一种滑模控制新型幂次趋近律的设计与分析
张国山,李现磊
一种滑模控制新型幂次趋近律的设计与分析
张国山,李现磊
(天津大学电气自动化与信息工程学院,天津 300072)
针对传统趋近律存在的抖振问题,以及全局收敛速度较为缓慢的情况,本文通过对以往的多种幂次趋近律和指数趋近律进行对比分析,提出了一种新型幂次趋近律.该趋近律在以往幂次趋近律的基础上通过函数改进和新型函数的引入,实现了系统的快速收敛和无抖振.首先,新型幂次趋近律通过改进变指数项,在避免了系统收敛到滑模面时变指数项存在的抖振问题的同时,保留了变指数项在系统远离滑模面时优于比例项和幂次项的快速收敛性.其次,新型幂次趋近律引入了正切函数,在初始状态可知的条件下通过调节正切函数参数能够实现系统更快速的收敛性.本文通过理论证明了新型幂次趋近律能够实现系统快速收敛到滑模面且无抖振,并提出了趋近律中的参数设定方法,保证了系统在有界扰动条件下能够实现有限时间内快速地收敛到期望稳态精度.最后,通过对多种趋近律进行对比仿真验证了该趋近律的有效性,并通过系统在有界扰动下的仿真验证了参数设定方法的正确性,航天器姿态机动控制仿真进一步验证了新型幂次趋近律和参数设定方法的有效性和正确性.
滑模控制;正切函数;幂次趋近律;全局快速收敛
滑模变结构控制在理想情况下对满足匹配条件的不确定性和外界干扰具有完全鲁棒性.传统滑模控制由于实际开关控制中不可避免的空间滞后、时间延迟等问题导致了高频抖振现象[1],为了解决抖振问题,国内外学者提出了趋近律方法、动态滑模控制方法[2]以及高阶滑模方法[3]等.我国学者高为炳院士[1]提出了经典的趋近律概念,主要有:等速趋近律、指数趋近律、幂次趋近律和一般趋近律.指数趋近律具有通过调节参数提升系统状态远离滑模面时的收敛速度,并削弱抖振的特性,进而开始了以指数趋近律为基础的新型趋近律的研究.Fallaha等[4]在保持控制器稳态跟踪性能的同时,用动态适应被控系统变化的指数函数,设计了一种非线性趋近律,改善了收敛过程的动态特性并削弱抖振.Xiong等[5]基于文献[4]中的设计理念提出了快速指数趋近律(FERL),在保证收敛速度的同时,进一步削弱了抖振.Pandey等[6]提出了一种新型的自适应趋近律,使得系统在极短时间内到达滑模面,且抖振可以忽略不计.上述趋近律大多以等速趋近律和指数趋近律有机结合来进行削弱抖振、增快收敛速度,由于传统滑模控制中符号函数问题,抖振并未完全消除.Liu等[7]提出了新型指数趋近律(NERL),通过在基于Fallaha等[4]的设计理念中加入了幂次项,实现了优于传统指数趋近律的收敛特性.Mozayan等[8]为了进一步提升收敛速度并消除抖振现象,提出了增强指数趋近律(EERL),不同以往改进的指数趋近律,其添加了幂次趋近律和比例项来实现远离滑模面时的更快速收敛性和无抖振现象.幂次趋近律采用幂次项使得系统接近滑动模态时趋近速度放缓,消除了传统滑模控制的抖振现象.众多以幂次趋近律为基础的新型趋近律被提出.李鹏等[9]对幂次趋近律的稳态误差界进行了分析.Yu等[10]结合指数趋近律和幂次趋近律提出了一种快速幂次趋近律,主要以比例项提升初始状态远离滑模面时的收敛速度.梅红等[11]提出了一种双幂次趋近律用以实现机器人控制中状态快速收敛.张合新等[12]提出了一种新型的双幂次趋近律方法,并对其干扰稳态界进行了分析.李慧洁等[13]对双幂次趋近律的滑模控制方法进行有界扰动下的特性分析.廖瑛等[14]比较了快速幂次趋近律和双幂次趋近律不同阶段的收敛性,发现比例项在某些阶段比幂次项具有更快的收敛速度,进而提出新型双幂次组合函数趋近律,改善了动态特性,并且新型趋近律的变结构不在滑模面上且离滑模面较远,有效地消除了抖振现象.张瑶等[15]提出了新型的多幂次趋近律,引入了变指数项,实现了相较于双幂次趋近律的更快速的收敛性.蒲明等[16]提出了新型的变指数趋近律,将具有有限时间收敛的幂次项和变指数项进行组合实现了系统远离滑模面时更快速收敛性.Pan等[17]将双幂次趋近律与等速趋近律相结合,来实现变结构控制的全局快速收敛性,但是抖振问题伴随着等速趋近律在滑模面上的间断性而存在.
本文通过分析指数趋近律与幂次趋近律在远离滑模面时加快收敛速度的设计,并结合系统收敛到滑模面削弱或消除抖振的理念,提出一种新型幂次趋近律.此趋近律在保留以往幂次项的同时,引入改进的变指数趋近律和正切函数,实现了更快的收敛速度,最后通过仿真验证理论和方法的正确性和有效性.
1 新型幂次趋近律及其特性分析
新型幂次趋近律为
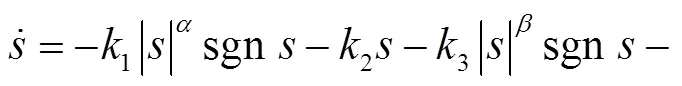
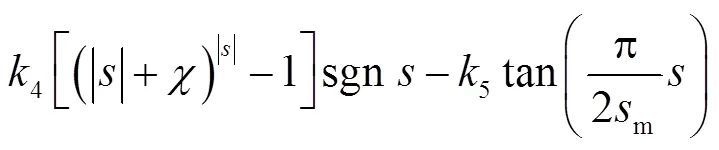
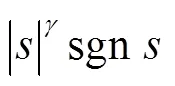
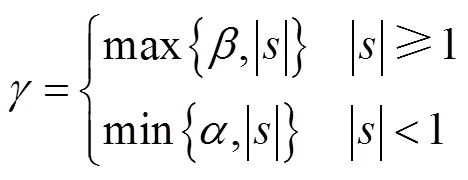
1.1 新型幂次趋近律分析

