Molecular mechanism of different viruses associated with autoimmunity
Arslan Habib, Zeeshan Ashraf, Irfan Ullah Khan, Amjad Ali, Dominic Kwesi Quainoo,Sajjad Ahmad Qamar, Umutumwa Eric Principe, Dur E Maknoon Razia
Abstract Different kinds of human chronic diseases may develop the mechanism of autoimmune diseases.As a group of disorders, in the Western world autoimmunity possess as the third most prevalent morbidity and mortality.However, the mechanism of most autoimmune diseases is still under investigation.Viral infection is the principal factor involved in the induction of autoimmune diseases other than genetic factors and cytokine activity.Different mechanisms have been proposed by which viral infection might interrupt tolerance to self and induce autoimmune cascade which eventually leads to the destruction of a specific type of cell or a whole-body organ.The autoimmune attack can be understood through the different immune systems and other possible mechanisms such as molecular mimicry,bystander activation and epitope spreading.In addition to genetic and viral factors,other environmental factors are also involved including bacterial, parasitic and fungal infections.However, different animal models have been studied which provide strong evidence that viruses induced AIDs as well as accelerated and increased lesions in conditions where self-tolerance is interrupted.In the current review, we discussed the virus-induced autoimmunity and the molecular mechanism which is associated with this phenomenon.Here we also discussed the different viruses such as rubella virus, enteroviruses, measles virus, human T-lymphotropic virus type1, human cytomegalovirus, human herpes virus-6, Epstein-Barr virus, rotavirus and some other viruses which modulate the development of AIDs.
Keywords:autoimmunity;viruses;immune tolerance;molecular mechanism
Introduction
When the immune system can not differentiate properly self and non-self antigens which produce abnormal immune feedback ultimately lead to autoimmune diseases (AID).Recently, more than 80 types of autoimmune complications have been recognized [1].However, the analysis of different autoimmune complications persist entirely understood, several factors associated with autoimmune feedback such as viral infection, age, genetics and environment.Among the genetically susceptible individuals, viral bodies have been recognized as significant environmental elements that induce the autoimmune sensation [2, 3].A different molecular mechanism has been proposed to describe the viral infections induced the autoimmunity (Figure 1).Conventionally, it was considered that viruses express structurally correlated antigens to self-antigens, which triggers B and T-cells to proceed cross-reactive feedback across both self-and nonself antigens, a process known as “molecular mimicry” [4].For several autoimmune infections, molecular mimicry has been illustrated such as Theiler’s murine encephalomyelitis virus-induced demyelinating disease(TMEV-IDD), virus-induced diabetes, Coxsackie virus-induced autoimmune myocarditis, herpes simplex virus (HSV)-induced stromal keratitis and several others [5-9].Furthermore, “bystander activation” is another hypothetical mechanism, through which an over-reactive and non-specific antiviral immune feedback produce a narrow pro-inflammatory condition as well as the discharge of self-antigens by the impaired tissue.Afterward,the self-antigens are engaged and offered by antigen-presenting cells(APC) to activate the earlier non-feedback, so far T-cells that are autoreactive in the locality induce autoimmunity [10].Another process is known as “epitope spreading”, which increased the number of selfantigens released by the induction of viral infection and also triggers the de novo stimulation of autoreactive cells, which may ultimately proliferate to target supplementary self-epitopes [9].Molecular imitation and bystander activation both mechanisms have been analyzed in the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) sample of multiple sclerosis (MS) [11], myasthenia gravis (MG) induced by West Nile virus(WNV) [12], TMEV-IDD [13], and different other diseases [9].However,different proposals have been suggested to observe the mechanism of virus-induced autoimmunity but a significant endowment of these mechanisms is not completely recognized.Almost 3-5% of our population is affected by autoimmune diseases (AIDs).Polymorphism has been observed after genome-wide experimental studies among the different genes, which are associated with immune activation and regulation predisposing to the occurrence of autoimmune disease [14, 15], however,expression of autoimmunity may only result after infection with different infectious agents[16].
