Mechanisms and status of research on the protective effects of traditional Chinese medicine against ischemic brain injury
Zhe-Tao Zhang,Cheng-Yun Hu,Fei-Biao Dai,Fei Tang,Chao-Liang Tang
1Department of Pharmacy, The First Affiliated Hospital of University of Science and Technology of China, Division of Life Sciences and Medicine, University of Science and Technology of China,Hefei 230036,China.2Department of Anesthesiology,Anhui Provincial Hospital,Wannan Medical College,Hefei 230001,China.3Department of Anesthesiology,The First Affiliated Hospital of University of Science and Technology of China,Division of Life Sciences and Medicine,University of Science and Technology of China,Hefei 230001,China.
Abstract Ischemic brain injury occurs when the metabolic needs of brain tissue cannot be met due to insufficient blood supply to the brain.It is one of the main causes of death and adult disability worldwide.The recurrence rate of ischemic brain injury is high.It places a heavy economic burden on families and society, and seriously affects human health and quality of life.In traditional Chinese medicine, ischemic stroke belongs to the category of “stroke”.The use of traditional Chinese medicine to treat stroke has a long history.After years of experimental research, a large amount of theoretical knowledge and practical experience have been accumulated.Promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis is the basis of traditional Chinese medicine theory on the treatment of ischemic stroke.Commonly used single Chinese medicines include Chuangxiong (Ligusticum chuanxiong hort), Danggui (Angelica sinensis),Danshen(Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge),Honghua(Carthamus tinctorius L.),Mudanpi(Moutan Cortex),and Huangqi(Astragali Radix).Buyang Huanwu decoction, Xinglou Chengqi decoction, Taohong Siwu decoction, and other traditional Chinese medicine prescriptions are believed to have a protective effect against brain damage caused by ischemic stroke.With the development of modern medical technology, the mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine treatments for ischemic brain injury has gradually been explored.This article reviews the mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine’s protection against ischemic brain injury and its current clinical application.
Keywords: traditional Chinese medicine; ischemic brain injury; stroke; brain protection;clinical application
Background
Stroke is a common pathology that seriously threatens human health and has become the second leading cause of death worldwide [1].Clinically, it is often divided into two types: hemorrhagic stroke and ischemic stroke, where ischemic stroke accounts for approximately 80%of all cases[2].Brain injury after ischemia is caused by a series of complex pathophysiological cascade reactions, including energy metabolism disorder, excitotoxicity, intracellular Ca2+overload,inflammatory response, and apoptosis [3, 4].These factors occur at different time points, influence and promote each other, and ultimately lead to irreversible brain tissue damage.After cerebral ischemia, irreversible neuronal damage occurs in the core area of the infarct due to cell necrosis in the brain tissue; however, the damage encountered in the penumbra is different.A series of complex reactions occur in the ischemic penumbra, which ultimately leads to neuronal damage, and this slower cell death provides an opportunity for the treatment of ischemic brain injury [4].In the treatment of ischemic stroke, after the reopening of blood vessels, persistent microcirculation and cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury are the main causes of secondary neuronal injury.Therefore, a comprehensive and in-depth elucidation of the pathogenic mechanism of ischemic brain injury and the search for new intervention targets and methods have important clinical practical significance for the prevention and treatment of ischemic brain injury.
Blood brain injury belongs to the category of “stroke” in the theory of traditional Chinese medicine, due to the similarity in their clinical symptoms, such as sudden fainting, violent seizures, and loss of consciousness [5].TheSynopsis of Golden Chamberwritten by the medical sage Zhong-Jing Zhang in the Eastern Han Dynasty of China(184 C.E.-220 C.E.) first used “stroke” to describe stroke patients.The Synopsis of Golden Chamberalso uses Renshen (Panax ginseng) to replenish vital energy, and Danggui (Angelica sinensis) and Chuangxiong (Ligusticum chuanxiong hort) to promote blood circulation[6].During the Sui and Tang Dynasties(581 C.E.-907 C.E.),many doctors began to have a richer understanding of stroke, building on the work of their predecessors.The famous Tang Dynasty physician Si-Miao Sun’sQianjin Prescriptionrecords more herbs used in the treatment of stroke, such as Mahuang (Ephedrae Herba), Guizhi(Cinnamomi Ramulus), Huangqi (Moutan Cortex), and Fuzi (Aconiti Lateralis Radix Praeparata) [7].Subsequently, with the development of Western medicine, the main ingredients of these representative herbs have been identified, and the mechanism underlying their efficacy in stroke therapy has been elucidated; for example, angelica polysaccharide, one of the main ingredients inAngelica sinensis, can increase the activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) in the serum, reducing the malondialdehyde(MDA), nitric oxide (NO), and nitric oxide synthase (NOS) content, to exert its antioxidant effect.
