Effects of Shenling Baizhu powder on endoplasmic reticulum stress related signaling pathway in liver tissues of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease rats
Ling Jin,Mao-Xing Pan,Yuan-Jun Deng,Xue-Hua Luo,Li Han,Yu-Pei Zhang*,Qin-He Yang*
1The First Affiliated Hospital of Jinan University,Guangzhou 510630,China.2Jinan University,Guangzhou 510632,China.
Abstract Background: According to our previous studies, Shenling Baizhu powder has an excellent preventive and therapeutic effect on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, but the prevention mechanism is still not clear.In this study, we intended to explore the effects of Shenling Baizhu powder on the endoplasmic reticulum stress related signaling pathway in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease rats’ liver tissues. Methods: After 16 weeks, the levels of serum total cholesterol,triglyceride, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, alanine transaminase and aspartate transaminase were evaluated by an automatic biochemical analyzer,and the levels of serum free fatty acid and hepatic total cholesterol and triglyceride were evaluated by commercial kits.Then, histological changes of the liver were observed by hematoxylin and eosin and oil red-O staining.Protein expression related to the liver unfolded protein response signalling pathway was assessed using Western blot analysis. Results: The results showed that Shenling Baizhu powder supplementation reduced serum total cholesterol,triglyceride, free fatty acid, alanine transaminase, and aspartate transaminase(P< 0.05 or P <0.01), as well as the levels of hepatic total cholesterol and triglyceride (P < 0.01).Pathological examination showed that Shenling Baizhu powder improved hepatic steatosis and lipid accumulation.The results of biochemical parameters and histological changes indicated that Shenling Baizhu powder administration exerted protective effects against nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.In addition, Shenling Baizhu powder decreased the protein expression levels of binding immunoglobulin protein, activating transcription factor 6, phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha, protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase and X-box binding protein 1s in the liver (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01). Conclusion: Shenling Baizhu powder can ameliorate high-fat diet-induced liver lipid metabolism disorder in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease rats.The mechanisms may be related to the inhibition of the expression of proteins related to unfolded protein response signaling pathways in endoplasmic reticulum stress.
Keywords: nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; Shenling Baizhu powder; endoplasmic reticulum stress; unfolded protein response signaling pathways
Background
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a clinical and pathological syndrome, and its distinctive feature is hepatocyte steatosis not due to alcohol and other liver injury factors [1].As a common chronic liver disease, it has an influence on approximately 25% of the world’s population [2].The pathogenesis of NAFLD is very complicated.The most widely accepted is the “two-hit hypothesis” and the “multiple parallel hits” theory [3, 4].According to this theory, a high-fat diet(HFD), obesity, insulin resistance and other factors cause excessive fat to accumulate in the liver.Then, the accumulation of liver fat triggers reactions such as oxidative stress, endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS),and mitochondrial dysfunction.The combined action of multiple factors induces chronic liver inflammation, which in turn leads to the progression of NAFLD [3].The persistence of the inflammatory response leads to further inflammation - necrosis cycle, resulting in fatty liver fibrosis or cirrhosis [1].
The endoplasmic reticulum is the largest organelle, specialized in protein folding processing and quality control in eukaryotic cells.It is also an important place for lipid synthesis.The homeostasis of the endoplasmic reticulum is essential for maintaining the normal physiological functions of cells [5].Factors such as free fatty acid(FFA), oxidative stress, and calcium imbalance will lead to ERS,activating the unfolded protein response (UPR) signaling pathway [5,6].The activation of the UPR signaling pathway involves three endoplasmic reticulum transmembrane proteins: inositol requiring enzyme 1 (IRE1), protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase(PERK)and activating transcription factor 6(ATF6).Under ERS,these three proteins dissociate from the binding immunoglobulin protein (BiP), thereby activating the UPR signaling pathway [6].As demonstrated in some studies, during the progress of NAFLD, a high fat diet will cause chronic ERS to continuously stimulate the UPR signaling pathway, promote liver lipid synthesis, and inhibit the decomposition and excretion of lipids in liver cells, thereby increasing liver fat accumulation.Furthermore, improving the ERS exerts an important effect in alleviating the progress of NAFLD [6, 7].