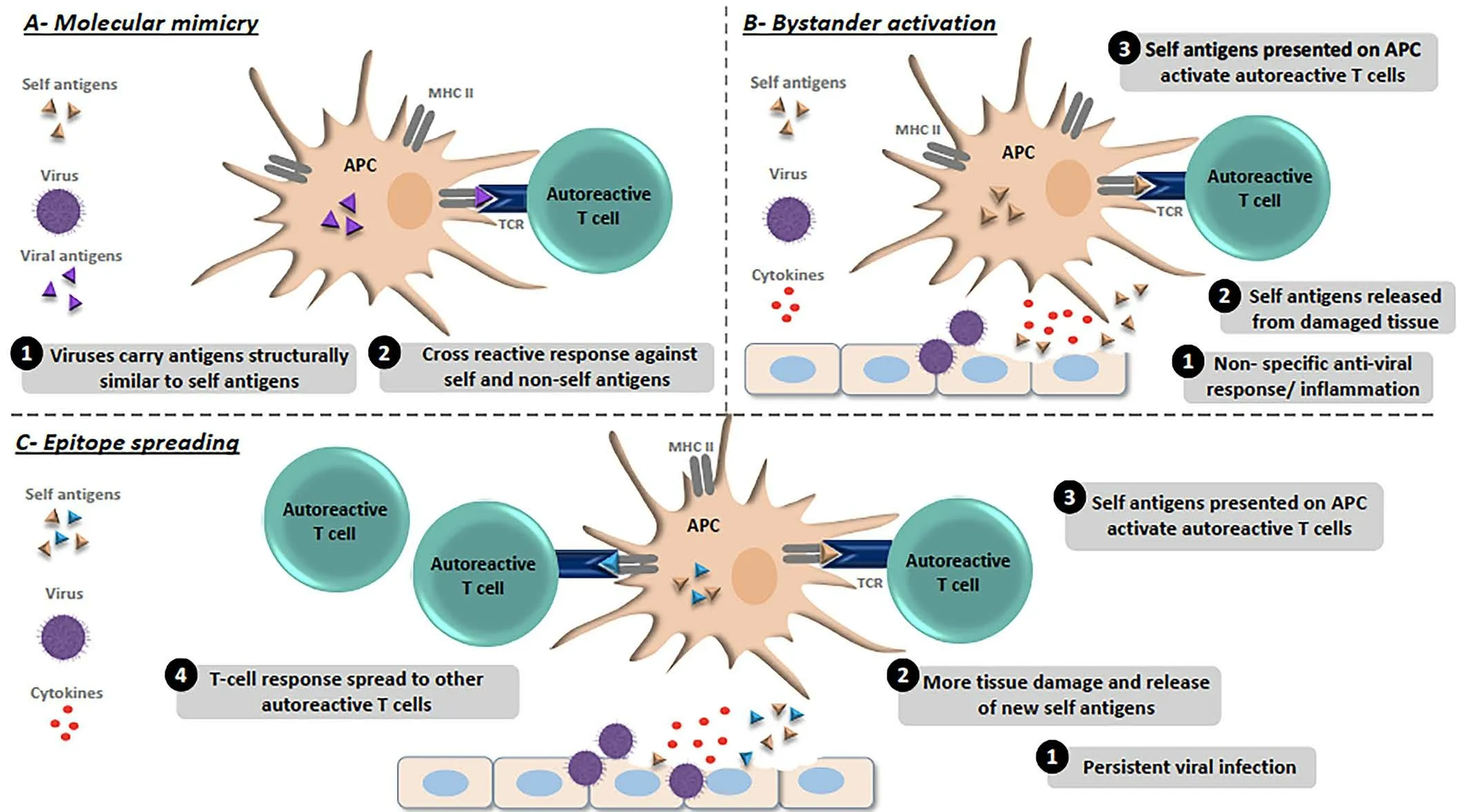
Figure 1 Molecular mechanism of virus-induced autoimmunity.(A) Molecular mimicry model; (1) Viruses acquire epitopes structurally analogous to self-epitopes.(2) Activation of autoreactive T cells initiated via presentation of viral epitopes by antigen presenting cells(APCs)that link to both self and non-self-antigens that induces tissue damage.(B) Bystander activation model; (1) Over reactive and non-specific antiviral immune feedback initiated to the release of self-antigens and inflammatory cytokines from the damaged tissue.(2) Self-antigen is absorbed and presented by APCs.(3) APCs initiated the autoreactive T-cells ultimately leading tissue damaging.(C)Epitope spreading model:(1)Constant viral infection.(2)Continue discharge of self-antigens and tissue damage.(3)Self-antigens are absorbed and presented by APCs.(4)Abnormal induction of increased autoreactive T-cells leading to autoimmunity[178].
Immune tolerance
The mechanism of autoimmune complications is important to learn for a better understanding of the pathogenesis of autoimmune disorders.The immune network competes to different challenges such as recognizing foreign antigens and immediately providing their feedback without triggering significant distress to the host cells.Furthermore, in addition to warding off antigens of the host, the immune system is confronted by the enlarged complications of differentiating commonly non-pathogenic symbiotic microbes from pathogens, this is crucial to hold the common beneficial correlation among the microbiome and the host.Many years of research have targeted to determine the principal mechanism, which is followed to accomplish the tolerance of adaptive immune.Central and peripheral mechanisms are both the division of the T-cell tolerance,distinct analysis of which has been broadly reviewed somewhere else[17, 18].In short, central tolerance is accomplished by the mechanism through which T lymphocytes are adopted during the development of the thymic.Lymphocytes undergo positive selection if they exhibit restriction of host MHC and lymphocytes with negative selection are those that show well response to host MHC.Central tolerance’s growth heavily depends on the devotion of the T-cell receptors.Central tolerance is invalidated by the mutation of downstream kinase and leads to autoimmune arthritis formation in a mouse model [19].AIRE is a transcriptional factor that plays an important role in the negative selection of T-cells, will further instance the significance of the central tolerance [20, 21].Negative selection will not take place if AIRE is absent it will result in the formation of clones of autoreactive T-cells, various autoimmune phenomena and autoantibodies [22-24].Multiple mutations are discovered in AIRE which further strengthened its role in autoimmune pathogenesis[25].