则系统是在实际有限时间稳定的,即在有限时间内到达平衡点的邻域内.



定理1:系统(1)将在有限时间内收敛于平衡点且无抖振.
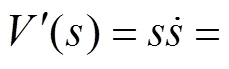


证明:记
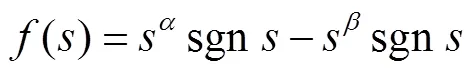
证明:由于

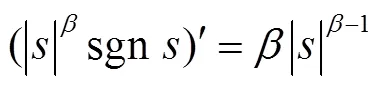

令



由上述分析可知,本文提出的新型幂次趋近律(1),结合双幂次项、比例项和改进的变指数项,并引用正切函数,以此达到了更完美的收敛效果.
定理2:新型幂次趋近律(1)在收敛的快速性上优于快速趋近律、双幂次趋近律、多幂次趋近律以及变指数趋近律.
1.2 稳态误差分析
考虑式(1)有不确定性扰动影响,系统变为


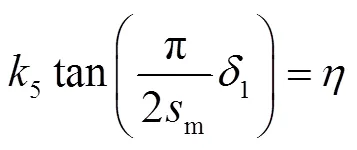



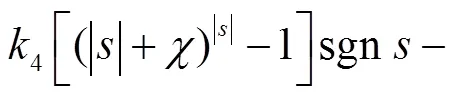
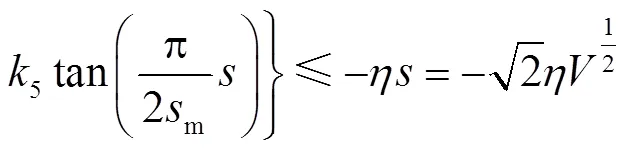
2 仿真分析
考虑单输入单输出非线性不确定性系统

2.1 快速收敛性仿真对比
对于确定系统(19),分别采用如下控制律.
(1) 快速幂次趋近律[9]为

(2) 双幂次趋近律[11-12]为


(4) 快速指数趋近律(FERL)[5]为

(5) 新型指数趋近律(NERL)[7]为
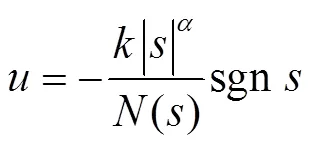
(6) 增强指数趋近律(EERL)[8]为

(7) 变指数趋近律[16]为

(8) 新型幂次趋近律为





对式(23)~(25)分析可知



由上述分析可知上述3种指数趋近律可以归类为参数变化的指数趋近律、参数变化的单幂次趋近律和参数变化的快速幂次趋近律.为了保证对比仿真的公平性,相同项的系数设定尽量相等.