In traditional Chinese medicine, Shenling Baizhu powder is a classic and effective prescription obtained fromPrescriptions of the Bureau of Taiping People’s Welfare Pharmacy, an official traditional Chinese medicine clinical book prepared during the Song dynasty about a thousand years ago(written by Shi-Wen Chen, during 1078 C.E.-1085 C.E.).Our previous studies have shown that Shenling Baizhu powder can alleviate NAFLD through anti-hepatic steatosis, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities [8, 9].However, the mechanism behind its protective effects is still not clearly defined.Since the activation of UPR signaling pathways in ERS plays an important role in the occurrence and development of NAFLD, in our current study, we intended to explore the mechanism of Shenling Baizhu powder in the treatment of NAFLD from the perspective of ERS and provide a molecular biological basis for using Shenling Baizhu powder to prevent and treat NAFLD.
Material and methods
Medicines
The original composition of Shenling Baizhu powder includes 10 plant materials (formula granules purchased from Tian Jiang Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Jiangyin, China), as listed in Table 1.The above-mentioned medicines were selected from the same batch of traditional Chinese medicine granules (delivery number: 9601159)provided by Tian Jiang Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.(Jiangyin, China).It is prepared through a series of modern technologies such as extraction,concentration, and drying of Chinese herbal medicines and fully dissolved with double distilled water before use.
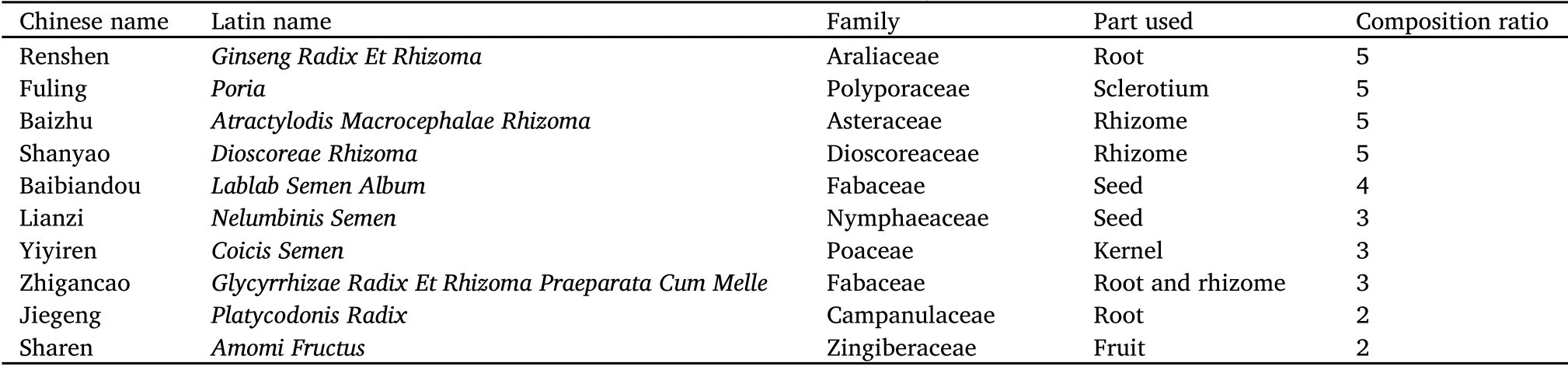
Table 1 Detailed information of Shenling Baizhu powder
Animals
Twenty-four 6-7-week-old specific pathogen-free male Sprague-Dawley rats, (200 ± 20) g body weight, were provided by Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine’s Laboratory Animal Center (animal license number: SCXK (Guangdong) 2013-0034) and raised in Jinan University’s Laboratory Animal Management Center(breeding environment certificate number: SYXK (Guangdong)2012-0117).All experimental procedures were conducted according to a protocol approved by the Laboratory Animal Ethics Committee of Jinan University (animal ethics number: 20130628015)
The basic feed was provided by Jinan University’s Laboratory Animal Management Center, and the high-fat feed was prepared and provided by the Guangdong Medical Laboratory Animal Center(license number: SCXK (Guangdong) 2013-0002).The high-fat feed was composed of maintenance feed, lard, cholesterol, bile salt and sucrose, uniformly mixed in the ratio of 83: 10: 1.5: 0.5: 5 and sterilized by cobalt-60 radiation.
