Pharmacological efficacy of the traditional Chinese medicinal formula Kun-Tai-1A in the treatment of letrozole-induced polycystic ovary syndrome
Leanne Lee Leung,Jing Xie,Ya-Cun Chen,Kar-Ho Lam,Hei Wan,Su-Lan Yu,Tzi-Bun Ng,George Pak-Heng Leung,Jin Yu,Ren-Min Yao,Shu-Jia Sun,Sydney Chi-Wai Tang,Hai-Yong Chen,Jia Zhao,Zhang-Jin Zhang,Calvin Kai-Fai Lee,Kalin Yan-Bo Zhang,Li-Xing Lao,Yun Feng,Xiang Lin*,Wei Meng,,0*
1School of Chinese Medicine,Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine,The University of Hong Kong,Hong Kong 999077,China.2School of Biomedical Sciences,Faculty of Medicine,The Chinese University of Hong Kong,Hong Kong 999077,China.3Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacy,Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine,The University of Hong Kong,Hong Kong 999077,China.4Workstation for Training and Research(Hong Kong Branch),Distinguished Professor Yu Jin Gynaecology of Chinese Medicine&Integrative Medicine,Hong Kong 999077,China.5Shanghai Taikuntang Chinese Medicine Hospital,Shanghai 200023,China.6Department of Medicine,Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine,The University of Hong Kong,Hong Kong 999077,China.7Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology,Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine,The University of Hong Kong,Hong Kong 999077,China.8Virginia University of Integrative Medicine,Virginia 22031,USA.9Department of Ophthalmology,Peking University Third Hospital,Beijing 100191,China.10Workstation of Zhu Nansun,National Master of Chinese Medicine,Hong Kong Branch of Zhu’s School of Gynaecology of Chinese Medicine from Shanghai,Hong Kong 999077,China.
Abstract Background:Polycystic ovary syndrome(PCOS)is an endocrine disorder that occurs in women of child-bearing age.Moreover,PCOS patients have decreased pregnancy rates and clomiphene citrate resistance.The traditional Chinese medicine formula Kun-Tai-1S(KT1S),consisting of the seahorse species hippocampus,has been reported to elicit therapeutic effects in patients with PCOS.However,given the limited resources and global demand for wild hippocampus,whether KT1S with or without hippocampus can elicit similar therapeutic effects has not been confirmed.Methods:KT1S and Kun-Tai-1A(KT1A,KT1S without dry hippocampus)were used to treat a letrozole-induced rat model of PCOS with an established disease.The serum levels of testosterone,luteinizing hormone,anti-Müllerian hormone,and estradiol were determined,the luteinizing hormone/follicle-stimulating hormone ratio was determined,and the ovarian pathology was evaluated.Results:Similar to the therapeutic effects of cyproterone acetate,both the KT1S and KT1A treatments reduced the body weight and ovarian and uterine indices in the rats with PCOS.The serum levels of testosterone,anti-Müllerian hormone,and luteinizing hormone and the luteinizing hormone/follicle-stimulating hormone ratio were significantly lower in the KT1S and KT1A treatment groups compared to the model group(P <0.01 and P <0.05,respectively).Moreover,the histopathological assessment results suggested that both the KT1S and KT1A treatments significantly ameliorated the PCOS pathology in the rats with an established disease,with a reduced number of cystic and atretic follicles and an increased number of corpora lutea being observed in the ovaries.Notably,there was no obvious difference in the disease outcomes between the KT1S-and KT1A-treated groups.Network pharmacology analysisrevealedthat4’,7-dihydroxyflavanone,sinpemineA,quercetin,8-isopentenyl-kaempferol,and luteolin in KT1A may promote estrogen signaling;furthermore,the nitric oxide regulation pathway is also closely involved.Conclusion:KT1A and KT1S treatments both significantly ameliorated the PCOS-related pathology in rats,suggesting that the hippocampus component is dispensable for KT1S-mediated amelioration.Given the limited resources and global demand for wild hippocampus for use in complementary medicines,our findings may help conserve this species.Together,our results suggest that KT1A is a promising approach for treating PCOS.
Keywords:polycystic ovary syndrome;traditional Chinese medicine;ovulation;Kun-Tai-1A;seahorse;endocrine disease
Background
Polycystic ovarian syndrome(PCOS)is an endocrine disease that is common in women of reproductive age[1,2].The clinical features of PCOS include hormonal disturbances,irregular menstrual cycles,and cessation of ovarian follicle growth,which causes cysts or multiple atretic follicles in the ovaries,leading to infertility[3].The main risk factors for PCOS include dyslipidemia,gestational diabetes,insulin resistance,and hyperandrogenism[4,5].Although insulin resistance and hyperandrogenism are considered the hallmarks of PCOS,their etiologies remain largely unclear[6].Alternatively,endocrine,environmental,genetic,and metabolic dysfunctions are also hypothesized to contribute to PCOS[7].Currently,the therapeutic management of PCOS is mainly focused on metabolic interference,such as rectifying irregular menstruation,anovulatory infertility,and hirsutism[8],while insulin control,reproductive hormone therapy,dietary therapy,and lifestyle guidance may also be beneficial[9].
Given the heterogeneous manifestations and complicated pathogenesis,diagnostic and classification criteria have been proposed to improve investigations of pathogenesis and drug screening.Recently,a letrozole-induced rat model of PCOS showed decreased serum levels of estradiol(E2)and progesterone but elevated testosterone(T)levels,as well as PCOS-related pathological hallmarks,including perturbed estrogen production,hyperandrogenism,and excessiveintraovarianandrogenlevels[10].Thus,the letrozole-induced rat model of PCOS may serve as a drug screening tool for the development of novel therapeutic strategies for PCOS[11].