图1 初始状态s0=0.5时s的收敛曲线
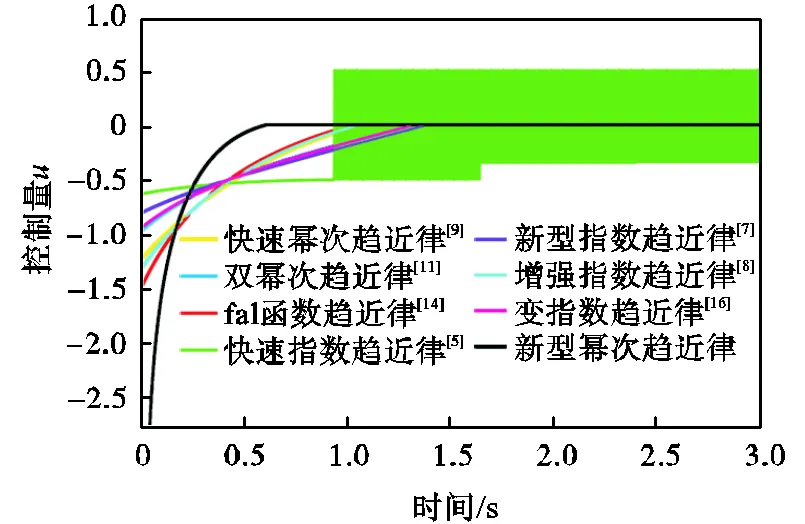
图2 初始状态s0=0.5时的控制量

图3 初始状态s0=5.0时s的收敛曲线

图4 初始状态s0=5.0时的控制量
2.2 稳态误差界仿真

图5 k1=4,a=(lg 2)/3时s的变化曲线

图6 k1=20,a=1/3时s的变化曲线

2.3 航天器姿态机动控制仿真
以航天器姿态机动控制系统为例,选取俯仰轴单轴机动情况进行仿真,考虑非线性系统[15]

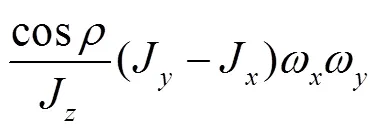


图7 不同趋近律下的航天器姿态跟踪情况

图8 不同趋近律下s的变化情况

图9 不同趋近律下的航天器控制量
图7~图9得到了与3和图4相近的结果,进一步验证了理论的正确性,收敛的快速性和趋近律的无抖振性.