Experimental procedures
After adaptive feeding for one week, we divided rats into the normal control (N) group, model (M) group and Shenling Baizhu powder group, each with 8 rats.It is well known that animal models simulating human disease would be a valuable tool to investigate the pathogenesis and pathophysiology of NAFLD.The HFD-induced NAFLD model has always been used for some time to provide a better understanding of this disease [10].In the previous study, our team used 16-week HFD to feed rats and successfully induced the rat NAFLD model through the evaluation of a pathological “gold standard” and biochemical index detection, which manifested the pathogenesis and histopathological characteristics of human NAFLD[9].With reference to the existing model building methods of our team, we established the NAFLD rat model as follows: the N groupHFD containing 37% of energy as fat, 22% as protein and 41% as carbohydrate for modeling.The Shenling Baizhu powder group was administered a dose of 30 g/kg/day by oral gavage (3 times the clinical equivalent dose, which is the optimal dose determined in the previous study [8]), and the other two groups were administrated with the same dose of experimental animal drinking water, one time a day for 16 consecutive weeks.Rats were housed in separate cages in a specific pathogen-free environment, with an ambient temperature of(22 ± 2) °C, 60% ± 5% humidity, and a standard 12-hour light/dark cycle.They were given free access to food and water.
Reagents
Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining solution and oil red-O (ORO) kit were purchased from Nanjing Jiancheng Technology Co., Ltd(Nanjing,China).Bicinchoninic acid protein assay kit was purchased from Beyotime Biology Co., Ltd.(Shanghai, China).Internal control β-actin antibody was purchased from Kangchen Bio-tech Co., Ltd.(Shanghai,China).Mouse anti-rat C/EBP-homologous protein (CHOP), rabbit anti-rat BiP, PERK, phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha (p-eIF2α), activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4), X-box binding protein 1s (XBP-1s) protein antibodies were purchased from Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.(Boston, Massachusetts, USA).Mouse anti-rat ATF6 and rabbit anti-rat inositol requiring enzyme 1 alpha(IRE1α) protein antibodies were purchased from Novus (Littleton,Colorado, USA).FFA, total cholesterol (TC), and triglyceride (TG) kits were purchased from Nanjing Jiancheng Technology Co., Ltd.(Nanjing, China).High-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) kit was purchased from Maccura Biotechnology Co., Ltd.(Chengdu,China).Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) kit was purchased from Dongou Diagnostic Products Co., Ltd.(Wenzhou, China).Alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST) kits were purchased from Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd.(Osaka, Japan).
Specimen collection
After 16 weeks of continuous administration, all rats were fed only with water for 12 h, and then anesthetized with 3% sodium pentobarbital (1 mL/kg) through intraperitoneal injection, and blood samples were taken from the abdominal aorta with a vacuum blood collection needle.Furthermore, some tissues from the same site of the right lobe of the rat liver (2 cm from the edge of the liver) were taken for related detection.
Histopathological examination of liver tissues
Several fresh liver tissues were taken from the same site,approximately 1.0 cm × 1.0 cm × 0.5 cm in size, fixed with neutral buffered formalin (10%), 3-5 μm thick paraffin sections were prepared, HE stained, mounted, and the pathological changes in liver tissues were observed using a microscope.In addition, several fresh liver tissues samples were taken, and small pieces of liver tissues were fixed on the Cryostat Microtome with optimum cutting temperature embedding agent for 15 min.The thickness of the sections was 8-10 μm, and the regular ORO staining was performed.Then, the distribution of lipid droplets in liver tissues was observed using a light microscope.