A Catalog of Tongrentang Pharmacy,the first Chinese medicine formula index,was written in 1706 by Feng-Ming Yue during the Qing Dynasty(1636 C.E.-1912 C.E.).the classic formula in traditional Chinese medicine Haima Bushen pills were first documented in this catalog and believed to benefit patients with reproductive system abnormalities.They are composed of Yinyanghuo(Epimedium Wushanense),Buguzhi(Fructus Psoraleae),Lujiaopian(Cornu Cervi Pantotrichum),Haima(dry hippocampus),Shanzhuyu(Cornus Officinalis),Niuxi(Radix Achyranthes Bidentatae),Gouqi(Fructus Lycii),etc.Yu et al.tried modifying this traditional Chinese medicine formula since the 1970s and finalized it in 1986,naming it Kun-Tai-1S(KT1S).The modified formula keeps the herbs ofEpimedium Wushanense,Fructus Psoraleae,Cornu Cervi,and dry hippocampus and adds the herbs of Beimu(Bulbus Fritillaria Cirrhosae),Guijia(Carapax et Plastrum Testudinis),Zaojiaoci(Spina Gleditsiae),and Shichangpu(Rhizoma Acori Tatarinowii)[12,13].Consistent with the previously defined differentiated clinical manifestations of PCOS[14],it was reported that KT1S could effectively ameliorate the PCOS pathology in patients with an improved level of hormone production[15].Further clinical studies have also reported the therapeutic effects of KT1S in restoring the ovulation rate and normalizing the hormone levels in patients with PCOS,particularly in those exhibiting clomiphene citrate resistance[16,17].
Cornu Cervi,Carapax et Plastrum Testudinis,and dry hippocampus are reported as being animal-derived medicines in theChinese Pharmacopoeia.Among them,Cornu CerviandCarapax et Plastrum Testudinisare being produced from industrial breeding methods,which support wild animal conservation efforts.Hippocampus is a bony fish that has been used in traditional Chinese medicine(TCM)for more than 600 years[18].Traditionally,dry hippocampus has been considered to nourish the kidney and liver,improving systemic circulation due to its “warm” characteristics.In addition,early studies reported that hippocampus is beneficial in male and female individuals with infertility[19,20].As a precious wild animal product,hippocampus is in high demand as a medical supplement in international trade.Theoretically,it may elicit synergistic effects on PCOS in combination with other components of KT1S,such asCarapax et Plastrum Testudinis[21].However,given the harsh conditions required for seahorse breeding,industrial cultivation usually requires high costs,and overfishing may occur.Thus,despite the increasing economic burden of PCOS,the sources of hippocampus are limited,and there is a lack of evidence on whether hippocampus is indispensable for treating PCOS[20,22].Therefore,we removed hippocampus from the KT1S to create the formulation Kun-Tai-1A(KT1A,KT1S without dry hippocampus)for comparing the treatments with and without hippocampus.This study aimed to identify the functional importance of hippocampus in KT1S as treatment for PCOS using a rat model.
Methods
Experimental materials
KT1A was composed of a 108 g TCM mixture consisting of 15 gEpimedium wushanense,12 gBulbus Fritillaria Cirrhosae,15 gFructus Psoraleae,15 gCarapax et Plastrum Testudinis,12 gCornu Cervi Pantotrichum,15 gSpina Gleditsiae,and 15 gRhizoma Acori Tatarinowii.The KT1S preparation was composed of 108 g KT1A plus 0.6 g dry hippocampus.All of the aforementioned Chinese medicines are listed in theChinese Pharmacopoeia.
Letrozole(50 mg/mL)was purchased from Intatrade Chemical GmbH(Muldestausee,Germany).Cyproterone acetate 35(CA35)/diane-35 was purchased from the National Prescribing Service(NPSMedicineWise,Melbourne,Australia).Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits for detecting the serum levels of T,luteinizing hormone(LH),follicle-stimulating hormone(FSH),E2,and anti-Müllerian hormone(AMH)were purchased from Biovision,Inc.(Milpitas,CA,USA).Hematoxylin and eosin(H&E)staining reagents included acidified ethanol(1 mL concentrated hydrochloric acid and 400 mL 70% ethanol),Harris hematoxylin with glacial acetic acid,and a working concentration of eosin phloxine stain(Poly Scientific R&D,Bayshore,New York,USA).A Varioskan Flash microplate reader(Thermo Fisher Scientific,Waltham,Massachusetts,USA)was used for the analysis.The centrifuge tubes were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich(St.Louis,Missouri,USA).The electronic analytical balance was obtained from Mettler Toledo(Columbus,Ohio,USA),and a Nikon microscope(E200;Tokyo,Japan)was used.For the animal experiments,56 female Sprague-Dawley rats(6 weeks old)were purchased from the Laboratory Animal Unit of the University of Hong Kong.All animal experiments were performed following an institutionally approved protocol and in accordance with the guidelines of the Committee on the Use of Live Animals in Teaching and Research of the University of Hong Kong(reference number:4716-18).
Extraction of KT1A and KT1S
All Chinese medicines of KT1A or KT1S were purchased from PuraPharm(batch No.KTI-A181024,Hong Kong,China),processed by Hong Kong Chinese Medicine Service Centre,Ltd.(Hong Kong,China),and identified by Chinese Manufacture’s Association testing and certification laboratories.A voucher specimen was stored at the Chinese Manufacture’s Association with the accession number AW0060195(0).
