HBsAg浓度对HBeAg阳性的慢性乙型肝炎患者恩替卡韦治疗效果的预测价值
王洁 朱姣娜 陈公英 刘静 龚玲 施军平

[關键词] 慢性乙型肝炎;慢性乙型肝炎表面抗原;肝炎e抗原;恩替卡韦;预测价值
[中图分类号] R512.62 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-9701(2021)16-0027-05
The predictive value of HBsAg concentration on the therapeutic effect of entecavir in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B patients
WANG Jie1 ZHU Jiaona2 CHEN Gongying1 LIU Jing1 GONG Ling1 SHI Junping1
1.The Affiliated Hospital of Hangzhou Normal University, Hangzhou 310000, China; 2.Ningbo Yinzhou NO.2 Hospital,Ningbo 315000, China
[Abstract] Objective To dynamically monitor the hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) level in patients with hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) positive chronic hepatitis B (CHB) receiving entecavir (ETV) treatment, and to explore the predictive value of the early HBsAg concentration for treatment effect. Methods A total of 62 HBeAg-positive patients with chronic hepatitis B received entecavir antiviral treatment for one year. The hepatitis B virus (HBV) serum markers, deoxyribonucleic acid quantification(HBV DNA), and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) were detected at 0, 4, 8, 12, 24, and 48 weeks. T-test, Pearson correlation analysis, and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve were used for analysis. Results 50 CHB patients had a virological response (VR+), and 12 CHB patients did not have a virological response (VR-). There was no significant difference in baseline of gender, age, ALT, and HBV DNA load between the two groups (P>0.05). The lg HBsAg concentration in the VR+ group was lower than that in the VR-group [(4.103±0.459) vs. (4.611±0.259), P=0.000]. Both groups of HBV-DNA decreased with the prolonged treatment time. The HBV DNA load in VR+ group was significantly lower than that in VR-group after treatment for 4 weeks, 8 weeks, 12 weeks, 24 weeks, and 48 weeks (P<0.05). The lg HBsAg of the two groups decreased with the prolonged treatment time. The lg HBsAg of VR+ group