Ophiopogonin D upregulates CYP2J3/EETs to activate Pl3K/AkteNOS pathway and rescue H2O2-induced H9c2 cell injury
HUANG Xiao-yan,ZHANG Zhao-yan,CHEN Bo-jun,GAO Yue
(1.The Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine,Guangzhou 510120,China;2.College of Life Science and Bioengineering,Beijing University of Technology,Beijing 100124,China;3.Institute of Radiation Medicine,Academy of Military Medical Sciences,Academy of Miliary Sciences,Beijing 100850,China)
Abstract:OBJECTlVE To explore the protective effect and mechanism of ophiopogonin D(OP-D)on oxidative stress injury of H9c2 cells induced by H2O2.METHODS An oxidative damage model of H9c2 cells was established by H2O2induction.The cells were divided into control group(cultured in serum-free medium for 28 h),H2O2injury model group(treated with H2O2400 μmol·L-1for 3 h),OP-D 5,10 and 20 μmol·L-1pretreatment groups(treated with H2O2400 μmol·L-1for 3 h after OP-D pretreatment for 24 h),and an inhibitor of CYP2J3,6-(2-proparglyloxyphenyl)hexanoic acid(PPOH)group(OP-D 20 μmol·L-1+PPOH 10 μmol·L-1,PPOH was added to the cells 1 h before OP-D treatment).Cell activity was measured by MTT method,levels of dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acid(11,12-DHET and 14,15-DHET respectively)were detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay(ELISA),while levels of malondialdehyde(MDA),nitric oxide(NO)and activity of lactate dehydrogenase(LDH),superoxide dismutase(SOD)were detected by assay kits.Flow cytometry(FCM)was used to detect reactive oxygen species(ROS)and apoptosis.Western blotting was used to detect the expressions of CYP2J3,Akt phosphorylation(p-Akt)protein and endothelial nitric oxide synthase phosphorylation(p-eNOS)protein in cells,and the possible mechanism by which OP-D reduces oxidative stress was further verified with PPOH.RESULTS H2O2400 μmol·L-1significantly inhibited H9c2 cell viability(P<0.01),and OP-D significantly increased the cell survival rate after H2O2injury(P<0.01).Different concentrations of OP-D increased the level of 11,12-DHET and 14,15-DHET(P<0.05,P<0.01).OP-D increased the level of NO in cells after H2O2-induced injury(P<0.05,P<0.01),enhanced the activity of SOD(P<0.05),and decreased the level of MDA and LDH(P<0.05,P<0.01).OP-D significantly reduced oxidative stress and apoptosis after H2O2injury(P<0.05,P<0.01).OP-D pretreatment increased the protein and mRNA expression of CYP2J3(P<0.05,P<0.01)and the phosphorylation of PI3K/Akt-eNOS pathway after H2O2injury(P<0.05,P<0.01).After PPOH was given in advance,the protective effect of OP-D was inhibited(P<0.05,P<0.01).CONCLUSlON OP-D can reduce H2O2-induced H9c2 cell damage,which may be related to the activation of PI3K pathway and the phosphorylation of its downstream factors Akt and eNOS by inducing CYP2J3 expression and increasing the contents of 11,12-DHET and 14,15-DHET.
Key words:ophiopogonin D;cytochrome P450 2J3;phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase;oxidative stress
Myocardial ischemia/reperfusion(I/R)injury is a complex pathological process characterized by calcium overload and oxidative stress.Myocardial I/R injury can cause a variety of changes in mitochondrial function and its structure[1-2],which are considered to be a main mechanism of myocardial injury[3].Antioxidant treatment is a possible approach to preventing myocardial injury[4-5].Excess ROS trigger oxidative stress in response to myocardial damage,leading to the development of reperfusion injury[6].Additionally,ROS can also affect the release of total NO produced by endothelial nitric oxide synthase(eNOS)[7],damaging endothelial function,which results in an increase in vascular tension and affects the pathological state of reperfusion injury.Therefore,inhibiting ROS overproduction can reduce the occurrence and development of reperfusion damage[8].In addition,H2O2can induce cell apoptosis by inhibiting the intracellular antioxidant system,and H2O2treated cells have become an important tool for the study of oxidative stress at the cellular level[9].
