Effects of Interaction of Soil Moisture and Organic Matter on Powdery Mildew Disease and Growth of Heracleum moellendorffii Hance
Liu Zai-min , Gao Xin-wen , Zhang Meng-yao , Li Kun Liu Wen-ting , Jiang Xin-mei , and Yu Xi-hong *
1 Key Laboratory of Biology and Genetic Improvement of Horticulture Crops (Northeast Region), Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin 150030, China
2 College of Horticulture and Landscape Architecture, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin 150030, China
Abstract: Taking annual Heracl'eum moellendorffii Hance as the material, this research studied the epidemic dynamics of H. moellendorffii Hance powdery mildew and plant growth by using the interactive methods of soil moisture and soil organic matter.The results showed that the interaction of higher soil moisture content (60%-80%) and soil organic matter content (75-100 g • kg-1) had few diseases, dosease index and area under disease progression curve (AUDPC) compared with those of other treatments, thus could effectivley control powdery mildew disease. Moreover, higher soil moisture and organic matter content increased the yield, contents of soluble sugar, soluble protein, vitamin C and coumarin in H. moellendorffii Hance.
Key words: H. moellendorffii Hance, irrigation and fertilizer management, powdery mildew, plant growth
Introduction
Heracleum moellendorffiiHance, as common wild vegetable of Heilongjiang Province, is not only tasted deliciously, but also contains compounds of flavone and coumarin richly that have remarkable anti-cancer effects (Liuet al., 2019), meanwhile, the accumulation of coumarin compounds in plant performs vital role in resisting biotic and abiotic stresses (Zhaoet al., 2017; Stefanieet al., 2018; Sunet al., 2019;Chezemet al., 2017; Gnonlonfinet al., 2012).H.moellendorffiiHance growing shadowing environment of forests can not satisfy the market need, because less wild resources, harvesting inconveniently, growing environment destroyed and so on. Consequently, it is necessary to conduct the artificial cultivation ofH.moellendorffiiHance in the filed and greenhouse. In recent years, the powdery mildew occurs seriously,impairing the quality and yields ofH. moellendorffiiHance, which is not conductive to the scale-production under the artificial cultivation ofH. moellendorffiiHance (Liuet al., 2019; Liuet al., 2021), therefore,the research related to the powdery mildew ofH.moellendorffiiHance has great significance.
As a wild herb, the controlling measures of powdery mildew disease ofH. moellendorffiiHance are mainly depending on agricultural methods rather than chemical prevention for plant growth perfecting. At present,the researches of agricultural methods controlling the occurrence of diseases mainly focus on rational arrangement of crops in the field (Sunet al., 2019),perfecting the management of irrigation and fertilization (Cossaniet al., 2012; Monet al., 2016; Zhuet al.,2017) and intercropping measures (Zhuet al., 2017;Qinet al., 2013; Jianget al., 2020; Caoet al., 2015).The irrigation and fertilization can influence the accumulation of phenols, flavonoids, free amino acids and soluble sugars of the plant that not only relate to the disease resistance of the host, but also affect infection stages of the disease (Jinet al., 2008; Lu, 2008). The condition of irrigation and fertilization managed in the field influences occurrences and epidemics of the powdery mildew greatly. Excessive application of nitrogen fertilizers and irrigation water results in plant populations, increasing and high field humidity, thus causing resistance of hosts reducing and the powdery mildew occurring seriously. In the management of red globe grape of facility, the powdery mildew is serious when nitrogen fertilizer is used too high or too low,and the occurrence of powdery mildew is controlled by adjusting irrigation amount (Chenet al., 2014). Niuet al. (2017) showed that the occurrence of wolfberry powdery mildew can be controlled effectively using agricultural measures which include reasonable planting density, controlling nitrogen fertilizer and irrigation amount and combining with pruning and removing diseased branches and leaves that can improve field ventilation and light transmission conditions. At present, Liuet al. (2019) had identified the powdery mildew infectingH. moellendorffiiHance as Erysiphe. Heraclei. Nevertheless, the study related to agricultural measures controlling the occurrence of the powdery mildew ofH. moellendorffiiHance in the field and greenhouse has not been reported.Therefore, based on practical production and combined with original growing environment ofH. moellendorffiiHance, using the measure of soil moisture interacting soil organic matter, controlling effects of the method of irrigation and fertilization on the powdery mildew ofH. moellendorffiiHance were studied, which will provide theoretical basis for agricultural controls ofH. moellendorffiiHance.
