and the author cooperation network showed that Xian-Li Meng(n = 3)and Ning Li(n = 3)published the most articles.In addition,Xian-Li Meng,Ning Li,Yi Zhang,and Xiao-Bo Wang formed a large and closely related cooperation network within the whole network(Figure 2A).Further analysis of their publications revealed that this group systematically studied classical prescriptions in Tibetan medicine,including the Ershiwuwei Lvxue pill(Chinese drug patented by the National Medical Products Administration(NMPA);approval number:Z54020070)comprising Lvxue(Equus AsinusLinnaeus),Xizangmaoru(Rhamnella Gilgitica),Jiangxiang(Dalbergia Odorifera),Tanxiang(Santalum Album),Hezi(Terminalia Bellirica)and 25 other herbs[18];the Duoxuekang capsule(Chinese drug patented by the NMPA;approval number:Z10980020)comprising Yuganzi(Phyllanthus Emblica),Hongjingtian(Rhodiola Crenulata),Shaji(Hippophae Rhamnoides),and Ganjiang(Zingiber Officinale)[19,20];and single drugs such as Yishoucao(Pterocephalus Hookeri)[21],Rhamnella Gilgitica[22],Xiaobo(Berberis Dictyophylla)[23],and Gansuxiaobo(Berberis Kansuensis)[24].The diseases studied included rheumatoid arthritis,type 2 diabetes,and brain injury.In the cooperation network of research institutions,the top three institutions in terms of the number of articles published were the Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine(n = 8),Chinese Academy of Sciences(n = 7),and Beijing University of Chinese Medicine(n =5).However,the Chinese Academy of Sciences had the highest degree centrality(0.10)in the cooperation network(Figure 2B).Further analysis of the national cooperation network revealed that research into Tibetan medicine was mainly concentrated in China,whereas a few foreign studies were concentrated in the USA,Canada,Pakistan,Russia,and Nepal(Figure 2C).These studies were published in theJournalofEthnopharmacology,FrontiersinPharmacology,Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine,Bulletin of Environmental Contamination Pollution and Toxicology,and others(Figure 2D).
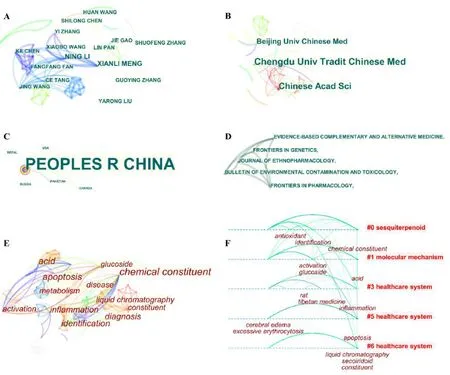
Figure 2 Visual analysis of academic publications related to Tibetan medicine in 2021.Co-occurrence network map representing co-authors(A),cooperative institutions(B),cooperative countries(C),journal sources(D),and keywords(E&F)of Tibetan medicine research results during 2021.In all network diagrams,the larger the font,the higher the frequency of the target object in the whole network.
The keyword co-occurrence network and cluster analysis showed that inflammation,chemical constituents,apoptosis,acid,medicine,diagnosis,and activation were frontier hotspots of Tibetan medicine research in 2021.Furthermore,these keywords were mainly clustered in the areas of healthcare systems,molecular mechanisms,and sesquiterpenoids(Figures 2E and 2F).The flavonoids in Duansuituercao(Lagotis Brachystachya)can relieve gout arthritis induced by monosodium urate crystals through regulating the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway and expressing the nucleotide-binding domain leucine-rich repeat containing family pyrin domain containing 3(NLRP3)in vitro and in vivo[25].Luteolin and apigenin fromLagotis Brachystachyareducehyperuricemia byinhibiting inflammatory signaling pathways and reducing and increasing uric acid production and excretion,respectively[26].Phenolic compounds derivedfromChangguopopona(VeronicaCiliata)reduce ethanol-induced liver injury in buffalo rat liver 3A cells by activating the AMPK/P62/Nrf2 pathway[27].In addition to investigations into the effects and mechanisms of Tibetan medicines,the chemical composition of some Tibetan medicines was also a popular topic,especially the application of contemporary separation technologies to material bases.These technologies included medium-pressure chromatography and two-dimensional reversed-phase-reversed-phase interaction liquid chromatography guided by online high-performance liquid chromatography(HPLC)-1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl(DPPH)assays[28],liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry(MS)-based qualitative analysis and pharmacokinetic integration network strategies[29],middle-pressure chromatogram isolated gel coupled with reversed-phase chromatography with hydrophilic groups[30],isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantitation combined with liquid chromatography-tandem MS[31],ultra-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight-MS/MS[31],online medium pressure chromatography tower and two-dimensional inversion/hydrophobic interaction chromatography based on online HPLC-DPPH assays[32].These analytical approaches have effectively revealed the potential material basis of Tibetan medicine.