OP-D is steroidal glycoside extracted from the traditional herbal medicine,Radix Ophiopogonis.This compound has been pharmacologically evaluated for its antioxidant[10-11],anti-ischemic,and anti-inflammatory properties[10].However,the underlying mechanism is poorly understood.Cytochrome P450 2J2(CYP2J2)and its rat homologue(CYP2J3),which metabolize arachidonic acid into four epoxyeicosatrienoic acids(EETs;5,6-EET,8,9-EET,11,12-EET,and 14,15-EET),are expressed at high levels in the heart[12].EETs are unstable and can be enzymatically hydrated to the corresponding stable metabolite dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acids(DHETs)by soluble epoxide hydrolases(sEHs).CYP2J2 and its metabolites EETs have a diverse range of effects on the vasculature,including the regulation of inflammation,oxidative stress,apoptosis,and cardiac hypertrophy[13-14].Our previous findings also support these conclusions[15-17].
The activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway is involved in the myocardial protective effect of EETs in myocardial I/R injured rats[18-19],and NO is an important signaling molecule that reduces myocardial injury in many I/R models[20-21].Our previous results showed that the activation of CYP2J3/EETs with OP-D increased the eNOS phosphorylation and subsequent NO release through the PI3K/Akt pathway,thereby protecting against myocardium I/R injury in rats[22].In this study,we further confirmed that the protective effect of OP-D is mediated by activation of CYP2J3/EETs and eNOS/NO pathway.We measured the antioxidant and cardioprotective efficacy of OP-D with H9c2 cardiomyocytes in anin vitroH2O2-induced oxidative stress model.
1 MATERlALS AND METHODS
1.1 Cell,reagents,antibodies and equipments
H9c2 cells were obtained from the ATCC(Manassas,VA,USA)and were incubated in glucose-free DMEM.OP-D(purity 98%;molecular weight 855.017 g/mol)isolated from the traditional Chinese herbal agent Aadix Ophiopogonis Japonicus was purchased from Shanghai Yuanye Biotechnology Co.,Ltd.(Shanghai,China).H2O2,6-(2-proparglyloxyphenyl)hexanoic acid(PPOH),and TRIzol Reagent were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Co.(St.Louis,MO,USA).Fetal bovine serum(FBS)was supplied by Gibco(Grand Island,NY,USA).Phosphate buffer solution(PBS)and Dulbecco′s modified Eagle′s medium(DMEM)were purchased from HyClone(Thermo Fisher Scientific,Waltham,MA,USA).CellTiter 96 Aqueous One Solution Cell Proliferation Assay was purchased from Promega(Madison,WI,USA).The kits for measuring LDH,MDA,SOD,and NO concentrations were purchased from Jiancheng Bioengineering Research Institute(Nanjing,Jiangsu,China).11,12-DHET and 14,15-DHET level ELISA kits(Detroit R&D,Detroit,MI).ROS Assay Kit and Annexin Ⅴ-FITC/PI Assay Kit(Beyotime Biotechnology,Shanghai,China).RIPA Lysis Buffer,Protease Inhibitor Cocktail,BCA Protein Assay Kit,Enhanced Chemiluminescence Reagent(Kangwei Century,Beijing,China).Primary antibodies used were anti-CYP2J3(rabbit polyclonal antibody,Boston,bs-2123R),anti-eNOS(rabbit polyclonal antibody,Abcam,GR14697-7),anti-phospho-eNOS(S1177)(rabbit polyclonal antibody,Abcam,GR8521-14),anti-Akt(rabbit polyclonal antibody,Cell Signaling Technology,4691),anti-phospho-Akt(Thr308)(rabbit monoclonal antibody,Cell Signaling Technology,4060),anti-GAPDH(mouse monoclonal antibody,Kangwei Century,CW0100M).Horseradish peroxidase conjugated anti-mouse and anti-rabbit IgG(Kangwei Century,CW0100M).FACS Calibur flow cytometer(BD Biosciences,San Jose,CA,USA).ABI Prism 7500(Applied Biosystems,Forster City,CA,USA).Image Quant LAS 500(Healthcare Bio-Sciences AB,Sweden).
1.2 Cell viability of H9c2 cells detected by MTT assay
The cells were seeded in 96-well plates at a density of 4×103cells per well in 100 μL of complete medium.The cells were pretreated with or without OP-D 5,10,or 20 μmol·L-1in serum-free medium for 21 h,followed by exposure to H2O2400 μmol·L-1for 3 h.At the same time,the control group(cells were in serum-free medium for 24 h)and the blank zero hole(serum-free medium for 24 h)without cells were set.Cell viability was determined by MTT assay.The cells were incubated for 4 h in an incubator with 10%MTT,and the cells were lysed with DMSO.The absorbance(A450nm)was detected at 450 nm wavelength with an enzyme marker.Cell survival rate(%)=(H2O2-treated groupA450nm-blank groupA450nm)/(control groupA450nm-blank groupA450nm)×100%.
