Characteristic Insights on Industrial Cyber Security and Popular Defense Mechanisms
Ming Wan,Jiawei Li,Ying Liu,Jianming Zhao,Jiushuang Wang
1 School of Information,Liaoning University,Shenyang 110036,China
2 School of Electronic and Information Engineering,Beijing Jiaotong University,Beijing 100044,China
3 Shenyang Institute of Automation,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Shenyang 110016,China
Abstract:Due to the deep integration of information technology and operational technology,networked control systems are experiencing an increasing risk of international cyber attacks.In practice,industrial cyber security is a significant topic because current networked control systems are supporting various critical infrastructures to offer vital utility services.By comparing with traditional IT systems,this paper first analyzes the uncontrollable cyber threats and classified attack characteristics,and elaborates the intrinsic vulnerabilities in current networked control systems and novel security challenges in future Industrial Internet.After that,in order to overcome partial vulnerabilities,this paper presents a few representative security mechanisms which have been successfully applied in today's industrial control systems,and these mechanisms originally improve traditional IT defense technologies from the perspective of industrial availability.Finally,several popular security viewpoints,adequately covering the needs of industrial network structures and service characteristics,are proposed to combine with burgeoning industrial information technologies.We target to provide some helpful security guidelines for both academia and industry,and hope that our insights can further promote in-depth development of industrial cyber security.
Keywords:industrial cyber threats;industrial characteristics;vulnerabilities;security mechanisms and viewpoints
I.INTRODUCTION
At present,Networked Control Systems have been successfully and widely applied in various critical infrastructures,including electric power stations,metallurgical and petrochemical plants,transportation systems,nuclear facilities,etc [1].To some extent,they can be regarded as a strategic industry which is related to the national economy and social development in breadth and depth.As described in[1],networked control systems,such as DCS (Distributed Control Systems),SCADA (Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition) and PLC (Programmable Logic Controllers),are always used to perform industrial activities(automated management,process control,data acquisition and monitoring,etc.) over various industrial Ethernets and fieldbus networks.Until now,we have already undergone three industrial revolutions,and are witnessing the fourth industrial revolution which strengthens the interaction and integration of new information communication technology and advanced manufacturing.Actually,the original ICSs(Industrial Control Systems) are enclosed and self-determining,and they always offer the closed-loop control and feedback[2,3].However,with the deep integration of IT(Information Technology)and OT(Operational Technology),the state of“isolated information island”has been gradually broken[4].Especially,in order to maximize resource utilization and production efficiency,some new strategies,such as Industrial Internet[5]and Industry 4.0[6],have been widely recognized and developed.In these strategies,one of the common features is that they all emphasize the industrial application of emerging information technologies (Artificial Intelligence [7],Big Data [8],Internet of Things [9],Edge Computing[7,10],etc.).Under the positive effects of these technologies,networked control systems are also facing an increasing risk of international cyber attacks[4,11-14].
After Stuxnet in 2010 [15],a variety of industrial cyber attacks and intrusions continue to emerge and cause huge losses.According to the annual ICS vulnerability reports of famous industrial cybersecurity companies“Positive Technologies”and“Dragos”,the number of new vulnerabilities in ICS components rose by 30% from 2017 to 2018 [16],and a total of 438 ICS vulnerabilities,in which more than 25% advisories had no available patch,were identified in 2019[17].With the emergence of diversified attack ways,traditional simple attacks have evolved to more sophisticated and surreptitious APTs (Advanced Persistent Threats) [18],and most businesses (66% of the surveyed companies in 2018)believe that targeted attacks and APTs are a major concern in the area of OT/ICS cybersecurity,since their potential impact makes these businesses extremely threatening [19].Furthermore,APTs frequently exploit zero-day vulnerabilities to perform the targeted multi-step attacks,and they are hard to detect and defend because the sophisticated techniques can camouflage their activities [20].Traditionally,the experienced engineers willingly focus on the process safety,whose main purpose is to provide the ability of risk aversion and treatment against random or independent faults [3,21].However,the process safety mechanisms cannot protect networked control systems from malicious cyber attacks.Additionally,because of the industry-oriented communication protocols or the unique properties,the security technologies in traditional IT systems cannot be successfully applied in ICSs without any change[22-25].
Without regard to enterprise network,the current architecture of networked control systems can be divided into three areas [26-28]:in the bottom physical infrastructure,various field devices(sensors,actuators,etc.) are monitored and controlled by the programmable controllers(PLCs,DCS controllers,etc.);in the middle supervisory control network,some critical servers,historians and workstations perform the process control and the real-time data collection from the programmable controllers;in the upper process management area,some business workstations or their clients(HMI client,OPC client,etc.)can plan the production process and manage the daily production task.Moreover,the topologies of networked control systems are generally static,and different industrial communication protocols are designed as the interaction carriers between areas.Because this architecture is not built with security in mind[26,28],the increased connectivity and the documented protocols have brought great convenience to the hacker's invasion[29].
In this paper,from the characteristics of networked control systems,we first analyze their differences from traditional IT systems,and discuss their extrinsic cyber threats and intrinsic vulnerabilities.On this basis,we expound several representative security mechanisms applied in today's networked control systems.Moreover,these mechanisms can consider the availability of industrial devices and networks,and reduce the risks caused by traditional connatural vulnerabilities.Also,we present some popular security viewpoints which may be applied and developed to ensure the stabilization and reliability for future Industrial Internet,and these viewpoints properly incorporate novel security mechanisms into burgeoning industrial information technologies.
The main contributions of this paper are listed as follows:firstly,we summarize the special characteristics of networked control systems,including the differences from traditional IT systems and some incoming features of future Industrial Internet,and discuss the intrinsic vulnerabilities and new security challenges according to different security issues;secondly,we introduce a few representative security mechanisms which originally improve traditional IT defense technologies from the perspective of industrial availability,and analyze their advantages and disadvantages to suggest the corresponding improvement strategies;thirdly,combining with the burgeoning industrial information technologies,we present several popular security viewpoints which may be challenged to meet the specified requirements of internetworking,interconnection and interoperation,and these viewpoints may offer incomparable brightness to protect Industrial Internet.
Based on the above contributions,our major objective involves the following three aspects:To begin with,by summarizing the attack classification and traditional vulnerabilities in today's networked control systems,we raise three possible cyber security challenges according to new features of Industrial Internet,and we hope that these challenges may become one of the major concerns in industrial cyber vulnerabilities;Next,by introducing some security mechanisms successfully applied in today's networked control systems,we provide an in-depth discussion on the advantages and disadvantages of each security mechanism,and hope that these can point out a direction for further research and improvement;Finally,by combining with burgeoning industrial information technologies,we present several popular security viewpoints which have started to be explored by some researchers,and hope that they can bring some new opportunities or breakthroughs for industrial cyber security researches.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows:Section II summarizes industrial characteristics of networked control systems.Section III outlines some devastating industrial cyber threats in recent years,and analyzes the intrinsic vulnerabilities in networked control systems and new security challenges in Industrial Internet.Section IV describes a few representative security mechanisms which have been successfully applied in today's networked control systems.Also,we provides several popular security viewpoints which may be developed and applied to protect Industrial Internet in Section V.Finally,Section VI provides some concluding remarks regarding this research.
II.INDUSTRIAL CHARACTERISTICS OF NETWORKED CONTROL SYSTEMS
To meet the large-scale requirements of modern industry automation,networked control systems have quickly developed and integrated the applications of computing,automatic controlling,communication and diagnosis technologies.In general,networked control systems used to form a stable multi-layer structure [26-28],and all devices in the same or different layers connect to each other by various communication networks,typically including industrial Ethernet[30],CAN bus network,industrial wireless network[31],etc.Without considering the common IT services,industrial characteristics of networked control systems can involve two aspects:the characteristics of industry-oriented software/hardware platforms and the characteristics of industrial communication networks.In the first aspect,the industry-oriented software/hardware platforms are built on proprietary hardware modules,operating systems and application components.For instance,most PLCs belong to programmable embedded electronic devices,which are designed with various embedded real-time operating systems (such as VxWorks andµCLinux) and have highly reliable logic control programs and self-diagnosing functions[32].In the second aspect,industrial communication networks,especially supervisory control networks,always use the specialized industrial communication protocols to accomplish an efficient data transaction(such as control commands),and they have the properties of quick response and few network failures[33].