Mongolian medicine
Mongolian medicine is a unique medical theory and treatment method that is not only a rich cultural heritage of the Mongolian people but also an important part of traditional Chinese medicine.Analysis of academic reports associated with Mongolian medicine revealed that Jing-Kun Lu published two articles,whereas all other authors published only one,and the cluster of purple lines indicated a close cooperative relationship among these authors(Figure 3A).In Mongolian medicine,Mengguluobo(Scabiosa Comosa)and Lanpenhua(Scabiosa Tschilliensis)are traditionally used to treat liver diseases.Lu et al.used network pharmacology and experimental validation to uncover the common pharmacological mechanisms ofScabiosa ComosaandScabiosa Tschilliensisin treating liver fibrosis[33].In addition,this group analyzed the efficacy and potential mechanisms of the Sanwei Tanxiang powder(Chinese drug patented by the NMPA;approval number:Z20027786),comprising Guangzao(Fructus Choerospondiatis),Roudoukou(Myristica Fragrans),andSantalum Album.This traditional Mongolian and Tibetan medicine improves myocardial ischemia-reperfusion,relieves angina and improves the recovery of patients with coronary heart disease[34].The top three institutions in the research cooperation network in descending order were the Inner Mongolia University for Nationalities(n = 6),Inner Mongolia Medical University(n = 3),Yunnan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine(n = 2),and Minzu University of China(n = 2).Inner Mongolia Medical University had the highest degree centrality(0.02)in the cooperation network(Figure 3B).Research associated with Mongolian medicine in the national cooperation network was mainly concentrated in China,followed by Mongolia(Figure 3C)and were published in theJournal of Ethnopharmacology,Frontiers in Pharmacology,American Journal of Translational Research,Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine,Chemistry of Natural Compoundsand others(Figure 3D).
The research hotspots of Mongolian medicine in terms of the keyword co-occurrence network and cluster analysis were activation,extract,antioxidant,antioxidation,expression,anxiety,apoptosis,inflammation,in vitro,alkaloid,and cell.These keywords were primarily clustered in research associated with pharmacological activities and acute lung injuries(Figures 3E and 3F).For example,nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 targets the active ingredients in Qiwei Putao powder(Chinese drug patented by the NMPA;approval number:Z21020282),comprising Baiputaogan(Vitis Vinifera),Shigao(Gypsum Fibrosum),Honghua(Carthamus Tinctorius),Shiliu(Punica Granatum),Xiangfu(Cyperus Rotundus),Rougui(Cinnamomum Cassia),and Gancao(Glycyrrhiza Uralensis).Its potential mechanism for treating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease has been determined through systematic pharmacological prediction and verification[35].Others have used such prediction and verification to reveal the mechanism of the classical ancient Mongolian prescription,Guanxin Shutong capsule(Chinese drug patented by the NMPA;approval number:Z20020055)comprising Suanzao(Choerospondias Axillaris),Danshen(Salvia Miltiorrhiza),Dingzixiang(Syzygium Aromaticum),Bingpian(Dryobalanops Aromatica),and Qingpizhu(Bambusa Textilis)in treating cerebrovascular diseases with multiple targets[36].Furthermore,the potential pharmacological effects and mechanisms of some single drugs have been revealed,such as Tangsongcao(Thalictrum Minus),a common Mongolian folk medicine.Thalictrum Minusimproves acute lung injury induced by particulate matter via inhibiting the release of inflammatory cytokines and alleviating oxidative damageassociatedwiththeAMPK-Nrf2/KEAP,MAPKs-NLRP3/caspase-1,and apoptotic pathways[37].Dishaogua(Cynanchum Thesioides)is a popular traditional Mongolian medical herb that is used to treat abdominal pain and diarrhea.A water extract ofCynanchum Thesioidesalso benefits visceral hypersensitivity in patients with irritable bowel syndrome and exerts favorable effects on the composition,structure,and function of the gut microbiota[38].The chemical composition of some compounds and single drugs in Mongolian medicine has been revealed using HPLC-quadrupole time-of-flight-MS/MS combined with zebrafish behavior trajectory analysis to identify the antidepressant components of the methanol extract of Mongolian Anshen Buxin Six pills(Chinese drug patented by the NMPA;approval number:Z20063939)comprising Muxiang(Aucklandia Costus),Myristica Fragrans,Choerospondias Axillaris,Syzygium Aromaticum,Fengxiangshuzhi(Liquidambar Formosana),Asian water buffaloes(Bubalus Bubalis),and yellow cattle(Bos Taurus Domesticus)[39].The chemical composition of the active site of Liaochicao(Odontites Vulgaris)was identified using ultra-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole-exactive high-resolution-MS,and its potential mechanism in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis has been verified by a combination of network pharmacology and experimentation[40].