Central tolerance is spurt by various autoreactive T-cells even with thymic assortment mechanism [26].Some of these cells are seen in people with multiple sclerosis, type 1 diabetic patients and healthy people [27-29].Prevention of activation of T lymphocytes does not develop disorders because they are under the influence of peripheral tolerance.Various factors that assist in peripheral tolerance are apoptotic deletion,lymphocyte limited trafficking and energy promotion.This peripheral tolerance is seen in both animals and humans.Associated loci of costimulatory molecules are linked with various autoimmune diseases through GWAS analysis [30].Any mutation in FOXP3 will develop lethal autoimmunity [31].From various significant experiments, it is clear that irregulating T-cells and T-regulatory cells are key in autoimmunity development [32, 33].The intrinsic immune system retort to pathogens and damaged tissues so plays a key part in immune tolerance.Participation of dendritic cells in peripheral and central tolerance is an example of it [34].NK cells through receptors of inhibitory cell surface take part in immune tolerance.Autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, alopecia areata, and lupus erythematosus have associations with the immunoglobulin-like inhibitor receptor’s mutation [35-37].Moreover,T-cells show response indirectly by secretion of cytokines and directly by deletion of autoreactive T cells[38,39].
Infection and autoimmunity
The function of microorganisms in the formation of autoimmune illness is best understood by emphasizing several of the putative pathologic processes at work.Microbe-linked autoimmune disorders that are supposed to be developed through a diversified classic procedure like epitope or molecular imitation of self-antigens, recognition of earlier unidentified self-antigens by the immune system, activation of polyclonal T-cells regulated by superantigens along with the inflated release of cytokines and auto-reactive T- lymphocyte bystander activation.Notably,the properties of viruses and bacteria that create a stock of T-cell subsets indicated in autoimmunity are still under study [40, 41].The following are key instances of autoimmunity caused by bacterial and viral infections.Particularly there is a clear association between autoimmunity and bacterial infections, while autoimmune disorders are frequently supposed to be developed due to molecular mimicry.Streptococcus pyogenesis a gram-positive bacterium that is considered to be a cause of pharyngeal infection that develops rheumatic fever which is one of the most examined cases.The antibody response of the host is tested against epitope (N-acetyl-D-glucosamine) the main carbohydrate of the bacterial cell along with M-protein, a viral component.These antibodies also react with antigens namely cardiac myosin, laminin and vimentin, present on the atrioventricular and semilunar valves of the host.As an outcome, the antibody response of the host creates serious clinical sequelae for example heart valve dysfunction,carditis and rheumatic fever[42].
Another autoimmune disease related to past infection is post-infectious glomerulonephritis.StreptococcusandStaphylococcus nephritogenicstrains encode specific exotoxins [43, 44].The glomerulus is not severely harmed by these contain or poisons, nor they are a location of active bacterial cell contamination.Instead, molecular imitation harms the glomerulus via the mechanism of cross-reactive antibodies.Clinical therapy treatment of the above immune system situations has been formed by these revelations and the job of microbes in immune system illness pathogenesis.For instance,an infected individual determined to have postirresistible glomerulonephritis or rheumatic fever is regularly treated with a course of anti-microbial focused on bacterial source control for the populace everywhere regardless of whether the individual’s underlying pharyngitis has decreased surgically or by microbial location.In the developed world, this general strategy has been effective, with a decrease in the frequency of both of these illnesses, coinciding with an increase in the usage of empiric antibiotics for the treatment of pharyngitis[45].
Moreover, analogous results in autoimmune diseases connected to viruses have yet to be realized, owing in part to insufficient knowledge of their part in generating auto-immunity, along with intrinsic difficulties in virus detection and efficient anti-viral therapies.Some of the early studies establishing a connection between viral contamination and auto-immune disorders development exemplify the complicated relationship between viruses and autoimmune disorders.In the 1970s and 1980s, researchers discovered a link between newborn lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) and polyomavirus infection and immune complex glomerulonephritis, as well as related mortality [46].Intriguingly, further research revealed that LCMV infection suppresses the generation of two rat samples of autoimmune diabetes [47, 48], a disease characterized by autoantibodies and reactive T-lymphocytes regulated destruction of islets of the pancreas [49].The discovery that singles viral contamination poses distinct risk factors for the production of glomerulonephritis and type 1 diabetes emphasizes the complicated connection between viral infection and autoimmune[50].