Detection of biochemical indicators
After being placed for 30 min at room temperature, the abdominal aortic blood was centrifuged (4 °C, 3,000 r/min, 10 min), and the upper serum was first collected and then placed in a centrifuge tube.The 7600 fully automatic biochemical analyzer (Hitachi, Ltd., Tokyo,Japan) was used to detect the serum TG, TC, HDL-C, LDL-C, ALT, and AST levels.Serum FFA,hepatic TC and TG levels were measured using a commercial kit according to the manufacturer’s protocols.Briefly,the serum to be measured was added to a 96-well plate, and the reaction solution was added according to the manufacturer’s protocol.After mixing, the mixture was incubated at 37 °C for 5 min.The absorbance value was measured at 546 nm wavelength with a microplate reader, and the FFA content was calculated.At the same time, 100 mg of liver tissues were weighed and mixed with 0.9 mL isopropanol in a centrifuge tube.Liver homogenate was prepared,centrifuged (4 °C, 3,000 r/min, 10 min), and the supernatant was collected for measurement.Then, the supernatant was added to a 96-well plate, and the reaction solution was added according to the manufacturer’s protocols.After mixing, the mixture was incubated at 37°C for 5 min.The absorbance value was detected at a wavelength of 510 nm with a microplate reader to detect TC and TG contents.
Western blot analysis.
Western blotting was used to measure the protein expression of the UPR signalling pathway in the liver.β-actin was used as the endogenous control to normalize the data.Proteins were extracted from approximately 100 mg of liver tissue with radioimmunoprecipitation assay lysates and quantified with a bicinchoninic acid protein concentration determination kit.Equal amounts of protein from each group were separated by 10% sodium dodecyl sulphate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and transferred onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes (Millipore, Germany).The membranes were incubated with the corresponding primary antibodies at 4 °C overnight, and the antibodies used in this study were rabbit anti-rat BiP (1: 1,000 dilution), mouse anti-rat CHOP (1:1,000 dilution), mouse anti-rat ATF6 (1: 1,000 dilution), rabbit anti-rat PERK (1: 1,500 dilution), rabbit anti-rat p-eIF2α (1: 1,000 dilution), rabbit anti-rat ATF4 (1: 1,500 dilution), mouse anti-rat IRE1α (1: 1,000 dilution) and rabbit anti-rat XBP-1s (1: 1,000 dilution).Subsequently, membranes were incubated with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated anti-rabbit or anti-mouse secondary antibody(1: 3,000 dilution) at room temperature for 1 h and were visualized with an enhanced chemiluminescence detection system exposed to X-ray film (Eastman Kodak Company, Rochester, New York, USA).
Statistical analysis
All data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation and were analyzed with SPSS 22.0 software (IBM Corp., Armonk, New York,USA).One-way analysis of variance was performed to compare the means between groups; when the variance was homogeneous, the Bonferroni method was employed to establish comparisons between groups; when the variance was not homogeneous, Tamhane’s T2 test was carried out to establish comparisons; values ofP< 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
Pathological observation of liver tissues
For histological analyses, liver tissues were stained with HE and ORO staining.As shown in Figure 1, according to results of the HE staining,the liver lobules of the N group rats were normal in structure, outlines were clear, hepatic cords were arranged in a neat and radial manner around the central vein, hepatic sinusoids were normal, hepatocytes were polygonal with clear borders, without obvious pathological changes, with clear nuclear structure, located in the center of the cell,and rich in cytoplasm.By comparison, the liver lobules of the rats in the M group were difficult to identify, the liver cord was disordered,and the hepatocytes were swollen like a balloon; there were vacuoles of varying sizes in the cytoplasm, mainly vesicles, and in the lobules and in the portal area, there were inflammatory cell infiltrates, and it was difficult to find normal hepatocytes.The above changes indicate that the fatty liver model was successful and showed moderate fatty change.By comparison with the M group rats, the lipid droplets in the Shenling Baizhu powder group were significantly reduced, and the fatty degeneration of hepatocytes in the Shenling Baizhu powder group was significantly improved.According to results of the ORO staining, the hepatocyte nucleus of rats in the N group was blue, there were no obvious lipid droplets in the hepatocytes, the hepatocyte gap was clear, and the liver sinusoid structure was normal.Hepatocytes of the M group rats were significantly enlarged, diffuse red-stained lipid droplets were seen, and the lipid droplets in adjacent liver cells were fused into a sheet, and the cell boundaries were not clear.By comparison with the M group, the lipid droplets in the Shenling Baizhu powder group were significantly reduced.
