Evaluation genotoxicity of acetylnerolin based on quantitative structure-activity relationship model and in vitro tests
WU Yin-nan,TANG Wan,YIN Jing,LIU Yang,WANG Yu-xin,3,LU Yi-hong,3
(1.Department of Pharmaceutical Analysis,Xuzhou Medical University,Xuzhou 221004,China;2.Jiangsu Institute for Food and Drug Control,Nanjing 210019,China;3.Key Laboratory for Impurity Profile of Chemical Drugs,National Medical Products Administration,Nanjing 210019,China;4.Suqian People′s Hospital of Nanjing Drum-Tower Hospital Group,Suqian 223800,China;5.Affiliated Suqian Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University,Suqian 223800,China)
Abstract:OBJECTlVE To evaluate the genotoxicity of naproxen(NPX)impurities acetylnerolin(Ace).METHODS The genotoxicity of Ace was predicted by ADMET,Derek and Sarah with the quantitative structure-activity relationship(QSAR).The chromosomal aberration and bacterial reverse-mutation(Ames)tests were performed to verify the above results.In chromosomal aberration tests,CHL cells were incubated with Ace 10,20 and 40 mg·L-1for 4 h in the presence or absence of metabolic activation system solution(S9 mix).Methyl methane sulfonate(MMS)20 mL·L-1without S9 mix and cyclophosphamide(CP)12 mg·L-1with S9 mix served as positive control.The number of chromosomes in each aberrant metaphase(including fissure,exchange,ring,break and polyploid)was counted and recorded,when the distortion rate less than 5%was considered negative and more than 10%was considered positive.In Ames test,the potential mutagenicity was evaluated using five strains of S.typhimurium(TA97,TA98,TA100,TA102 and TA1535).They were treated with Ace 5,25,125 and 625 μg per plate with or without S9 mix and incubated for 48-72 h.When without S9 mix,Dexon 50 μg per plate served as positive control for TA97 and TA98,MMS 2.0 μL per plate served as positive control for TA100 and TA102,and sodium azide 1.5 μg per plate served as positive control for TA1535.When with S9 mix,2-AF 100 μg per plate served as positive control for TA97,TA98 and TA100,1,8-dihydroxyanthraquinone(100 μg per plate)served as positive control for TA102 and CP 50 μg per plate served as positive control for TA1525.When the number of colonies was at least two-fold that of the negative control,the compound was considered mutagenic.RESULTS Although the Derek and Sarah software predicted that the NPX impurities were not genotoxic,ADMET data showed that Ace could induce chromosomal aberrations.The distortion rate of Ace 40 mg·L-1was greater than 5%,but less than 10%.The distortion rate of Ace was less than 5%when <20 mg·L-1.Consistent with the results of ADMET,Ace might induce chromosomal aberrations.Ames test results showed that Ace did not significantly increase the number of bacteria(5-625 μg per plate)compared with the negative control.Contrary to the ADMET results,Ace had no mutagenicity.CONCLUSlON Ace has potential chromosomal mutagenicity.For life-long usage of NPX,the content of Ace should be reduced from 0.15%of conventional impurities to 0.015%.
Key words:chromosomal aberration;quantitative structure-activity relationship;naproxen
It is important to control impurities in drug products.Impurities not only affect the efficacy of drugs,but also cause adverse reactions in patients,Genotoxic impurities(GTIs)are especially important as they can directly or indirectly cause mutagenic and carcinogenic damage to cellular DNA.Naproxen(NPX)in Fig.1 is a non-steroidal antiinflammatory drug used extensively for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis[1].Although the previous EP9.0[2]contains comparatively comprehensive information on the impurities of NPX,there are no reports on the systematic examination of toxicity of various impurities of NPX.Therefore,studying the toxicity of NPX impurities and establishing their appropriate and reasonable limits are the key to ensuring the drug′s safety.