In order to explain industrial characteristics,the differences between current networked control systems and traditional IT systems have been researched by both academia and industry [1,21,34-37].Originally,networked control systems are totally different from traditional IT systems,and they are regarded as one isolated system which uses some specialized control protocols,software and hardware.However,with the application of information communication technology,networked control systems start to employ general-purpose PCs(Personal Computers),OSs(Operating Systems)and network protocols,and their architecture and design increasingly resemble the ones of traditional IT systems.Even so,networked control systems still have notable characteristics distinguished from traditional IT systems.Especially,in the aspect of security attribute's priority,networked control systems put more emphasis on the high-availability and real-time characteristics,and IT systems prefer to the confidentiality.Table1 shows the detailed differences between current networked control systems and traditional IT systems.Although these differences cannot try to cover all possible situations,they can express some essential and unique characteristics of networked control systems.Moreover,the differences can also reflect the distinctive vulnerabilities in networked control systems,and cause some possible conflicts with traditional IT security mechanisms.
As one new industry modality,Industrial Internet is the representative of future intelligent manufacturing,and can provide the characterized ability to support the development of intelligent industries.At present,the researchers have proposed some emerging theoriesand technologies to promote Industrial Internet[5,7-10,38],and these theories and technologies also bring a series of novel characteristics,which are partly summarized as follows:firstly,the integration of IT and OT can transform the human-centric features in traditional IT systems to the device-centric features in Industrial Internet;secondly,the dynamic allocation of service networks can transform the fixed network system to the flexible network system which is oriented by various industrial services;thirdly,the interconnection and interoperation can transform the semi-isolated network structure in current networked control systems to the wide-open network platform in Industrial Internet.
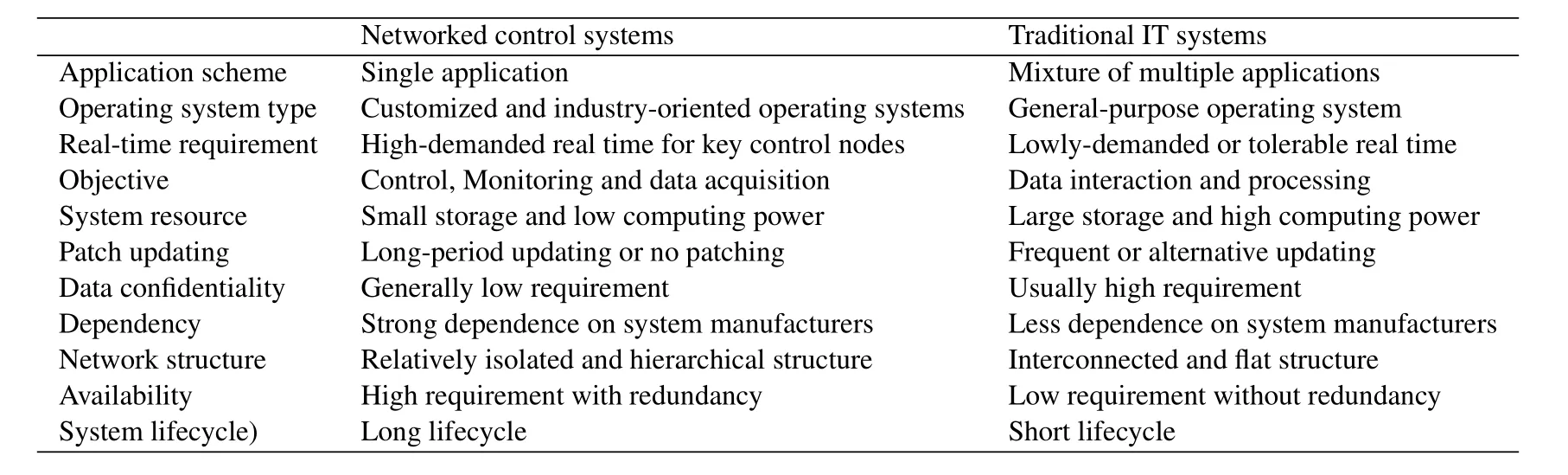
Table1.Main differences between current networked control systems and traditional IT systems.
III.CYBER THREAT AND VULNERABILITY IN CURRENT NETWORKED CONTROL SYSTEMS
3.1 Cyber Threat and Attack Classification
Along with the further application of information communication technology,industrial cyber security is facing severe challenges,and draws increasing attention from the ICS or manufacturing perspective[39,40].Figure1 lists the illustrative industrial security incidents from 2010 to 2019,and each representative incident has caused an adverse social impact and huge economic loss.In short,the main reasons can be summarized in two parts:the intrinsic system weaknesses[41]and the uncontrollable IT threats[34].Furthermore,the intrinsic system weaknesses can be regarded as the internal system deficiencies,and the uncontrollable IT threats can be considered as the external adversary invasions.As one of the greatest threats,the targeted attack [21]must conform to two abovementioned factors.On the one hand,the system weaknesses must exist and be exploited by the attackers to perform destructive operations.On the other hand,the attacking path must be successfully established to access the target.
The basic properties of cyber security include integrity,confidentiality,availability,authentication,and non-repudiation [42].For the malicious attackers,their main purpose is to damage these cyber security properties by using various sophisticated information technologies.Actually,current cyber threats in ICSs have developed with the tendency of multilateral directions and ranks,and they are hardly detectable and preventable.According to different attack purposes,the attacks in networked control systems can be roughly classified into five types,including Denial of Service type,protocol exploiting type,control seizing type,information gathering and destroying type and forging spoofing type.Table2 describes the detailed attack classification in networked control systems,and explains the corresponding attack characteristics and samples.In particular,the above-mentioned industrial security incidents make a comprehensive application of multiple attack types.For example,Stuxnet exploits the zero-day flaw of WinCC software to seize its control,and gathers the PLC's information to forge malicious control commands.Additionally,APTs are not assigned to any type in our statistics,and the major reason is that APTs systematically compromise the targeted network or system for a prolonged period by a group of sophisticated and coordinated attackers[43].More precisely,a general APT can refer to the following six steps:intelligence gathering,point of entry,command and control communication,lateral movement and persistence,asset/data discovery,and data exfiltration[44].In order to achieve an aggressive effect,each step may consist of multiple simple attacks mentioned in Table2.In practice,Stuxnet can be regarded as one typical example of APTs.
3.2 Vulnerability Analysis
Essentially,current networked control systems follow the combined strategy of IT and OT.Accordingly,they not only inherit the traditional connatural vulnerabilities,but also face new security challenges due to the incoming characteristics of emerging IT technologies.
In the aspect of traditional connatural vulnerabilities,the relative achievements have been widely researched and discussed by both academia and industry [1,21,28,34,45].According to NIST SP 800-82 [1],the vulnerabilities of networked control systems fall into three categories:1) industrial platform vulnerabilities [46,47],such as operating system or database weaknesses,industrial application software bugs and field control device flaws.Due to these vulnerabilities,industrial devices may become the most direct attack targets.2)industrial network vulnerabilities [48,49],such as industrial communication protocol vulnerabilities.Moreover,the skilled attackers can launch remote attacks by exploiting these vulnerabilities.3) security policy and procedure vulnerabilities [50,51],such as inattentive access management policies,unused system updates and irrelevant security patching configuration.Furthermore,these vulnerabilities can result in the negligence of industrial security management,and expose the loophole to the opportunistic attackers.In particular,the above three categories of vulnerabilities directly relate to the root causes of many security problems in current networked control systems,and also severely affect the development and construction of future Industrial Internet.Table3 shows our collection of current vulnerabilities in networked control systems according to the work in[1,21,28,34,45].Differently,we classify industrial platform configuration vulnerability into security policy and procedure vulnerabilities,and the main reason is that we consider the configuration belongs to the human-based management pattern which needs the guide of relevant security policies.
Different from current networked control systems,Industrial Internet will apply various emerging technologies to get the realization of automatic,intelligent,integrated and global manufacturing.Therefore,Industrial Internet will possess some novel features,which may bring about new challenges for industrial cyber security [36,52].The new challenges can be briefly summarized as:
Endnote security challenges:Industrial Internet emphasizes the unprecedented integration of IT and OT,and this situation can change the traditional CAN Bus connection of industrial field devices to the direct IT connection to public information systems.So,the potential security holes of industrial field devices can be directly exposed to Internet,and make them more vulnerable to malicious attacks.