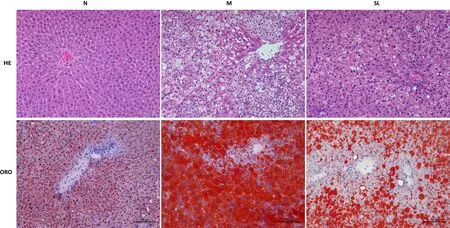
Figure 1 Representative images of HE staining (magnification, 200×) and ORO staining (magnification, 200×) of the liver.N, normal control group; M, model group; SL, Shenling Baizhu powder group; HE, hematoxylin and eosin; ORO, oil red-O.
Changes in serum and liver lipid content of rats
As shown in Figure 2, compared to the N group, serum TC, TG, LDL-C levels, FFA content, liver tissue TC, TG content of M group rats were significantly increased (P< 0.05,P< 0.01), while the HDL-C level was significantly decreased (P< 0.01); by comparison with the M group, the serum TC, TG and FFA content, liver tissue TC and TG content of the Shenling Baizhu powder group were decreased by varying degrees (P< 0.05,P< 0.01), and the changes in serum HDL-C and LDL-C content were not statistically significant (P> 0.05).All of the results indicate that Shenling Baizhu powder can regulate abnormal biochemical parameters in the rats with NAFLD.
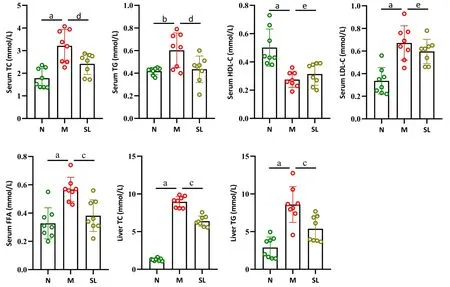
Figure 2 The results of biochemical parameter measurements.Values are presented as the mean ± standard deviations.Differences were assessed by ANOVA.a, P < 0.01 vs the N group; b, P < 0.05 vs the N group; c, P < 0.01 vs the M group; d, P < 0.05 vs the M group; e, no significance; N, normal control group; M, model group; SL, Shenling Baizhu powder group; TC, total cholesterol; TG, triglyceride; HDL-C,high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; FFA, free fatty acid.
Changes in serum ALT and AST levels of rats
As shown in Figure 3, compared to the N group, the serum ALT and AST levels of the M group rats were significantly increased (P<0.01);compared to the M group, the serum ALT and AST levels of the Shenling Baizhu powder group rats were significantly decreased (P<0.01), indicating that Shenling Baizhu powder can reduce serum ALT and AST levels in NAFLD rats.
Figure 3 Results of serum ALT and AST measurements.Values are presented as the mean ± standard deviations.Differences were assessed by ANOVA.a,P<0.01 vs the N group;c,P<0.01 vs the M group;N,normal control group;M,model group;SL,Shenling Baizhu powder group;ALT,alanine transaminase; AST, aspartate transaminase.
Effect of Shenling Baizhu powder on the UPR signaling pathway in the livers of NAFLD rats.
As shown in Figure 4, by comparison with the N group, the expression levels of BiP, CHOP, ATF6, PERK, p-eIF2α, ATF4, IRE1α and XBP-1s proteins of the M group rats were significantly upregulated (P< 0.05,P< 0.01); compared with the M group, the expression levels of BiP,ATF6, PERK, p-eIF2α, and XBP-1s proteins of the Shenling Baizhu powder group rats were significantly downregulated (P< 0.01,P<0.05), and the expression levels of CHOP, ATF4 and IRE-1α proteins showed a downregulating trend, but not statistically significant (P>0.05).