was significantly lower than that of VR- group after treatment for 4 weeks, 8 weeks, 12 weeks, 24 weeks, and 48 weeks (P<0.05). The area under the ROC curve of lg HBsAg concentration was the largest at 8 weeks of treatment (AUC=0.992, P<0.05). The Youden index of cut-off value 3.945 IU/mL was the largest(0.960). Conclusion The lg HBsAg≤3.945 IU/mL at 8 weeks of ETV treatment can be used as an index to predict the virological response of ETV treatment for one year.
[Key words] Chronic hepatitis B; Chronic hepatitis B surface antigen; Hepatitis e antigen; Entecavir; Predictive value
乙型病毒性肝炎是由乙型肝炎病毒(Hepatitis B virus,HBV)引起的一类常见肝病,流行病学调查结果显示,全球约2.5亿人为慢性HBV感染者[1],有15%~40%发展为肝衰竭、肝硬化和肝细胞癌(Hepatocellular carcinoma,HCC)[2]。调查显示,我国1~59岁一般人群乙型病毒性肝炎表面抗原(Hepatitis B surface antigen,HBsAg)携带率为7.18%[3-4]。据此推算,我国现有慢性HBV感染者约9300万人,其中慢性乙型肝炎患者约2000万例[5]。目前慢性乙型肝炎患者的治疗以抗病毒为主,恩替卡韦已逐渐成为我国目前主要的一线抗病毒药物,如何通过对早期治疗反应的观察,从而进一步优化治疗以提高远期疗效,预防肝硬化、肝癌的发生成为新的研究热点。据报道,HBsAg水平或治疗期间HBsAg水平与机体的长期病毒学应答、血清学应答及HBsAg阴转状况有良好的相关性[6]。本研究对62例ETV治疗的HBeAg阳性 CHB患者随访1年,动态监测恩替卡韦(Entecavir,ETV)治疗前后HBsAg浓度、乙肝脱氧核糖核酸(Hepatitis B deoxyribonucleic acid,HBV DNA)载量、丙氨酸氨基转移酶(Alanine aminotransferase,ALT)水平的变化,探讨HBsAg浓度对HBeAg阳性的HBV患者恩替卡韦治疗效果的预测价值,现报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选择2014年1月至2017年11月在杭州师范大学附属医院肝病科住院及门诊接受恩替卡韦初治(0.5 mg/d)的HBeAg阳性CHB患者62例,其中男47例,女15例,每例收集6个时间点(0、4、8、12、24、48周)的血清样本。纳入标准:①诊断标准符合2015年《慢性乙型肝炎防治指南》[7]者;②年龄18~65岁,有能力理解和签署知情同意书者;③HBsAg阳性≥6个月,且HBeAg阳性者;④HBV DNA≥2×104 IU/mL者;⑤血清ALT>2倍正常值上限者。排除标准:①既往使用过拉米夫定、阿德福韦、恩替卡韦、替比夫定、替诺福韦,或前6个月内接受干扰素治疗者;②6个月内接受过免疫抑制剂或其他免疫调节剂治疗者;③慢性甲型肝炎、丙型肝炎、丁型肝炎及原发性胆汁肝硬化、自身免疫性肝病等可能会引起肝脏损伤的疾病者;④妊娠或哺乳期妇女;⑤依从性差、失访者。此研究经杭州师范大学附属医院医学伦理委员会批准,所有入组患者均签署知情同意书。根据ETV治疗1年后HBV DNA是否低于检测值下限将纳入病例分为病毒学应答组(Virological response,VR+)50例和病毒学无应答组(Virological nonresponse,VR-)12例。
1.2 方法
所有入选患者均给予口服恩替卡韦(正大天晴药业集团股份有限公司,国药准字H20100019,YBH004,规格:0.5 mg,片剂)0.5 mg/d抗病毒治疗,连续服用1年。
1.3 观察指标
在用药治疗前、治疗4周、8周、12周、24周以及48周时采集血样。①采用雅培ARCHITECT i2000型化学发光仪及其配套试剂(美国雅培公司)测定HBV标志物(包括HBsAg、HBsAb、HBeAg、HBeAb、HBcAb);②采用Anadas9850荧光定量PCR仪(厦门安普利公司)和HBV DNA定量检测试剂盒(湖南圣湘公司)测定HBV DNA;③采用AU5800全自动生化分析仪(Beckman Coulter,美国)测定肝功能指标。