Network security changes:Industrial Internet can dynamically configure various network services,and establish a service-oriented reconfigurable network system from the traditional fixed network structure.Therefore,some attack behaviors may dynamically change with the service-oriented reconfigurable network,and the passive static security functions and strategies in traditional networked control systems may be no longer applicable and sustainable.
Security supervision changes:Industrial Internet changes the semi-closed network structure to the wideopen network platform,and this interconnectivity and intercommunication can provide more entries and paths for APTs.Thus,it can cause serious problems for the network monitoring and management.
Based on the analysis of the foregoing two subsections,we give an attack example of malicious code infection in Figure2,and our main purpose is to make them easier to understand and study.
IV.CURRENT SECURITY MECHANISMS IN NETWORKED CONTROL SYSTEMS
Compared with the confidentiality,networked control systems enhance the high availability to realize the real-time control during the manufacturing process.In practice,security mechanisms are a class of additional services to prevent the intentional or misuse damages,and the applications of different security mechanisms may affect the availability more or less.However,the availability does not conflict with the confidentiality in networked control systems,and they possess the intersection which can be considered as the boundary conditions.Although these boundary conditions are difficult to quantify due to diversified requirements of various industrial applications,one common purpose of these boundary conditions is to ensure the adequate security without affecting the essential industrial availability.From the perspective of the characteristics of networked control systems,current security mechanisms can comprehensively consider their particularities (system architecture,industrial communication protocols,computing resource,etc.) [53],and overcome their vulnerabilities to guarantee the stabilization and reliability.
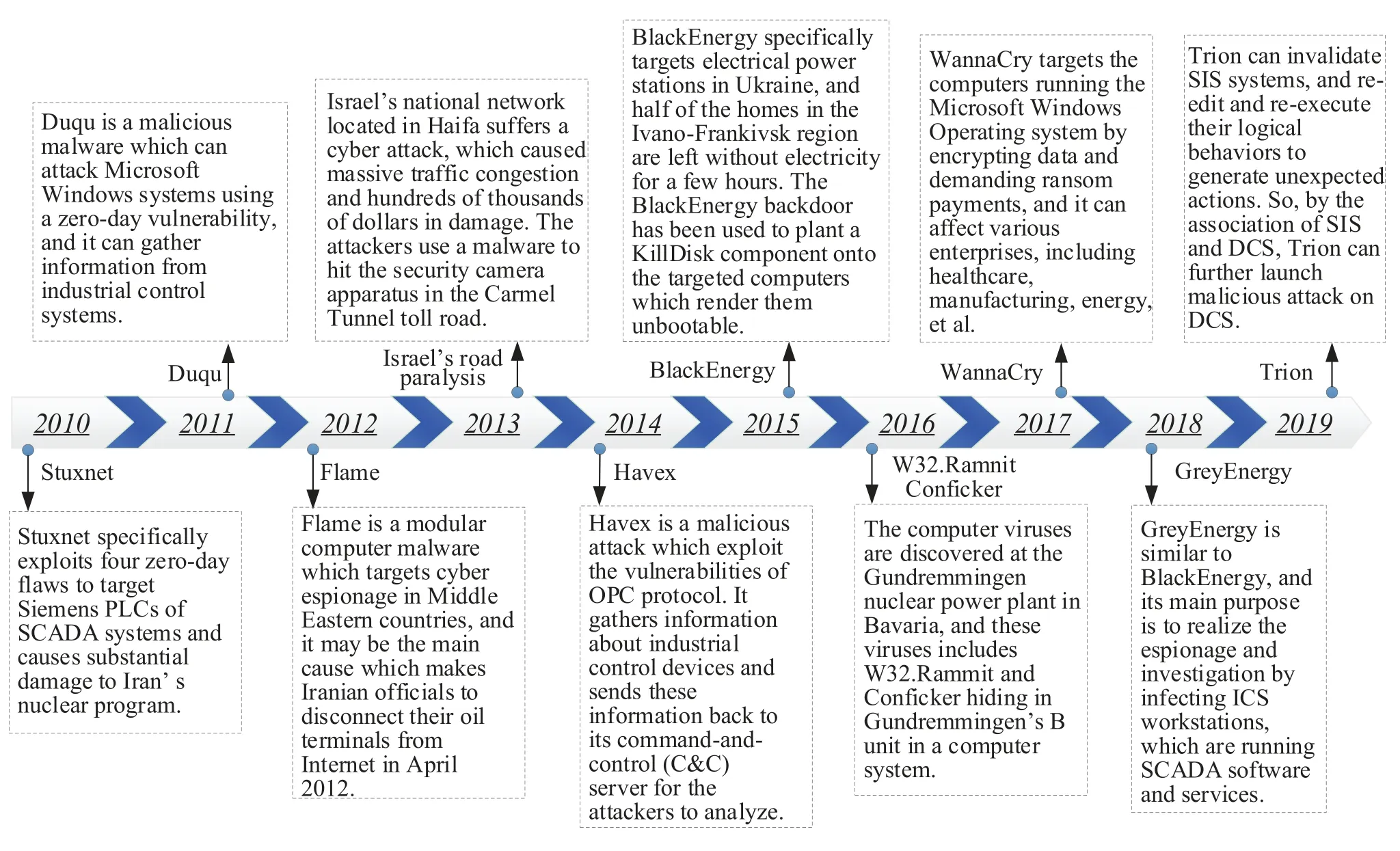
Figure1.Illustrative industrial security incidents from 2010 to 2019.
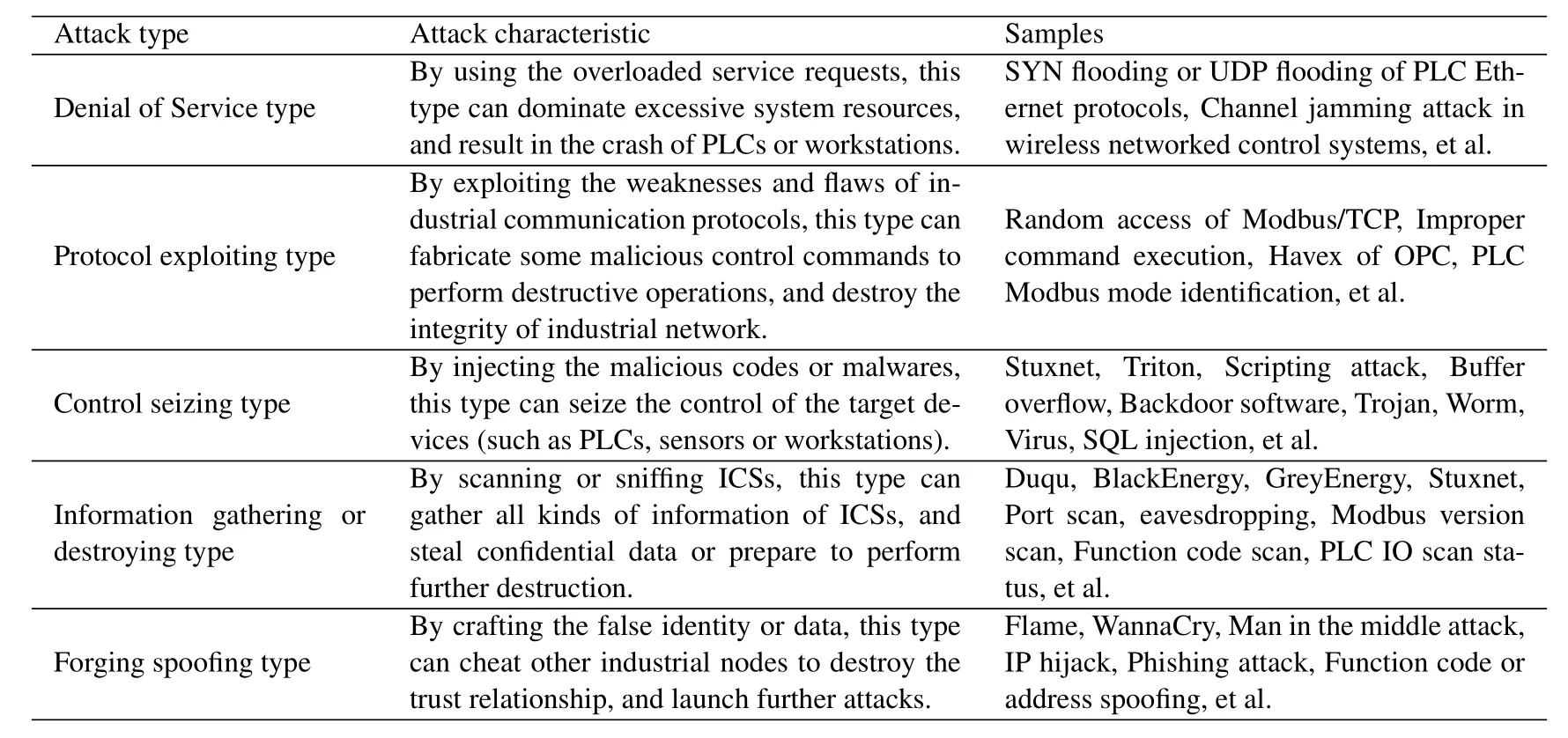
Table2.Simple attack type and characteristic in networked control systems.
