Effects of Qingwen Baidu decoction on coagulation and multiple organ injury in rat models of sepsis
Bei-Tian Jia,Yu-Lin Wu,Jia-Bao Liao,Wen-Ju He,Dong-Qiang Wang,Feng Chen,Qing-Yun Zhao,Cui-Han Wang,Jun-Li Guo,Yu-Hong Bian,Huan-Tian Cui
1Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Tianjin 301617,China.2Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital,Tianjin 300060,China.3Jiaxing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Zhejiang 314033,China.4Tianjin First Central Hospital,Tianjin 300190,China.5Taian Municipal Hospital,Shandong 271099,China.6Tianjin Hospital of Integration of Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine/Nankai Hospital,Tianjin 300102,China.7Hebei Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Hebei 050013,China.8Shandong University,Shandong 301600,China.
Abstract Background:Sepsis-induced coagulopathy and multiple organ dysfunction syndromes are the leading causes of death in patients with sepsis.Qingwen Baidu decoction(QWBD)can effectively improve the clinical manifestations of sepsis and ease inflammation,but its effects on coagulation functions and multiple organ injuries remain unclear.Methods:100 healthy,male Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into the sham group,the cecal ligation and puncture(CLP)group,the low-dose QWBD group,and the high-dose QWBD group,with 25 rats in each group.The sepsis model was established using CLP.Blood was collected to measure platelet count,serum creatinine(Cr),blood urea nitrogen(BUN),alanine aminotransferase(ALT),and aspartate aminotransferase(AST)levels,as well as coagulation function.The total protein in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid(BALF)was determined in each group of rats.The lung,liver,and kidney tissues were harvested,and statistics were calculated on the wet-to-dry(W/D)weight ratio.Changes in histopathology and thrombin level were evaluated in each group.The remaining ten rats in each group were observed daily to record the number of surviving rats.Such observation was made consecutively for 7 days to calculate survival rates.Results:After model establishment,ALT,AST,Cr,and BUN levels were significantly elevated(P <0.01)).The BALF protein content and lung W/D weight ratio were significantly increased(P <0.01).Furthermore,the survival rate of rats was significantly reduced in the CLP group compared with the sham group.After the treatment,rats in the high-dose QWBD group had lower ALT(P <0.05),AST(P <0.01),Cr(P <0.05),BUN(P <0.01)levels,lower BALF protein content(P <0.05)and lower lung W/D weight ratio(P <0.01)than the CLP group.However,rats in the high-dose QWBD group had significantly better pathological changes in the lung,liver,and kidney compared to the sham group.After the treatment,the platelet level in the peripheral blood was elevated(P <0.05)and both activated partial thromboplastin time and prothrombin time were significantly shortened(P <0.01).The fibrinogen level was significantly increased(P<0.01).Finally,thrombin positive expression areas in the lung,liver,and kidney were significantly decreased in the high-dose QWBD group.Conclusion:QWBD can improve coagulation disorders caused by sepsis and has a protective effect on multiple organ injuries in rats.
Keywords:sepsis;Qingwen Baidu decoction;coagulation function;multiple organ injury
Background
Sepsis is a major medical issue globally and is commonly cited as the leading cause of death in critically ill patients.Its incidence is increasing around the world each year[1-3].Sepsis is defined as life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection.It is a common complication in severe trauma,burn injury,war injury,as well as shock,infection,and major surgical operations.It is a systemic inflammatory response caused by various infections[4].Sepsis is often complicated by coagulation disorders or disseminated intravascular coagulation(DIC)in severe cases[5,6].The incidence of DIC is as high as 25% to 50% in patients with sepsis[7].DIC is characterized by endothelial dysfunction and causes failure of other organs.Excessive thrombin generation and subsequent fibrin deposition exacerbate inflammation and ischemia,leading to organ injury[8].Numerous studies have reported that DIC is an independent risk factor for organ dysfunction and death in patients with sepsis[6,7].Therefore,DIC may be an important therapeutic target for sepsis.A top priority is the development of a reliable method for the prompt treatment of DIC.