The mixtures were washed and soaked with 17 volumes(weight/volume)of water overnight.The mixtures were then decocted for 2 hours and filtered to remove the debris.The decoction process was repeated two more times before precipitation was performed.The mixture was then centrifuged at 2,000 g at room temperature for 15 min,and the supernatant was further concentrated to half of the sample volume and lyophilized for subsequent experiments.
Kun-Tai-1G(KT1G)
KT1G,the granular form of KT1A,was formulated by Chinese Medicine Pharmacy at the University of Hong Kong to mimic clinical practice.
Vaginal smears
The normal rat estrous cycle was defined as the occurrence of 1-2 days of estrus over a period of 4-5 consecutive days[23].While holding the rats,saline was introduced into the vagina using a syringe without a needle,and the vagina was rinsed 3-5 times.The rinsed saline containing the vaginal smear was spread on a glass slide and observed under a light microscope to examine the histopathological changes,such as the abundance of epithelial cells,cornified cells,and leukocytes[24].A prolonged estrus cycle can be reflected by changes in the vaginal cytology,which serves as a diagnostic indicator for identifying diseased rats[25].
PCOS establishment and animal randomization
Briefly,the rats were administered either 1 mg/kg vehicle or 1 mg/kg letrozole in the same volume of 1% aqueous solution of carboxymethylcellulosesodium,whichwasintragastrically administered at 2 mL/kg for 21 days.During this period,vaginal smears were collected daily and evaluated microscopically using Giemsa staining for estrus cycle determination,as previously described[10].The rats with letrozole-induced PCOS were selected based on the combined results of a continuous vaginal smear and high plasma T level.The rats without any of the pathological signs were excluded from the study.Forty-eight rats weighing(170 ± 10)g,including healthy and letrozole-induced PCOS rats,were included in this study and divided into eight groups.The healthy rats administered 2 mL/kg body weight of 1% aqueous solution of carboxymethylcellulose sodium were allocated to the normal group(i.e.,rats without any treatment).The PCOS rats were randomized into seven groups(n = 6 rats per group),including the PCOS model and treatment groups.Treatment with 2 mg/kg CA35 was used as a positive control.Given that the dosage prescribed for patients is 12 g per 60 kg/day,the equivalent dosages for the rats were 1.24 g/kg(12.00 g/60 kg × 6.2 = 1.24 g/kg).The doses were set as 0.75 g/kg KT1A(KT1A_L),1.5 g/kg KT1A(KT1A_M),3 g/kg KT1A in solution(KT1A_H)or in the granular form(KT1G),and 1.5 g/kg KT1S,in accordance with the translation algorithm[26].
Upon being administered an injection of 1 mg/kg letrozole,the rats became completely acyclic and exhibited cystic follicles in their ovaries that resembled the key features of human PCOS[27-29].The PCOS-model rats treated with KT1A preparations,KT1S,or CA35 received the respective drugs(10 mL/kg body weight)by intragastric administration for 10 days,while the rats in the normal and PCOS model groups received an intragastric administration of 0.2%carboxymethylcellulose sodium.
Measurement of serum hormone levels after treatment with KT1A,KT1G,KT1S,and CA35
Rats were fasted overnight after the administration of the last drug.On the 22ndday of the experiment,blood samples were collected from the orbital venous plexus of each rat,and these blood samples were centrifuged at 2,000 rpm for 15 min.The supernatants were collected and stored at-80 °C.Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits for the LH,FSH,E2,AMH,and T were purchased from Biovision,Inc.(San Jose,California,USA)and used to quantify the serum levels of these hormones in the PCOS rats,following the manufacturer’s protocols.Briefly,using these pre-coated plates,sera or standards were added for conjugation by horseradish peroxidase,followed by incubation with the detection antibody.Finally,the plates were developed using the indicated substrates before the analysis was performed.
Collection of ovaries and uteri
The ovaries and uteri were removed and weighed after sacrificing the rats with an overdose of anesthesia.Ovarian and uterine index values were calculated using equations(1)and(2):
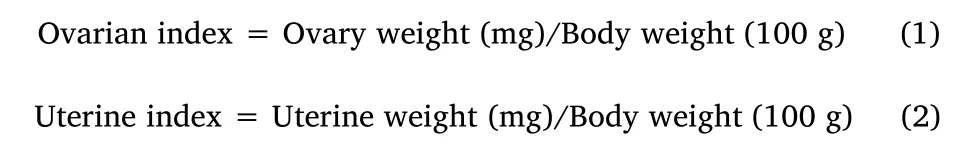
H&E staining of ovaries
Dissected rat ovaries were subjected to H&E staining to examine the histological changes.Briefly,after the ovaries were dissected,they were rinsed with phosphate-buffered saline and fixed in 10% formalin overnight.They were then dehydrated in a series of ethanol and xylene solutions(80% to 100%)and embedded in paraffin.The paraffin-embedded sections were stained with H&E,and the histopathological changes were evaluated using a Nikon E200 light microscope(Tokyo,Japan).The cystic and atretic follicles and corpora lutea of the ovarian tissue sections were enumerated in 10 sections for each ovary sample.