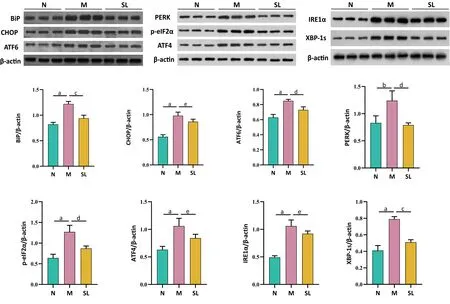
Figure 4 Western blot analysis of protein levels associated with the UPR signaling pathway in rat liver.Values are presented as the mean ±standard deviations.Differences were assessed by one-way analysis of variance.A,P<0.01 vs the N group;b,P<0.05 vs the N group;c,P<0.01 vs the M group; d, P < 0.05 vs the M group; e, no significance; N, normal control group; M, model group; SL, Shenling Baizhu powder group; BiP,binding immunoglobulin protein; CHOP, C/EBP-homologous protein; ATF6, activating transcription factor 6; PERK, protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase; p-eIF2α, phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha; ATF4, activating transcription factor 4; IRE1α,inositol requiring enzyme 1 alpha; XBP-1s, X-box binding protein 1s; UPR, unfolded protein response.
Discussion
In China, with the change in lifestyle, the prevalence rate of NAFLD is increasing rapidly and showing a trend towards a younger age.At present, the prevalence rate of NAFLD in China was about 29%, which has exceeded the global average prevalence rate, and has brought a huge burden to Chinese society [11].With the development of the disease, some patients with NAFLD can develop gradually to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis from a simple fatty liver, and some patients can develop liver fibrosis and cirrhosis, and even develop hepatocellular carcinoma [12].
In Chinese medical literature, there is no “fatty liver” disease name.According to its onset characteristics and clinical manifestations, it can be attributed to “hypochondriac pain”,“aggregation-accumulation”, “phlegm turbidity”, “accumulation syndrome”, etc (the name of diseases in traditional Chinese medicine theory).As to the etiology and pathogenesis of fatty liver, traditional Chinese medicine believes that eating too much fatty foods and sweets for a long time will damage the spleen.Consequently, the spleen transportation gets impaired due to deficiency, leading to internal stagnation of fluid-dampness, dampness retained internally, phlegm turbidity stagnated, food accumulated and not digested, ultimately leading to damp and turbid phlegm accumulation, and obstruction of the liver meridian, forming the fatty liver [13].Clinically, NAFLD patients are mainly characterized with obesity, less movement and talking, much phlegm in the pharynx, loose stools, fat tongue with large tooth marks, thick and greasy tongue coating and other characteristics of spleen deficiency and dampness.These indicate that spleen deficiency and excessive dampness are key in the pathogenesis of NAFLD.Shenling Baizhu powder is a classic and effective prescription for treating the spleen deficiency and dampness syndrome in traditional Chinese medicine.As reflected in our previous studies, Shenling Baizhu powder could alleviate NAFLD through anti-hepatic steatosis, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities[14, 15].However, the mechanism behind its protective effects is still unclear.In the present experiment, we established an NAFLD rat HFD model.It is simple and easy to operate, has a high success rate, good reproducibility, and is similar to the pathogenesis of human NAFLD.The pathological results of this experiment show that lipids accumulated markedly in the liver cells of the M group, and the serum TC, TG, LDL-C, FFA, ALT, AST content, and liver tissue TC and TG content were significantly higher than those in the control group.This demonstrates that we successfully developed an NAFLD rat model.In comparison with the M group, Shenling Baizhu powder can significantly reduce the fat accumulation in the liver tissues of NAFLD rats, and reduce the serum TC, TG, FFA, ALT, AST, and liver TC and TG levels.Together, these data demonstrated that Shenling Baizhu powder was effective in protecting against NAFLD in rats.