Fluid resuscitation,antibiotic therapy,vasoactive drug therapy,symptomatic treatment or supportive therapy are common in the treatment of sepsis by western medicine.Among these,the use of anti-infective therapy or antibiotics is a particularly important approach[9].The early and appropriate use of antibiotics is closely related to the improvement of the survival rate[10].However,the heavy use of antibiotics in clinics promotes the pathogenic bacteria in patients to have high resistance to commonly used clinical antibiotics and enhance multidrug resistance[11].The mortality rate of patients with severe sepsis has been reported up to 40%[12].Studies of new therapies targeting immune cells,inflammatory mediators,and the coagulation system have all failed to reduce the mortality rate of sepsis[13].Other studies have suggested that traditional Chinese medicine can improve the clinical symptoms of sepsis and effectively reduce the mortality rate based on syndrome differentiation.For instance,the empirical formula Chinese medicine Qiangxin 1 formula(created by Professor Li-Juan Huang based on her clinical experience,mainly composed of Shuihonghuazi(Fructus Polygoni Orientalis),Huangqi(Astragali Radix),Fuling(Poria Cocos),Danshen(Salvia Miltiorrhiza),and Wuweizi(Schisandra Chinensis)can lower the mortality rate of mice with sepsis through the endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria pathways[14].Astragalus polysaccharide combined with ibuprofen can effectively decrease the generation of inflammatory mediators in the serum of septic rats by regulating the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway[15].Originating from theArcane Essentials from the Imperial Library,Xijiao Dihuang decoction mainly consists of Xiniujiao(Rhinoceros Horn),Shengdi(Radix Rehmanniae),Shaoyao(Paeonia Lactiflora),and Mudanpi(Cortex Moutan Radicis).It has been shown to increase the survival rate of septic rats and simultaneously inhibit the expression of nuclear factor-k-gene binding p65 and hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha[16].
Qingwen Baidu decoction(QWBD)was recorded inA View of Epidemic Febrile Diseases with Rasheswritten by Shi-Yu Yu,a famous febrile disease expert in the Qing Dynasty,in 1794.QWBD is a major prescription medicine used to treat febrile diseases.Febrile disease is a general term describing diseases that have a fever as the main symptom.Based on disease classification in modern medicine,febrile diseases can be roughly divided into two categories.These include acute infectious diseases and non-infectious diseases.Japanese encephalitis,epidemic hemorrhagic fever,lobar pneumonia,and sepsis are classified as acute infectious diseases.Heatstroke,summer fever in children,and acute leukemia are considered non-infectious diseases.QWBD consists of Shengshigao(Gypsum Fibrosum),Radix Rehmanniae,Shuiniujiao(Cornu Bubali),Huanglian(Rhizoma Coptidis),Zhimu(Rhizoma Anemarrhenae),Xuanshen(Radix Scrophulariae),Zhizi(Fructus Gardeniae),Jiegeng(Radix Platycodonis),Huangqin(Radix Scutellariae),Paeonia Lactiflora,Lianqiao(Fructus Forsythia),Cortex Moutan Radicis,Xianzhuye(Herba Lophatheri),and Gancao(Radix Glycyrrhizae).In China,several clinical studies have shown that QWBD has had curative effects in the clinical treatment of sepsis[17-19].Modern pharmacological studies have confirmed that QWBD exerts its medicinal effects by reducing endotoxin levels,regulating immune and inflammatory mediators,resisting platelet aggregation,lowering blood viscosity,improving microcirculation,analgesia,and sedation,strengthening the heart,and causing diuresis[19,20].Its composition ofGypsum Fibrosum,Radix Scutellariae,andFructus Forsythiahave neutralizing effects on endotoxin in experimental animals.Additionally,Rhizoma Coptidis,Radix Scutellariae,Fructus Gardeniae,andCortex Moutan Radiciscan inhibitEscherichia coli,Klebsiella pneumoniae,influenza virus,and herpes simplex virus with their antibacterial and antiviral effects[21].The paeonol inCortex Moutan Radiciscan scavenge free radicals,mitigate lipid peroxidation damage,and inhibit the synthesis and release of inflammatory factors in local inflammation[22].Moreover,QWBD can also exert a protective effect on sepsis-induced acute lung injury in rats through the JAK2/STAT3 and IKKα/NF-κB signaling pathways.However,its effect on coagulation function in sepsis has not been studied[23].In this study,a rat model of sepsis was established using cecal ligation and puncture(CLP)to investigate the effects of QWBD on survival rate,coagulation function,and related organ functions of septic rats.We aim to lay a foundation for further studies that focus on the mechanisms of QWBD in the treatment of sepsis.
Methods
Laboratory animals
A total of 100 male Sprague-Dawley rats weighing 200 ± 20 g were purchased from Beijing Huafukang Bioscience Co.,Ltd.(Beijing,China).All rats were given one week of adaptive feeding and ad libitum access to food and sufficient clean water in a quiet environment with a relative humidity of 55%-60%.This experiment was approved by the Laboratory Animal Welfare &Ethics Committee of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine(approval No.TCM-LAEC2020046).
Establishment of rat sepsis model
An animal model of sepsis was established by CLP in rats[24].Rats were starved but given access to water for 12 hours prior to surgery.Skin in the center of the anterior abdomen was disinfected after rats were anesthetized with isoflurane.A 2.0-cm incision was made in the center of the abdomen.After the cecum was removed,the mesentery and cecum were dissociated.The end of the cecum was ligated at 5 mm from the ileocecal region,using a 3-0 surgical suture.The through-holes were punctured twice at about 0.8-1.0 cm from the intestinal wall on both sides of the distal appendix root using a syringe needle(20G,inner 0.58 mm).Then,a small amount of intestinal content was squeezed out.Next,a 3.0 × 0.5 × 30.0 mm drainage strip was placed in the through-hole of the cecum,and the cecum was put back into the abdominal cavity.Finally,the incision was sutured.In accordance with the criteria for an animal model of sepsis-induced acute lung injury,we found that the lung tissue was pathologically damaged,the permeability of the alveolar-capillary barrier was increased,and the alanine aminotransferase(ALT),aspartate aminotransferase(AST),and blood urea nitrogen(BUN)levels were elevated in this CLP group.