1.4 统计学方法
所有统计分析均借助SPSS 21.0统计学软件完成,服从正态分布的计量资料以(x±s)表示,采用t检验;非正态分布资料以[M(P25,P75)]表示,采用秩和检验。HBV DNA与HBsAg的关联性采用Pearson相关分析和线性拟合分析进行相关性分析;采用受试者工作曲线(Receiver operator characteristic curve,ROC)分析血清HBsAg预测ETV抗病毒治疗慢性乙型肝炎的有效性,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 一般情况
本组62例患者经1年ETV抗病毒治疗后,50例患者评定为病毒学应答组(VR+),其中男39例,女11例,平均年龄(34.041±8.260)岁;12例为病毒学无应答组(VR-),其中男8例,女4例,平均年齡(36.582±11.681)岁。两组患者的性别、年龄、ALT、HBV DNA比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05);两组HBsAg水平比较,差异有统计学意义(P=0.000)。见表1。
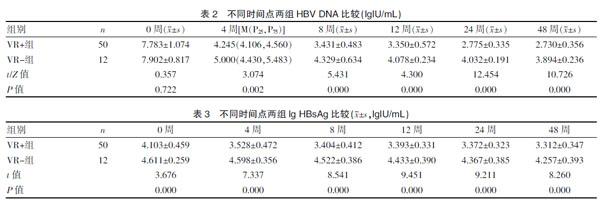
2.2 HBV DNA和HBsAg变化趋势
服用ETV治疗的1年内,VR+组和VR-组HBV DNA水平及HBsAg均呈下降趋势。VR+组和VR-组HBV DNA均随治疗时间延长而下降。基线时两组HBV DNA载量比较,差异无统计学意义[(7.783±1.074) vs.(7.902±0.817),P=0.722],4周时两组HBV DNA载量比较,差异有统计学意义[4.245(4.106, 4.560) vs. 5.000(4.430,5.483),P=0.002],8周时VR+组HBV DNA载量低于VR-组,差异有统计学意义[(3.431±0.483)vs.(4.329±0.634),P=0.000],12周时VR+组HBV DNA载量明显低于VR-组,差异有统计学意义[(3.350±0.572) vs.(4.078±0.234),P=0.000],24周时VR+组较VR-组HBV DNA载量明显降低,差异有统计学意义[(2.775±0.335) vs. (4.032±0.191),P=0.000],48周时VR+组HBV DNA载量较VR-组明显降低,差异有统计学意义[(2.730±0.356) vs. (3.894±0.236),P=0.000]。见表2。
两组lg HBsAg均随治疗时间延长而下降。两组各时间点比较,基线时VR+组lg HBsAg较VR-组低,差异有统计学意义[(4.103±0.459) vs. (4.611±0.259),P=0.000],4周时VR+组lg HBsAg较VR-组低,差异有统计学意义[(3.528±0.472) vs.(4.598±0.356),P=0.000],8周时VR+组lg HBsAg低于VR-组,差异有统计学意义[(3.404±0.412) vs.(4.522±0.386),P=0.000],12周时VR+组lg HBsAg明显低于VR-组[(3.393±0.331) vs.(4.433±0.390),P=0.000],24周时VR+组lg HBsAg较VR-组明显降低,差异有统计学意义[(3.372±0.323) vs.(4.367±0.385),P=0.000],48周时VR+组lg HBsAg较VR-组明显降低,差异有统计学意义[(3.312±0.347) vs. (4.257±0.393),P=0.000]。见表3。
2.3 HBsAg和HBV DNA相关性分析
以HBV DNA水平为横坐标,HBsAg为纵坐标,绘制散点图,行直线回归分析,二者呈显著正相关(r=0.422,P<0.05)。见图1。
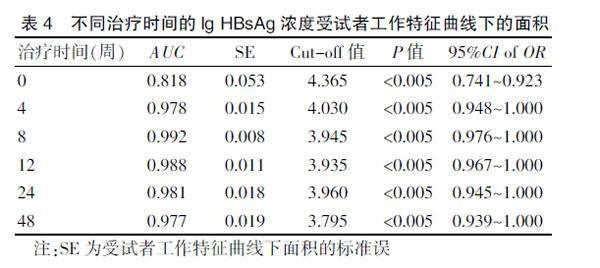
2.4 HBsAg预测ETV抗病毒有效的ROC曲线
ETV治疗前后各时间点lg HBsAg浓度预测1年病毒学应答的ROC曲线分析结果见封三图5、表4。基线、治疗4周、8周、12周、24周、48周的ROC曲线下面积(Area under the CHIVe,AUC)分别为0.818、0.978、0.992、0.988、0.981、0.977;并在治疗第8周时达到最大值(P<0.005)。ROC曲线的坐标点提示,当lgHBsAg为3.945 lgIU/mL时对应的Youden指数达到最大(其值为0.960。注:Youden指数=敏感度+特异度-1),治疗8周时lg HBsAg≤3.945 IU/mL可作为预测ETV治疗1年病毒学应答的指标,Cut-off值见表4。