4.1 Access Control
Access control,or called communication control,is a popular security mechanism in today's networked control systems,and its typical applications are industrialfirewall and NetGap [28,54-57].Based on the defense-in-depth strategy of NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology),this security mechanism can deeply parse industrial communication packets according to the specific protocol format[58],and enhance the relative isolation by filtering malicious attack flows.Furthermore,the access control successfully introduces DPI (Deep Packet Inspection) technology,and matches the parsed contents with the default white-listing rules.By this way,this mechanism can block the improper control commands carried in industrial communication packets,and establish different security zones in industrial control networks.Until now,many industrial communication protocols have been supported,typically including Modbus/TCP,DNP3,OPC Classic,etc.,and the corresponding performance evaluation focuses on throughput,latency,packet loss rate,concurrent connection number and connection rate [28].The primary advantage of this mechanism is that it belongs to one straightforward and effective method to prevent cyber attacks,which break the white-listing rules or violate industrial communication protocol specifciation.However,there are still some defciiencies to be improved:1) current white-listing rules cannot provide enough granularity,and they usually limit the defense in breadth and depth;2) the setting of default white-listing rules is performed artifciially,and it may cause serious accidents if any setting error occurs;3) as one matured security middleware,it may affect the real-time operations of ICSs in some degree[56].Specially,it is worth mentioning that some researchers have already started to propose the rule selflearning approaches for industrial friewalls [59,60],but the self-learning effectiveness needs to be further discussed if they are applied in real-world industrial control networks.
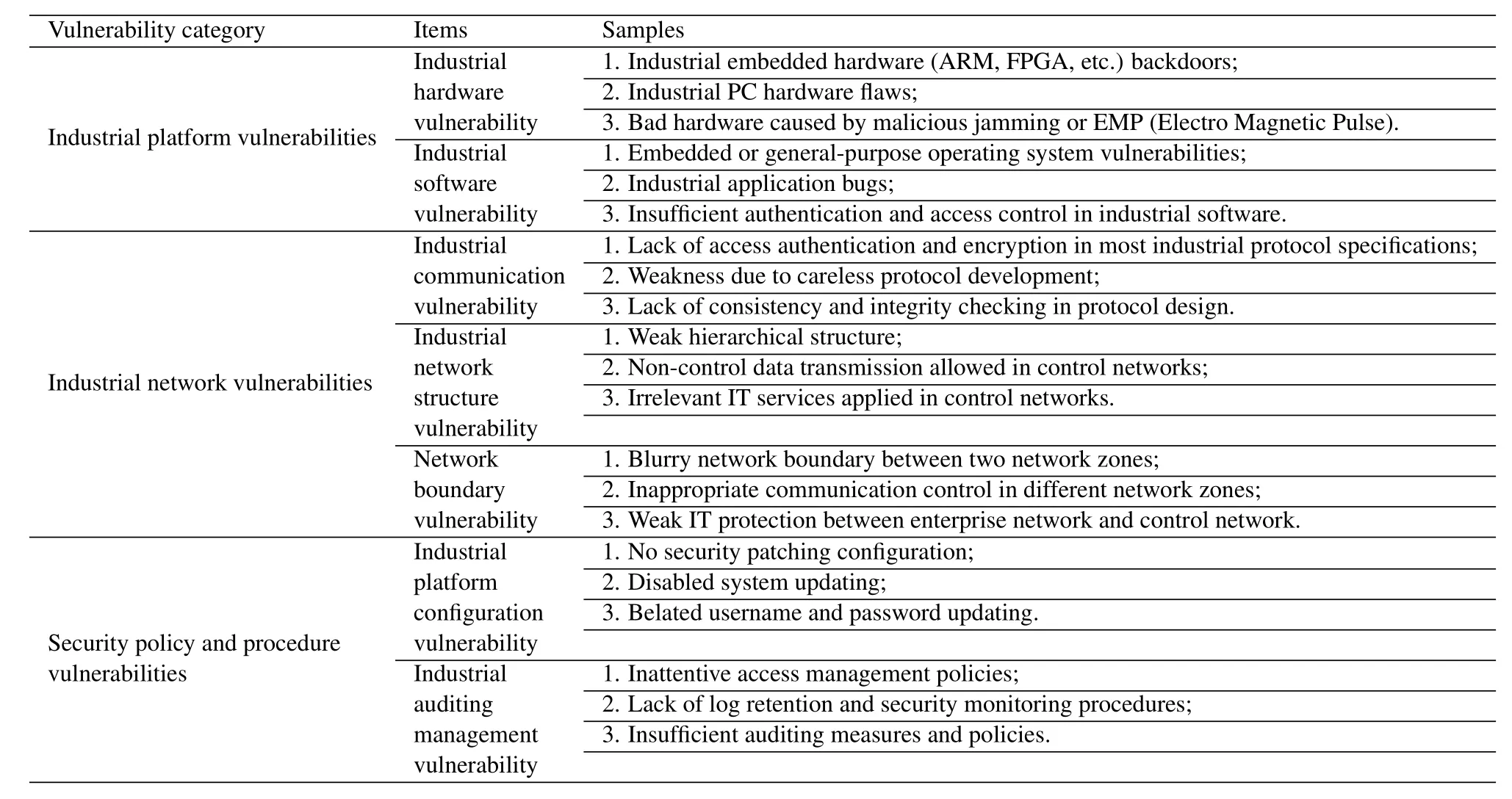
Table3.Detailed vulnerabilities of current networked control systems.
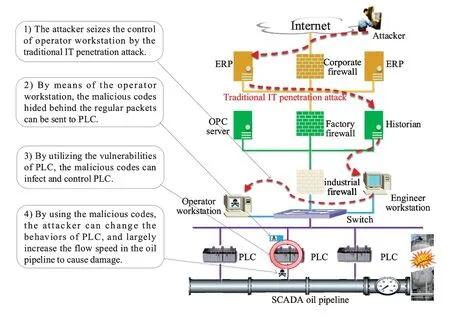
Figure2.An attack example of malicious code infection in petroleum SCADA system.