Preparation of QWBD
QWBD was prepared with the following:50 g ofGypsum Fibrosum(voucher specimen number(VSN):2021120501),20 g ofRadix Rehmanniae(VSN:2021120502),9 g ofCornu Bubali(VSN:2021120503),10 g ofRhizoma Coptidis(VSN:2021120504),12 g ofRhizoma Anemarrhenae(VSN:2021120505),12 g ofRadix Scrophulariae(VSN:2021120506),9 g ofFructus Gardeniae(VSN:2021120507),9 g ofRadix Platycodonis(VSN:2021120508),9 g ofRadix Scutellariae(VSN:2021120509),9 g ofPaeonia Lactiflora(VSN:2021120510),9 g ofFructus Forsythia(VSN:2021120511),9 g ofCortex Moutan Radicis(VSN:2021120512),6 g ofHerba Lophatheri(VSN:2021120513),and 6 g ofRadix Glycyrrhizae(VSN:2021120514).The above herbs were accurately weighed,and eight times the volume of water was added to decoct for 30 minutes to a concentration of 2 g/mL of raw drug for future use.This product was provided by the Pharmacy of the First Teaching Hospital of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine.It was identified as genuine by the raw drug teaching and research section of the College of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine.It was stored in the College of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine,Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine.
Grouping and dosage regimen
A total of 100 rats were equally divided into the sham group,the CLP group,the low-dose QWBD group,and the high-dose QWBD group using the random number table method.The septic model was established with CLP in rats of the CLP group,the low-dose QWBD group,and the high-dose QWBD group.Meanwhile,rats in the sham group only had the abdominal wall incised and sutured without undergoing CLP[25,26].After model establishment,rats in the sham group and the CLP group were given 2 mL of normal saline by intragastric administration.Rats in the low-dose QWBD group and high-dose QWBD group were given QWBD raw drugs at 7.5 g/kg and 15 g/kg,respectively,by intragastric administration once every 12 hours.The high dose was the human equivalent dose.The animal dose and the human equivalent dose were calculated based on the body surface area[27].
Ten rats were selected from each group to calculate the survival rate.After CLP was performed,the number of surviving rats in each group was counted daily for seven consecutive days:
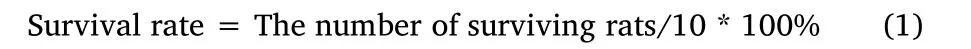
The survival curve was drawn according to the survival rate calculated each day.The remaining 15 rats in each group were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of pentobarbital sodium(50 mg/kg)at 24 hours after model establishment and administration.Blood,lung,liver,and kidney tissues were harvested for subsequent testing.
Platelet and coagulation tests
Rats were anesthetized 24 hours after model establishment and administration.The abdominal cavity was opened and the blood was drawn from the abdominal aorta.200 μL of blood was collected into EDTA-K2 anticoagulant vacuum blood collection tubes,followed by gentle mixing and settlement at room temperature 25 °C for 15 minutes.Blood samples were then analyzed for platelet count by an automatic hematology analyzer(Sysmex XT-2000iv,Kobe,Japan).Another 200 μL of blood was drawn and placed in a sodium citrate anticoagulant vacuum blood collection tube.After gently mixing,these samples were used for analysis of prothrombin time(PT),activated partial thromboplastin time(APTT),thrombin time,and fibrinogen(FIB)levels by an automatic coagulation analyzer(Sysmx CA-510,Kobe,Japan).Platelet count and coagulation tests were completed within 2 hours of blood collection.
Determination of total protein in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid(BALF)in rats of each group
Rats were anesthetized 24 hours after model establishment and administration.The skin of the throat was cut and the surrounding tissues were dissociated using forceps,to expose the rat trachea.The needle tip of a 1-mL syringe needle was cut off and ground smooth.Next,the needle tip was inserted from the thyroid cartilage of the rat to ligate and fix the cecum using a silk thread.Then,1 mL of 1×phosphate-buffered saline was injected into the lungs twice,and aspiration of BALF was performed at 1 minute after each injection.The collected BALF was centrifuged at 4 °C 2,500 r/min for 10 minutes.The supernatant was cryopreserved at-80 °C.The protein content was detected with a BCA Protein Assay Kit(PC0020,Solarbio,Beijing,China).