Network pharmacology analysis
The oral bioavailability and drug-like properties were considered criteria for screening the active ingredients ofEpimedium Wushanense,Bulbus Fritillaria Cirrhosae,Spina Gleditsiae,andRhizoma Acori Tatarinowiiin the Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology database(http://ibts.hkbu.edu.hk/LSP/tcmsp.php).Fructus psoraleae,Carapax et Plastrum Testudinis,andCornu Cervi Pantotrichumwere obtained from the Bioinformatics Analysis Tool for Molecular Mechanism of Traditional Chinese Medicine platform(http://bionet.ncpsb.org/batman-tcm).PCOS-related genes were searched using the GeneCards(https://www.genecards.org/),Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man platform(http://omim.org/),and PharmGKB databases(https://www.pharmgkb.org/).The intersection of the targets from KT1S and PCOS is indicated using the Venn diagram tool.Furthermore,the targets of KT1A in PCOS were imported into the STRING database(https://string-db.org/)to observe the relationship between the target genes,which was utilized to construct the protein-protein interaction network.The plugin CytoNCA(http://apps.cytoscape.org/apps/cytonca)in Cytoscape 3.7.0 was employed to screen the hub genes by calculating three typical centrality attributes:the degree centrality(DC),betweenness centrality(BC),and closeness centrality(CC).Functional annotation and enrichment analyses of hub genes were performed using DAVID(https://david.nicifcrf.gov/).The biological processes of target gene ontology(GO)enrichment and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes(KEGG)pathway analyses were performed.
Data analysis
All data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation.Student’st-test and one-way analysis of variance were performed to analyze the quantitative data.All statistical tests were performed two-sided,and statistical significance was set asP<0.05.
Results
KT1A treatment reduced body and ovary weights in PCOS rats
Body weight after treatment was determined in all rats(Figure 1A).Compared to the normal group,the PCOS rats showed a significant increase in body weight(1.13-fold,P<0.01).This was consistent with previous findings that patients with PCOS are usually obese[30].As expected,the rats treated with CA35,which was used as a positive control,exhibited a lower body weight than the untreated PCOS rats(P<0.01).Similarly,the rats in the KT1A_M,KT1G,and KT1S treatment groups also showed a lower body weight compared with the untreated PCOS rats(P<0.01).Notably,the effect of KT1A on body weight was dose-dependent(KT1A_H >KT1A_M >KT1A_L).The rats treated with KT1G had body weights similar to those of the rats treated with KT1A_M,whereas the rats treated with CA35 had body weights similar to those of the rats treated with KT1A_L(Figure 1A).
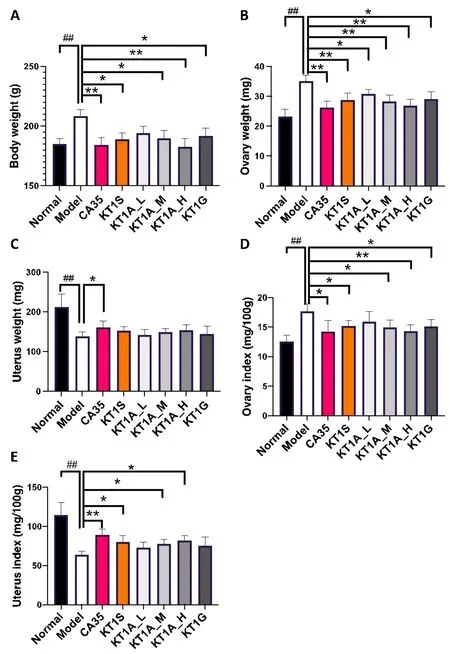
Figure 1 Effect of KT1A,KT1G,KT1S and CA35 on PCOS model rats.The(A)body weight,(B)ovarian weight and(C)uterine weight of the PCOS model rats were compared with those of normal rats and rats treated with KT1A,KT1G,KT1S and CA35.The measurement of ovarian(D)and uterine(E)indices in the normal group;the PCOS model group and the KT1A_L-,KT1A_M-,KTA1_H-,KT1G-,KT1S-and CA35-treated PCOS model groups.Data were analyzed by a one-way one-way analysis of variance and are presented as the mean ± standard deviation.*P <0.05,**P <0.01 vs.the model group and##P <0.01 vs.the normal group.KT1A,Kun-Tai-1A;KT1G,Kun-Tai-1G;KT1S,Kun-Tai-1S;CA35,cyproterone acetate 35;PCOS,polycystic ovarian syndrome;KT1A_L,0.75 g/kg KT1A in solution;KT1A_M,1.5 g/kg KT1A in solution;KT1A_H,3 g/kg KT1A in solution.
The ovarian weight was also measured for each rat(Figure 1B).The PCOS group rats showed a 1.5-fold increase in the ovarian weight compared with the rats in the normal group(P<0.01).However,this effect was abolished by KT1A,KT1G,KT1S,and CA35 treatments(P<0.05,P<0.05,P<0.01,andP<0.01,respectively).Consistently,KT1A also elicited a dose-dependent(KT1A_H >KT1A_M >KT1A_L)effect on ovarian weight.The rats treated with KT1S and those treated with KT1G had ovarian weights similar to those of the rats treated with KT1A_M,whereas the rats treated with CA35 had ovarian weights similar to those of the rats treated with KT1A_H(Figure 1B).
In contrast to the ovarian weight trends,the PCOS rats showed a significantly reduced uterine weight compared with the normal group(P<0.01,Figure 1C).Notably,the CA35 group had the largest uteri among all of the PCOS groups(P<0.05).Although KT1A did not significantly affect the uterine weight,we found slight differences between the various treatment groups,and the effect of KT1A treatment was dose-dependent(KT1A_H >KT1A_M >KT1A_L,Figure 1B).
KT1A treatment reduced ovarian and uterine index values in PCOS rats
The enlargement of the ovaries is a hallmark of PCOS,as this is observed in patients with PCOS[31].Consistently,the ovarian index values(mg/100.00 g)were 1.40-fold higher in the PCOS model group than in the control group(P< 0.01,Figure 1D).A statistically significant decrease in the ovarian index values was observed in groups treated with KT1A_M,KT1G,KT1S,and CA35 compared to the PCOS model group(P<0.05).The effect of KT1A on the ovarian index values was dose-dependent(KT1A_H >KT1A_M >KT1A_L).No significant differences in the ovarian index values were observed between the KT1A_M,KT1S,and KT1G groups(Figure 1D).