Traditional Korean medicine
Korean medicine is a traditional medical system formed and developed based on the inherent Korean culture.It has absorbed the theories of traditional Chinese medicine and combines them with the practical experience of preventing and treating diseases among Korean nationals.The results of our analysis of research associated with traditional Korean medicine showed that Yi Zhang published the most(n = 2)articles in the author cooperation network and also had the highest centrality(0.01)in the entire cooperation network(Figure 4A).Furthermore,a literature review revealed that these two articles reviewed the phytochemistry and pharmacology of medicinal fungi of the genusPhellinusand plants of the genusNardostachys[41,42].The institutions cooperation network revealed that the Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University,Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Chinese Academy of Sciences,and Beijing University of Chinese Medicine each published two reports.The top three institutions with the highest centrality in the cooperation network were Beijing University of Chinese Medicine,Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,and Chinese Academy of Sciences,with values of 0.24,0.23,and 0.12,respectively(Figure 4B).Most investigations into traditional Korean medicine were conducted in China(n = 13),South Korea(n = 5),and England(n = 2)(Figure 4C).The findings were published in theIntegrative Medicine Research,Journal of Advanced Research,Phytomedicine,Journal of Ethnopharmacology,andFrontiers in Medicine(Figure 4D).
The keyword co-occurrence network displayed that activation,clinical trial,anti-inflammatory activity,antibacterial,data mining,flavonoid,ethnomedicine,and hepatotoxicity were hot topics in traditional Korean medicine research during 2021(Figure 4E).The first was a study of pharmacological effects and mechanisms of the traditional Korean medicine ERM210 comprising nine oriental medicinal herbs.It inhibits the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via the reactive oxygen species/mitochondria-dependent apoptosis signaling pathway[43].Rehepugongying(Taraxacum Platycarpum)is a traditional Korean medicinal herb used to treat hepatitis,boils,jaundice,and other diseases.Polysaccharides fromTaraxacum Platycarpumroots exert immunomodulatory effects on RAW264.7 cells,leukemia cells in mouse macrophage,through the MAPK and NF-κB pathways[44].In addition,traditional Korean medicine investigations include clinical trials and data mining[45-48].For example,a comprehensive review of clinical trials of ginseng between 1979 and 2018 using bibliometrics included institutional cooperation,national cooperation,types of ginseng preparations,administration routes,and clinical trial safety[48].Overall,basic research on traditional Korean medicine is limited and needs to be further strengthened.