1.3 Concentration of 11,12-DHET and 14,15-DHET level detected by ELlSA
EETs are unstable and can be enzymatically hydrated to the corresponding stable metabolite DHETs by sEHs.To evaluate the EET level,ELISA kits were used to determine the concentration of 11,12-DHET and 14,15-DHET.The cells was treated with OP-D 5,10,or 20 μmol·L-1in serumfree medium for 24 h,and the control group(cells were in serum-free medium for 24 h)were set.ELISAs were performed according to the manufacturer′s instructions.The control group was used as the reference baseline.
1.4 Level of MDA,NO and activity of LDH,SOD detected by assay kits
Cells were divided into control group(serumfree medium processing),model group(H2O2400 μmol·L-1with 3 h),different concentrations of OP-D pretreatment groups(5,10,20 μmol·L-1with 24 h and then stimulated by 400 μmol·L-1H2O2for 3 h),PPOH intervention group(OP-D 20 μmol·L-1and PPOH 10 μmol·L-1,PPOH was added to cells 1 h before OP-D treatment).Levels of MDA,NO and activity of LDH,SOD were detected after exposure to H2O2with assay kits according to the manufacturer′s protocols.
1.5 lntracellular ROS detected by flow cytometry
Cell grouping was conducted in the same way as in 1.4.A 2′-7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate(DCFH-DA)ROS Assay Kit was used to detect the generation of ROS in H9c2 cells.Cells were incubated with DCFH-DA 10 μmol·L-1in DMEM at 37℃for 20 min and were detected with a flow cytometer within 30 min.
1.6 Cell apoptosis detected by flow cytometry
Cell grouping was conducted in the same way as in 1.4.Cells were treated with AnnexinⅤ-FITC/PI Assay Kit.Cells were gently resuscitated with 195 μL Annexin Ⅴ-FITC binding solution,5 μL V-FITC was added,and gently mixed.After 10 μL PI was added,the cells were gently mixed,incubated at room temperature(20-25℃)for 10-20 min under dark conditions,and then placed in an ice bath.Cell apoptosis was analyzed by flow cytometer.
1.7 Protein expression of CYP2J3,Akt and eNOS detected by Western blotting
Cell grouping was conducted in the same way as in 1.4.Protein was isolated from H9c2 cells after incubation in RIPA Lysis Buffer supplemented with Protease Inhibitor Cocktail on ice for 20 min.The lysis buffer was centrifuged at 4℃and 12 000×gfor 10 min,and the supernatants were collected.The protein concentration was measured with BCA Protein Assay Kit.Protein samples were separated using 10%SDS-PAGE and transferred onto a polyvinylidene fluoride membrane.Subsequently,membranes were blocked with 5%skim milk for 3 h.The membrane was incubated with primary antibodies(CYP2J3 antibody was diluted with TBST solution at 1∶500;eNOS,p-eNOS,Akt,and p-Akt antibodies were diluted with TBST solution at 1∶1000)at 4℃overnight.Subsequently,the PVDF membrane was washed 5 times with TBST and put into the corresponding HPR labeled secondary antibody(diluted according to the antibody instructions).The blots were incubated with secondary antibodies at room temperature for 1 h.Finally,the membranes were treated with Enhanced Chemiluminescence Reagent and visualized with ImageQuant LAS 500.GAPDH served as an internal control,while the relative expression level of the target protein was expressed by the integral absorbance ratio of the target protein to the internal reference protein.
1.8 mRNA expression of CYP2J3 detected by reverse-transcription PCR
Cell grouping was conducted in the same way as in 1.4.After the experimental treatment,total RNAs were isolated using TRIzol Reagent.The total RNA was reverse-transcribed with a Transcriptor First-strand cDNA Synthesis Kit(Roche,Basel,Switzerland)to obtain the cDNAs.Real-time quantitative PCR was performed in ABI Prism 7500 using the TransScript SYBR Green Master Mix kit.Each target gene was quantified,with GAPDH serving as an internal control.The following primers were used:CYP2J3,forward(F)5′-CATTGAGCTCACAAGTGGCTTT-3′and reverse(R)5′-CAATTCCTAGGCTGTGATGTCG-3′;GAPDH,F 5'-GGCCTCCAAGGAGTAAGACC-3′and R 5′-AGGGGAGATTCAGTGTGGTG-3′.
1.9 Statistical analysis
All data was expressed as±s.Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS 16.Comparisons between groups were performed by a one-way analysis of variance,followed by Bonferroni's post hoc test.P<0.05 was considered statistically significant differences.