At present, neuroprotective agents in ischemic brain injury show the most potential for research and development; however, their side effects also limit their clinical applications [8].Between 1998 and 2016, more than 12,000 acute stroke patients participated in trials for neuroprotective treatments targeting free radicals, ion channels,excitotoxicity, immune regulation, and inflammation.Common clinical drugs include magnesium, verapamil, nimodipine, edaravone,statins, minocycline, and citicoline [9].However, the results of these trials were unsatisfactory.For example, the large-scale field administration of stroke therapy-magnesium trial [10] showed that compared with placebo, magnesium sulfate did not improve the primary outcome.Edaravone has been approved for use in Japan and China; however, its clinical efficacy is not supported by high-quality data, and adverse reactions, such as abnormal liver function, occur during treatment.Therefore, the development of new therapeutic agents or combination therapies is urgently needed.According to the composition of medicines, Chinese medicine can be divided into single Chinese medicine, paired Chinese medicines, and Chinese medicine compounds.Chinese medicines have the unique advantages of having multiple components, multiple targets, and multiple effects.In recent years, many experimental studies have shown that traditional Chinese medicine has good effects in the prevention and treatment of ischemic brain injury [11].This review will discuss the prevention and treatment mechanisms and clinical application of traditional Chinese medicine in ischemic brain injury according to modern clinical theories to provide new ideas and a theoretical basis for the prevention and treatment of ischemic brain injury.
Ischemic brain injury in Chinese and Western medicine
Ischemic stroke is a type of cerebrovascular disease in modern clinical medicine, and in traditional Chinese medicine, it belongs to the category of “stroke” due to the similarity in their clinical symptoms.According to the classic clinical book of traditional Chinese medicine,Synopsis of Golden Chamber, the name “stroke” was created, and its symptoms were summarized as insufficient concealment [12].
Modern Western medicine states that ischemic brain injury is caused by various factors, including hypotension, infection, brain trauma, and cerebrovascular sclerosis, which lead to a sudden decrease or complete interruption of blood perfusion of local brain tissue.The lack of blood perfusion causes neuronal ischemia and hypoxia in the ischemic area, energy metabolism disorders, and damage to the surrounding tissues, such as congestion and swelling[13], which leads to changes in the patient’s state of consciousness and muscle tension.
The pathological mechanisms underlying ischemic brain injury are complicated.The ischemic brain tissue is not supplied with sufficient oxygen; this means that neurons cannot maintain normal transmembrane ion gradients and homeostasis, which in turn leads to cell excitotoxicity, inflammation, oxidative stress, nitrifying stress,and apoptosis[4, 14].After ischemia, adenosine triphosphate levels in the local brain tissue are depleted, leading to the release of intracellular Na+and the extracellular excitatory amino acid,glutamate.The increase in Na+concentration can cause cell edema,and the released glutamate binds to α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptors and passes through ion channels to increase the level of intracellular Ca2+, leading to mitochondrial failure and apoptosis, thereby causing neuronal energy metabolic disorders and excitotoxicity [15-18].
In addition, after cerebral ischemia, immune cells produce reactive oxygen species, which stimulate endothelial cells, causing oxidative stress and promoting the expression of autophagic factors, leading to neuronal autophagy [19].Glial cells, peripheral immune cells, and endothelial cells activated during ischemia synthesize many pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines to participate in the inflammatory response, increasing the permeability of the blood-brain barrier (BBB), further aggravating brain edema and eventually leading to neuronal necrosis [15].