Lung wet-to-dry(W/D)weight ratio
Upon sacrifice,the right lung tissue was taken,weighed,and placed in a 60 °C oven for 48 hours to achieve a constant weight.Then the lung W/D weight ratio was calculated:
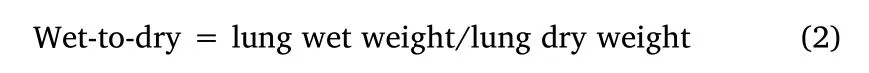
Hematoxylin and eosin(H&E)staining
After sacrifice,the lung,liver,and kidney tissues of rats in each group were collected,fixed with formalin solution,embedded in paraffin,and cut into 3 μm thick slices.The slices received the conventional H&E staining and were sealed with neutral balsam.Histopathological changes of the rats in each group were observed under an optical microscope(ELWD 0.3T1-SNCP,Nikon,Beijing PDV Instrument Co.,Ltd.,Beijing,China).
Immunohistochemical
Antigen retrieval was performed after the slices were deparaffinized and hydrated.The slices were permeabilized with 0.5% Triton X-100(T8200,Solarbio,Beijing,China)for 5 minutes,blocked with 5%Bovine Serum Albumin(SW3015,Solarbio,Beijing,China),and incubated at 37 °C for 1 hour.The slices were incubated overnight at 4 °C using the primary thrombin antibody(D61D5,CST,Danvers,Massachusetts,USA,source:rabbit)(1:500),washed with phosphate-buffered saline three times,and then incubated for 1 hour at room temperature using the secondary antibody(ab205718,Abcom,Cambridge,UK,source:goat).Slices were then washed with phosphate-buffered saline three times.Later,the slices were stained with the conventional 3,3’-diaminobenzidine staining,counterstaining,dehydration,and transparency.Finally,tissues were sealed with neutral balsam.Histopathological changes of the rats in each group were observed under an optical microscope.The positive expression area was quantified using Image Pro Plus(version 6.0).The average optical density was calculated with the following formula:
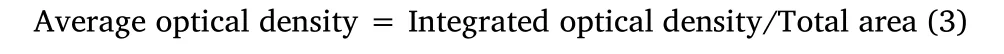
Statistical processing
The experimental results were analyzed using the statistical software SPSS Statistics(version 20.0).Measurement data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation.One-way analysis of variance was used for comparison of mean values among multiple groups.P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Effect of QWBD on the survival rate of septic rats
At 7 days after model establishment and administration,the survival rates of rats were 100% in the sham group,33.3% in the CLP group,46.67% in the low-dose QWBD group,and 60% in the high-dose QWBD group(Figure 1).This indicated that QWBD intervention could significantly increase the survival rate of septic rats.After CLP was performed,the number of surviving rats in each group was counted daily for seven consecutive days:
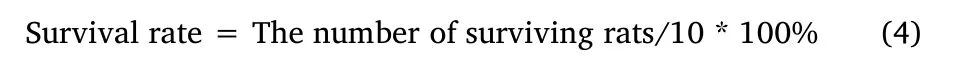
Effect of QWBD on lung,liver,and kidney functions and histopathological changes in septic rats
According to the results at 24 hours after model establishment and administration,BALF protein content was significantly elevated in the CLP group,compared with the sham group(P<0.01)(Figure 2A).Conversely,BALF protein content was decreased in the high-dose QWBD group,compared with the sham group(P< 0.05).Furthermore,the lung W/D weight ratio was significantly increased in the CLP group compared with the sham group(P<0.01).Meanwhile,the lung W/D weight ratio was significantly decreased in the high-dose QWBD group compared with the CLP group(P<0.01)(Figure 2B).Liver function tests showed that serum levels of ALT and AST were significantly elevated in the CLP group(P< 0.01),compared with the sham group.Compared with the CLP group,the high-dose QWBD group had a lower serum ALT level(P<0.05),and a significantly lowered serum AST level(P<0.01)(Figures 2C and 2D).Kidney function tests showed that the serum levels of creatinine(Cr)and BUN(P<0.01)were significantly elevated in the CLP group compared with the sham group.Compared with the CLP group,the high-dose QWBD intervention reduced serum levels of Cr(P<0.05)and BUN(P<0.01)in CLP rats(Figures 2E and 2F).These results demonstrate that QWBD can improve lung,liver,and kidney function in septic rats.
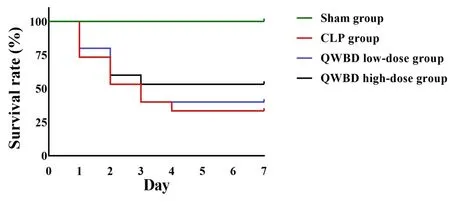
Figure 1 Effect of QWBD on the survival rate of septic rats.QWBD,Qingwen Baidu decoction;CLP,cecal ligation and puncture.