2 RESULTS
2.1 Effect of OP-D pretreatment on viability of H9c2 cells
As shown in Fig.1,compared with control group,the viability of H9c2 cells in H2O2200 to 500 μmol·L-1for 3 h and H2O2300-500 μmol·L-1for 2 h significantly decreased(P<0.01).In particular,the cell viability was reduced to nearly 64.7%of that of the control group after 3 h exposure to 400 μmol· L-1H2O2.Thus,400 μmol· L-1H2O2for 3 h was chosen to produce H2O2-induced cell injury in subsequent experiments.Compared with H2O2group,cell viability was increased in OP-D 5,10,and 20 μmol· L-1pretreatment groups in a concentration-dependent manner(P<0.01).OP-D 5,10,and 20 μmol·L-1were chosen to evaluate the anti-oxidative stress.
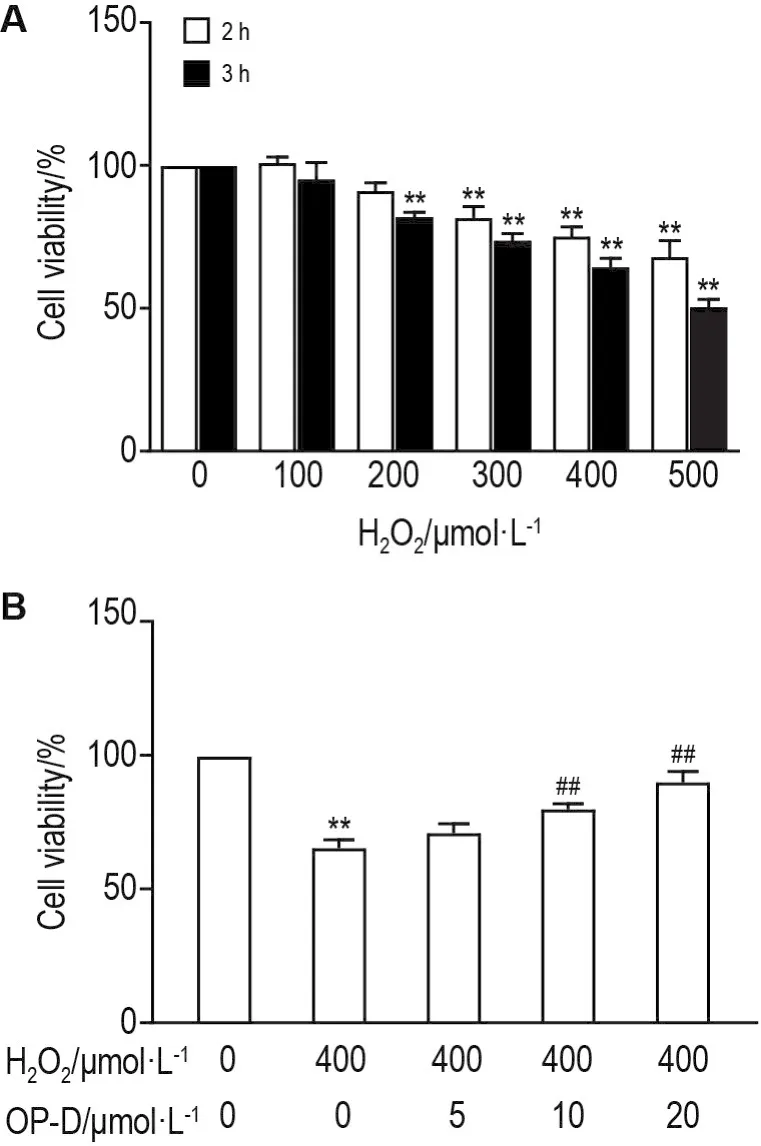
Fig.1 Effect of ophiopogonin D(OP-D)pretreatment on cell viability of H9c2 cells exposed to H2O2by MTT assay.A:H9c2 cells were treated with H2O2100,200,300,400,and 500 μmol·L-1for 2 h or 3 h,respectively;B:H9c2 cells were pretreated with OP-D 5,10 and 20 μmol·L-1for 3 h and then exposed to H2O2400 μmol·L-1for 3 h.±s,n=6.**P<0.01,compared with control(0)group;##P<0.01,compared with H2O2group.
2.2 Effect of OP-D pretreatment on concentration of 11,12-DHET and 14,15-DHET level in H9c2 cells
As shown in Fig.2,compared with control group,concentrations of 11,12-DHET and 14,15-DHET were increased in a concentration-dependent manner in OP-D group(P<0.05,P<0.01).