Modern clinical theories of traditional Chinese medicine regarding protective mechanisms of ischemic brain injury
In China, the use of traditional Chinese medicine to treat stroke has a long history.The promotion of blood circulation to remove blood stasis is the fundamental treatment for ischemic stroke according to traditional Chinese medicine theory.Commonly used single-agent medicines based on traditional Chinese medicine theory includeLigusticum chuanxiong hort,Angelica sinensis, Danshen (Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge), Honghua (Carthamus tinctoriusL.), Chishao(Paeoniae Radix Rubra), andMoutan Cortex.
In modern pharmacological research,Ligusticum chuanxiong horthas been shown to have multiple effects, including improving the microcirculation, anti-platelet aggregation, analgesia,anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidation, and cell protection [19].Its active ingredients are mainly ligustrazine, ferulic acid, and ligustilide [20].Ligustrazine can reduce the content of MDA in the serum, increase the activity of SOD, exert antioxidant effects, control blood flow rate,promote blood circulation, and exert anti-platelet aggregation and anti-thrombosis effects, consequently reducing the infarct size and water content, improving nerve function [21], downregulating the expression of meridian Bax mRNA [22], inhibiting the Bax/Bcl-2 and caspase-3 apoptotic pathway, activating phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase(PI3K) and phospho-Akt protein [23], and inhibiting neuronal apoptosis.Ligustrazine antagonizes Ca2+, improves hypoxia, relaxes vascular smooth muscle, resists atherogenesis, and has a protective effect against ischemia-reperfusion [24].Ferulic acid can exert an inhibitory effect on inflammatory molecules through the extracellular regulated protein kinases (ERK) signaling pathway, inhibit the activation of microglia, and further inhibit neuroinflammation [25].Ligustilide can reduce intracellular MDA content, increase SOD activity, increase extracellular NO content and intracellular NOS activity, increase intracellular hypoxia inducible factor-1 α, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression, and tubulin content,resist cell oxidative damage, and regulate blood vessel endothelial cell function [26].
Angelica sinensisnourishes blood, promotes blood circulation,regulates menstruation, and relieves pain.Its main active components include angelica polysaccharide, ferulic acid, and ligustilide.Angelica polysaccharide can increase the activity of SOD and GSH-Px in the serum and reduce the content of MDA, NO, and NOS to exert its antioxidant effect.It can reduce the tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α)and interleukin (IL)-1β and the expression levels of Toll-like receptor(TLR) 4 and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), p65 protein, and inhibit the activation of the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway[27].It also regulates the levels of the apoptosis-related proteins, Bcl-2 and Bax, and downregulates the expression of p-Raf1, phospho-mitoge-activated protein kinase 2, and p-ERK1/2 in the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway[28], inhibiting cell apoptosis in ischemic brain tissue, and reducing neurological deficits in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury.Ferulic acid can inhibit the nuclear translocation of NF-κB p65 [29],reduce the inflammatory response of nerve cells, inhibit miRNA-9,reduce the expression of acetylcholinesterase, and brain-derived neurotrophic factor [30], and has a neuroprotective effect after ischemia and hypoxia injury.This lactone can also interfere with intracellular Ca2+metabolism, reduce the level of TNF-α in ischemic tissues, improve neurological damage caused by ischemia-reperfusion[31], and reduce the area of cerebral infarction, cerebral edema, and vascular permeability.
Salvia miltiorrhiza Bungeactivates blood circulation, removes blood stasis, and relieves pain.The main components include tanshinone,danshensu, and salvianolic acid, which have good anti-inflammatory,antioxidant, and anti-apoptotic activities.Among them, salvianolic acid A reduces cerebral ischemic damage through the Akt pathway[32].Salvianolic acid B can increase SOD and GSH-Px activity in the tissues, reduce the MDA content, and reduce the NOS activity to exert an antioxidant effect; it can also inhibit vascular flow caused by VEGF.Increased permeability, thereby reducing vascular permeability, can protect against ischemic stroke by activating the PI3K/Akt/GSK3p/p-catenin signaling pathway [33].Tanshinone IIA can reduce levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, and other inflammatory factors; β-catenin, p53, and Bax mRNA and protein levels [34]; inhibit Wnt/β-catenin/p53 signaling pathway-mediated inflammation and apoptosis,and cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury.