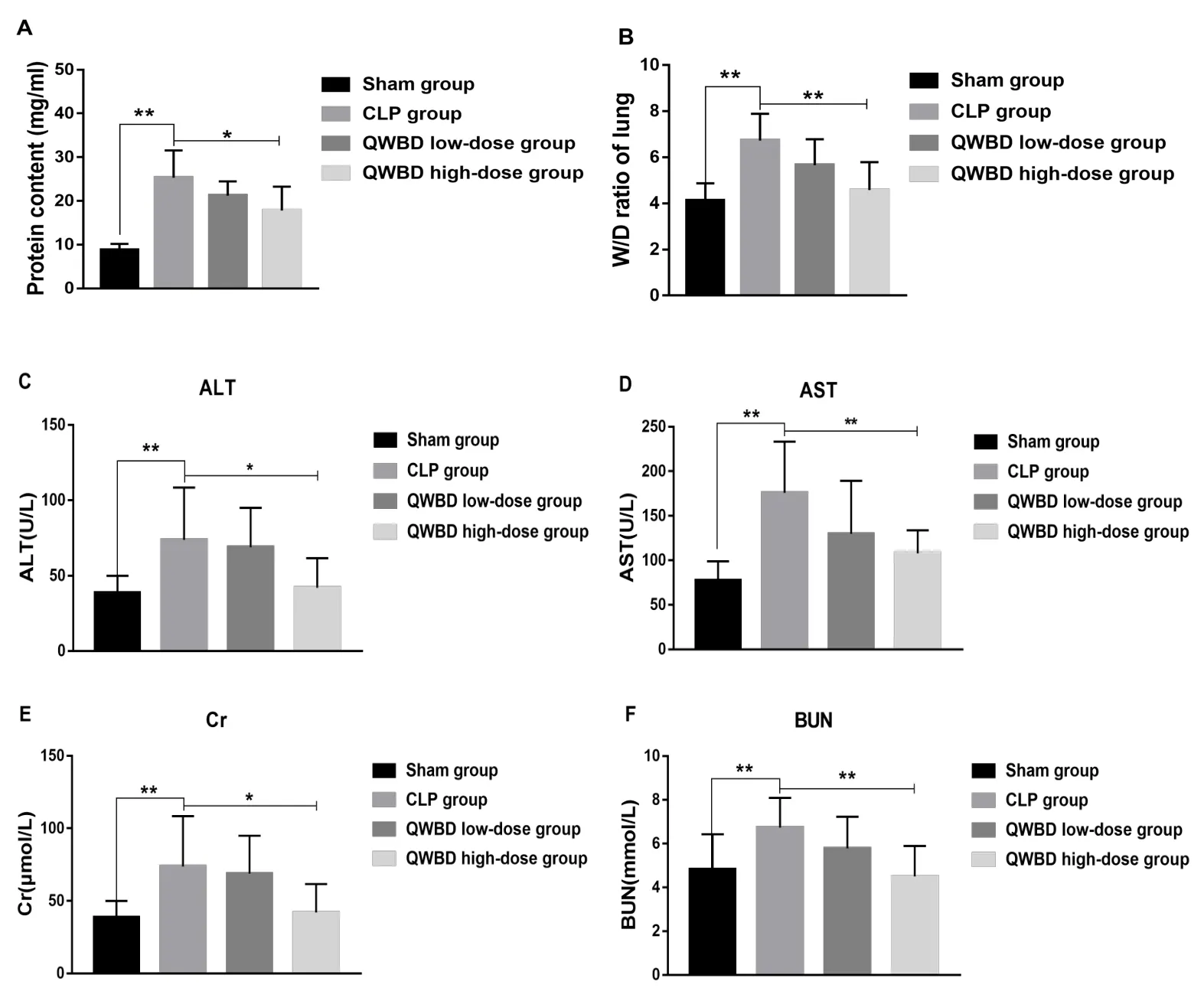
Figure 2 Effects of QWBD on lung,liver,and kidney function in septic rats.Rats were anesthetized 24 hours after model establishment and administration.The skin of the throat was cut,and BALF was collected from rats of each group to determine the protein content(A).The right lung tissue was removed,weighed,and placed in a 60°C oven for 48 hours to achieve constant weight,and the lung W/D weight ratio(B)was calculated.The abdominal cavity was opened and blood was drawn from the abdominal aorta.A biochemical analyzer was used to analyze the effects of QWBD on serum levels of ALT(C),AST(D),Cr(E),and BUN(F)in septic rats.Values are presented as mean ± standard deviation,n = 15.*P <0.05,**P <0.01.QWBD,Qingwen Baidu decoction;CLP,cecal ligation and puncture;W/D,wet-to-dry;ALT,alanine aminotransferase;AST,aspartate aminotransferase;Cr,creatinine;BUN,blood urea nitrogen.