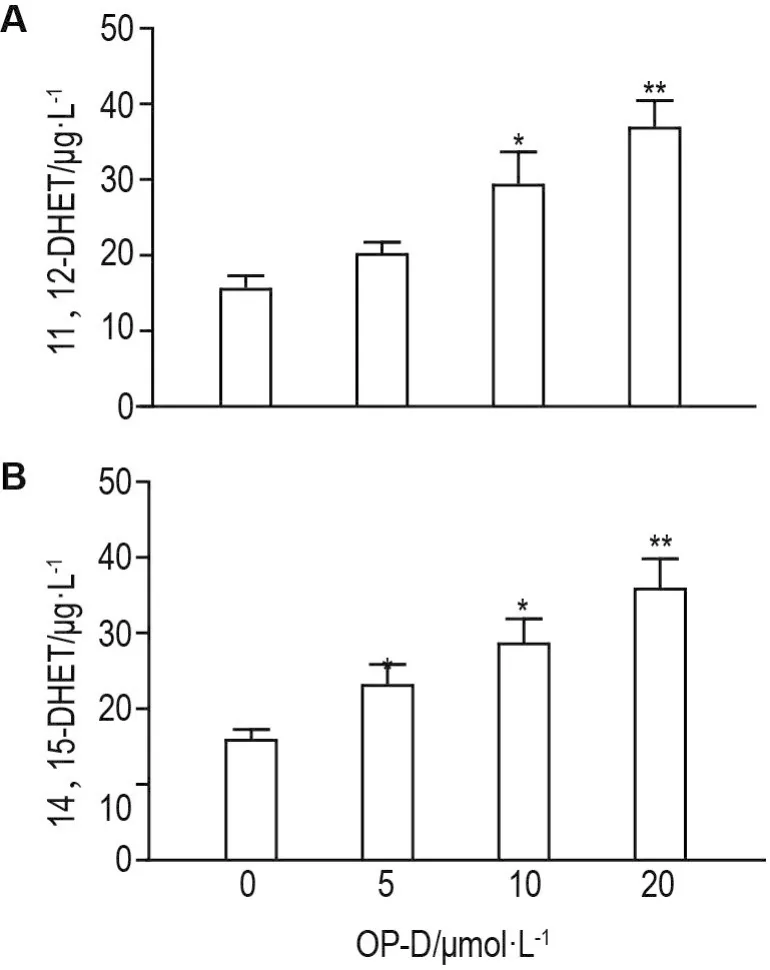
Fig.2 Effect of OP-D on 11,12-DHET and 14,15-DHET level in H9c2 cells detected by ELlSA.H9c2 cells were treated with OP-D 5,10 and 20 μmol·L-1for 24 h.±s,n=6.*P<0.05,**P<0.01,compared with control(0)group.
2.3 Effect of OP-D on activity of SOD,LDH and content of MDA,NO in H9c2 cells
As shown in Fig.3,compared with control group,activity of LDH and content of MDA increased(P<0.05,P<0.01),while the content of NO and the activity of SOD decreased in H2O2group(P<0.05,P<0.01).Compared with H2O2group,the activity of LDH and content of MDA decreased,but the content of NO and activity of SOD increased in a concentration-dependent manner in OP-D pretreatment group(P<0.05,P<0.01).Compared with OP-D 20 μmol· L-1treated group,PPOH 10 μmol·L-1and OP-D 20 μmol·L-1co-treatment could reverse the decreasing activity of LDH,content of MDA,NO and increasing activity of SOD(P<0.01).
2.4 Effect of OP-D treatment on oxidative stress and apoptosis in H9c2 cells
As shown in Fig.4,levels of intracellular ROS and apoptosis were significantly elevated in H2O2group compared with the control group(P<0.01).Compared with H2O2group,OP-D treatment significantly protected cells from ROS generation and apoptosis in a concentration-dependent manner(P<0.05,P<0.01).Compared with H2O2+OP-D 20 μmol·L-1group,pretreatment with the inhibitor PPOH abolished the OP-D scavenging effect on ROS generation(P<0.05).

Fig.3 Effect of OP-D on activity of lactate dehydrogenase(LDH)and superoxide dismutase(SOD),content of malondialdehyde(MDA)and nitric oxide(NO)in H9c2 cells detected by ELlSA.H9c2 cells were treated with PPOH 10 μmol·L-1+OP-D 5,10 and 20 μmol·L-1for 24 h and then stimulated by H2O2400 μmol· L-1for 3 h.x ± s,n=6.*P<0.05, **P<0.01,compared with control(0)group;#P<0.05,##P<0.01,compared with H2O2400 μmol·L-1group; △△P<0.01,compared with H2O2400 μmol·L-1+OP-D 20 μmol·L-1group.