Such factors as free fatty acids, high blood sugar, oxidative stress,and calcium imbalance can break the homeostasis of the endoplasmic reticulum of liver cells, leading to ERS [6, 16].Studies have shown that the UPR signaling pathway is activated during ERS and participates in the process of liver lipid metabolism [17].The activation of the UPR signaling pathway involves three kinds of transmembrane proteins on the endoplasmic reticulum membrane,namely IRE1, PERK and ATF6.Under physiological conditions, these three proteins bind to the endoplasmic reticulum molecular chaperone BiP and remain in an inactive state.Under ERS, these three proteins dissociate from BiP, thus activating a series of downstream UPR signaling pathways, mainly including the IRE1/XBP1,PERK/eIF2α/ATF4/CHOP and ATF6 pathways [18].After IRE1 is activated, it induces the cleavage of XBP1, generates transcription factor XBP-1s, and then promotes lipid synthesis [6].After PERK is activated, phosphorylation of PERK activates eIF2α, promotes the transcription of ATF4, and further induces transcription of CHOP,leading to fatty acid β oxidation disorders [19, 20].The activated eIF2α can inhibit the synthesis of apolipoprotein ApoB100, hinder the assembly and secretion of very low-density lipoprotein, and lead to the accumulation of liver fat [21].Furthermore, ATF6 affects the lipid synthesis and accumulation in liver cells by regulating the expression of SREBP2 and the assembly and secretion of very low-density lipoprotein [7, 22].These show that during the ERS process, the three pathways,namely, IRE1, PERK and ATF6,play a key role in regulating liver lipid metabolism by affecting liver lipid synthesis, fatty acid oxidation, and secretion of hepatic very low-density lipoprotein.Therefore, improving ERS is of great significance to alleviate the progression of NAFLD.In the present study, the ERS-related protein BiP in the M group rats’ liver tissues was significantly upregulated,and the IRE1/XBP1, PERK/eIF2α/ATF4/CHOP and ATF6 pathway-related proteins were also significantly upregulated,suggesting that there is ERS in the liver of NAFLD rats, and the UPR signal pathway is activated.Intriguingly, this process was attenuated by Shenling Baizhu powder administration.Based on previous studies demonstrating the crucial role of ERS in the progression of NAFLD,our findings seem to support the hypothesis that Shenling Baizhu powder could alleviate NAFLD by inhibiting the expression of proteins related to the UPR signaling pathway, improving ERS, and reducing lipid accumulation may be an important factor (Figure 5) [23, 24].
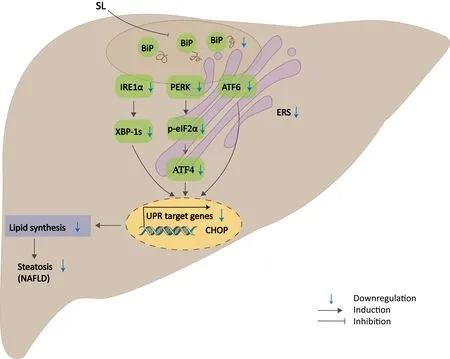
Figure 5 The proposed underlying mechanism of Shenling Baizhu powder on NAFLD rats.Shenling Baizhu powder alleviated NAFLD by inhibiting the expression of proteins related to the UPR signaling pathway, improving ERS and reducing lipid accumulation.NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; UPR, unfolded protein response; ERS, endoplasmic reticulum stress; SL, Shenling Baizhu powder; BiP, binding immunoglobulin protein; CHOP, C/EBP-homologous protein; ATF6, activating transcription factor 6; PERK, protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase;p-eIF2α, phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha; ATF4, activating transcription factor 4; IRE1α, inositol requiring enzyme 1 alpha;XBP-1s,X-box binding protein 1s.
Conclusion
Taken together, the results of our study investigated the preventive and therapeutic effects of Shenling Baizhu powder on NAFLD.Its lipid-lowering and liver-protecting mechanisms probably have anti-NAFLD effects by reducing the activation of the UPR signaling pathway and improving ERS.Therefore, this study provided novel insights into the underlying mechanisms of Shenling Baizhu powder against NAFLD.
 Traditional Medicine Research2022年1期
Traditional Medicine Research2022年1期
- Traditional Medicine Research的其它文章
- The artificial intelligence watcher predicts cancer risk by facial features
- Evaluation of bioactive flavonoids in Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium from different regions and its association with antioxidant and α-glucosidase inhibitory activities
- Exploring the anti-diabetic effects and the underlying mechanisms of ethyl acetate extract from Sophora flavescens by integrating network pharmacology and pharmacological evaluation
- Artificial neural network techniques to predict the moisture ratio content during hot air drying and vacuum drying of Radix isatidis extract
- Safety of Lycium barbarum L.:more information needed
- Mechanisms and status of research on the protective effects of traditional Chinese medicine against ischemic brain injury