According to H&E staining results of the lung tissue,the alveolar septum was significantly thickened,and pulmonary interstitial edema and alveolar edema were accompanied by inflammatory cell infiltration in the CLP group,compared with the sham group.Microscopic observation showed that the pathological damages were milder in the high-dose QWBD group and the low-dose QWBD group compared with the CLP group.For instance,the infiltration,edema,and destruction of alveolar inflammatory cells were significantly alleviated in a dose-dependent manner(Figure 3,upper line).H&E staining of the liver tissue showed that disorganized and necrotic liver cells,and obvious inflammatory cell infiltration were observed in the CLP group compared with the sham group.Meanwhile,orderly liver cells and reduced inflammatory cell infiltration in the liver tissue were observed in the high-dose QWBD and low-dose QWBD groups(Figure 3,middle line).H&E staining of the kidney tissue suggested the presence of local degeneration and atrophy of the renal tubules and inflammatory cell infiltration in the renal interstitium in the CLP group compared to the sham group.Compared with the CLP group,the lesion was improved in both the high-dose QWBD and low-dose QWBD groups,and more significantly enhanced in the high-dose QWBD group(Figure 3,bottom line).These results indicate that QWBD can improve the pathological manifestations of the lung,liver,and kidney in septic rats.
Effect of QWBD on the coagulation function of septic rats
Platelet count results showed that the platelet level in the peripheral blood was significantly decreased in the CLP group compared with the sham group(P<0.01).However,platelet count was elevated in the high-dose QWBD group compared with the CLP group(P<0.01)(Figure 4A).Coagulation tests showed that the APTT and PT were significantly prolonged(P<0.01)and the FIB level was significantly decreased(P<0.01)in the CLP group compared with the sham group(Table 1).The APTT and PT were significantly shortened(P<0.01)and the FIB level was significantly elevated(P< 0.01)in the high-dose QWBD group compared with the CLP group(Table 1).

Table 1 Effect of QWBD on the coagulation function of septic rats
Immunohistochemical analysis showed that the positive expression areas of thrombin in the lung,liver,and kidney tissues were significantly increased in the CLP group(P<0.01,P<0.05,P<0.01,respectively)compared with the sham group.The positive expression areas of thrombin in the lung,liver,and kidney tissues were decreased in the high-dose QWBD group(P<0.01,P<0.05,P<0.05,respectively)compared with the CLP group(Figure 4B-E).This finding indicates that QWBD can effectively regulate the coagulation function of septic rats,thereby further improving the symptoms and prognosis of sepsis.
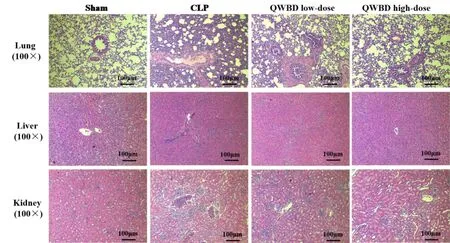
Figure 3 Effects of QWBD on histopathological changes of septic rats.At 24 hours after model establishment,the lung,liver,and kidney tissues of rats in each group were collected,fixed with formalin solution,embedded in paraffin,and cut into 3 μm thick slices.The slices underwent the conventional H&E staining and were sealed with neutral balsam.Histopathological changes of the rats in each group were observed under an optical microscope(screen magnification=×100,scale bar=100 μm).QWBD,Qingwen Baidu decoction;CLP,cecal ligation and puncture;H&E,hematoxylin and eosin.