In contrast,a significant reduction in the uterine size was observed in the PCOS model rats(P<0.01 vs.the normal group,Figure 1E).This effect was partially rescued in animals treated with KT1A_M,KT1A_H,and KT1S(P<0.05)and CA35(P<0.01).The increase in uterine index values induced by KT1A was also dose-dependent(KT1A_H > KT1A_M > KT1A_L),but there was no significant difference in the uterine index values between the rats treated with KT1S and those treated with KT1A_M.
KT1A treatment modulated serum hormone levels in PCOS model rats
Clinical findings suggest that the levels of serum hormones,such as T,LH,FSH,E2,and AMH,are biomarkers for the pathogenesis of PCOS[32].The LH/FSH ratio has also been used as an important parameter[33],although recent evidence indicates that this ratio has a low sensitivity for predicting PCOS[34].Consistent with the findings observed in clinical practice,the serum levels of T and LH and the LH/FSH ratio were significantly elevated in PCOS-model rats but were reduced by CA35 treatment(P<0.01 orP<0.05,Figure 2A-C).KT1A,KT1G,and KT1S elicited therapeutic effects in PCOS,with suppressed serum levels of T and LH and a decreased LH/FSH ratio being observed(P<0.01 andP<0.05);the KT1A treatment had a dose-dependent effect.Notably,there were no significant differences in these parameters between the KT1A_M and KT1S treatment groups.
E2is an ovarian steroid hormone that controls oocyte development during the reproductive cycle and the development and maintenance of female sex characteristics[35].A pilot study reported low serum levels of E2in letrozole-treated patients with PCOS,which was associated with an increased number of ovarian follicles[36].Indeed,compared with the normal group,we also observed a 1.30-fold decrease in the serum E2level in the PCOS model group(P<0.01),whereas CA35 treatment partially increased the E2level(P<0.05,Figure 2D).Notably,the KT1A,KT1S,and KT1G treatments only slightly,not significantly,affected the serum E2level.
PCOS is also associated with an elevated serum AMH level,particularly in pregnant patients;furthermore,neuroendocrine disturbances within the fetus may facilitate PCOS development in offspring when they reach adulthood[37].Likewise,the PCOS model group exhibited 1.38-fold higher serum AMH level than the normal group(P<0.01),but the AMH level decreased upon CA35 treatment(P<0.01,Figure 2E).As expected,the serum AMH levels in the KT1A,KT1S,KT1G,and CA35 treatment groups were lower than the serum AMH level in the normal group(P<0.05 andP<0.01).
KT1A treatment ameliorated ovarian pathology in PCOS rats
To investigate the histopathological changes in the target organs,the ovaries from all rats were dissected and compared.The PCOS rats had larger ovaries with more cystic follicles than the normal control rats(Figure 3A-B).These effects were significantly improved by KT1A treatment,which resulted in a decrease in the ovarian size and decrease in the number of cystic follicles(Figure 3C-H).H&E staining was performed to assess tissue damage in the rat ovaries.The number of cystic and atretic follicles and corpora lutea were determined in the PCOS rats(Figure 3I-P).The results suggest that the ovarian cortex in the normal group contained fewer and a smaller distribution of ovarian follicles at different developmental stages.Large corpora lutea were observed,and the luteal cells were well-developed(Figure 3I).In contrast,a dense distribution of ovarian tissues was observed in the PCOS model group(Figure 3J),and the number of cystic and atretic follicles was significantly higher(3.90-fold)compared with the number in the normal group(P<0.01,Table 1).In addition,the numbers of corpora lutea and granulosa cells were lower in the PCOS model group compared with the normal group,with a loose structure observed between the granulosa cells in the PCOS group(P<0.01,Table 1).
The PCOS-related pathology was significantly ameliorated in the rats treated with KT1A_L,KT1A_M,KT1A_H,KT1G,KT1S(P<0.01),and CA35(P<0.05),with a 1.6-fold to 2.5-fold decrease in the number of cystic and atretic follicles in the ovarian tissues compared with the normal group(Table 1).Moreover,the number of corpora lutea was increased in the KT1A_MKT1S(P<0.05)and KT1A_L(P<0.01)groups than in the normal group.