4.2 Intrusion Detection
In order to identify industrial cyber attacks,intrusion detection in networked control systems [61-63]is an effective security mechanism,because it can scarcely limit the available and real-time characteristics of industrial communication due to its bypass (or threeparty monitoring) technology [24].Furthermore,intrusion detection in networked control systems can be classified into two categories:misuse detection and anomaly detection.Moreover,misuse detection uses the exploited attack signatures or rules to distinguish known attacks [64,65],and this mechanism has fine detection accuracy and stability.However,it need use the prior knowledge on known attacks to search their attack traces.Differently,anomaly detection only uses normal network features to train a regular industrial communication model,and identifies misbehaviors by comparing with the observed industrial data[66].Although its detection accuracy needs to be improved and perfected,it is worth mentioning that this mechanism has well-behaved ability to identify novel or unknown attacks,which are common occurrences to cause serious accidents in today's networked control systems.According to the work in [24]and[67],statistical-based,knowledge-based and machine learning-based approaches are three typical categories of anomaly detection approaches in networked control systems.In the statistical-based cases [68,69],one typical approach is to learn the industrial communication traffic profile,and its main advantage is that it can successfully distinguish abnormal behaviors which do not comply with the normalized communication traffic pattern.However,these approaches cannot escape some obvious shortcomings:1)the metric setting of traffic profile should change dynamically with different industrial communication activities,but it is incredibly hard to achieve this target;2) it is nearly impossible to fully describe industrial communication characteristics by simply using the statistical distribution.In the knowledge-based cases [70,71],an expert system or a specification-based model is built to identify normal industrial communication behaviors,and the fine robustness and flexibility become their main advantage.Although these approaches can promote a powerful separation between legitimate industrial activities and cyber attacks,the main drawbacks are listed as follows:1) the detection accuracy and efficiency are entirely dependent on the highquality expert knowledge;2) the training system or model involves a large amount of prior knowledge,and it is difficult to measure the corresponding deviation.In the machine learning-based cases,many approaches,such as clustering technique [72],neural network [25,73],genetic algorithm [74],fuzzy logic[75]and support vector method [24,76],are adopted to train an explicit or implicit model to discriminate different communication behaviors.Moreover,these approaches can require increased emphasis on artificial intelligence technologies,and automatically learn industrial communication interactions to characterize behavior patterns.Although the above approaches are promising for further development of anomaly detection,there are still some technical difficulties to sort out:1) it is imperative to reduce the false positive or false negative rate for the unknown protocol specification and message format [77];2) some critical processes (such as feature extraction and detection engine optimization) have their own insufficiencies and flaws,and the corresponding researches should be extended in breadth and depth;3) single approach or simple combination cannot satisfy the demand of accurate APT detection,because APTs frequently exploit zero-day vulnerabilities and have their“low-andslow” attack patterns.In order to effectively detect APTs,the provenance-based detection approach becomes one of the most promising state-of-art ways to track stealthy intrusions.Moreover,this approach may have good application prospects in industrial intrusion detection,because it can offer rich contextual and historical information to analyze industrial abnormal activities without predefined attack signatures[78,79].
4.3 Security Testing and Vulnerability Exploiting
Current networked control systems are suffering unending and diversified cyber attacks,and one critical reason is that they cannot escape from various kinds of loopholes.In practice,there are three main effective security mechanisms to discover these loopholes in networked control systems:security testbeds[80-83],honeypots[65,84],and vulnerability exploiting [85-88].Furthermore,for the security testbeds and honeypots,the researchers can build one simulated control system by using industry-oriented software and hardware to implement some partial technological processes,and further analyze the weaknesses of this simulated system by launching or attracting a variety of cyber attacks.Specially,a major advantage of these mechanisms is that the testbeds or honeypots can record and track each process or activity in multi-step attacks.Additionally,they not only directly find security weaknesses of industrial software or hardware by using the penetration testing,but also perform the correlation and impact analysis on multistep attacks.However,these mechanisms cannot convey a comprehensive representation of security statuses in networked control systems,and the applied authenticity of simulated system also needs to be further evaluated.For the vulnerability exploiting,its major goal is to mine the vulnerabilities of industrial protocols and embedded devices.In particular,two effective approaches have been widely developed:known vulnerability scanning and unknown vulnerability mining.Based on the proprietary vulnerability databases,such as CVE(Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures),NVD (National Vulnerability Database)and OSVDB (Open Source Vulnerability Database),the known vulnerability scanning approach generates testing cases to scan the targets and find the unpatched bugs,and this approach has succeeded in high working efficiency and easy implementation.However,its main shortcoming is that this approach is highly unprofitable to unknown attacks due to the precondition of published or exploited cases.Differently,the unknown vulnerability mining approach,regarded as an automatic robustness testing technique,can not only remark known flaws,but also exploit some zero-day flaws by establishing a fuzzy testing engine.In general,it takes considerable time and attention to generate and traverse all fuzzy testing cases,and it is difficult to achieve a fine success rate.Even so,the researches on the zero-day exploiting prior to the attackers are of much more importance in realistic cases.Besides,these two approaches are only available for offline testing due to the requirements of uninterrupted industrial activities.
4.4 Situational Awareness
In order to ensure the comprehensive security and stability,networked control systems not only need the real-time intrusion detection when cyber attacks occur,but also require the effective security trend prediction before cyber attacks occur.As an acknowledged security mechanism,situational awareness in networked control systems can have a good ability to accurately predict the system security status in the period ahead [89,90].At this stage,the researches on situational awareness in networked control systems are still in their infancy:on the one hand,the researchers have already proposed some specific demands to realize the situational awareness in networked control systems [91,92];on the other hand,combined with traditional IT technologies,some researchers have begun the corresponding technical exploration to strengthen the adaptive security and management[93,94].However,the targeted designs and unique requirements still need to be improved,and the reasons are briefly summed up as follows:1) different security requirement levels for networked control systems are still unclear,and the security boundary conditions need more argumentations;2) due to the specific system structure and communication characteristics,it is a daunting task for the researchers to improve the situational awareness in networked control systems;3) the characteristics of interconnection and interoperation in Industrial Internet will cause a new hard nut to situational awareness,because they substantially enlarge the mutual relationship and influence of various industrial components.
4.5 Risk Assessment
Or more precisely,risk assessment in networked control systems looks more like a security measure than a security technology.After performing risk assessment,the engineers or managers can understand the security weaknesses,and know how to deal with the security issues and minimize the impact of uncertain incidents [21,95-97].Furthermore,risk assessment can analyze and grasp the latent security risks in the whole or partial system,and its main process involves four procedures:start-up,field implementation,risk analysis and proposal evaluation.According to final proposals,the engineers or managers can perform some professional improvements to enhance the overall system security.In today's ICSs,there are many risk assessment methods,typically including:highlevel attack tree and Markov decision[98],fuzzy probability Bayesian network [99]and multimodel-based incident prediction[100].In short,risk assessment is an important step to address the critical security challenges in networked control systems.According to the work in [97],risk assessment for networked control systems still needs to be developed and perfected,and some typical reasons include the following:1)the misoperation or failure may be confused with cyber attacks,and risk assessment should enhance its discriminating ability;2) the redundant human factors may influence the stability and accuracy of assessment results;3) the reliability of probabilistic data in risk assessment methods needs further improvement and strengthening;4) the comprehensive tools for all risk assessment procedures need to be supported.
4.6 IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) Security Mechanisms
Under the development of Industrial Internet and Industry 4.0,IIoT represents an inevitable technology trend to realize industrial intelligent manufacturing,and it can be considered as an important component of Internet of Things[101].Similarly,it also faces many serious security challenges,and is increasingly targeted by known or novel cyber attacks[102,103].In practice,the fundamental network structure of IIoT is wireless sensor network,which is more vulnerable to cyber attacks.Aiming at defending different attacks,the researchers have proposed some security mechanisms:for the DoS attack,the work in[104]presents a secure framework against DoS attacks,and this framework uses the distributed optimal scheduling to supply a resilient approach in the fog supporting IIoT environment;for the time synchronization attack,the work in[105]designs an enhanced secure time synchronization protocol for IEEE 802.15.4e-based industrial internet of things;for the sinkhole and Sybil attacks,the work in [106]implements a robust trust-aware routing framework for dynamic wireless sensor networks;for the inside keyword guessing attack,the work in[107]proposes a certificateless public key authenticated encryption with keyword search scheme,which is more secure and effective than other schemes;for the malicious access,the work in [108]puts forward a security level-based architecture for IoT-CI (Internet of Things-Critical Infrastructure)devices,and the low power security primitives are introduced to ensure sufficient security of IoT devices;for the information gathering attack,the work in[109]develops a detailed Quality-of-Service(QoS)modeling for multipath TCP to provide the data protection in IIoT networks,and the work in[110]presents a hybrid privacy-preserving scheme which may bring a new idea to both location and identity protection against a dynamic adversary in distributed wireless IIoT architectures.Apart from these,the work in[111]focuses on the possible attacks in the IIoT layered architecture,and gives a comprehensive survey of potential security threats and preventive measures.Without the wide application of IIoT in today's industrial environment,many existing security mechanisms are still placed in the experimental or theoretical research stage,and their feasibility and effectiveness in practical applications require further exploration.
V.POPULAR SECURITY VIEWPOINTS TO PROTECT INDUSTRIAL INTERNET
In this section,we provide several popular security viewpoints which may be developed and applied to protect current networked control systems or future Industrial Internet.In particular,these viewpoints can take into account industrial network structures and industrial service characteristics,and completely combine with burgeoning industrial information technologies.