2.5 Effect of OP-Donprote in expression of CYP2J3,Akt and eNOS phosphorylation in H9c2 cells
As shown in Fig.5,compared with control group,mRNA and protein expression levels of CYP2J3 were both decreased in H2O2group(P<0.05),but compared with H2O2group,they were increased in a concentration-dependent manner in OP-D pretreatment group (P<0.05,P<0.01).Compared with OP-D treated group,epoxygenase inhibitor PPOH and OP-D co-treatment could reverse the increase of CYP2J3 expressions(P<0.05,P<0.01).
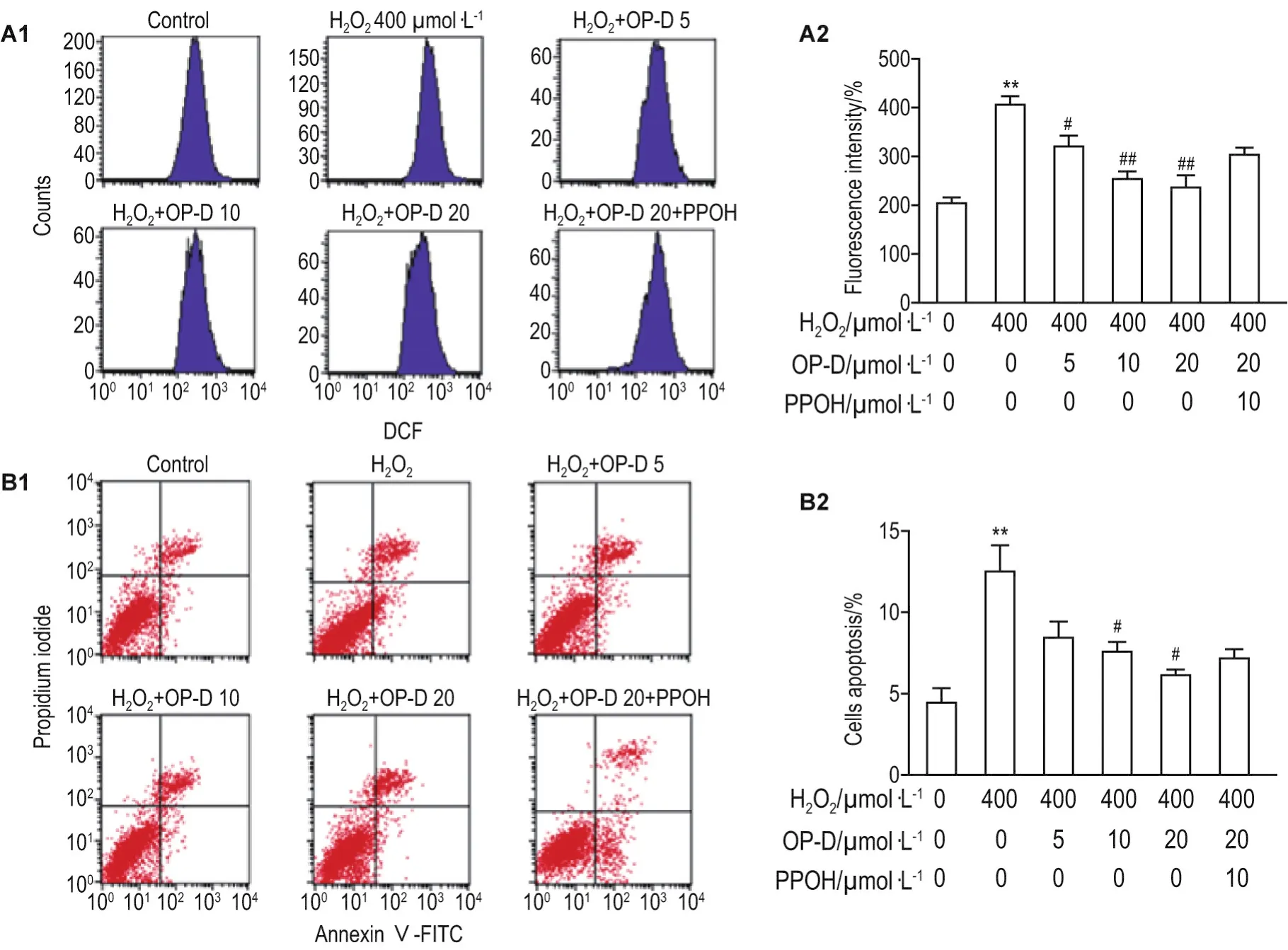
Fig.4 Effect of OP-D on reactive oxygen species(ROS)level(A)and cell apoptosis(B)in H9c2 cells by flow cytometry.A2 and B2 were quantitative results of A1 and B1,respectively.H9c2 cells were treated with 6-(2-proparglyloxyphenyl)hexanoic acid(PPOH)10 μmol·L-1+OP-D 5,10 and 20 μmol·L-1for 24 h and then stimulated by H2O2400 μmol·L-1for 3 h.±s,n=6.**P<0.01,compared with control group;#P<0.05,##P<0.01,compared with H2O2-treated group;△P<0.05,compared with H2O2+OP-D 20 μmol·L-1group.