Viruses associated with autoimmunity

Rubella virus(RV)
Several abnormalities in the development of several organs in infants are due to congenital rubella syndrome (CRS), which is said to be developed due to the transfer of RV from pregnant women to their babies most probably during the first trimester [51, 52].A solid genetic proof of T1D is the higher frequency rate of HLA-DR3 haplotype in CRS individuals[53].In the development of T1D autoimmune disorder, HLA-DR3 is supposed to be a liable haplotype, moreover, the higher implications of the HLA-DR3 haplotype in CRS patients presents strong genetic proof of T1D association [54, 55].Animal investigations have found that newly born babies infected with RV can develop diabetes mellitus in hamsters[56].Moreover, one investigation showed that RV-regulated antibodies are present in individuals with several autoimmune dysfunctions with a potentially increased range of IgM and IgG rubella-regulated antibodies in these under observation patients compared with relatively healthy individuals.However, the examination does not include the tested individuals who were taking immunosuppressive therapies which can notably increase the range of RV regulated antibodies alter the evaluated observation[57].
Enteroviruses
Enteroviruses are thought to be the most likely viral causes of type 1 diabetes in humans [58].Since 1969, there has been a seasonal increase in the prevalence of type 1 diabetes following enterovirus infections[59,60].The function of enteroviruses in type 1 diabetes has been studied for over forty years, the etiological connection remains unknown [61].When compared to nondiabetic controls, siblings with type 1 diabetes have a higher frequency of enterovirus infections.Furthermore, higher levels of antibodies of enterovirus were present in pregnant women whose babies went on to develop type 1 diabetes [62].Furthermore, numerous studies have found a link between enteroviral infections and beta-cell autoimmunity.For instance, in diabetes mellitus type I genetically vulnerable kids, the seasonal prevalence of auto-antibodies mirrored the seasonal development of enterovirus contamination, indicating that enteroviruses play a role in auto-immune diabetes mellitus [63].Another research indicates enterovirus contamination was shown to coincide with the initial development of diabetes-related autoantibodies [64].Elshebani et al.discovered that some enterovirus strains obtained from type 1 diabetes patients impacted beta cell activity and caused cell death in vitro [65].Similarly,enteroviruses have been discovered in diabetic patients’ intestinal biopsies, implying the potential of a continuing chronic enterovirus infection in the gut mucosa of type 1 diabetes patients [66].In addition, a recent systematic analysis of 24 published articles found a strong link between enteroviruses and autoimmunity/type 1 diabetes[67].
Measles virus(MV)
MV has primarily been linked to MS.Anti-MV antibodies have been found in the CSF of around 75% of MS patients, according to research [68].The researchers discovered that MV-directed antibody titers were greater in MS patients’ serum compared to healthy controls [69].Anti-MV IgG antibody levels often decline with age following a measles illness or immunization [70].However, one research revealed that MV antibody levels in both blood and CSF of MS patients rose with time [71].In addition to MS, numerous studies have documented the presence of elevated anti-MV antibody titers in individuals suffering from other diseases, including discoid lupus erythematosus [72], as well as chronic active hepatitis [73].In the latter, a connection has been found between higher MV antibody titers and the existence of anti-nuclear antibodies, as well as autoantibodies targeting smooth muscle[74].
Human t lymphotropic virus type 1(HTLV-1)
HTLV-1 is not only linked with the formationof HTLV-1 driven myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/SP) but it has also been found to be associated with arising of other diseases for example uveitis and SS [75].Contamination of CD4 TT-cells by HTLV-1 may be due to various disorders, Tax which is a viral protein that has an important role in the transcription of virus and changes the expression of various cellular transcription elements like NF-jB, serum response factor (SRF), cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) and activator protein 1 (AP-1)may affect the signaling pathway regulators and stages or activity of key transcription elements [76].Various investigations on HAM/TSP-infected individuals evolved that the stages of expression Treg-defining transcription forkhead box P3 (FOXP3) gene were smaller in these patients and as a result a decreased value of anti-inflammatory cytokines released from Tregs like IL-10 and TGF-β [77].Moreover, HTLV-1 contaminated T lymphocyte cells and a provirus HTLV DNA were reported in the synovial fluid and synovium of RA-infected persons.An antibody named Anti-HTLV-1 concentrations has also shown to be found increasing in ACTD and RA patients [78].Moreover, Tax mRNA was found to be expressed in the synovial cells of patients having HTLV-1-associated joint diseases[79].Also, a higher frequency expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines like C-X-C motif chemokine 10 (CXCL10), which is also known as IFN-c induced protein 10 (IP-10) and chemokine C-C motif ligand 5 (CCL5) was reported implying that HTLV-1 contaminate and produce alterations in SGECs that may suggest it possible inclusion in the formation of SS[80].