图10 s的变化曲线

图11 航天器俯仰角的跟踪误差曲线
3 结 语
本文通过对多种幂次趋近律进行分析,对不同函数组合的趋近律进行了对比说明,通过结合以往幂次趋近律中的双幂次项和指数项,并通过改进变指数项,加入基于已知初始状态下的正切函数项,提出了多函数组合趋近律,实现了系统全局的快速收敛,且无抖振.同时给出了一级驱动项中参数设定规则,在有扰动时,可使新型幂次趋近律有限时间收敛到期望精度.通过仿真验证了本文新型幂次趋近律的优 越性.
[1] 高为炳. 变结构控制的理论及设计方法[M]. 北京:科学出版社,1996.
Gao Weibing. Theory and Design Method of Variable Structure Control[M]. Beijing:Science Press,1996(in Chinese).
[2] Koshkouei A J,Burnham K J,Zinober A S I. Dynamic sliding mode control design[J]. IEE Proceedings-Control Theory and Applications,2005,152(4):392-396.
[3] Laghrouche S,Plestan F,Glumineau A. Higher order sliding mode control based on integral sliding mode[J]. Automatica,2007,43(3):531-537.
[4] Fallaha C J,Saad M,Kanaan H Y,et al. Sliding mode robot control with exponential reaching law[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics,2011,58(2):600-610.
[5] Xiong L,Li P,Li H,et al. Sliding mode control of DFIG wind turbines with a fast exponential reaching law[J]. Energies,2017,10(11):1788-1806.
[6] Pandey A,Agrawal R,Mandloi R S,et al. Sliding mode control of dynamic voltage restorer by using a new adaptive reaching law[J]. Journal of the Institution of Engineers,2017,98(6):579-589.
[7] Liu Y F,Wang Z J,Xiong L Y,et al. DFIG wing turbine sliding mode control with exponential reaching law under variable wind speed[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems,2017,96:253-260.
[8] Mozayan,Seyed M,Saad M,et al. Sliding mode control of PMSG wind turbine based on enhanced exponential reaching law[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics,2016,63(10):6148-6159.
[9] 李 鹏,马建军,郑志强. 采用幂次趋近律的滑模控制稳态误差界[J]. 控制理论与应用,2011,28(5):619-624.
Li Peng,Ma Jianjun,Zheng Zhiqiang. Sliding mode control approach based on nonlinear integrator[J]. Control Theory and Applications,2011,28(5):619-624(in Chinese).
[10] Yu S,Yu X,Shirinzadeh B,et al. Continuous finite-time control for robotic manipulators with terminal sliding mode[J]. Automatica,2005,41(11):1957-1964.
[11] 梅 红,王 勇. 快速收敛的机器人滑模变结构控制[J]. 信息与控制,2009,38(5):552-557.
Mei Hong,Wang Yong. Fast convergent sliding mode variable structure control of robot[J]. Information and Control,2009,38(5):552-557(in Chinese).
[12] 张合新,范金锁,孟 飞,等. 一种新型滑模控制双幂次趋近律[J]. 控制与决策,2013,28(2):289-293.
Zhang Hexin,Fan Jinsuo,Meng Fei,et al. A new double power reaching law for sliding mode control[J]. Control and Decision,2013,28(2):289-293(in Chinese).
[13] 李慧洁,蔡远利. 基于双幂次趋近律的滑模控制方法[J]. 控制与决策,2016,31(3):498-502.
Li Huijie,Cai Yuanli. Sliding mode control with double power reaching law[J]. Control and Decision,2016,31(3):498-502(in Chinese).
[14] 廖 瑛,杨雅君,王 勇. 滑模控制的新型双幂次组合函数趋近律[J]. 国防科技大学学报,2017,39(3):105-110.
Liao Ying,Yang Yajun,Wang Yong. Novel double power combination function reaching law for sliding mode control[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology,2017,39(3):105-110(in Chinese).
[15] 张 瑶,马广富,郭延宁,等. 一种多幂次滑模趋近律设计与分析[J]. 自动化学报,2016,42(3):466-472.
Zhang Yao,Ma Guangfu,Guo Yanning,et al. A multi power reaching law of sliding mode control design and analysis[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica,2016,42(3):466-472(in Chinese).
[16] 蒲 明,蒋 涛,付克昌. 输入受限约束下的无抖振有限时间稳定趋近律设计[J]. 控制与决策,2018,33(1):138-145.
Pu Ming,Jiang Tao,Fu Kechang. Finite time stable chattering-free reaching law design with bounded input[J]. Control and Decision,2018,33(1):138-145(in Chinese).
[17]Pan J,Li W,Zhang H. Control algorithms of magnetic suspension systems based on the improved double exponential reaching law of sliding mode control[J]. International Journal of Control,Automation and Systems,2018,16(6):2878-2887.
[18] 马广富,朱庆华,王鹏宇,等. 基于终端滑模的航天器自适应预设性能姿态跟踪控制[J]. 航空学报,2018,39(6):141-151.
Ma Guangfu,Zhu Qinghua,Wang Pengyu,et al. Adaptive prescribed performance attitude tracking control for spacecraft via terminal sliding-mode technique[J]. Acta Aeronautica Sinica,2018,39(6):141-151(in Chinese).
Design and Analysis of a New Power Reaching Law for Sliding Mode Control
Zhang Guoshan,Li Xianlei
(School of Electrical and Information Engineering,Tianjin University,Tianjin 300072,China)
To address the chattering problem and slow global convergence speed of the traditional reaching law,this study compared and analyzed the previous power law and exponential reaching law and proposed a new power reaching law,which achieved chatter-free fast global convergence of the system through the improvement of functions and introduction of new functions on the basis of the previous power reaching law. First,by improving a variable exponential term,the new power reaching law avoided the chattering problem of the exponential term when the system converged to the sliding surface,and retained the fast global convergence of the variable exponential term over the proportional and power terms when the system was far from the sliding surface. Second,the new power reaching law introduced a tangent function,which could achieve fast global convergence of the system by adjusting the tangent function parameters under the condition that the initial state is known. This study proved through the theory that the new power reaching law enables the system to quickly converge to the sliding surface without chattering and proposed the parameter setting method for the reaching law to ensure that the system can quickly converge to the desired steady-state accuracy within a finite time in case of bounded disturbance in the system. Finally,the effectiveness of the reaching law is verified by comparing simulations of multiple reaching laws. The correctness of the parameter setting method is verified by conducting simulations of the system under bounded disturbance. The spacecraft attitude control simulation further verified the validity and correctness of the new power reaching law and parameter setting method.
sliding mode control;tangent function;power reaching law;global fast convergence
TK13
A
0493-2137(2020)11-1112-08
10.11784/tdxbz201907050
2019-07-19;
2020-01-19.
张国山(1961— ),男,博士,教授.
张国山,zhanggs@tju.edu.cn.
国家自然科学基金资助项目(61473202).
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(No. 61473202).
(责任编辑:孙立华)