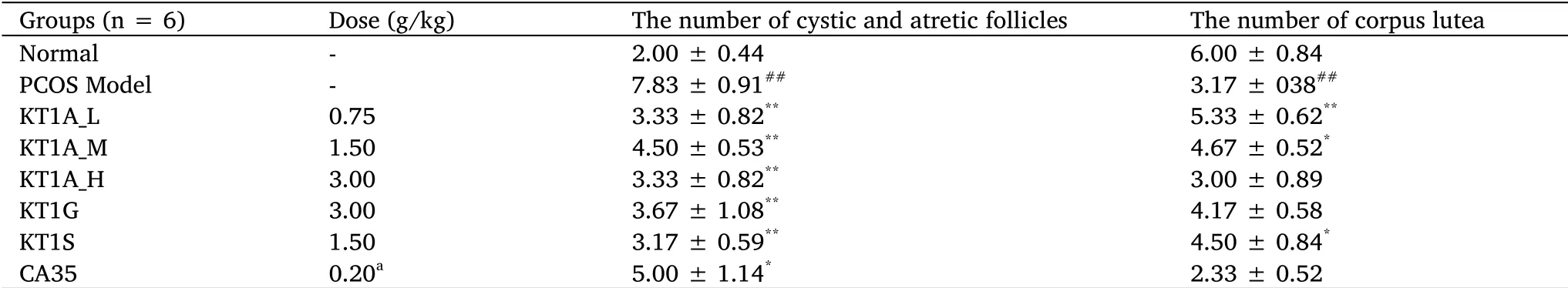
Table 1 Effects of KT1A on ovarian tissues from normal rats,PCOS model rats,PCOS model rats treated with KT1A,KT1G,KT1S and CA35
Network pharmacology research
To understand the possible mechanis ms underlying the above mentioned effects on the PCOS pathogenesis,network pharmacology was designed and implemented to identify the active compounds of KT1A and to predict the potential therapeutic mechanism of KT1A against PCOS.A total of 1,381 target genes of the identified compounds were collected from the Bioinformatics Analysis Tool for Molecular Mechanism of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology databases,whereas 1,102 PCOS-related genes were found in the GeneCards,Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man,and PharmGKB databases.About 169 common targets were shared with PCOS after removing duplicate common targets(Figure 4A),among which 14 hub genes were determined according to their rank by degree(Figure 4B).GO enrichment and KEGG pathway analyses suggested that 4’,7-dihydroxyflavanone,sinpemineA,quercetin,8-isopentenyl-kaempferol,and luteolin in KT1A may enhance estrogen signaling,while nitric oxide signaling pathways are also closely involved(Figure 4C-D).
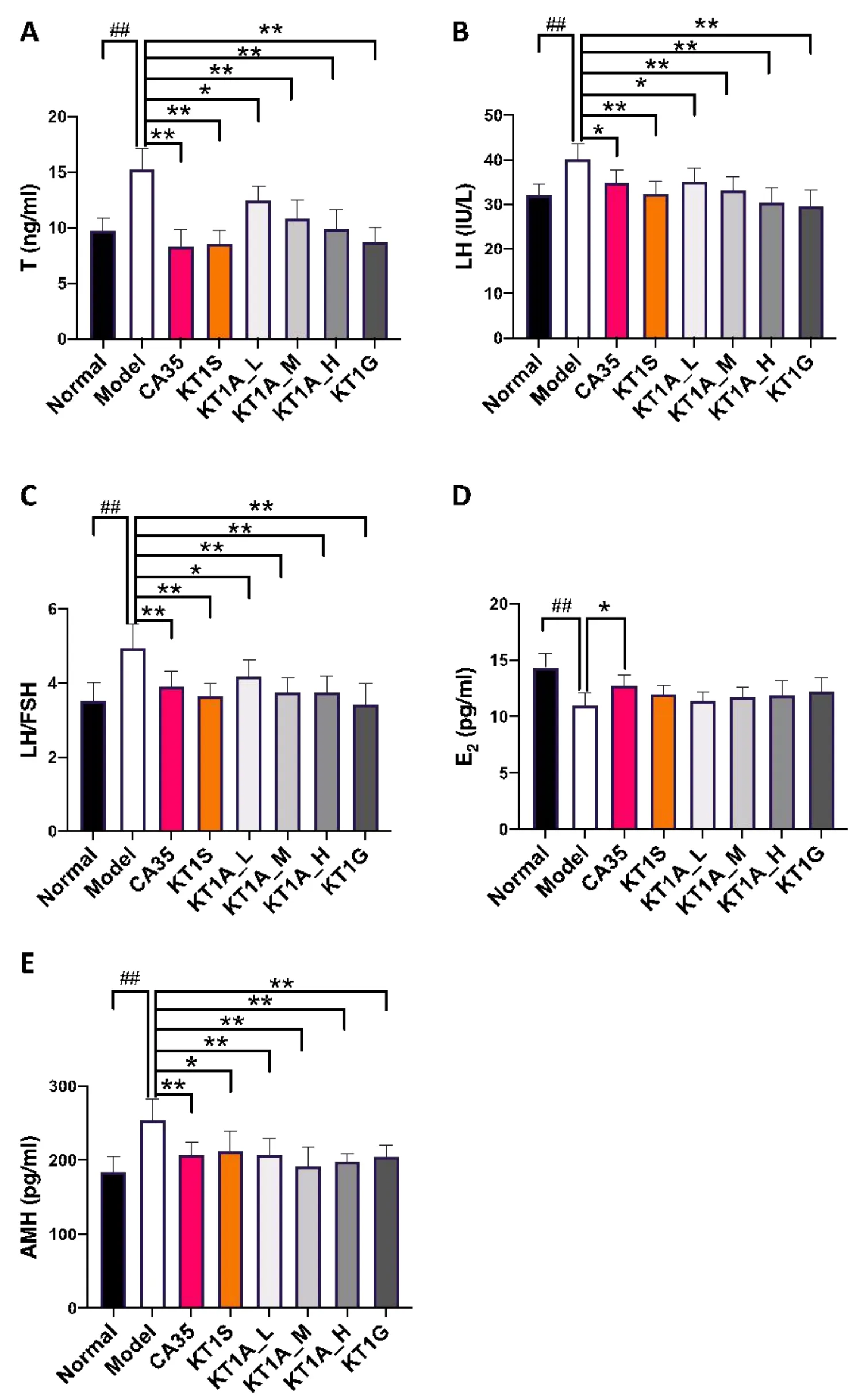
Figure 2 Effects of KT1A,KT1G,KT1S and CA35 on serum hormone levels.Serum(A)T,(B)LH,(C)LH/FSH,(D)E2 and(E)AMH levels were determined after treatment with KT1A_L,KT1A_M,KTA1_H,KT1G,KT1S and CA35.Data were analyzed by a one-way ANOVA and are presented as the mean ± standard deviation.*P <0.05,**P <0.01 vs.the model group and##P <0.01 vs.the normal group.KT1A,Kun-Tai-1A;KT1G,Kun-Tai-1G;KT1S,Kun-Tai-1S;KT1A_L,0.75 g/kg KT1A in solution;KT1A_M,1.50 g/kg KT1A in solution;KT1A_H,3.00 g/kg KT1A in solution;CA35,cyproterone acetate 35;T,testosterone;LH,luteinizing hormone;FSH,follicle-stimulating hormone;E2,estradiol;AMH,anti-Müllerian hormone.