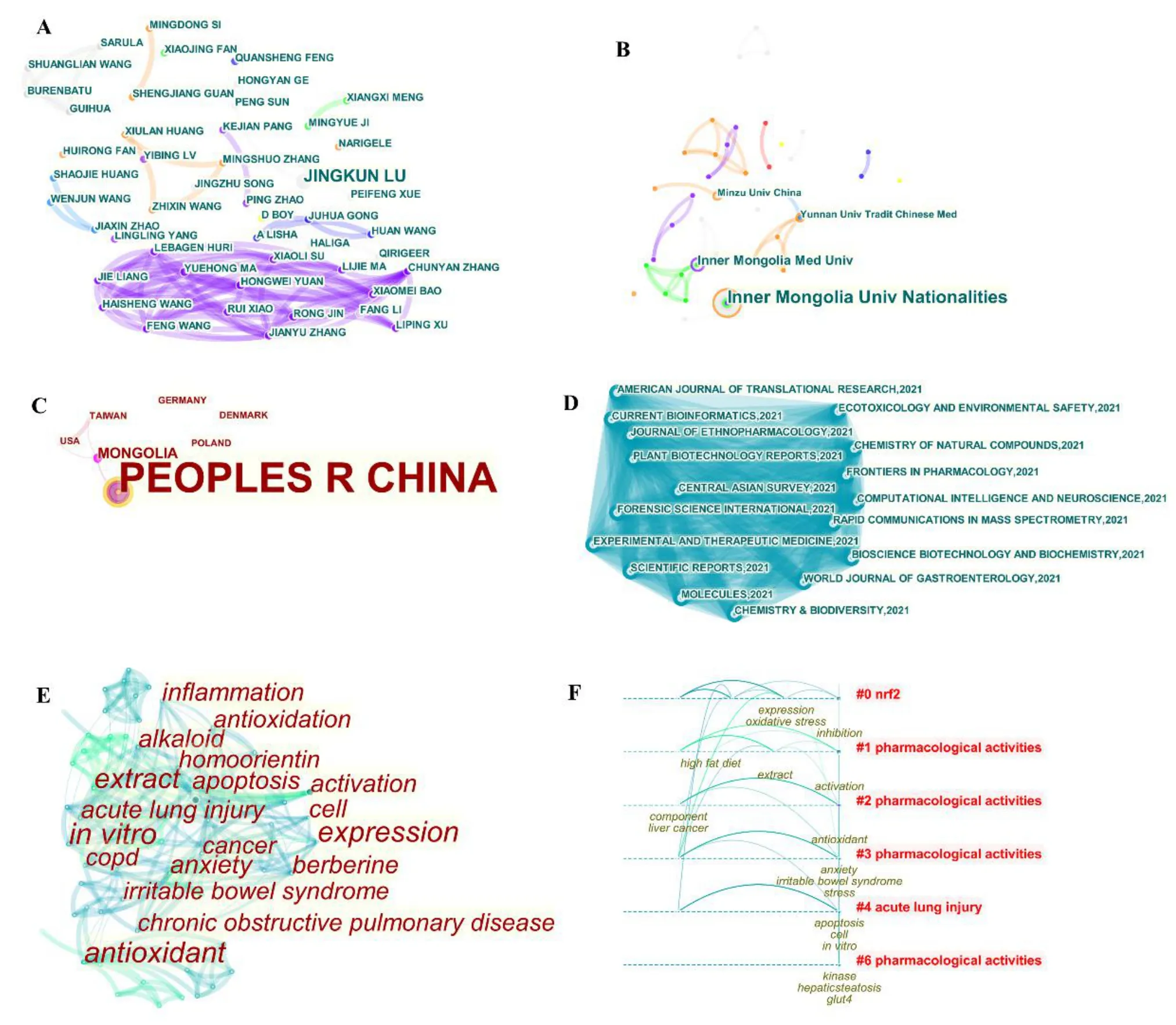
Figure 3 Visual analysis of academic publications related to Mongolian medicine in 2021.Co-occurrence network map representing co-authors(A),cooperative institutions(B),cooperative countries(C),journal sources(D),and keywords(E &F)of Mongolian medicine research results during 2021.In all network diagrams,the larger the font,the higher the frequency of the target object in the whole network.

Figure 4 Visual analysis of academic publications related to Traditional Korean medicine in 2021.Co-occurrence network map representing co-authors(A),cooperative institutions(B),cooperative countries(C),journal sources(D),and keywords(E)of traditional Korean medicine research results during 2021.In all network diagrams,the larger the font,the higher the frequency of the target object in the whole network.