Carthamus tinctoriusL.is a traditional Chinese medicine used to promote blood circulation, remove blood stasis, and relieve pain.The main ingredient inCarthamus tinctoriusL.extract is safflower yellow,in which hydroxysafflor yellow A is the main active ingredient; this promotes blood circulation and removes blood stasis [35].Carthamus tinctoriusL.extract increases SOD, GSH-Px, and catalase enzymes activity in the brain tissue, reduced the content of MDA[36],removed excessive oxygen free radicals, and reduced the damage of inflammatory factors to the brain tissue.Hydroxysafflor yellow A can protect the integrity of mitochondrial structure, improve brain energy metabolism, inhibit the release of lactate dehydrogenase and NO, and reduce IL-1β and TNF-α levels [37], protecting brain neurons and inhibiting inflammatory responses.It increases platelet derived growth factor levels, activates the PI3K/Akt pathway, and plays a neuroprotective effect [38, 39]; activates TLR4 protein, regulates the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, maintains blood stability of the brain barrier,and reduces brain edema [40], in turn reducing blood viscosity,anti-platelet aggregation, and improving blood circulation in the brain[41].
Yinxing (Ginkgo bilobaL.) is a traditional Chinese herbal medicine that has been widely used to treat brain diseases for thousands of years.Ginkgo bilobaL.extract EGb-761 contains approximately 24%ginkgo flavonoid glycosides, 6% terpene lactones, and a small amount of bilobalide [42].Flavonoids and terpene trilactones are generally considered the biologically active ingredients in EGb-761 [43].EGB-761 not only increases blood flow after cerebral ischemia [44],but also reduces reperfusion injury after blood flow recovery by enhancing the scavenging effect of free radicals [45].It has been proven that EGB-761 can reduce excitotoxicity by inhibiting the release of glutamate caused by ischemia [46], reduce infarct volume,inhibit cell apoptosis, and improve neurological function [47].EGb-761 can also exert a neuroprotective effect by increasing the expression of hypoxia inducible factor-1 α [48] and targeting autophagy cells in neurons [49].Ginkgolide N can effectively reduce NOS activity and NO production, and indirectly reduce the content of peroxynitrite to reduce cerebral ischemic damage[50].
Moutan Cortexis a traditional Chinese medicinal material used to invigorate Qi.The main components of astragalus extract are total astragalus glycosides and astragalus polysaccharides, of which astragaloside IV is the main active ingredient.Astragaloside IV can significantly increase SOD, GSH-Px, and catalase enzymes and reduce MDA content in brain tissue [51].Activation of Akt promotes the binding of hexokinase-II and mitochondria [52], ensuring the structural and functional integrity of mitochondria and thus protecting neurons from apoptosis.It can also increase the expression of zonula occludens-1 protein in endothelial cells [53], downregulate the IL-1β content, inhibit the expression of matrix metallopeptidase 9 protein [54], and weaken the permeability of BBB to maintain stability(Figure 1).
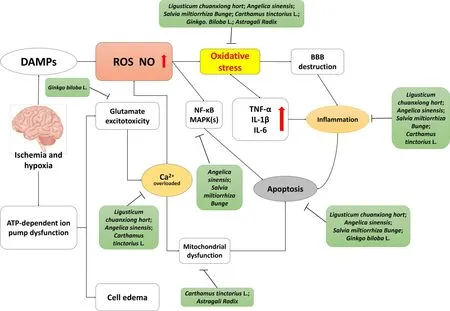
Figure 1 Mechanisms of five traditional Chinese medicines for the protection of ischemic brain injury.There are many molecular patterns of brain ischemia-induced damage.Current research shows that Chinese herbal medicine can play a protective role at multiple targets, thereby reducing brain damage after cerebral ischemia.→: promote; ├: restrain; DAMPs, damage associated molecular patterns; ROS, reactive oxygen species; NO, nitric oxide; BBB, blood-brain barrier; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α; IL, interleukin; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; MAPK mitogen-activated protein kinase; Ligusticum chuanxiong hort,Chuangxiong; Angelica sinensis, Danggui; Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge, Danshen; Carthamus tinctorius L., Honghua;Ginkgo biloba L., Yinxing; Moutan Cortex, Huangqi.