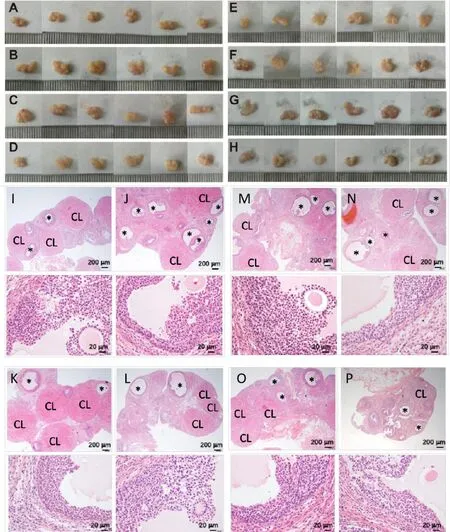
Figure 3 Effects of KT1A,KT1G,KT1S and CA35 on ovarian tissues in rats with PCOS.Ovaries of rats from the(A)normal group;(B)PCOS model group;KT1A-treated groups,including rats treated with(C)KT1A_L,(D)KT1A_M and(E)KTA1_H;and(F)KT1G-treated group.Positive control groups included rats treated with(G)KT1S and(H)CA35.The H&E staining of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections of ovarian tissues were performed.Microscopic examination of tissue sections from the(I)normal group;(J)PCOS model group;KT1A-treated groups,including rats treated with(K)KT1A_L,(L)KT1A_M and(M)KTA1_H;and(N)KT1G-and(O)KT1S-and(P)CA35-treated groups.The upper panels from I-P show magnified histology and the bottom panels present an overview.KT1A,Kun-Tai-1A;KT1G,Kun-Tai-1G;KT1S,Kun-Tai-1S;CA35,cyproterone acetate 35;PCOS,polycystic ovarian syndrome;KT1A_L,0.75 g/kg KT1A in solution;KT1A_M,1.5 g/kg KT1A in solution;KT1A_H,3 g/kg KT1A in solution;H&E,hematoxylin and eosin;CL,corpus lumen;*cystic and atretic follicles.
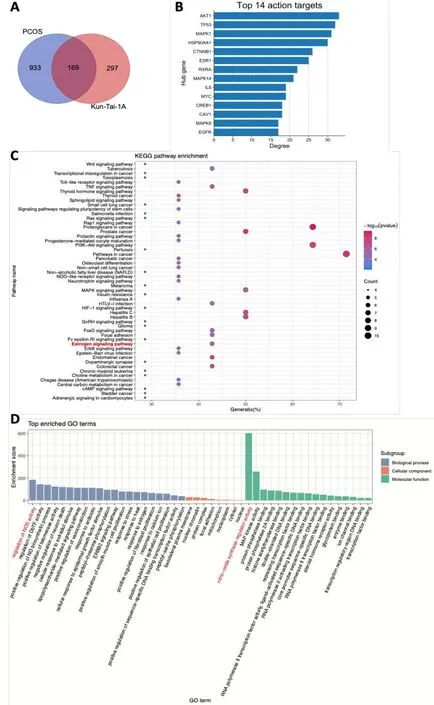
Figure 4 Network pharmacology analysis of KT1A against PCOS.Venn diagram of common targets in KT1A and PCOS.Left circles represent disease targets that are obtained from PCOS,and right ones are drug targets for KT1A.The middle part represents the intersection of disease and drug targets.(B)The top-ranking hub genes by degree.The hub genes of KT1S against PCOS were selected by CytoNCA.The more forward the ranking,the more significant the hub gene.(C)Scatter plot of KEGG pathway analysis.It was considered significant statistically when the P-value was less than 0.05.Seventy dots in the plot show seventy KEGG pathway terms enriched.The color of each does expresses its P-value.The size of the bubble represents the count of each pathway.(D)Histogram of GO enrichment analysis.Significance level: P-value was less than 0.05.8 cell components(orange bars),31 molecular functions(green bars),and 30 biological processes(blue bars)were enriched in the functional analysis.The P-value was indicated by the Enrichment Score(vertical axis).The larger the Enrichment Score,the smaller the P-value.KT1A,Kun-Tai-1A;KT1S,Kun-Tai-1S;PCOS,polycystic ovarian syndrome;KEGG,Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes;GO,gene ontology.
Discussion
In Western medicine,the clinical management of PCOS varies,but it mainly involves a combined oral administration of contraceptive and/or metabolic drugs supplemented with psychological support and lifestyle modifications[32].However,there is a paucity of clinical evidence-based guidelines for medical practitioners to follow[30,38].
Excess androgen production and elevated LH levels are considered the most indicative biochemical features in PCOS[39].As aromatase catalyzes the rate-limiting step in the biosynthesis of estrogen from androgen,it has been speculated that aromatase inhibition through a reduction in estrogen production in the hypothalamus and pituitary may increase LH secretion via the negative feedback of estrogen[10].Thus,a deficiency in aromatase activity may contribute to
intraovarian dysregulation of steroidogenesis and PCOS development.Rat models,particularly the letrozole-induced rat model of PCOS,are considered suitable models for screening potential therapeutic drugs for treatment in human patients with PCOS.The pathology of the PCOS rat model includes ovulatory dysfunction,polycystic ovaries,and high plasma levels of T and LH[10,29].Therefore,in this study,this model was used to determine the therapeutic effect of KT1A on PCOS.