Uyghur medicine
Uyghur medicine is the scientific accumulation and summarization inherited from people of ancient Western regions and Uyghur laborers who later migrated to these regions during long-term struggles against various diseases.The analysis of publications associated with Uyghur medicine in 2021 revealed that Qiang Yin(n = 2)published the most papers in terms of author interaction.One article reveals the mechanism of Qingrekasen granule(Chinese drug patented by the NMPA;approval number:Z65020172),which mainly consists of Juju(Cichorium Intybus).The underlying mechanism through which Qingrekasen granule protects podocytes and maintains renal tubule function was determined by combining metabolomics with network pharmacology.This drug treats nephrotic syndrome by promoting autophagy and anti-apoptosis through the expression of AKT serine/threonine kinase 1,caspase 3,B-cell lymphoma 2-like 1,and mammalian target of rapamycin.Metabolomics results showed that D-glutamate and D-glutamine metabolism and aspartate,alanine,and glutamate metabolism were the main targeted metabolic pathways for nephrotic syndrome treatment in rats[49].Another study by this group explored the mechanism of the Hanchuan Zupa granule(Chinese drug patented by the NMPA;approval number:20063931)for treating asthma.Network pharmacological analysis and experimental validation strategies revealed that the Hanchuan Zupa granule significantly inhibits ovalbumin-induced inflammation through the PI3K/Akt and Fc epsilon RI signaling pathways[50].Four major cooperative clusters were formed in the entire interaction network,indicating a close cooperative relationship among these authors(Supplementary Figure 2A).The institutions with the most publications were the Xinjiang Uyghur Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd.(n =2)and Xinjiang Medicine University(n = 2)in the cooperative network of research institutions.Furthermore,Xinjiang Uyghur Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd had the highest degree centrality(0.08)in the cooperative network(Supplementary Figure 2B).Research associated with Uyghur medicine in the national cooperation network was mainly concentrated in China.Moreover,the academic results were mainly published in theJournal of Ethnopharmacology,Molecular Nutrition &Food Research,Frontiers in Pharmacology,Annals of Human Biology,andMolecular Medicine Reports(Supplementary Figure 2C).
The analysis of keyword co-occurrence networks revealed apoptosis,asthma,toxicology,airway responsiveness,molecular docking,in vitro,glutamine synthetase,autophagy,and others as research hotspots for Uyghur medicine in 2021(Supplementary Figure 2D).Among these,the phytochemical components,pharmacology,pharmacokinetics,toxicology,quality control,and other aspects of single drugs in Uyghur medicine have been systematically summarized.These include Luotuoci(Alhagi Sparsifolia)[51]and Moshizi(Quercus Infectoria)[52]that provide a basis for their further development and utilization.The traditional Uyghur medicine prescription,abnormal Savda Munziq,primarily consists of 10 herbs,including Xunyicao(Lavandula Angustifolia),Huixiang(Foeniculum Vulgare),Niushecao(Anchusa Italica),Dijin(Euphorbia Humifusa),Xiangfengcao(Melissa Officinalis),and Tiexianjue(Adiantum Capillus Veneris).This prescription alleviates oxidative stress and secondary mitochondrial-related apoptosis through the Erk/p90RSK/Bad pathway,thus protecting the healing progress of early burn wounds in rats[53].Yingzuidou(chickpeas)has been a natural Uyghur medicine in Xinjiang,China for 2,500 years.A metabolomic and microbiota study revealed that an extract of Yingzuidou restored the intestinal ecology and metabolic profile,improving the symptoms of metabolic syndrome and metabolism in rats with type 2 diabetes.This provides evidence that Yingzuidou could function as a prebiotic to prevent diabetes[54].Alhagi Sparsifoliaextract also protects against intestinal inflammation in ulcerative colitis by regulating the TLR4-dependent NF-κB pathway[55].