Modern clinical theories of traditional Chinese medicine prescriptions regarding mechanisms of protection against ischemic brain injury
According to previous studies, traditional Chinese medicine prescriptions have certain protective effects against inflammation,oxidative stress, excitotoxicity, increased oxygen free radical levels,and BBB damage caused by ischemic brain injury, and they also have characteristics such as having multiple targets and multiple pathways.Modern pharmacological studies have shown that the active ingredients of traditional Chinese medicine can reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, inhibit endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis, and regulate BBB permeability, thereby promoting the repair of brain tissue and further improving the function of brain tissue [55, 56].Traditional Chinese medicine is based on different pathogeneses of ischemic brain injury, and there are also types of Chinese medicine with different pharmacological effects.
The classic Chinese medicine prescription, Buyang Huanwu decoction, includesMoutan Cortex,Angelica sinensis,Ligusticum chuanxiong hort,Radix paeoniae rubra, andCarthamus tinctoriusL.[53,54].Experimental studies in animals have shown that Buyang Huanwu decoction protects the brain through a variety of mechanisms[57].First, it can inhibit the infiltration of natural killer cells by inhibiting NF-κB-mediated chemotaxis, reduce levels of inflammatory factors, maintain the BBB integrity, and improve the prognosis of ischemic brain injury [58].Second, it can increase blood vessel density, promote angiogenesis, improve cerebral circulation, and produce brain protection by regulating SIRT1/VEGF pathway [59].Moreover, it can inhibit cell apoptosis by inhibiting the reduced Nox4/ROS pathway, induce angiogenesis, and promote the recovery of nerve function [60].In addition, Buyang Huanwu decoction can also reduce the production of TNF-α and IL-6 in the brain of the rat cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury model.Increased levels of anti-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-10 and transforming growth factor-β, reduce inflammation and protect brain tissue [61].
The classic Chinese medicine prescription Huatan Tongluo decoction is composed ofLigusticum chuanxiong hort,Salvia miltiorrhizaBunge,Carthamus tinctoriusL., processed Banxia (Rhizoma Pinelliae),and Zhiqiao (Aurantii Fructus).In animal models of ischemic brain injury, Huatan Tongluo decoction can block HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in brain tissue, thereby inhibiting the expression of inflammatory factors including TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β and exerting a protective effect [62].Huatan Tongluo decoction can partially inhibit the apoptosis of nerve cells and produce neuroprotective effects by inhibiting the apoptotic pathway initiated by endoplasmic reticulum stress [63], reducing the permeability of the BBB, protecting the brain by preserving the ultrastructure of cerebral cortex endothelial cells,and regulating the expression of microvascular endothelial cell constituent proteins[64].
The classic Chinese medicine prescription Banxia Baizhu Tianma decoction is composed ofRhizoma Pinelliae, Baizhu (Rhizoma Atractylodes macrocephala),Tianma(Gastrodiae Rhizoma),Fulin(Poria),and Gancao (Glycyrrhiza uralensisFisch.).In patients with acute cerebral infarction treated with Banxia Baizhu Tianma decoction, the levels of D-dimer, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, and fibrinogen were significantly lower, thereby improving neurological deficits [65].Although it has been used clinically for a long time, the pharmacological effects of Banxia Baizhu Tianma decoction on stroke have not been thoroughly explored, and there are few reports on its mechanisms of action; further research on its micro-mechanism is needed to widen its application.Yang compared the effects of edaravone alone and combined with Banxia Baizhu Tianma decoction in patients with cerebral infarction and found that the blood supply and nerve function of the brain were significantly better in patients given the combined treatment [66].
The classic Chinese medicine prescription Xinglou Chengqi decoction is mainly composed of Gualou (Trichosanthes kirilowii Maxim.), Dannanxing (Arisaema Cum Bile), Dahuang (Rhei Radix etRhizoma), and Mangxiao (Natrii Sulfas) [67].In a rat model of acute ischemic stroke, Xinglou Chengqi decoction increased the blood SOD content and reduced the MDA level, resulting in a significant decrease in brain tissue water content, which suggests that it may protect the brain by reducing oxygen free radical damage [68].It can also reduce the expression of serum IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6, and other pro-inflammatory factors in rats with cerebral hemorrhage, reduce cerebral edema caused by inflammation and damage to peripheral brain tissue neurons, and reduce BBB permeability, which in turn produces neuroprotective effects [69, 70].In addition, Xinglou Chengqi decoction can significantly reduce intracellular adhesion molecule-1 levels and increase the expression of VEGF in the ischemic penumbra, thereby protecting vascular endothelial cells and lengthening cell survival time[71].