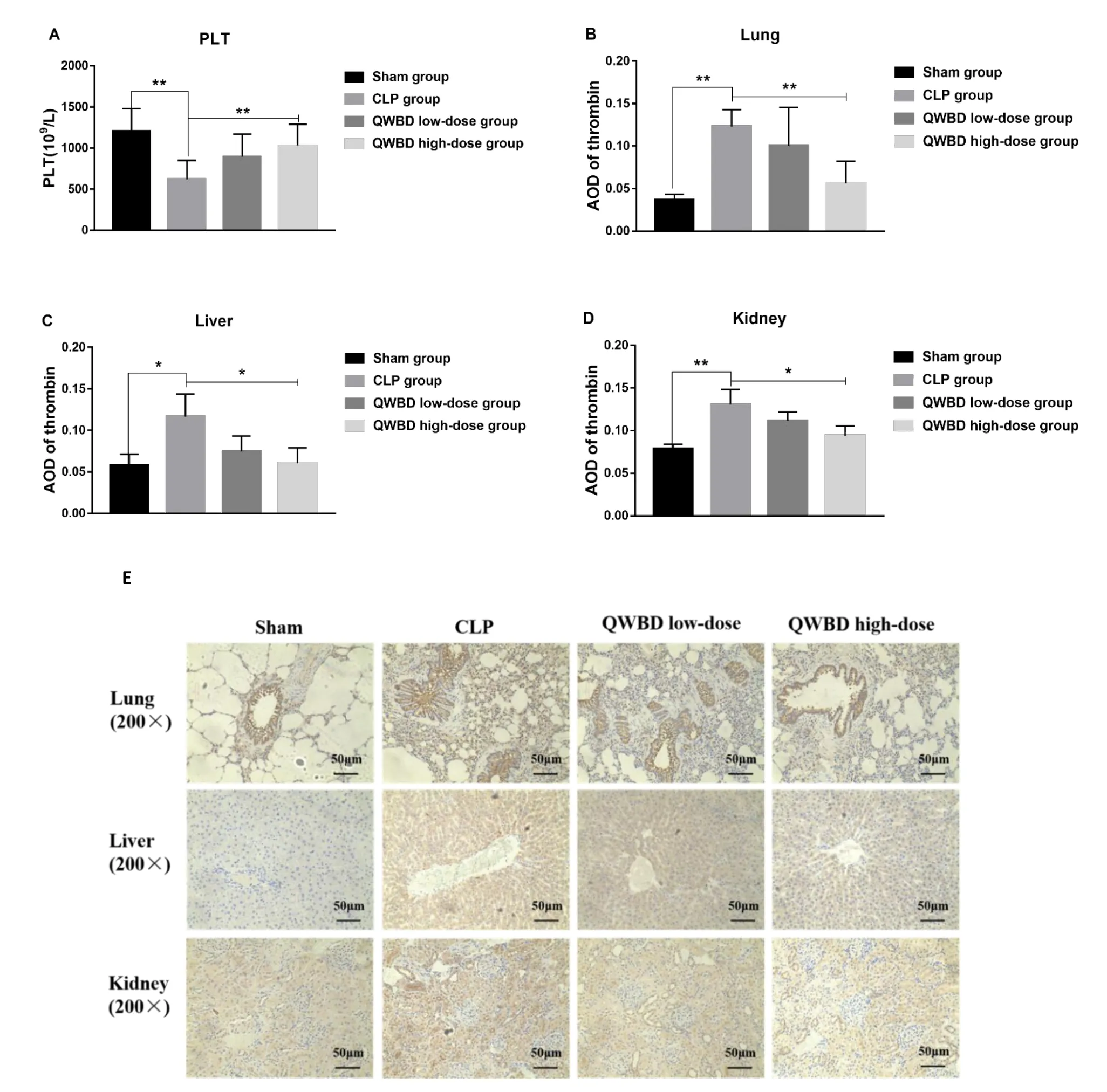
Figure 4 Effect of QWBD on coagulation function of septic rats.Rats were anesthetized 24 hours after model establishment and administration.Blood was collected from the abdominal aorta.An automatic hematology analyzer was used to analyze the effect of QWBD on serum platelet levels in septic rats(A).After rats were sacrificed,the lung,liver,and kidney tissues of rats in each group were collected to observe the effect of QWBD on thrombin-caused infiltration in the lung,liver,and kidney tissues by immunohistochemical(screen magnification = × 200,scale bar = 50 μm)(E).The positive expression area was quantified using Image Pro Plus(version 6.0),and the average optical density(B-D)was calculated with the formula:Average optical density = Integrated optical density/Total area.Values are presented as mean ± standard deviation,n = 15.*P <0.05,**P <0.01.QWBD,Qingwen Baidu decoction;CLP,cecal ligation and puncture;PLT,platelet;AOD,average optical density.
Discussion
According to epidemiological statistics,sepsis and septic shock occur in more than 19 million people in the world each year,and this number is on the rise[28]with the death proportion fluctuating between 1/6 and 1/3.Clearly,sepsis is a major health problem affecting the entire world[29].In this study,the survival rate of septic rats induced by CLP was consistent with real-world data and relevant literature reports[30].Our experiments demonstrated that ALT,AST,Cr,and BUN levels were significantly elevated in the CLP group compared with the sham group.Additionally,the alveolar septum was significantly thickened,pulmonary interstitial edema and alveolar edema were accompanied by inflammatory cell infiltration in the septic model group.Disorganized and necrotic liver cells with obvious inflammatory cell infiltration were also observed in the CLP group.Local degeneration and atrophy of the renal tubules and inflammatory cell infiltration in the renal interstitium were observed in the CLP group,meeting the criteria of a CLP-induced sepsis model[31,32].In this study,we observed that QWBD could significantly improve the survival rate of septic rats in a dose-dependent manner.This suggests that QWBD has a therapeutic effect on septic rats.
The excessive inflammatory response is an important early pathological process of sepsis and is involved in multiple organ injuries in the initial stages[33,34].Studies have shown that within 6-48 hours after CLP in rats,the levels of inflammatory factors are significantly elevated[35,36].Sepsis is often accompanied by the manifestation of impaired liver and kidney function[37].In this study,the serum levels of ALT,AST,Cr,and BUN,the biochemical indicators of liver and kidney functions were all elevated in the CLP group at 24 hours after model establishment.Relevant indicators of liver and kidney functions were significantly improved after QWBD intervention,suggesting that QWBD could improve the sepsis-associated impairment of liver and kidney functions.