3 讨论
我国是乙肝大国,对于乙肝抗病毒治疗过程中疗效的预测非常重要,目前关于CHB抗病毒治療效果的预测指标尚不统一,HBV DNA载量是较为关注的预测指标,包括治疗前及治疗过程中的变化情况均可在一定程度上预测远期的疗效。然而有研究表明,在HBV DNA低于PCR检测下限的CHB患者中仍可存在病毒活动,因此血清HBV DNA作为疗效评价的指标仍有一定的局限性。抗病毒治疗的最理想目标为HBsAg的清除甚至HBsAg血清学转换,这是接近临床治愈的目标,代表HBV感染者的免疫控制,可以实现安全停药或停药后不复发,并阻止其进一步进展为肝硬化、肝癌[8-9]。且随着HBsAg定量临床应用价值的不断研究发现,血清HBsAg浓度与血清HBV DNA载量及肝内cccDNA水平相关[10-11],可能是抗毒疗效预测的良好指标。HBsAg浓度与血清HBV DNA载量相结合反映HBV慢性感染者的病毒复制状态,准确评价抗病毒的治疗效果。近年来的一系列研究发现,HBV DNA与血清HBsAg具有良好相关性[12];血清HBsAg水平及其动态变化可以预测HBsAg清除甚至血清学转换,HBsAg可预测慢性乙型肝炎患者HBV感染不同阶段的病毒学应答情况[13]。本研究动态检测ETV治疗62例CHB患者的1年内血清HBsAg、HBV DNA水平变化发现,HBsAg浓度对恩替卡韦治疗的预后具有预测价值,与既往文献报道相似[10,14-15]。
本研究结果显示,抗病毒治疗后,无论是VR+组还是VR-组,血清HBsAg、HBV DNA水平均下降,且VR+组的下降幅度大于VR-组,尤其是治疗8周时VR+组HBsAg下降的幅度明显大于VR-组。本研究进一步从HBsAg与HBV DNA的相关性角度分析了其机制,发现HBsAg与HBV DNA呈明显的正相关,即血清HBsAg随着HBV DNA水平升高而升高,与既往的研究相一致[16]。且HBsAg的检测更为简单、经济、方便。因此,从实验室检测、经济学而言,HBsAg预测慢性乙型肝炎病毒疗效的价值均优于HBV DNA。
HBsAg基线浓度及治疗过程中的变化对NAs抗病毒疗效预测作用目前仍有争议。有研究认为,基线HBsAg浓度对NAs抗病毒疗效有较好的预测价值。也有研究显示,治疗期间HBsAg浓度变化的预测价值优于其基线水平的预测价值[17-19]。本研究结果显示,HBsAg浓度在ETV抗病毒治疗8周时ROC曲线下面积达到最大,临界值3.945 lgIU/mL时对应的Youden指数最大,并有良好的敏感度和特异度。李德忠等[20]研究显示,慢性乙型肝炎采用ETV治疗的前3个月血清HBsAg浓度下降幅度较大,与本研究结果相符。并在此基础上进一步证实,更早期即在治疗8周时HBsAg浓度下降就可以很好地预测1年的病毒学应答。
综上所述,ETV治疗8周时lg HBsAg≤3.945 IU/mL可作为预测ETV治疗1年病毒学应答的指标,但目前样本量有限,今后若能增加更多样本量,进一步明确其预测价值,可为临床上更好地管理和及早优化抗HBV治疗提供可靠的循证学依据。
[参考文献]
[1] Smith S,Harmanci H,Hutin Y,et al.Global progress on the elimination of viral hepatitis as a major public health threat:An analysis of WHO Member State responses 2017[J].JHEP Rep,2019,1(2):81-89.
[2] Nicolini LA,Orsi A,Tatarelli P,et al.Global View to HBV chronic infection:Evolving strategies for diagnosis,treatment and prevention in immunocompetent individuals[J].Int J Environ Res Public Health,2019,16(18):3307-3313.
[3] Hou J,Wang GQ,Wang FS,et al. Guideline of prevention and treatment for chronic hepatitis B (2015 Update)[J].Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology,2017,5(4):297-318.
