Th1/Th2及其细胞因子在脓毒症患者中的改变和临床价值
杨卫星 黄君 娄敏娟 林荣海


[關键词] Th1/Th2;细胞因子;脓毒症;临床价值
[中图分类号] R631 [文献标识码] B [文章编号] 1673-9701(2021)16-0056-04
Changes and clinical value of Th1/Th2 and its cytokines in patients with sepsis
YANG Weixing1 HUANG Jun2 LOU Minjuan1 LIN Ronghai1
1.Department of Critical Care Medicine, Taizhou Hospital of Zhejiang Province, Taizhou 317000, China; 2.Department of Neonatology, Taizhou Hospital of Zhejiang Province, Taizhou 317000, China
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the changes and clinical value of Th1/Th2 and its cytokines in patients with sepsis. Methods A total number of 320 patients with sepsis treated in our hospital from January 2017 to December 2019 were selected as the observation group, and 300 healthy people were selected during the same period as the control group. The observation group were divided into 2 subgroups according to the acute physiology and chronic health APACHE-Ⅱ score. Patients with APACHE-Ⅱ score <20 were classified as the non-critical subgroup(192 patients), and patients with APACHE-Ⅱ score ≥20 were classified as the critical subgroup (128 patients). The general clinical data of the two groups were collected. The serum levels of Th1, Th2, IFN-γ, and IL-4 in the observation group were compared with those in the control group before and after treatment. Results The general clinical data of the two groups were not significantly different (P>0.05). Before treatment, the Th1 proportion, Th1/Th2 ratio, IFN-γ level, and IFN-γ/IL-4 ratio in the observation group were significantly lower than those in the control group; the Th2 proportion and IL-4 level in the observation group were significantly higher than those in the control group. After treatment, the Th1 proportion, Th1/Th2 ratio, IFN-γ level, and IFN-γ/IL-4 ratio in the observation group were significantly increased, but still lower than those in the control group; the Th2 proportion and IL-4 level in the observation group were significantly decreased, but still higher than those in the control group. Before treatment, the Th1 proportion, Th1/Th2 ratio, IFN-γ level, and IFN-γ/IL-4 ratio in the critical subgroup were significantly lower than those in the non-critical subgroup; the Th2 proportion