It is widely accepted that structure determines function.Therefore,a fundamental reason for the change of function lies in the change of tissue structure.In the pathological tissue sections,varying degrees of edema,inflammatory infiltration,and necrosis were observed in the liver and kidney tissues of rats in the CLP group.Significant improvement was observed in the pathological changes of liver and kidney tissues of septic rats in both high-dose QWBD and low-dose QWBD groups,including decreased inflammatory cell infiltration,ameliorated apoptosis,and mitigated cell injury.Lung injury is also one of the important pathological changes in sepsis[38].Our study results indicated that at 24 hours after model establishment,BALF protein content was elevated,the lung W/D weight ratio was increased,and many inflammatory cells infiltrated the interstitium accompanied by obvious thickening of the alveolar septum,pulmonary interstitial edema,and alveolar edema.Fortunately,QWBD could significantly improve the lung tissue injury in septic rats.To summarize,QWBD has therapeutic effects on sepsis-induced organ injury.
Sepsis-induced coagulation disorder is an important mechanism involved in the pathological development of sepsis.Coagulopathy is also a crucial factor for the aggravation of sepsis and the occurrence of septic shock and even multiple organ dysfunction syndromes[39,40].The degree of sepsis-induced coagulation disorder may range from a mild decrease in platelet count to prolonged clotting time that can be clinically detected.DIC may occur in severe cases[41].Excessive activation of the coagulation system,consumption of massive coagulating substances,secondary fibrinolysis,impairment of the anticoagulation system,and extensive thrombosis in the microcirculation that leads to organ failure are the main clinical characteristics of sepsis-induced DIC[42].The mortality rate in septic patients with DIC is twice the mortality rate in those without DIC[43].Studies have shown that thrombocytopenia occurs in approximately 40% of patients with severe sepsis[44],and plays a critical role in thrombosis,inflammation,and immune regulation[45].In this study,the number of platelets decreased significantly 24 hours after the model was established by CLP.After administration of QWBD,the number of platelets increased significantly compared with the CLP group,and the difference was statistically significant.This indicates that QWBD could significantly elevate the platelet level.PT is an important indicator reflecting the extrinsic coagulation system[46],while APTT is the most reliable indicator for evaluating the level of intrinsic coagulation factors[47].Prolongation of the above indicators indicates an elevated risk of thrombosis in the body.FIB can form insoluble fibrin under the action of thrombin to exert a hemostatic effect[48].In sepsis,the coagulation function is excessively activated,and massive tissue factors and FIB are consumed to form the thrombus.Our study results showed that QWBD could significantly shorten PT and APTT,increase the FIB level,and effectively improve coagulation function.Thrombin is a key enzyme in the coagulation process.When vascular tissue is damaged,the release of plasma factor,tissue factor,and platelets lead to the generation of prothrombin activators,which convert prothrombin into active thrombin,thus promoting the conversion of plasma FIB into insoluble fibrin[49].Thrombin is the core of activation of the coagulation and fibrinolytic systems.When studying blood disorders including thrombosis and blood stasis,thrombin can be used as an important target of drugs for treating such disorders[50].Immunohistochemical findings showed that the positive expression of thrombin was significantly decreased in the lung,liver,and kidney tissues after the QWBD treatment.This suggests that QWBD could suppress the activation of thrombin,thereby improving coagulation in sepsis.
The main material basis for sepsis to cause coagulation disorders and multiple organ injury is that many inflammatory mediators and lipid metabolites enter the blood circulation and accumulate in multiple organs and tissues to induce necrosis of the corresponding tissue cells.In addition to the inflammation theory,ferroptosis is a novel manner of cell death,and its role in the onset and progression of sepsis is being increasingly studied[51,52].
This experiment has confirmed that QWBD can effectively improve the impaired coagulation function and multiple organ injury in sepsis,but its mechanism of action is unclear.Whether QWBD can improve the symptoms of sepsis by suppressing the inflammatory response,improving ferroptosis in tissues,or by other means,remains to be determined.
Conclusion
Overall,our study confirms that QWBD can effectively improve the coagulation disorder in septic rats.Meanwhile,QWBD has a protective effect on the lung,liver,and kidney tissues,while also improving the survival rate of septic rats.These findings lay a foundation for further studies on the mechanisms of QWBD in treating sepsis,and provide a scientific basis for the clinical use of QWBD for the treatment of sepsis.
 Traditional Medicine Research2022年3期
Traditional Medicine Research2022年3期
- Traditional Medicine Research的其它文章
- Traditional Chinese medicine:an important broad-spectrum anti-coronavirus treatment strategy on COVID-19 background?
- Anti-asthmatic mechanism of the Huashanshen dripping pill via suppressing contraction of the airway smooth muscle
- Application of network pharmacology in the prevention and treatment of COVID-19 by traditional Chinese medicine
- Pharmacological efficacy of the traditional Chinese medicinal formula Kun-Tai-1A in the treatment of letrozole-induced polycystic ovary syndrome
- Recent advances in research on natural product inhibitors of SREBPs
- Integrated UHPLC-MS and network pharmacology to explore the active constituents and pharmacological mechanisms of Shenzao dripping pills against coronary heart disease