Materials and Methods
Plant material and field experiment
The annualH. moellendorffiiHance, as the experimental material, was cultivated by Laboratory of Facility Environment and Vegetable Cultivation, and Erysiphe. Heraclei isolated fromH. moellendorffiiHance growing in the field was used in this experiment.This experiment was conducted at the glasshouse of Facility Horticultural Centre of Northeast Agricultural University, and the plants for the powdery mildew occurrence assaying were grown in an environment controlled glasshouse at 25℃±2℃ under an 14/10 h light/dark cycle with RH at 70%±10%.
The seed ofH. moellendorffiiHance was sowed in October of 2017 and 2018, and in the late April of 2018 and 2019, the seedlings growing to two true leaves were transplanted in a nutrient bowl of 8 cm×8 cm, then planted in a pot with 32 cm height and 28 cm diameter after 40 days of transplantation, in June. After growth recovering, five individual plants of each treatment were selected, and inoculated the powdery mildew using the spore suspension method as the source center of fungus. The experiment applied the interactive method of soil moisture and soil organic matter, with the soil moisture content dividing into 50%-60%, 60%-70% and 70%-80% and 80%-90%, respectively, and soil organic matter content 25,50, 75 and 100 g • kg-1, respectively, 16 treatments totally (Table 1).

Table 1 Treatment of soil moisture and soil organic matter
The control group (CK) with soil moisture content of 70%-80% and soil organic matter content of 25 g • kg-1was set up. In this experiment, the soil water tester(MET-1000+) was used for the convenient determination of soil moisture content, when the soil moisture content fell to the lower limit of each treatment, the water was replenished to the maximum level timely.Simulated treatment of soil organic matter reached the treatment content by adding organic fertilizer in pot experiment.
Measurement items and methods
After the plants inoculated powdery mildew, the fungus occurrences ofH. moellendorffiiHance were investigated and measured. The occurrence ofH. moellendorffiiHance powdery mildew was investigated by five point sampling method (Liuet al., 2015) that each point selected 10 strains, and investigated the powdery mildew occurring of all the leaves with intervals of 10 days and calculated the disease incidence,disease index and the area under disease progression curve (AUDPC). The method about the disease level classification and the calculation of the disease occurring were performed as description by Liuet al(2021).