Zhuang medicine
During a prolonged struggle against natural disasters and diseases,the Zhuang people created a material,spiritual,and organizational culture and gradually formed a medical culture system with their national characteristics.The results of our analysis of literature associated with Zhuang medicine revealed that all authors in the author cooperation network published only one article.In addition,we found six cooperative clusters in the entire network(Supplementary Figure 3A).In the cooperation network of research institutions,Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine(n = 3)and Guangxi Medical University(n = 3)published the most articles.The institution with the highest centrality in the cooperation network was the Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine(0.67)(Supplementary Figure 3C).Among them,investigators at Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine used a multi-center,randomized,parallel,controlled clinical trial to explore the efficacy and safety of the Zhuang medicated thread moxibustion and when used in combination with Western medicine,it had good efficacy in the treatment of psoriasis vulgaris,with no obvious adverse reactions[56].Liang et al.analyzed the active ingredients and mechanisms of the empirical formula Qintengtongbi decoction,which mainly comprises Qinjiao(Gentianae Macrophyllae),Weilingxian(Clematidis Radix),Sifangteng(Cissus Hastata),Qingfengteng(Caulis Sinomenii),and Fangji(Stephaniae Tetrandrae).Their network pharmacology results helped reveal and clarify the effects of this formula in treating rheumatoid arthritis and provided a scientific basis for further study of its mechanism[57].In addition,Li et al.combined this method with experimental verification to determine the antihypertensive effects of the empirical formula Zhuang folk Lei-gong-gen formula granule,consisting of Mohanlian(Eclipta Prostrata),Tufuling(Smilax Glabra),and Jixuecao(Centella Asiatica),in a spontaneously hypertensive rat model.They further clarified its potential active ingredients and its antihypertensive mechanism.Lei-gong-gen formula granule reduced blood pressure in the spontaneously hypertensive rat models;this may be associated with upregulated proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src expression,activated PI3K/Akt/NOS3 signaling pathway,improved serum nitric oxide levels,and promoted vasodilation.Additionally,nicotinic acid in Lei-gong-gen formula granule might have antihypertensive effects[58].The national cooperation network analysis showed that investigations into Zhuang medicine were mainly concentrated in China.These findings were published in theJournal of Ethnopharmacology,Natural Product Communications,Chinese Medicine,andChinese Journal of Integrative Medicine(Supplementary Figure 3B).The keyword co-occurrence network showed that acid,alkane,activation,component analysis,blood pressure,and anti-rheumatoid arthritis were the hotspots of Zhuang medicine research during 2021(Supplementary Figure 3D).Duiyeyoumagen(Viburnum Taitoense)has a long history as a folk medicine for treating fractures,rheumatism,and relieving pain among ethnic minorities in Southwest China,especially in the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region.Wu et al.found that an ethyl acetate extract ofViburnum Taitoenseexerts anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects,especially the triterpenoids in the plant[59].Moreover,Liao et al.showed that essential oil extracted from the leaves of Ainaxiang(Blumea Balsamifera)hasanti-inflammatoryeffectson lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW264.7 cells,possibly by decreasing the activity of the TLR4-NF-κB signaling pathway and inhibiting the activation of NLRP3 inflammasomes[60].
Miao medicine
Miao medicine is derived from an unremitting struggle against nature,society,and disease by generations of Miao people and is an important guarantee for their survival,reproduction,and development.We analyzed publications associated with Miao medicine.The author cooperation network showed that Jun Chen,Ping Li,and Wei-Wei Tang published more than two articles and had a close cooperative relationship(Figure 5A).The research institutions and national cooperation network revealed five institutions with two or more publications:China Pharmaceutical University(n = 3),Chinese Academy of Sciences(n = 2),Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine(n = 2),Minzu University of China(n = 2),and Guizhou University of Chinese Medicine(n = 2).The Chinese Academy of Sciences had the highest centrality(0.13)in the entire cooperation network.Most research on Miao medicine was conducted in China(Figure 5B).The articles were published in theChinese Journal of Natural Medicine,BMC Plant Biology,Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine,Journal of Ethnopharmacology,andPhytomedicine(Figure 5C).The keyword co-occurrence network showed that ethnomedicine,activation,acid,inflammasome activation,chemical constituent,fibrosis,gut microbiota,and berberine were hotspots in Miao medicine research during 2021(Figure 5D).The Miao medicinal formula Jinwu Jiangu capsule mainly comprises Gouji(Cibotium Barometz),Qiannianjian(Homalomena Occulta),Xiaohuaqingfengteng(Sabia Parviflora),Heiguteng(Gardneria Angustifolia),Jianghuang(Curcuma Longa),Sanqi(Panax Notoginseng),Shaoyao(Paeonia Lactiflora),andGlycyrrhiza Uralensis.This formula regulates autophagy by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in rheumatoid arthritis[61].Xu et al.found that compound Q-1 extracted from the Miao medicine Tiekuaizi(Helleborus Thibetanus)alleviates type II collagen-induced arthritis in rats via the NF-κB signaling pathway[62].Multivariate statistical analysis[63]and network pharmacology[64]have been applied to reveal the potential pharmacological effects and mechanisms of Miao medicine.