Fig.5 Effect of OP-D on protein and mRNA expression of cytochrome P4502J3(CYP2J3)(A and B),protein expression of p-Akt and p-eNOS(C)by Western blotting.See Fig.4 for the cell treatment.IA:integrated absorbance.A2 and C2 were quantitative results of A1 and C1,respectively.±s,n=6.*P<0.05,compared with control group;#P<0.05,##P<0.01,compared with H2O2group;△P<0.05,△△P<0.01,compared with H2O2+OP-D 20 μmol·L-1group.
As shown in Fig.5,compared with control group,H2O2treatment significantly decreased the protein expression of p-Akt and p-eNOS(P<0.05).Compared with the H2O2group,OP-D pretreatment increased levels of p-Akt and p-eNOSversustotal Akt and eNOS(loading controls)(P<0.05,P<0.01).Compared with H2O2+OP-D 20 μmol·L-1group,OP-D 20 μmol·L-1+PPOH co-treatment decreased the expression of p-eNOS(P<0.05).
3 DlSCUSSlON
Many pathophysiological mechanisms are considered related to myocardialI/R injury,including oxidative stress,cell death,calcium overload,and pressure/mechanical stress[22-24],although oxidative stress and cell apoptosis are key factors in I/R injury[25].Increased ROS has been observed in mitochondria during the initial phase of reperfusion[23,26].When reperfusion occurs,endothelial cells and macrophages generate ROS and activate nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate(NADPH),NO release,NF-κB,and pro-inflammatory cytokines.In addition,excessive ROS will cause inflammation,apoptosis and dysfunction of distal organs,further aggravating I/R injury.Apoptosis plays an important role in the process of reperfusion and the occurrence of cardiac dysfunction[27-28].The mitochondrial pathway activated by oxidative stress is an intrinsic pathway of apoptosis.In order to better understand the I/R injury in cellular levels,many cellular models have been established.Among them,H2O2is usually used to mimic I/R injury inin vitroexperiments[25,29].
Radix Ophiopogon Japonicus is a traditional Chinese herbal medicine commonly used to treat cardiovascular diseases,and OP-D is a steroidal glycoside recently isolated fromOphiopogon Japonicus.Nevertheless,little is known about the mechanism of OP-D as a therapeutic agent for cardiovascular disec2 and EETs can protect the heart,brain,and aortic endothelial cells against I/R injury by suppressing ROS production,inhibiting apoptosis,and attenuating mitochondrial impairment.Our previous studies[15-17]demonstrated that OP-D-mediated CYP2J2 expression increased EETs levels and reduced Ang Ⅱ-induced inflammatory response,cardiac hypertrophy,abnormalities in Ca2+homeostasis and apoptosis,which are associated with maintaining endothelium oxidative homeostasis.In addition,OP-D inhibits mRNA levels of antioxidant and apoptotic genes in a dose-dependent manner in human umbilical vein endothelial cells[10].In the present study,downregulation of both mRNA and protein levels of CYP2J3 was observed in the H2O2group compared with the control group.Moreover,as expected,co-treatment with OP-D increased the mRNA and protein expression levels of CYP2J3 in a time-dependent manner,a phenomenon that was reversed by pre-incubation with PPOH.Also,OP-D increased the concentration of 11,12-DHET and 14,15-DHET in a dose-dependent manner in case of H2O2-induced myocardial injury.sEH hydrolyzes EETs to DHETs which less biologically active.Our data is consistent with the idea that enhanced cardiac CYP2J2 activity may result in increased levels of circulating EETs.
The role of oxidative stress in myocardial I/R injury has been demonstrated in our previous studies[5,22].Excessive production of ROS leads to oxidative stress,which is a harmful process that leads to structural damage to cells through lipid peroxidation,inactivation of various proteins and DNA damage.Hence,we investigated the effects of OP-D on the cell viability and levels of MDA,NO and LDH,SOD activity.The cell viability was apparently increased after incubation with OP-D under H2O2-induced conditions.LDH leakage and MDA content indirectly indicate the degree of cell injury.Indicators of oxidative stress,such as MDA content and SOD activity,play an important role in myocardial pathophysiology.The MDA content and LDH activity were increased in the H2O2-treated group compared with the control group,whereas SOD activity was reduced.Treatment with OP-D decreased the LDH activity and MDA content and increased SOD activity.Additionally,ROS generation and cell apoptosis were also upregulated in H2O2-treated H9c2 cardiomyocytes.Pretreatment with OP-D dose-dependently suppressed intracellular ROS generation and cell apoptosis in H2O2-treated H9c2 cells.The adjustment of the above indicators by OP-D was completely reversed when cells were co-incubated with PPOH.This suggests that one of the cardioprotective mechanisms of OP-D ligands is via CYP2J3/EETs,as previously reported.