5.1 Trusted Computing for Industrial Programmable Devices
Most of active industrial programmable devices(such as PLCs and DCS controllers) are not designed to avoid cyber security risks,and the vulnerabilities of their operating system and software can always be exploited by the hackers.As mentioned before,some additional security mechanisms (such as industrial firewalls) only provide an external protective measure which cannot satisfy the requirements on high availability and reliability in certain circumstances.As a feasible security mechanism,trusted computing can improve the self-defense ability of industrial programmable devices [112,113].However,the trusted computing module embedded in the motherboard necessarily occupies some storage and computing resources of industrial programmable devices,and the corresponding availability may also be unavoidably limited.In order to resolve this problem,the trusted co-processing unit can be designed to integrate the trusted computing module with FPGA,and takes advantage of FPGA's storage and computing power to perform the trusted computing.Figure3 describes the application of trusted co-processing unit in industrial programmable devices.On the one hand,during the system boot phase the trusted co-processing unit can verify the integrity of important codes,including BootLoader,OS image,control engine codes,etc.On the other hand,during the system running phase the trusted co-processing unit can provide some additional security functions,such as access authentication,encrypted communication and digital signature.In conclusion,trusted computing can be considered as an applicable mechanism to improve the intrinsic security of industrial programmable devices.
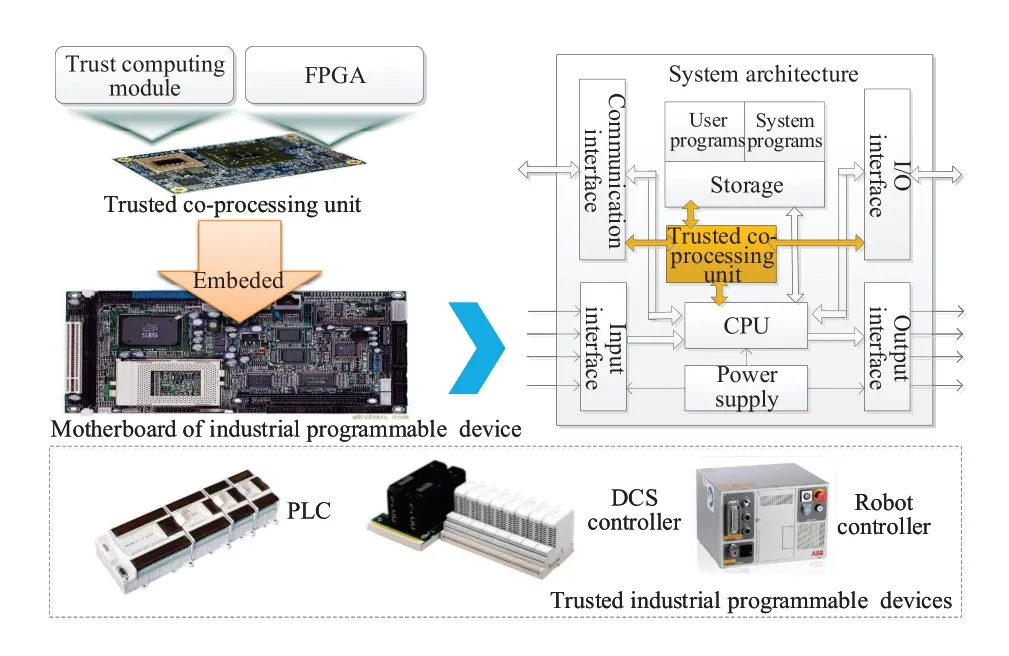
Figure3.Trusted co-processing unit in industrial programmable devices.
5.2 Software-Defined Security Mechanism
Compared with traditional industrial control networks,Industrial Internet has the distinguishing characteristics of customized services and collaborative organization patterns,which can dynamically change its network structure with different services.Therefore,traditional static defense mechanisms in today's networked control systems may be no longer applicable.Based on SDN (Software-Defined Networking) technology [114],the network architecture can be decoupled into two parts:control plane and data plane.From this point,the software-defined security mechanism can offer a dynamic security configuration according to different service demands.Furthermore,the controllers can gather diversified security defense functions in the form of software appliances,and distribute the corresponding defense functions into the switches according to the specific network resources and different security requirements.After the deep packet parsing,the switches can perform different network security defenses by using the downloaded software.Based on the centralized control and dynamic configuration,this security mechanism can implement the security optimization of the whole industrial network with the guidance of security requirements,and ensure the security and stability from the network level.Figure4 shows the dynamic configuration of security defense functions based on SDN architecture.Deserved to be mentioned,the similar researches or preliminary introductions have been announced by both industry and academia[77,115-118].
5.3 Edge Security Service Based on Edge Computing
As a burgeoning information technology,edge computing is hopefully applied in future networked control systems[119-121],and it is interchangeable with fog computing[122].Moreover,one significant characteristic of edge computing is that it can enable network edge devices to perform additional computing services,for example,a switch or gateway at the edge of LAN can be regarded as an edge computing device to accomplish additional functions.Particularly,as a connecting link between cloud services and IoT services,edge computing can not only receive and process service requests from the end users,but also perform the computing tasks from the clouds.Based on this special location,many services and benefits can be provided by edge computing,and the edge security service is a representative and important sample.As depicted in Figure5,edge computing can offer multiple security services,including application security,data security,network security and device security.For instance,on the side of device security,one switch at the edge of LAN can perform an authentication process to ensure the identity authenticity of IoT devices.In brief,edge security service can be regarded as a newly developing mechanism with great potentiality to strengthen industrial cyber security,and some relevant research achievements have been achieved by a few outstanding scholars[123-126].
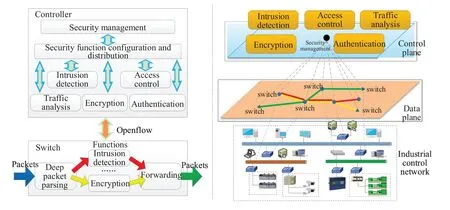
Figure4.Dynamic configuration of security defense functions based on SDN architecture.
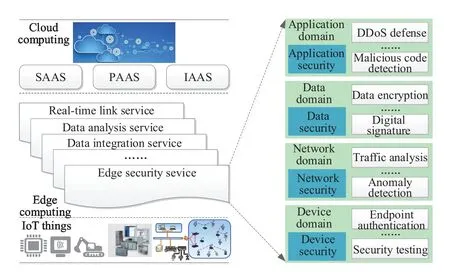
Figure5.Edge security services provided by edge computing.
5.4 Security Mechanisms Based on Big Data Analysis
With the development of Industrial Internet,the amount of data in networked control systems is becoming larger and larger,and big data analysis is a powerful tool to improve the efficiency of data processing and save software and hardware resources[127,128].Similarly,big data analysis not only can be successfully applied in industrial regular control and information processing [8],but also may provide an opportunity for specific applications which contribute to industrial cyber security.For example,the big data computing for digital forensics on industrial control systems has been proposed [129].Additionally,another illustrative case is situational awareness based on big data analysis in smart grid[130],and Figure6 shows a situational awareness architecture which uses big data analysis to correlate various industrial logs,data and traffic.What's more,with the real-time extraction of system logs and security logs,this mechanism can recognize and associate diversified industrial behaviors,and use big data analysis to monitor and visualize dynamic security statuses of networked control systems.However,industrial big data also brings kinds of cyber security risks [131,132],and the researchers should avoid these adverse security factors when they design some security mechanisms based on big data analysis.