During the harvesting period of the plant, the yield per plant was determined, and the changes of growths mainly including natural plant height and leaf expansions and maximum leaf area were determined.Moreover, the qualities mainly including soluble sugar,soluble protein, vitamin C and coumarin ofH. moellendorffiiHance were confirmed. Contents of the soluble sugar, soluble protein, Vitamin C and coumarin were determined using the method of Anthrone-Sulfuric acid colorimetry, coomassie bright blue G-250 and ascorbic acidand imperatorin (Li, 2000), respectively.
Statistical analyses
The data were processed and analyzed by Excel 2016 and SPASS 21.0, and the WPS 2019, GraphPad Prism 8.01 and OrignPro 8.6 were used to draw diagram.
Results
Interaction of soil moisture and soil organic matter influence occurrences of H. moellendorffii Hance powdery mildew
The research demonstrated that the interaction of soil moisture and organic matter, to some extent, influencedH. moellendorffiiHance powdery mildew occurrences (Tables 2 and 3).
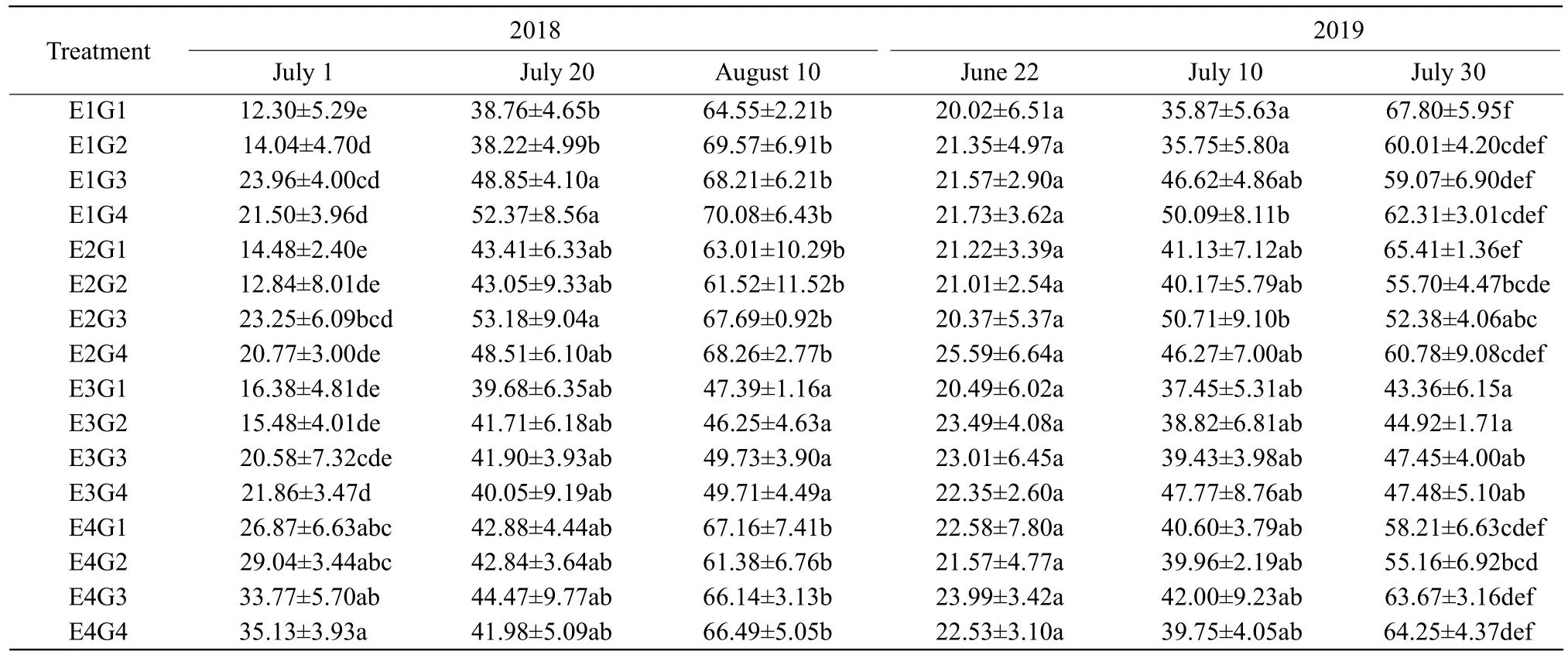
Table 2 Interaction of soil moisture and soil organic matter impact leaf disease incidence of H. moellendorffii Hance powdery mildew
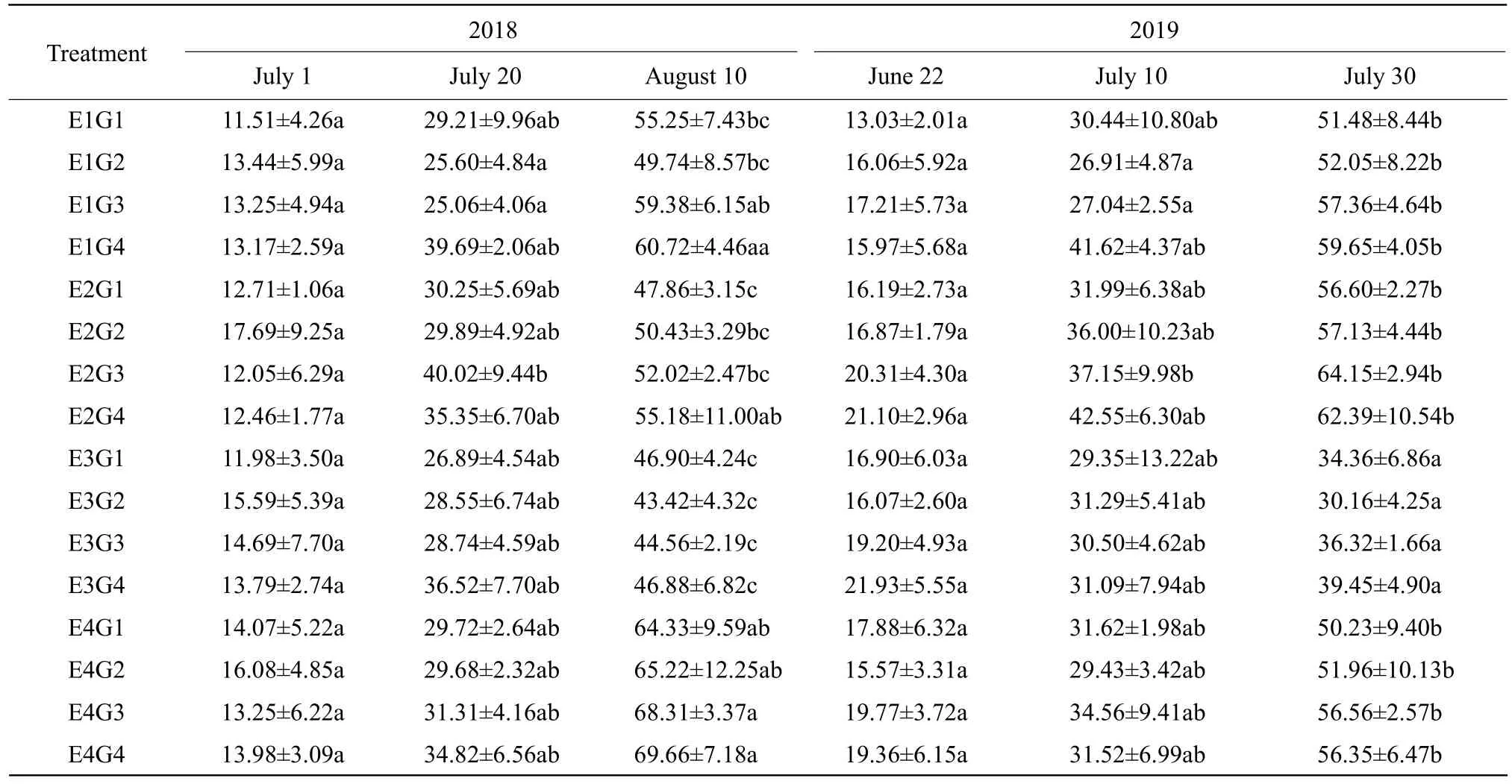
Table 3 Interaction of soil moisture and soil organic matter impact leaf disease index of H. moellendorffii Hance powdery mildew
In the early and middle stages of disease investigation, during 2018-2019, the interaction of different soil moisture contents and soil organic matter contents had no significant effects on the occurrence of powdery mildew and leaf disease incidence and index showed no significant difference among treatments. Nevertheless, at the end stage of disease investigation, the interaction with higher soil moisture contents and higher soil organic matter contents could control the powdery mildew occurring and the disease incidence and index were significantly lower compared with other interactive treatments.In the entire period of disease investigation, as the same soil moisture contents, the leaf disease incidence had no distinct difference under various contents of soil organic matter, while the disease index increased with soil organic matter contents improved. In general, excessive low or high soil moisture interacted with soil organic matter that was conductive to the powdery mildew occurrences ofH. moellendorffiiHance.