and IL-4 level in the critical subgroup were significantly higher than those in the non-critical subgroup. After treatment, the Th1 proportion, Th1/Th2 ratio, IFN-γ level, IFN-γ/IL-4 ratio in the critical subgroup were significantly increased, but still lower than those in the non-critical subgroup; the Th2 proportion and IL-4 level in the critical subgroup were significantly decreased, but still higher than those in the non-critical subgroup. Conclusion Patients with sepsis have decreased Th1/Th2 ratio and IFN-γ/IL-4 ratio. As the disease worsens, such ratios decrease more significantly, and immune function is suppressed. After treatment, the conversion of Th1 to Th2 is corrected. The Th1/Th2 ratio can be used to determine immune status.
[Key words] Th1/Th2; Cytokines; Sepsis; Clinical value
脓毒症可引发休克、多器官功能衰竭,甚至死亡[1-3]。脓毒症死亡的患者脾脏内出现大量凋亡的T淋巴细胞,T淋巴细胞数目及功能显著下降[4]。机体免疫系统内CD4+T淋巴细胞重要的一个亚群是辅助性T细胞(helper T cell,Th细胞),根据细胞的具体功能又分为Th1细胞、Th2细胞,共同反映免疫系统的功能状况[5],Th1分泌的细胞因子主要有γ-干扰素(interferon-γ, IFN-γ)、白细胞介素-2(interleukin-2, IL-2),Th2分泌的细胞因子主要有白细胞介素-4(interleukin-4, IL-4)、白细胞介素-10(interleukin-10, IL-10)。机体炎症反应-抗炎反应的免疫平衡基础是Th1/Th2平衡,Th1/Th2、IFN-γ/ IL-4可对机体的免疫功能产生重要影响[7]。本课题旨在研究Th1/Th2及其细胞因子在脓毒症患者中的改变和临床价值,现报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1临床资料
选择2017年1月至2019年12月我院治疗的脓毒症患者进行研究,纳入标准:均符合由《中国严重脓毒症/脓毒症性休克治疗指南(2014版)》拟定的脓毒症临床诊断标准[8];年龄为18~75岁;发病24 h内入院。排除标准:患有恶性肿瘤;合并心、肝、肾、肺等其他重要器官的功能受损;患者生命体征不稳定或有休克风险;有慢性感染性疾病、传染性疾病、免疫性疾病等;近期接受抗生素、激素、免疫调节剂等药物治疗;处于妊娠期、哺乳期;患有精神类疾病,无法配合研究。
根据上述标准,共纳入320例脓毒症患者作为本课题的观察组,选择同时期来我院体检的300例健康人作为对照组。本课题已通过我院医学伦理委员会审议,患者及其家属均签署本研究的知情同意书。
1.2方法
收集研究对象的一般临床资料,如年龄、性别、体质量指数(BMI)等。观察组患者入院后进行积极的液体复苏治疗、对症支持治疗等。观察组根据急性生理与慢性健康APACHE-Ⅱ评分[6]分为2个亚组:APACHE-Ⅱ评分<20分为非危重亚组(n=192),APACHE-Ⅱ评分≥20分为危重亚组(n=128)。采集观察组入院治疗前、治疗5日后及对照组的晨起空腹外周静脉血标本各5 mL,将各组标本分为2份,分别采用酶联免疫吸附法(ELISA)检测血清中IFN-γ、IL-4水平,使用流式细胞仪测定Th1、Th2细胞数目及比值,其中,以IFN-γ+CD4+CD3+ T细胞代表Th1细胞,以IL-4+CD4+CD3+ T细胞代表Th2细胞。
1.3统计学分析
采用SPSS 22.0统计学软件对本次研究的数据进行统计处理分析,计量资料以均数±标准差(x±s)表示,采用t检验;计数资料采用χ2检验,以P<0.05表示差异具有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1两组的一般临床资料比较
两组的一般临床资料,如年龄、性别、BMI比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),具有可比性。见表1。
2.2 观察组治疗前、后与对照组Th1/Th2水平比较