The classic Chinese medicine prescription, Taohong Siwu decoction,is based on Siwu decoction supplemented by two Chinese medicines,Tiaoren (Persicae Semen) andCarthamus tinctoriusL.It is a representative prescription for the effective basic treatment of stroke for promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis.An increasing number of studies have shown that Taohong Siwu decoction has beneficial effects in terms of anti-oxidation, ischemia,and protection of nerve cells in ischemic brain areas [72].Wu found that Taohong Siwu decoction can inhibit hypoxia inducible factor-1 α and TNF-α activation, thereby inhibiting the inflammatory response in the brain and cell apoptosis, and exerting its protective effect against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in middle cerebral artery occlusion model rats [73].Taohong Siwu decoction can alleviate the damage of vascular endothelial cells and maintain their normal secretory function; endothelial progenitor cells can promote the repair of endothelial injury, increase the number of endothelial progenitor cells, and promote cell functions.High-concentration Taohong Siwu decoction exhibited the best interventional effect at 24 h after intervention [74].In clinical application, for patients with acute cerebral infarction, if Taohong Siwu decoction is administered in the early stages, the postoperative recovery effect will be more obvious;moreover, the treatment is extremely safe (Figure 2) [75].
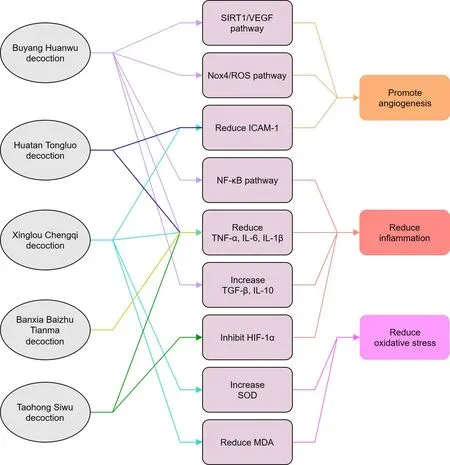
Figure 2 Research progress of signal pathways on five kinds of traditional Chinese medicine prescriptions for the treatment of stroke.Research on pharmacological action signal pathways has found that traditional Chinese medicine prescriptions can exert anti-inflammatory,anti-oxidant and promote angiogenesis effects through multiple targets.Classic Chinese medicine prescription Buyang Huanwu decoction includes Huangqi (Moutan Cortex), Danggui (Angelica sinensis), Chuangxiong (Ligusticum chuanxiong hort), Chishao (Radix paeoniae rubra) and Honghua(Carthamus tinctorius L.).Classic Chinese medicine prescription Huatan Tongluo decoction is composed of Ligusticum chuanxiong hort, Danshen(Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge), Carthamus tinctorius L., processed Banxia (Rhizoma Pinelliae), Zhiqiao (Aurantii Fructus), etc.Classic Chinese medicine prescription Banxia Baizhu Tianma decoction is composed of Rhizoma Pinelliae, Baizhu (Rhizoma Atractylodes macrocephala), Tianma (Gastrodiae Rhizoma), Fulin (Poria), Gancao (Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch.), etc.Classic Chinese medicine prescription Xinglou Chengqi decoction which mainly includes Gualou (Trichosanthes kirilowii Maxim.), Dannanxing (Arisaema Cum Bile), Dahuang (Rhei Radix et Rhizoma), Mangxiao (Natrii Sulfas).Classic Chinese medicine prescription Taohong Siwu decoction is based on Siwu decoction, supplemented with 2 Chinese medicines Tiaoren(Persicae Semen)and Carthamus tinctorius L.ICAM-1,intracellular adhesion molecule-1;TNF-α,tumor necrosis factor α;NF-κB,nuclear factor-κB;IL,interleukin; TGF-β,transforming growth factor-β; HIF-1α, hypoxia inducible factor-1 α; SOD, superoxide dismutase; MDA, malondialdehyde.