During 2018-2019, lower or higher soil moisture interacting with soil organic matter could inhibit the growth ofH. moellendorffiiHance, and resulted in the powdery mildew occurring seriously and higher ACDPC (Fig. 1). The experiment indicated that higher soil moisture contents from 70% to 80%, interacted with soil organic matter contents, from 75 g • kg-1to 100 g • kg-1, which could control the occurrence of powdery mildew effectively, and AUDPC ofH. moellendorffiiHance significantly decreased compared with other treatments.
Interaction of soil moisture and soil organic matter influence growth of H. moellendorffii Hance
The experiment demonstrated that soil moisture interacting with organic matter could produce some influences onH. moellendorffiiHance growths (Table 4).In the entire period, under the same soil moisture treatments, nature growth height, leaf expansions and maximum leaf areas of the plant increased gradually with the contents of soil organic matter elevated.As the same organic matter contents, except for the combination of higher soil moisture and soil organic matter, nature growth height, leaf expansions and the maximum leaf areas of the plant increased gradually when the contents of soil moisture increased. In all the interaction treatments, with the interactive treatment of higher soil moisture, from 70% to 80%, organic matter was 100 g • kg-1, the leaf expansions, maximum leaf areas and natural growth height were significantly higher compared with other interactive treatments,while soil organic matter interacted with soil moisture which was excessive low or high, natural growth height,leaf expansions and maximum leaf areas were lower than those of other interactive treatments. It was noted that those interactions of soil moisture were higher and organic matter was beneficial to the increasing of yields per plant (Fig. 2), and among these treatments, when the soil moisture contents increased from 70% to 80%,interacted with soil organic matter content, which was 100 g • kg-1, the per plant yield was the highest compared with that of other interactive treatments.