The PI3K/Akt pathway is one of the most potent intracellular mechanisms for promoting cell survival[30].The PI3K/Akt-eNOS activation pathway is likely a key contributor to the cardioprotective effects of CYP2J3/EETs in I/R injury.OP-D treatment significantly increased p-Akt protein expression after H2O2treatment.Based on previous studies,we hypothesized that OP-D affects the upregulation of p-Akt,which was correlated with an increase in CYP2J3 protein levels and mRNA expression.This conclusion has been validated in our previous animal experiments[22].The eNOS/NO signaling pathway mediates the cardioprotective effects of EETs during ischemia.In early reperfusion,increased production of ROS is accompanied by reduced availability of NO.NO plays an important role in cardioprotection against I/R injury and EETs induce NO production in various tissues.Our present results suggest that OP-D can induce the phosphorylation of eNOS(Ser1177)as well as a transient increase in NO production in H9c2 cells.In this regard,we observed that the beneficial effects of OP-D were abolished by CYP2J3 antagonist PPOH,suggesting the effects were OP-D specific,consistent with our previously published data.Our data is consistent with the finding that CYP2J3 overexpression can cause high levels of circulating 11,12-DHET and 14,15-DHET,and that EETs can increase PI3K/Akt pathway activity.
We investigated the underlying signal transduction mechanisms,focusing on the induction of CYP2J3 and its effect on the PI3K/Akt and eNOS/NO pathways.Our findings indicate that OP-D exerts its protective effects by inhibiting the ROS activation of H2O2-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis,at least partially via activation of CYP2J3 and upregulation of EETs in H9c2 cells,eventually promoting activation of the PI3K/Akt and eNOS/NO signaling pathways(Fig.6).Therefore,OP-D shows clear protection against cardiovascular damage,which deserves further experimental and clinical research.OP-D-induced CYP2J3/EETs overexpression could offer new insights into ways to prevent and treat oxidative stress and apoptosis in myocardial injury.
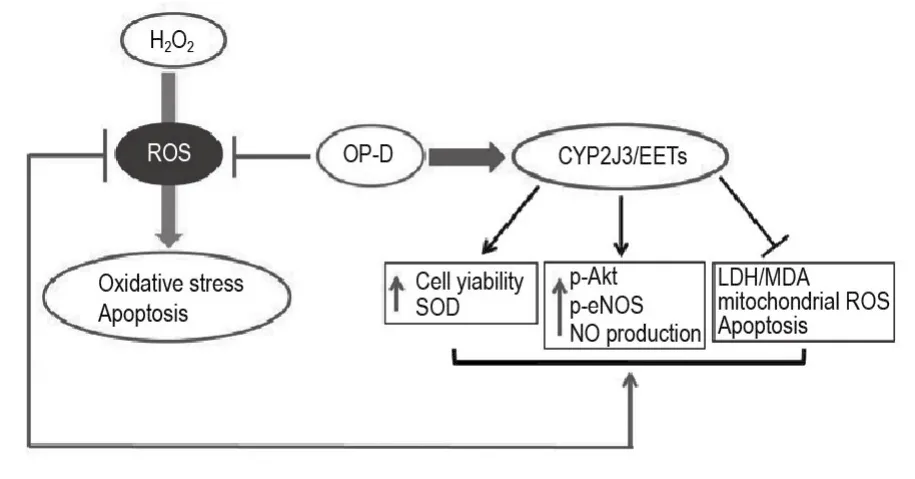
Fig.6 Mechanism of OP-D in H9c2 cells following H2O2treatment.Via potentiation of CYP2J3/EETs,OP-D exerts a multifaceted effect upon the oxidative stress that is the hallmark of H2O2-injury in H9c2 cells.EETs are known to upregulate the PI3K/Akt-eNOS in the oxidative stress pathway[14].In so doing,OP-D activates CYP2J3 and increases EETs(11,12-DHET and 14,15-DHET)which both enhance cell viability,SOD and reduce mitochondrial ROS mediated myocardial oxidative stress and apoptosis.Similarly,OP-D increases p-Akt,p-eNOS and NO content by upregulating CYP2J3/EETs,both of which are associated with maintained cardiomyocyte homeostasis.Via all of these mechanisms,H2O2-induced oxidative stress is both inhibited and reversed.