Human cytomegalovirus(HCMV)
There is another known human herpesvirus called HCMV which is linked with many autoimmune disorders.It has been shown in many cases that immunocompetent HCMV infected persons have almost no or little symptoms.Individuals with HCMV infection can acquire many chronic systematic disorders like splenomegaly, nephritis, colitis, and encephalitis many in subjects with adjusted immunity [81].Most of the properties of this virus can lead the HCMV to participate in the development of autoimmunity which includes its global spread, its broad range of target cells and tissues [82], its remarkable ability to change immune function[83], and its perseverance through alternative stages of lytic replication and latency [84].HCMV has also been associated with a chronic connective tissue disease called systematic sclerosis also known as scleroderma which is characterized by many disorders like the abnormal proliferation of fibroblast, accumulation of extracellular matrix protein in the skin tissues, vascular injury and an increase and decrease of CD4þ T-cells and CD8þ T-cells respectively [85].Many studies have been shown that the concentration of HCMV antibodies is higher in systemic sclerosis(SSc) patients when compared with control [86].The ex vivo examination on the inoculation of man’s dermal fibroblast along with umbilical cord epithelial with anti-UL94 leads to the linkage of novel antigen-2 (NAG-2)by HCMV antibody that resulted in endothelial cells apoptosis however fibroblasts did not show apoptosis [87].Moreover, the HCMV antibodies level against anti-UL94 were also seen to be increasing in individuals with the enhanced diffuse type of this disorder [88], which is also according to a hypothesis given by Pandey and LeRoy which states that HCMV acts as an enhancer of SSc [89].Tan and Kunkel [90], discovered the first autoantibody in patients with SLE in 1966 and is called anti-Sm.To make a core of high stable smaller nuclear ribonucleoprotein (snRNP), the Smproteins bind with the small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) U1, U2, U4, U5 and U6 [91].In an investigation, it was shown that the identification of autoantibodies was highly obvious in SLE infected individuals having the higher potential of anti-HCMV IgG antibodies[92].
Human herpes virus-6(HHV-6)
Herpes Virus 6 of humans can establish latency in monocytes,lymphocytes, bone marrow along with the Central Nervous System with a potential of later reactivation.Moreover, this virus can cause exanthema subitum or roseola infantum in kids with age below two years [93].In addition to the disease known as encephalitis in both children as well as in adults, this disease has also been associated with many other disorders such as seizures [94], disseminated demyelination [95], and basal ganglia infarction in children [96, 97].In 1993, there were two types of HHV-6 were discovered named HHV-6A and HHV-6B [98].These variants are quite similar following their genome but have different biological and immunological potential [99].This virus has also been found to be linked with autoimmune disorder development.The very first such proof was reported in an investigation that showed the appearance of an HHV-6A antigen in the oligodendrocytes extracted from MS-infected individuals,and its absence in healthy control [100].In another examination, the association was revealed by finding the high intensity of HHV-6A/B-directed antibodies in MS patients when they were compared with relatively healthy persons taken as control along with identification of HHV-6A/B DNA in the brain cells, CSF and serum founded in MS-patients[101, 102].Interestingly, it was demonstrated in an investigation that there is a linked peptide sequence between human basic protein myelin that consists of seven similar kinds of amino acid residues and HHV-6A protein U24.Importantly, the immune system reactions stimulated by antibodies and T-lymphocytes which are directed towards this type of arrangement were potentially high in MS-infected individuals indicating a mechanism of molecular imitation to be happening [103].However, this linkage has also been challenged by many investigations [104].A study identified 1gM anti-HHV6 only in one MS-patient out of 198 while on the other side 1.8 % of individuals were detected positive for the HHV-6 virus and had very little median viral potential of 2.2 copies/ml[105].