Fig. 1 Interaction of soil moisture and soil organic matter impact leaf disease index of H. moellendorffii Hance powdery mildew

Table 4 Effects of soil moisture and soil organic matter interaction on H. moellendorffii Hance growth

Fig. 2 Effects of soil moisture and soil organic matter interaction on H. moellendorffii Hance yields
Soil moisture interacting with soil organic matter influence H. moellendorffii Hance quality accumulation
The interaction of soil moisture and soil organic matter could make a difference on quality accumulation ofH. moellendorffiiHance (Fig. 3). At the entire period of treatments, under the treatment of higher soil moisture contents, high contents of soil organic matter were conductive to the accumulation of soluble sugar, soluble protein, vitamin C and coumarin of plants. It could be observed, with the same contents of soil organic matter, contents of soluble sugar, soluble protein, vitamin C and coumarin increased along with the soil moisture contents increased. In addition, higher soil moisture contents from 70% to 80% interacted with high soil organic matter contents from 75 g • kg-1to 100 g • kg-1which significantly improved the accumulation of soluble sugar, soluble protein, vitamin C and coumarin of plants, and compared with other treatments, con-tents of soluble sugar, soluble protein,vitamin C and coumarin were significantly elevated under above treatments. When the soil moisture contents were too low or high, soil moisture interacted with soil organic matter that was not conductive to the accumulation of soluble sugar, soluble protein, vitamin C and coumarin of plants, indicating that soil moisture had more effects onH. moellendorffiiHance quality accumulation compared with soil organic matter.

Fig. 3 Effects of soil moisture and soil organic matter interaction on H. moellendorffii Hance qualities
Discussion
The management of irrigation and fertilizer can make large effects on powdery mildew occurrences of the plant. Insufficient fertilization, soil water shortage and delayed irrigation result in crop growth and development stunting, increasing crop susceptibility to powdery mildew infection. In addition, the application of nitrogen fertilizer partially and excessive irrigation can cause plants growth excessing, plants dense and poor ventilation in the field, thus causing the occurrence and prevalence of powdery mildew. While rational management of water and fertilizer, combining application of N, P and K nitrites and focusing on drainage and humidity reduction could effectively inhibit the epidemics of crop powdery mildew (Rémyet al., 2005). In this research, when the soil moisture was lower or higher, the disease occurred rapidly with high disease incidence and index ofH. moellendorffiiHance powdery mildew, due to the drought or high humidity environment that resulted in poor growth and development of the plant, which accelerated the infection of powdery mildew fungus.H. moellendorffiiHance belonging to the leafy vegetable grew shade environment of forests, enjoying the soil containing rich organic matter, and under field cultivation conditions, with appropriate soil moisture, the plant absorbed more organic matter benefiting to the accumulation of nutritional qualities and the increasing of yields (Yuet al., 2018). The research demonstrated that higher soil moisture contents with 60%-80% interacted with high soil organic matter contents from 75 g • kg-1to 100 g • kg-1facilitated growths and developments ofH. moellendorffiiHance, and improved the powdery mildew related resistance of plants with the disease occurred slightly compared with other treatments. In this research, low soil moisture excessively was not conductive to the absorption of soil organic matter,accompanied with lower accumulation of vitamin C and coumarin. While, with high soil moisture excessively, plants short, less amounts of leaves, and even the occurrence of dead strains were observed,indicating that the treatment of high or low soil moisture excessively was a kind of adversity stress forH. moellendorffiiHance which did not make for growths and developments of the plant.
Conclusions
This research demonstrated that the interaction of soil moisture and organic matter could, to some extent,influence the occurrence ofH. moellendorffiiHance powdery mildew and plants' growth. The soil moisture,from 60% to 80%, interacting with soil organic matter, from 75 g • kg-1to 100 g • kg-1, effectively inhibited the occurrence ofH. moellendorffiiHance powdery mildew, meanwhile, benefited to growths and developments of plants compared with other interactive treatments. With above treatments, the disease incidence and index ofH. moellendorffiiHance powdery mildew occured weakly, moreover, the accumulation of soluble sugar, soluble protein, vitamin C and coumarin of plants was elevated significantly.
 Journal of Northeast Agricultural University(English Edition)2021年2期
Journal of Northeast Agricultural University(English Edition)2021年2期
- Journal of Northeast Agricultural University(English Edition)的其它文章
- Identification of QTLs Associated with Resistance to Pseudomonas syringae pv. Glycinea in Soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr)
- Development of an Artificial Diet for Effective Oral Delivery of dsRNA to Soybean Pod Borer, Leguminivora glycinivorella (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae)
- Grain Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency of Hybrid Rice in Response to High Plant Density and Nitrogen Rate
- Index Design and Comprehensive Evaluation of Germplasm Resources of Fruits Based on Mathematical Model of AHP and FCE: Sterculia nobilis Smith as a Case
- Comparative Analysis of Bacillus thuringiensis Vip3Aa57 and Vip3Aa62 Insecticidal Activities
- Comprehensive Evaluation of Processing Quality of Tibetan Native Hulless Barley Variety by Factor Analysis