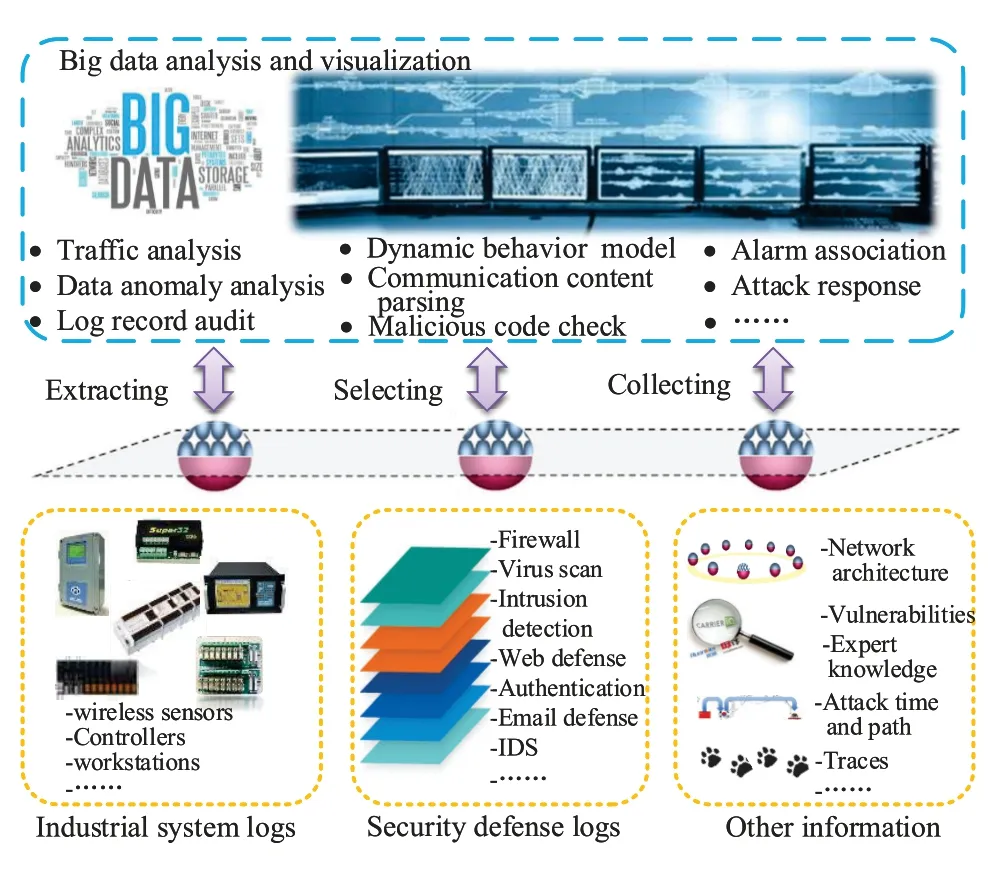
Figure6.Situational awareness architecture based on big data analysis in networked control systems.
5.5 Integration Of Security and Safety
Both security and safety have a great influence on the reliability of networked control systems,and they should be considered and developed together.On the one hand,security and safety are related because cyber attacks can result in safety issues.On the other hand,security and safety may be conflicted because they are two different areas with their own focuses [133].In order to resolve these conflictions,some researchers have already started to integrate security and safety in networked control systems.The work in [134]puts forward a risk-based task scheduling approach to integrate both security task and safety task and achieve the real-time risk control.The work in[135]describes some technical issues and topics to bridge functional safety and cyber security of SIS/SCS.The work in[136]proposes a model based approach for SCADA safety and security joint modelling,which can provide a risk analysis framework to evaluate industrial information and control architectures.The work in [137]proposes to rely on the safety cases to derive safety and security constraints in an interconnected way.After our extensive researches on the integration of security and safety,we should try to make efforts in three aspects:firstly,we should take full advantage of some common technologies between them,for instance,integrity checking is a typical one;secondly,the confliction should be properly addressed by using additional mechanisms,such as real-time scheduling or strategy trade-off;thirdly,we should establish the complementary and feedback mechanism,for example,we can use the security testing to check safety software.
5.6 Blockchain for Industrial Activities
In recent years,blockchain [138,139],which firstly facilitates secure online transactions,has become a hot research topic in recent years.Furthermore,blockchain is a decentralized and distributed digital ledger which is used to record transactions,and it allows the participants to inexpensively verity and audit transactions.Because of the decentralized structure,blockchain eliminates the risks which come with data being held centrally,that is,its network does not involve the vulnerabilities of centralized points which can be exploited by the hackers.Additionally,some blockchain security methods use encryption and digital signature technologies to provide data confidentiality and authenticity.Based on the above characteristics,a new assumption is that blockchain may have another successful application in industrial activities[124,140-143],especially when industrial data acquisition requires high trusts in IIoT networks.
We give a brief summary of current security mechanisms and popular security viewpoints in Table4,which also presents the vertical and horizontal comparisons of some typical security services.More specifically,the vertical comparison summarizes the characteristics of each industrial security service,and analyzes its most noticeable shortage worthy of careful consideration.Differently,the horizontal comparison focuses on several distinguishing approaches in the same security service,and investigates the comparable superiority and deficiency of each approach.
VI.CONCLUSION
This paper presents some insights on industrial cyber security and its development from the characteristics of networked control systems,and our main purpose is to provide some helpful security guidelines for both academia and industry.More specifically,we first classify the cyber threats in current networked control systems,and analyze their intrinsic vulnerabilities and some new challenges brought by Industrial Internet.After that,we outline some security mechanisms which have been successfully applied in today's networked control systems,and provide several popular security viewpoints by combining with burgeoning industrial information technologies.
Different from other similar studies [4,11-14,34-36,39-41,45,51,53],our main technique route can be concluded below:by enumerating recent industrial cyber threats and analyzing their attack characteristics,we summarize traditional connatural vulnerabilities in current networked control systems,and propose some novel security challenges in future Industrial Internet.Based on the existing vulnerabilities,we introduce some typical security mechanisms applied in today's ICSs,and analyze the potential problems of each security mechanism from our own point of view.Along with various burgeoning technologies,we depict the main design principles of popular security viewpoints,and discuss their superiority and deficiency by illustration of several fragmentary researches.According to the above technique route,the essential innovations ofthis paper briefly include:
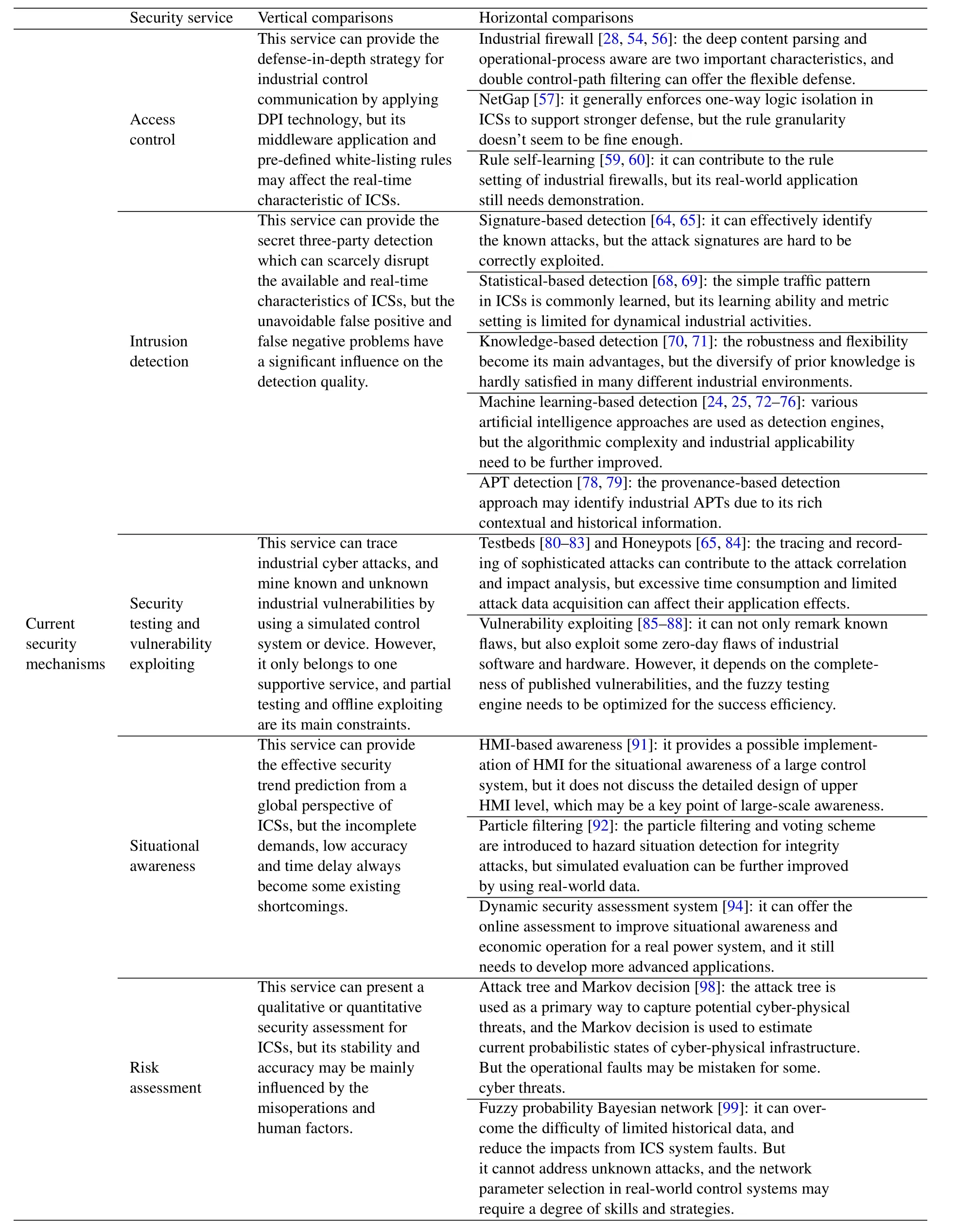
Table4.Vertical and horizontal comparisons of some typical security services.