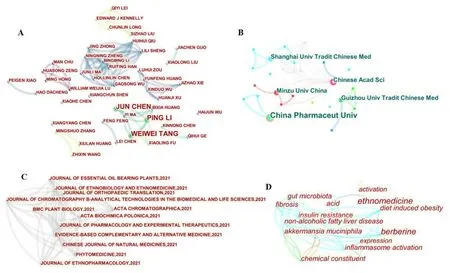
Figure 5 Visual analysis of academic publications related to Miao medicine in 2021.Co-occurrence network map representing co-authors(A),cooperative institutions(B),journal sources(C),and keywords(D)in Miao medicine research results during 2021.In all network diagrams,the larger the font,the higher the frequency of the target object in the whole network.
Conclusion and perspective
Recently accumulated evidence has shown that many herbal medicine extracts or components can be used to prevent and treat various diseases such as rheumatic immune diseases[65,66],cancer[4,67,68],neurodegenerative diseases[69,70],and liver disease[71,72].However,ethnic medicine faces the same problems as traditional Chinese medicine.Owing to the complexity of its components,multiple targets and pathways lead to various effects,and their mechanisms of action are unclear.However,interdisciplinary research strategies,such as network pharmacology[73],artificial intelligence[74],transcriptomics[75],metabolomics[76],and gut microbiota analyses[77]have proven effective for revealing the effector components and potential mechanisms of ethnic medicines and have promoted the development of studies associated with CMTM.
We conducted a bibliometrics analysis during 2021 of traditional Tibetan,Mongolian,Uyghur,Korean,Zhuang,and Miao medicines studied and developed in China.Overall,the number of traditional medicine-related publications by different ethnic groups is increasing.Among them,the research interests of Yi Zhang include traditional Tibetan and Korean medicine.In fact,research on Tibetan medicine was mainly conducted by Zhang et al.Most CMTM-related studies were conducted in China,which is the main force in this field.Furthermore,research on Tibetan,traditional Korean,Mongolian,and other ethnic medicines is ongoing in other countries,indicating that CMTM is gradually becoming recognized by foreign investigators.However,cooperative publications between China and other countries are relatively scant.In terms of research institutions,most are universities,especially those with a distinctive focus on traditional Chinese medicine.Some were from hospitals or research institutes,but cooperation among institutions is deficient.Therefore,exchange and cooperation among many countries and institutions should be strengthened so that advantages in technology,equipment,and instruments can be shared and the continuous development of CMTM-related research can be promoted.Journal analysis showed that most published studies were in the field of alternative and complementary medicine,such as theJournal of Ethnopharmacology,Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine,andEvidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.Among them,theJournal ofEthnopharmacologyhas published articles about all types of ethnic medicines.This indicates that many investigators have affirmed the findings of ethnic medicine in this journal which is an authority on the subject.
Keywords reflect the main content and core themes of articles.High-frequency keywords are often used to reflect current hot topics[78].Our co-occurrence and cluster analysis of keywords in the literature using the CiteSpace software showed that various ethnic groups are currently focusing on the pharmacological activity and phytochemical composition of ethnic medicines.This indirectly indicates that efficacy evaluation and material basis research of ethnic medicine are hotspots and future trends.Furthermore,keywords such as gut microbiota and autophagy that appear in some ethnic medicine studies reflect innovative directions of research topics.This might also be a continuous mainstream trend to promote CMTM-related research.
In summary,our findings provide valuable information for further investigation into CMTM and emphasize the developmental trends of CMTM using visual atlas analysis.In addition,our findings provide a rationale for promoting cooperation and communication among potential collaborators and research institutions.
 Traditional Medicine Research2022年3期
Traditional Medicine Research2022年3期
- Traditional Medicine Research的其它文章
- Traditional Chinese medicine:an important broad-spectrum anti-coronavirus treatment strategy on COVID-19 background?
- Anti-asthmatic mechanism of the Huashanshen dripping pill via suppressing contraction of the airway smooth muscle
- Application of network pharmacology in the prevention and treatment of COVID-19 by traditional Chinese medicine
- Pharmacological efficacy of the traditional Chinese medicinal formula Kun-Tai-1A in the treatment of letrozole-induced polycystic ovary syndrome
- Recent advances in research on natural product inhibitors of SREBPs
- Integrated UHPLC-MS and network pharmacology to explore the active constituents and pharmacological mechanisms of Shenzao dripping pills against coronary heart disease