治疗前,观察组Th1占比及Th1/Th2比值明显低于对照组(P<0.05)、Th2占比明显高于对照组(P<0.05);治疗后,观察组Th1占比及Th1/Th2比值明显提高(P<0.05)、Th2占比明显下降(P<0.05),但观察组Th1占比及Th1/Th2比值仍明显低于对照组(P<0.05)、Th2占比仍明显高于对照组(P<0.05)。見表2。
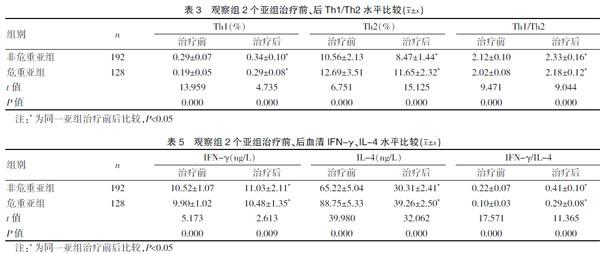
2.3 观察组2个亚组治疗前、后Th1/Th2水平比较
治疗前,危重亚组Th1占比及Th1/Th2比值明显低于非危重亚组(P<0.05)、Th2占比明显高于非危重亚组(P<0.05);治疗后,两亚组Th1占比及Th1/Th2比值明显提高(P<0.05)、Th2占比明显下降(P<0.05),但危重亚组Th1占比及Th1/Th2比值仍明显低于非危重亚组(P<0.05)、Th2占比仍明显高于非危重亚组(P<0.05)。见表3。
2.4 观察组治疗前、后与对照组血清IFN-γ、IL-4水平比较
治疗前,观察组IFN-γ及IFN-γ/IL-4比值明显低于对照组(P<0.05)、IL-4明显高于对照组(P<0.05);治疗后,观察组IFN-γ及IFN-γ/IL-4比值明显提高(P<0.05)、IL-4明显下降(P<0.05),但观察组IFN-γ及IFN-γ/IL-4比值仍明显低于对照组(P<0.05)、IL-4仍明显高于对照组(P<0.05)。见表4。
2.5 观察组2个亚组治疗前、后血清IFN-γ、IL-4水平比较
治疗前,危重亚组IFN-γ及IFN-γ/IL-4比值明显低于非危重亚组(P<0.05)、IL-4明显高于非危重亚组(P<0.05);治疗后,两亚组IFN-γ及IFN-γ/IL-4比值明显提高(P<0.05)、IL-4明显下降(P<0.05),但危重亚组IFN-γ及IFN-γ/IL-4比值仍明显低于非危重亚组(P<0.05)、IL-4仍明显高于非危重亚组(P<0.05)。见表5。
3 讨论
脓毒症可由创伤、手术、严重感染等引发,严重者可引起患者休克或死亡。近年来,随着抗菌药物的研发及应用、外科手术的进步,脓毒症的预防及治疗有较大进展,但死亡率仍较高[9]。据研究,免疫功能失调、炎症反应、基因多样性等均可影响脓毒症的发生,其中,炎症反应-抗炎反应的平衡失调可诱发脓毒症的病情加重,甚则休克、多器官功能衰竭[10-11]。据报道,脓毒症患者的在不同阶段机体免疫系统可处于抑制、激活、紊乱等不同的状态[12]。正常的机体免疫系统内,Th细胞分化为Th1、Th2两种,其中,Th1细胞分泌的促进炎症反应的细胞因子IFN-γ、IL-2主要参与机体的细胞免疫,Th2细胞分泌的抗炎症反应的细胞因子IL-4、IL-10主要参与机体的体液免疫,Th1、Th2及其分泌的多种细胞因子,可互相调节、抑制,维持Th1/Th2平衡[13-14]。若机体发生免疫应答反应,某种Th细胞可反馈性地强化自身并抑制另一种Th细胞,出现Th1/Th2失衡[15]。
据报道,脓毒症患者体内,巨噬细胞在机体组织受损或者内毒素等因子的刺激下,可释放大量白细胞介素-1-β(IL-1β)、α-肿瘤坏死因子(TNF-α)、前列腺素E2(PGE2)[16-17],PGE2对IFN-γ、IL-2等细胞因子的释放具有强烈的抑制作用,对IL-4、IL-10等细胞因子的释放具有明显的刺激作用,可导致Th1向Th2的转化[18]。机体下丘脑-垂体-肾上腺轴在脓毒症患者感染的刺激下,可分泌大量糖皮质激素,进而诱发IkB合成、抑制NF-kB及炎症因子的分泌,增强Th2细胞的分化[19-20]。本研究发现,治疗前,观察组Th1占比、Th1/Th2比值、IFN-γ水平、IFN-γ/IL-4比值均明显低于对照组,Th2占比、IL-4水平明显高于对照组,可见,脓毒症患者出现Th1、IFN-γ下降,Th2、IL-4增多,Th1向Th2转化,出现免疫抑制,与前人报道一致。治疗后,观察组Th1占比、Th1/Th2比值、IFN-γ水平、IFN-γ/IL-4比值均明显提高,但仍低于对照组,Th2占比、IL-4水平明显下降,但仍高于对照组,可见,治疗可纠正免疫抑制状态,但仍未达到正常水平。本研究中观察组根据患者病情分为两个亚组,发现治疗前危重亚组Th1占比、Th1/Th2比值、IFN-γ水平、IFN-γ/IL-4比值均明显低于非危重亚组,Th2占比、IL-4水平明显高于非危重亚组,可见,脓毒症病情较重者Th1向Th2转化及免疫抑制程度更重。治疗后,危重亚组Th1占比、Th1/Th2比值、IFN-γ水平、IFN-γ/IL-4比值均明显提高,但仍低于非危重亚组,Th2占比、IL-4水平明显下降,但仍高于非危重亚组,可见,危重亚组经过治疗仍处于较重的免疫抑制状态,治疗效果不如非危重亚组。
综上,脓毒症患者出现Th1细胞免疫应答下降、Th2细胞免疫应答提高,Th1/Th2比值、IFN-γ/IL-4比值降低,机体免疫功能处于抑制状态,治疗后,可纠正Th1向Th2转化,可根据Th1/Th2比值判断机体的免疫状态。脓毒症患者机体免疫功能的进一步转变,仍有待深入研究。
[参考文献]
[1] 徐烔烔,林丽君,黄盈盈.乌司他丁对脓毒症患者Th1/Th2和HMGB1表达的影响[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2019,29(17):2589-2593.