Consistent with the TCM principle,Yu et al.suggested that KT1S may be beneficial for patients[40-42].Indeed,KT1S treatment elicited beneficial effects in patients with PCOS,improving their ovulation and pregnancy rates[43].In addition,recent studies on chemical profile analyses in clinical trials and animal studies have also implicated the therapeutic potential of the herbal components in KT1S,such asCarapax et Plastrum Testudinis[44],in postmenopausal management[45].Thus,given the different mechanisms of contraceptive drugs,unlike the common side effects of current treatments[46],there were no obvious adverse effects reported from KT1S treatment in clinical practice.
KT1S is the first Chinese medicinal complex demonstrating a therapeutic effect on PCOS in vivo.KT1S treatment decreased the body weight and ovarian weight in a rat model of PCOS,and these effects may help lower the risk of diabetes and improve the menstrual cycle[47].Based on the observed decrease in the ovarian and uterine index values,our study suggests that both KT1S and KT1A may be beneficial in lowering the risk of follicular excretion disorder and maintaining homeostasis of the reproductive system for patients with PCOS.Indeed,network pharmacology analysis revealed that KT1A may enhance estrogen signaling.Furthermore,anti-inflammatory therapy is also considered a beneficial strategy for patients with PCOS.Notably,the KEGG pathway enrichment analysis indicated that regulation of nitric oxide,an effector molecule in inflammation,is strongly involved in the KT1A-mediated therapeutic effects.Although networkpharmacologyanalysissuggestedthat 4’,7-dihydroxyflavanone,sinpemineA,quercetin,8-isopentenyl-kaempferol,and luteolin may contribute to the captioned pathways,there is currently no direct evidence showing whether and how these compounds modulate aromatase activity;thus,for elucidating this,further mechanistic studies need to be performed in the future.Moreover,KT1A may also contribute to lowering the risk of hyperandrogenemia in patients with PCOS[48],suggesting the potential application of KT1A in combination therapies with androgen receptor blockers[49].
In the rat model of PCOS used in the current study,CA35 was used as a positive control because it is known to have a progestogenic effect by blocking peripheral androgen receptors and has been widely used as first-line treatment for patients with PCOS[50].However,increasing evidence suggests that CA35 treatment has adverse side effects,including possible fetal malformations,an elevated risk of endometrial cancer,and a low pregnancy rate[51,52].Moreover,CA35-resistance has been observed in patients with PCOS,particularly during pregnancy[48].This study provides an alternative therapeutic approach for the treatment of patients with PCOS,especially non-responders to CA35 or those with resistance to this compound.Here,KT1A was shown to be efficacious in restoring the serum hormonal homeostasis,decreasing the number of cystic and atretic follicles,and improving the corpora lutea,which helped the PCOS rats recover their ovarian function.Given that commercialized KT1S is encapsulated in a granule form,in this study,the granular form of KT1A,termed KT1G,also elicited comparable effects.Future clinical trials with standardized KT1A products may help determine the effectiveness of KT1A in patients with PCOS.
Dry hippocampus,especially the large,pale,and smooth species,is considered to be rich in medicinally effective components,and thus it has a high medicinal value in TCM.Currently,the cultivation of seahorses usually requires strict control of water temperature,water quality,and cultivation density.The industrial breeding of seahorses is usually of a high cost and is associated with an unsatisfactory yield.Thus,fishing of seahorses in the wild remains common.Given the limited resources for cultivating seahorses,the price of dry hippocampus is increasing[18].Dry hippocampus is internationally traded as a TCM,at a rate of approximately 20 million per annum,and it would be catastrophic to continue harvesting wild hippocampus to meet the high demand of its use in supplement formulations[53].Moreover,the efficacy of hippocampus in PCOS treatment in clinical practice remains unclear.This study demonstrated that hippocampus was dispensable in the KT1A formulation for treating rats with PCOS.Therefore,TCM formulations containing hippocampus may not be essential for the treatment of PCOS in clinical practice.This would help to reduce the demand for using hippocampus in TCM and,more importantly,support the conservation of the wild hippocampus species.
Conclusion
Our study is the first to demonstrate the therapeutic effects of KT1S and KT1A,particularly attenuation of serum hormone production and improvement of ovarian pathology,in a rat model of PCOS.Network pharmacology suggests that estrogen signaling and nitric oxide regulation may be closely involved in these therapeutic effects.Importantly,the lack of hippocampus did not compromise the therapeutic effects of KT1S.Thus,our findings may also help conserve this precious species.
 Traditional Medicine Research2022年3期
Traditional Medicine Research2022年3期
- Traditional Medicine Research的其它文章
- Traditional Chinese medicine:an important broad-spectrum anti-coronavirus treatment strategy on COVID-19 background?
- Anti-asthmatic mechanism of the Huashanshen dripping pill via suppressing contraction of the airway smooth muscle
- Application of network pharmacology in the prevention and treatment of COVID-19 by traditional Chinese medicine
- Recent advances in research on natural product inhibitors of SREBPs
- Integrated UHPLC-MS and network pharmacology to explore the active constituents and pharmacological mechanisms of Shenzao dripping pills against coronary heart disease
- Effects of Qingwen Baidu decoction on coagulation and multiple organ injury in rat models of sepsis