[4] Yan LB,Liao J,Han N,et al.Association between hepatitis B virus infection and metabolic syndrome in Southwest China:A cross-sectional study[J]. Sci Rep,2020,10(1):6738.
[5] Yan JY,Li ZQ,Yu ZJ,et al.Management of individuals with chronic hepatitis B virus infection and persistent normal or mildly elevated aminotransferase levels[J]. J Cell Biochem,2019,120(4):6632-6641.
[6] Celik M,Arabul M,Ceki C,et al.Clinical utility of hepatitis B surface antigen levels during the natural history and treatment of chronic hepatitis B infection[J].Prz Gastroenterol,2014,9(3):164-167.
[7] 中華医学会肝病学分会,中华医学会感染病学分会.慢性乙型肝炎防治指南(2015年更新版)[J].临床肝胆病杂志,2015,31(12):1941-1960.
[8] Fujiwara N,Friedman SL,Goossens N,et al. Risk factors and prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma in the era of precision medicine[J].J Hepatol,2018,68(3):526-549.
[9] Mf Akbar S,Al-Mahtab M, I Khan S. Nature of host immunity during hepatitis B virus infection and designing immune therapy[J]. Euroasian J Hepatogastroenterol,2018,8(1):42-46.
[10] Peng CY,Lai HC,Su WP,et al. Early hepatitis B surface antigen decline predicts treatment response to entecavir in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J].Sci Rep,2017,7: 42 879.
[11] Kim SS,Lee D,Lee MH,et al.Association of on-treatment serum hepatitis B surface antigen level with sustained virological response to nucleons(t)ide analog in patients with hepatitis B e-antigen positive chronic hepatitis B[J].Hepatol Res,2013,43(3):219-227.
[12] Karra VK,Chowdhury SJ,Ruttala R,et al. Clinical significance of quantitative HBsAg titres and its correlation with HBV DNA levels in the natural history of hepatitis B virus infection[J].J Clin Exp Hepatol,2016,6(3):209-215.
[13] Liu C,Wu W,Shang H,et al.Prediction value of serum HBV large surface protein in different phases of HBV infection and virological response of chronic hepatitis B patients[J]. Clin Chim Acta,2018,481:12-19.
[14] Zhang XX,Li MR,Xi HL,et al. Dynamic characteristics of serum hepatitis B surface antigen in Chinese chronic hepatitis B patients receiving 7 years of entecavir therapy[J]. Chin Med J (Engl),2016,129(8):929-935.
[15] Preda CM,Baicus C,Negreanu L,et al. Effectiveness of entecavir treatment and predictive factors for virologic response[J]. Rev Esp Enferm Dig,2014,106(5):305-311.
[16] Yang N,Feng J,Zhou TC,et al.Relationship between serum quantitative HBsAg and HBV DNA levels in chronic hepatitis B patients[J].Med Virol,2018,90(7):1240-1245.
[17] Cho JY,Sohn W,Sinn DH,et al. Long-term real-world entecavir therapy in treatment-na?觙ve hepatitis B patients:Base-line hepatitis B virus DNA and hepatitis B surface antigen levels predict virologic response[J]. Korean J Intern Med,2017,32(4):636-646.
[18] Brouwer WP,Chan HLY,Brunetto MR,et al.Repeated measurements of hepatitis B surface antigen identify carriers of inactive HBV during long-term follow-up[J].Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol,2016,14(10):1481-1489.
[19] Seto WK,Cheung KS,Wong DK,et al. Hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance during nucleoside analogue therapy:Surface antigen kinetics,outcomes,and durability[J].J Gastroenterol,2016,51(5):487-495.
[20] 李德忠,曾勇彬.監测HBsAg浓度对HBeAg阳性的慢性乙型肝炎患者恩替卡韦治疗反应的预测价值[J].中华临床感染病杂志,2014,37(2):96-99.
(收稿日期:2020-11-03)