Summary
It is well known that all ischemic brain injury, as a disease with high disability and mortality rates, will have sequelae such as headache,nervousness, ataxia, and mental retardation if not treated promptly.Therefore, its related pathological processes, pathogenesis, and development mechanisms have received considerable attention from researchers.In modern clinical medicine, Western medicine plays a dominant role; however, there is no particularly effective method for treating ischemic brain injury in Western medicine.Therefore, the treatment and mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine have attracted increasing attention from most scholars.At present,investigations on the mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine treatment for ischemic brain injury is mostly focused on animal experiments, and its clinical use is relatively limited.Based on the results of modern pharmacological studies, we should take full advantage of the multi-target, multi-level, and multi-channel nature treatment of traditional Chinese medicine and explore the possible roles and mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine treatment(Figure 3).Traditional Chinese medicine practitioners have dialectically applied treatments according to various syndromes of ischemic brain injury.After years of practice, they have gained rich experience in medication with definite efficacy and high patient acceptance, which can provide theoretical scientific guidance for the research and development of new drugs and clinical drug selection for the treatment of ischemic brain injury.However, there is a problem with the small sample size in current studies on the efficacy of traditional Chinese medicine.Therefore, large-scale, high-quality randomized controlled studies should be carried out clinically in the future to provide a more scientific and reasonable basis for the expanded application of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of ischemic brain injury.
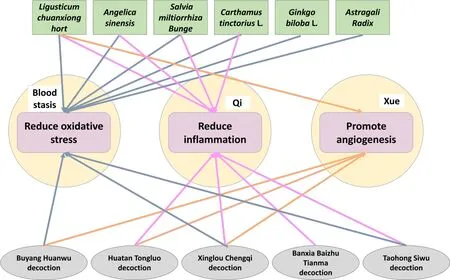
Figure 3 The target of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of stroke.The theory of traditional Chinese medicine believes that the mechanisms of Chinese herbal medicines and prescriptions for the treatment of stroke include: replenishing Qi, nourishing blood, and removing blood stasis, which are consistent with the current research findings to reduce inflammation, promote angiogenesis, and reduce oxidative stress.Classic Chinese medicine prescription Buyang Huanwu decoction includes Huangqi (Moutan Cortex), Danggui (Angelica sinensis), Chuangxiong(Ligusticum chuanxiong hort), Chishao (Radix paeoniae rubra) and Honghua (Carthamus tinctorius L.).Classic Chinese medicine prescription Huatan Tongluo decoction is composed of Ligusticum chuanxiong hort, Danshen (Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge), Carthamus tinctorius L., processed Banxia(Rhizoma Pinelliae), Zhiqiao (Aurantii Fructus), etc.Classic Chinese medicine prescription Banxia Baizhu Tianma decoction is composed of Rhizoma Pinelliae, Baizhu (Rhizoma Atractylodes macrocephala), Tianma (Gastrodiae Rhizoma), Fulin (Poria), Gancao (Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch.), etc.Classic Chinese medicine prescription Xinglou Chengqi decoction which mainly includes Gualou (Trichosanthes kirilowii Maxim.), Dannanxing (Arisaema Cum Bile), Dahuang (Rhei Radix et Rhizoma), Mangxiao (Natrii Sulfas).Classic Chinese medicine prescription Taohong Siwu decoction is based on Siwu decoction, supplemented with 2 Chinese medicines Tiaoren (Persicae Semen) and Carthamus tinctorius L.
 Traditional Medicine Research2022年1期
Traditional Medicine Research2022年1期
- Traditional Medicine Research的其它文章
- The artificial intelligence watcher predicts cancer risk by facial features
- Evaluation of bioactive flavonoids in Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium from different regions and its association with antioxidant and α-glucosidase inhibitory activities
- Exploring the anti-diabetic effects and the underlying mechanisms of ethyl acetate extract from Sophora flavescens by integrating network pharmacology and pharmacological evaluation
- Effects of Shenling Baizhu powder on endoplasmic reticulum stress related signaling pathway in liver tissues of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease rats
- Artificial neural network techniques to predict the moisture ratio content during hot air drying and vacuum drying of Radix isatidis extract
- Safety of Lycium barbarum L.:more information needed