Epstein-barr virus(EBV)
A herpes virus is known as EBV which give rise to infectious mononucleosis(IM) has been characterized by autoimmune disorders like systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) disorders which can harm many vital organs along with joints and skin and can cause a mark similar to the shape of a butterfly on face part and bone diseases known as rheumatoid arthritis,harming the synovial membrane of several joints leaving pain and swallowing of the part.Many examinations have reported that despite the higher potential of viral bodies in peripheral blood mononuclear cells(PBMCs) of individuals when they were compared with relatively healthy persons [106], there is also a high concentration of EBV-directed antibodies in RA and SLE sufferers.Furthermore, early antigen (EA), EBV nuclear antigen-1 (EBNA-1) and viral coat antigen (VCA), -directed antibodies have also been identified with an increased level in serum of SLE individuals, while only sixty-six percent of healthy persons taken as controls were tested seropositive [107].There are also raised concentrations of EA/D-directed IgA that have been detected in SLE patients with a ratio of more than half but none were observed in healthy controls [108].Furthermore, higher potential of mRNA intimation of the BV viral antigen glycoprotein 350 (gp350), EBNA1, BamHI Z leftward open reading frame 1 (BZLF1), latent membrane protein-1 (LMP-1), LMP2 and viral IL-10 has been found in SLE infected persons [109].It has also been reported in a study that EBV-directed CD8þT-cell activity that has an important part in diminishing EBV-contaminated cells is decreased in SLE-infected individuals that leading to a low level of containment of the disease[110].Another autoimmune disease known as Multiple sclerosis (MS) has also been associated with EBV and has the potential to harm the central nervous system (CNS) causing disabilities.It has been found that the presence of EBV contamination in teenagers can lead to a high-risk factor of acquiring MS with high levels of anti-EBV antibody titers[111].
Rotavirus
Many investigations have reported that rotavirus has an important part in the development of autoimmunity both in human as well as in animal samples revealing bystander development of autoimmunity.In a study,Honeyman et al.reported that RRV antibodies may hinder auto-immunity to beta islets of the pancreas in high-level risk children based on serological analysis of islets autoantibodies and rotavirus antibodies [112].Furthermore, another larger investigation reported that rotavirus infections rarely hinder beta islets autoimmunity in genetically susceptible kids[113].Several investigations on “rhesus monkey” (RRV) infection in NOD rats reported that rotavirus can produce diabetes mellitus without infection of pancreatic islets cell, however, this development involves the presence of insulitis which depends on the release and involvement of the proinflammatory cytokine of Th1 activation [114, 115].Interleukin protein 1 and 6, the individual pro-inflammatory cytokines are found to decrease Treg performance and allow uncontrolled adaptive auto-immune reactions.There are many factors including infection time, age of candidate and status of insulitis found to change the results of infections in the form of decreasing, increasing, or ultimately not affecting the development of diabetes mellitus [115].Furthermore, rotavirus development of diabetes mellitus is strain-specific, because rat’s infection is with RRV but not with the CRW-8 that is a serotype of RRV of an Australian porcine which crossreact with RRV serotype3 of humans has increased disease production[116].Pane et al.suggested that rotavirus diabetes mellitus increase in NOD rats take place but it is a bystander activation: Rotavirus decreases dsRNA produce Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) signals, that leads to the production of interferon type-I and lymphocyte activation, which includes autoreactive T cells, that exacerbate diabetes mellitus-associated autoimmunity [114].Although Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) has been intimated in the bystander activation and the melanoma differentiation protein 5 (MDA5), may also have a major part in rotavirus producing interferon type-I expression, and hence diabetes mellitus development.If virally caused diabetes can arise from the non-specific procedure which does not involve viral infection of pancreatic cells, e.g., proinflammatory cytokine response and activation of lymphocyte, this revealed that many other such kinds of viruses can produce similar types of effects [117], thus more investigations in the area are required.
Other viruses
Many other viruses like mumps and measle related to theParamyxoviridaefamily and rubella viruses that are associated with theTogaviridaefamily can cause viral diseases which have an association with autoimmune disabilities.Measles and mumps diseases are specifically related to the induction of diabetes mellitus (type 1) [118].Both viral infections have the potential to develop and infect the beta islets [119, 120].In addition,both viruses can cause demyelination disease [121].Viruses related to theFlaviviridaefamily, for example, dengue virus (DENV), zika virus (ZIKV)have also a linkage with autoimmune diseases that include recently suggested DENV-induced SLE and ZIKV-produced Guillain-BarrÀ syndrome and lupus nephritis [122, 123].Another virus from theRetroviridaefamily called T-lymphotropic type 1 virus (HTLV-1) has also been linked with Central Nervous System autoimmunity, which gives rise to myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis [9].Many latest investigations desired to find the contribution of viral loads causing Central Nervous System diseases.It was reported that anti-viral immune reactions crossreact with NMDA receptors cells of humans (2A subunit) [124], which are ion channel proteins found in nerve cells [124], and are the main cause for excitatory glutamatergic transmission.There is also previously reported Pentapeptide linkage similarity between viral proteins and the human NMDA 2A receptor cells[125].
While taking into account the previous knowledge from experimental and epidemiological animal experiments, there is a broad scale of viral bodies that are accused to start an autoimmune mechanism.Table 1 concludes the studies demonstrating viral produced autoimmunity in many different types of living beings along with reported mechanisms.Notably, it gets clear from available studies that there is not only one origin that have the potential of hindering autoimmunity.It has been shown that the growth of autoimmune disorders followed by viral disease is a multifactorial procedure that depends on different factors.Furthermore,while finding that viral disorders can lead to autoimmunity or protection from various immune diseases like diabetes mellitus and CD [126, 127],which may be dependent on many responsible elements that include viral strain, infection dose, host-immune response, genetic predisposition and time of infection[128].