[2] 李岑,黄栋,王予川,吴大琴,等.Th1/Th2、Th17/Treg及其相关转录因子在儿童脓毒血症早期体液中的变化[J].贵州医药,2018,42(11):1286-1288+1299.
[3] 郝迎迎,虞竹溪,顾勤.脓毒症患者外周血Th1/Th2细胞水平及变化趋势与预后的关系[J].临床急诊杂志,2018, 19(5):303-305.
[4] Shim S,Soh SH,Im YB. Elicitation of Th1/Th2 related responses in mice by chitosan nanoparticles loaded with Brucellaabortus malate dehydrogenase, outer membrane proteins 10 and 19[J]. Int J Med Microbiol,2020,310(1):151362.
[5] Wu D,Liu Y,Pang N. PD-1/PD-L1 pathway activation restores the imbalance of Th1/Th2 and treg/Th17 cells subtypes in immune thrombocytopenic purpura patients[J]. Medicine(Baltimore),2019,98(43):e17608.
[6] 程晓迎,王磊.APACHEⅡ评分联合尿中性粒细胞明胶酶相关载脂蛋白检测对脓毒症合并急性肾损伤的预测价值[J].临床误诊误治,2020,33(6):57-62.
[7] 奚耀,赵雷,朱亮,等.升降散对脓毒症患者Th1/Th2失衡及相关调节因子的干预[J].实用医学杂志,2017,33(16):2784-2788.
[8] 黄鹤,田昭涛,黎檀实.脓毒血症中固有免疫细胞的调节机制研究进展[J].中国免疫学杂志,2016,32(4):576-583.
[9] 李强,吴建顺,李慧.罗格列酮治疗对脓毒症肺损伤患者血清HMGB1、TNF-α及Th1/Th2影响研究[J].中國生化药物杂志,2015,35(8):95-97.
[10] 方勤,蒋刚健,陈鑫.血必净注射液对急性脓毒症患者Th1/2、内毒素及免疫因子影响研究[J].中国生化药物杂志,2015,35(5):130-133.
[11] Song Q,Lin L,Chen L.Co-administration of N-acetylcysteine and dexmedetomidine plays a synergistic effect on protection of LPS-induced acute lung injury via correcting Th1/Th2/Th17 cytokines imbalance[J]. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol,2020,47(2):294-301.
[12] Su F,Xu L,Xue Y. Th1-biased immunoadjuvant effect of the recombinant B subunit of an Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin on an inactivated porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus antigen via intranasal immunization in mice[J]. J Vet Med Sci,2019,81(10):1475-1484.
[13] Yuan X,Li H,Shen YY. Clinical and Th1/Th2 immune response features of hospitalized children with human rhinovirus infection[J]. J Med Virol,2020,92(1):26-33.
[14] Chen B,Li H,Xia W. Imiquimod regulating Th1 and Th2 cell-related chemokines to inhibit scar hyperplasia[J]. Int Wound J,2019,16(6):1281-1288.
[15] 周思佳. 乌司他丁对脓毒症患者血Th1/Th2漂移的影响[D].大连医科大学,2015.
[16] Wang Z,Zhuo F,Chu P. Germacrone alleviates collagen-induced arthritis via regulating Th1/Th2 balance and NF-kappaB activation[J]. BiochemBiophys Res Commun,2019,518(3):560-564.
[17] Bok S,Seo H,Bae JH,et al. Allium hookeri root extract regulates asthmatic changes through immunological modulation of Th1/Th2 related factors in an ovalbumininduced asthma mouse model[J]. Mol Med Rep,2019,20(4):3215-3223.
[18] Bowen W,Batra L,Pulsifer AR. Robust Th1 cellular and humoral responses generated by the Yersinia pestis rF1-V subunit vaccine formulated to contain an agonist of the CD137 pathway do not translate into increased protection against pneumonic plague[J]. Vaccine,2019, 38(37):5708-5716.
[19] 周宇翔. 燒伤脓毒症小鼠早期Th1/Th2细胞ANXA1、GATA-3、T-bet表达的研究[D].中南大学,2014.
[20] 曹云. 脓毒症肺损伤患者外周血HMGB1、Treg、Th1/Th2、HLA-DR的变化及中西医结合治疗的随机双盲对照研究[D].大连医科大学,2014.
(收稿日期:2021-01-09)