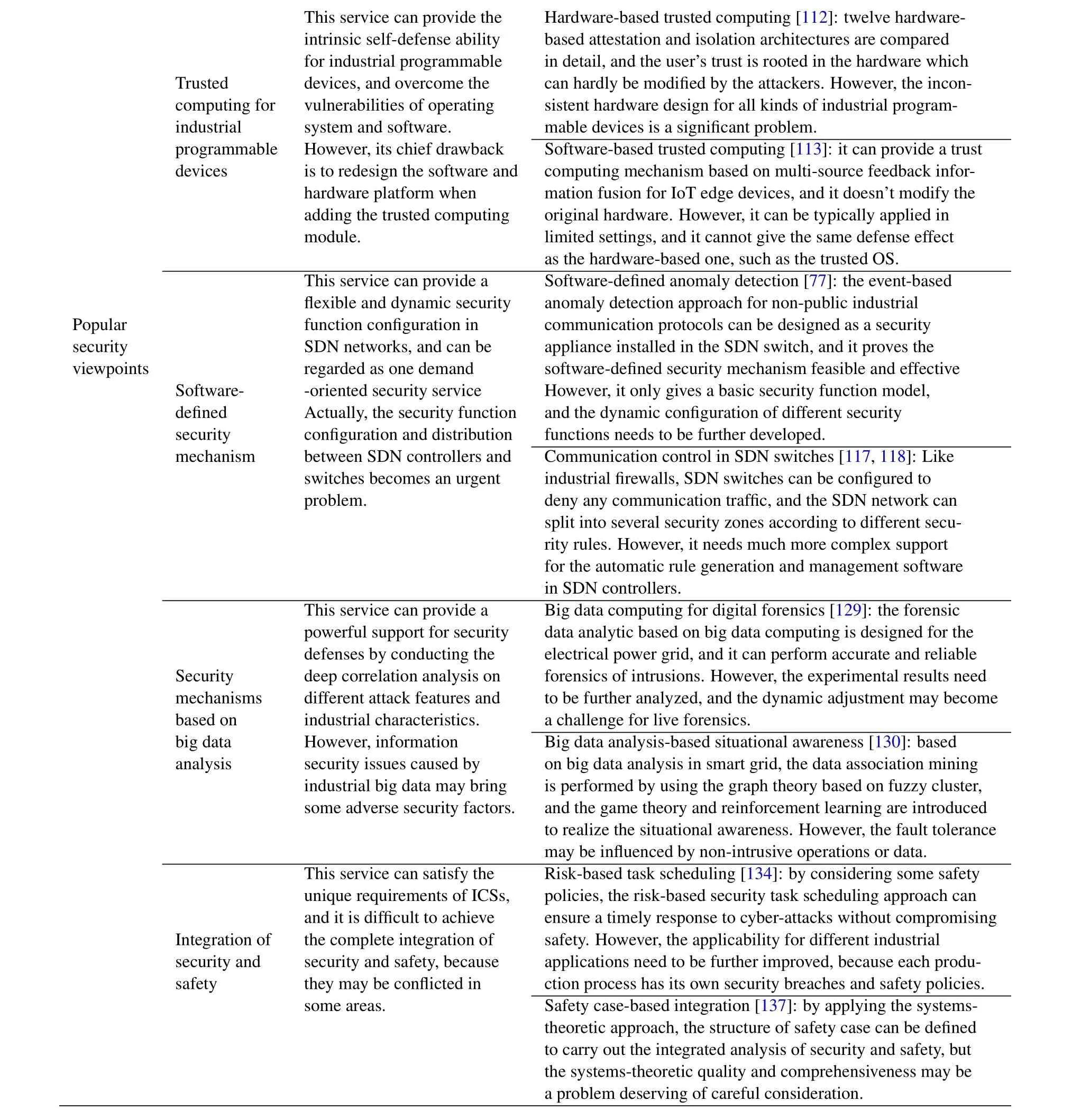
This service can provide the Hardware-based trusted computing[112]:twelve hardwareintrinsic self-defense ability based attestation and isolation architectures are compared for industrial programmable in detail,and the user's trust is rooted in the hardware which Trusted devices,and overcome the can hardly be modified by the attackers.However,the inconcomputing for vulnerabilities of operating sistent hardware design for all kinds of industrial programindustrial system and software.mable devices is a significant problem.programmable However,its chief drawback Software-based trusted computing[113]:it can provide a trust devices is to redesign the software and computing mechanism based on multi-source feedback inforhardware platform when mation fusion for IoT edge devices,and it doesn't modify the adding the trusted computing original hardware.However,it can be typically applied in module.limited settings,and it cannot give the same defense effect as the hardware-based one,such as the trusted OS.This service can provide a Software-defined anomaly detection[77]:the event-based flexible and dynamic security anomaly detection approach for non-public industrial Popular function configuration in communication protocols can be designed as a security security SDN networks,and can be appliance installed in the SDN switch,and it proves the viewpoints regarded as one demand software-defined security mechanism feasible and effective Software- -oriented security service However,it only gives a basic security function model,defined Actually,the security function and the dynamic configuration of different security security configuration and distribution functions needs to be further developed.mechanism between SDN controllers and Communication control in SDN switches[117,118]:Like switches becomes an urgent industrial firewalls,SDN switches can be configured to problem.deny any communication traffic,and the SDN network can split into several security zones according to different security rules.However,it needs much more complex support for the automatic rule generation and management software in SDN controllers.This service can provide a Big data computing for digital forensics[129]:the forensic powerful support for security data analytic based on big data computing is designed for the defenses by conducting the electrical power grid,and it can perform accurate and reliable Security deep correlation analysis on forensics of intrusions.However,the experimental results need mechanisms different attack features and to be further analyzed,and the dynamic adjustment may become based on industrial characteristics.a challenge for live forensics.big data However,information Big data analysis-based situational awareness[130]:based analysis security issues caused by on big data analysis in smart grid,the data association mining industrial big data may bring is performed by using the graph theory based on fuzzy cluster,some adverse security factors.and the game theory and reinforcement learning are introduced to realize the situational awareness.However,the fault tolerance may be influenced by non-intrusive operations or data.This service can satisfy the Risk-based task scheduling[134]:by considering some safety unique requirements of ICSs,policies,the risk-based security task scheduling approach can and it is difficult to achieve ensure a timely response to cyber-attacks without compromising Integration of the complete integration of safety.However,the applicability for different industrial security and security and safety,because applications need to be further improved,because each produsafety they may be conflicted in ction process has its own security breaches and safety policies.some areas.Safety case-based integration[137]:by applying the systemstheoretic approach,the structure of safety case can be defined to carry out the integrated analysis of security and safety,but the systems-theoretic quality and comprehensiveness may be a problem deserving of careful consideration.
1)Novel security challenges caused by the emerging features of Industrial Internet;
2) Comparative shortage analysis on each applied security mechanism;
3) Developable security viewpoints combined with burgeoning industrial information technologies.
Due to the contributions of this paper,we believe that our research can further promote in-depth development of industrial cyber security.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
This work was supported by the National Key R &D Program under Grant No.2018YFA0701604,and the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province under Grant No.2019-MS-149.
- China Communications的其它文章
- Edge Caching in Blockchain Empowered 6G
- Spectrum Prediction Based on GAN and Deep Transfer Learning:A Cross-Band Data Augmentation Framework
- Layered D2D NOMA
- Fully Connected Feedforward Neural Networks Based CSI Feedback Algorithm
- Erasure-Correction-Enhanced Iterative Decoding for LDPC-RS Product Codes
- Power Allocation for NOMA in D2D Relay Communications