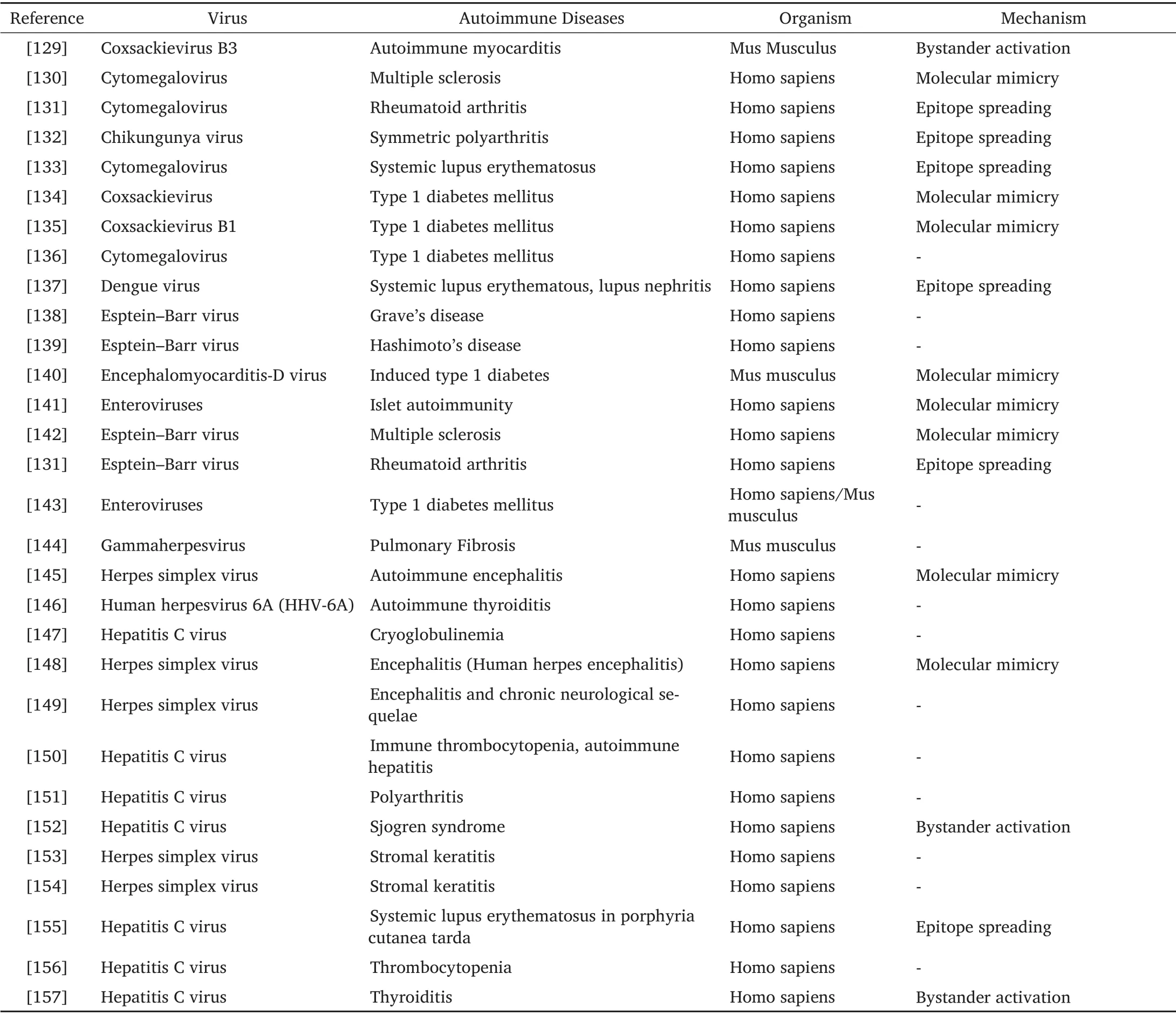
Table 1 Different viral infections which are associated with autoimmunity
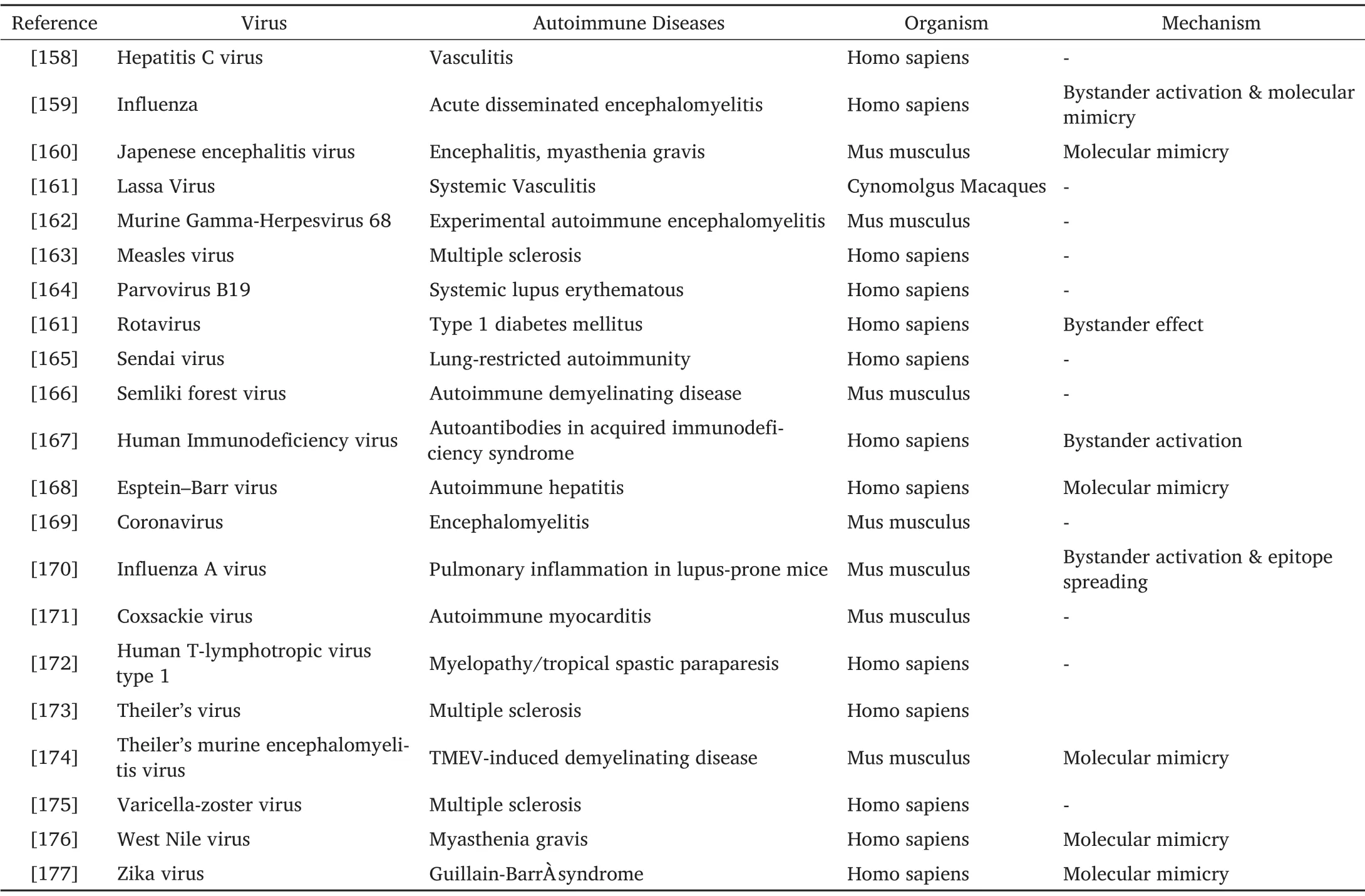
Table 1
To be continued
Conclusion
Autoimmunity development mostly depends on a combination of different factors such as genetic, damaged immune system and different environmental triggers like a viral infection.The degree of all such factors in the contribution of autoimmune diseases is still not confirmed and the current evidence is still inadequate to explain the involvement in the induction of AIDs of each element.Furthermore, viruses play their role as a trigger, regulators and accelerators of autoimmune diseases.Several animal models explain the role of viruses in lesion development but any such evidence about the virus’s induction for human AIDs is not accessible.However, viruses play a significant role in the triggering and regulation of activated autoreactive lymphocytes other than interrupting the silent autoreactive lymphocytes.Recent data illustrated that viruses can induce AIDs by different mechanisms such as molecular mimicry, bystander activation, epitope spreading and magnification of infected B cells.Accordingly, further research about epidemiology and the molecular mechanism is needed for understanding the different inducers and enhancers of autoimmune pathways.Such outcomes may enlighten the possible ways that how viruses induced autoimmunopathies as well as treatment strategies.
- Life Research的其它文章
- Increased internet addiction during COVID-19 pandemics
- Intracranial hemangiopericytoma with right-sided aortic arch:a case report and summary of experience
- Advances of biodegradable magnesium-based implants for orthopaedics
- Low expression of novel biomarker RCSD1 predicts poor prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma
- Graft rejection after deep anterior lamellar keratoplasty in fellow eye in macular corneal dystrophy:a case report
- Utility of convalescent plasma for addressing the COVID-19 infection:brief review and case reports