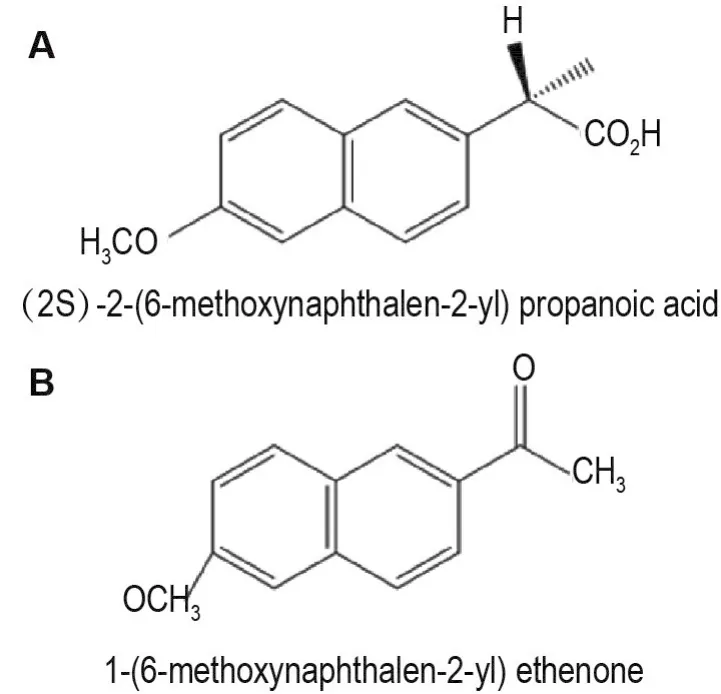
Fig.1 Chemical structures of naproxen(A)and acetylnerolin(B)
The latest guidelines from the European Medicines Agency(EMA)and US Food and Drug Administration(FDA)[3-4]address the assessment and control of genotoxicity and carcinogenicity of impurities in drugs.The International Conference on Harmonization of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use M7(ICH M7)regulations[5]set the threshold of toxicological concern(TTC)for GTIs.For common impurities,the qualification limit is less than 0.15%in drug products,whereas the TTC-based acceptable intake of 1.5 μg·d-1GTIs(classes 2 and 3)is considered to be protective for lifetime.The guidelines also recommend methods to evaluate the toxicity of impurities with a quantitative structure-activity relationship(QSAR)model[6].
Following the above guidelines for genotoxicity of impurities,we used the ADMET,and Derek Nexus,and Sarah Nexus software to predict the toxicity of NPX impurities.Among the impurities found in NPX,only acetylnerolin(Ace)(Fig.1)was suspected of inducing genotoxicity.We determined genotoxicity of impurity using chromosomal aberration and gene-mutation tests.Chinese hamster lung(CHL)cells were used in the chromosomal aberration test,and five test strains(Salmonella typhimuriumTA97,TA98,TA100,TA102,and TA1535)were used in the bacterial reverse-mutation(Ames)test.According to the results ofin vitropredicted toxicity,we recommended that the limit of Ace in NPX is established in line with FDA,EMA,and ICH guidelines.
1 MATERlALS AND METHODS
1.1 Cells,bacteria,chemicals and equipments
Chinese hamster lung(CHL)cells were provided by the Shanghai Institute for Food and Drug Control.Five strains ofS.typhimurium(TA97,TA98,TA100,TA102,and TA1535)were obtained from MOLTOX(Boone,NC,USA).
Ace(Sigma-Aldrich,Shanghai)with a purity of 98.0%was diluted with dimethyl sulfoxide(DMSO).The CO2incubator was purchased from Memmert(Schwabach,Germany).The temperature-controlled shaking table was from IKA Instrument Equipment(Staufen,Germany).
1.2 Genetic toxicity predicted by ADMET,Derek,and Sarah software
ADMET(version 7.2.0001;Simulations Plus,Inc,USA),Derek(version 6.0.1;Lhasa Limited,UK),and Sarah(version 3.0.0;Lhasa Limited,UK)software were used for toxicity assessment by predicting a range of various toxicity endpoints.The molecular structure was imported into the program in the mdl.mol format from ChemDraw.The ADMET and Sarah software predicted the potential toxicity of impurities by statistical models.Derek software predicted the potential toxicity of compounds according to expert knowledge systems.
1.3 In vitro chromosomal aberrations detected in Chinese hamster lung cells
CHL cells were grown in RPMI-1640 medium supplemented with penicillin(1×105U·L-1),streptomycin(100 g·L-1)and 10%calf serum at 37℃in an atmosphere containing 5%CO2.Three doses of Ace(10,20 and 40 mg·L-1)were chosen based on the 50%growth inhibitory concentration(IC50),both in the presence and absence of a metabolic activation system(S9 mix).DMSO was used as negative control.Methyl methane sulfonate(MMS)at 20 mL·L-1was used as positive control without S9 mix and cyclophosphamide(CP)at 12 mg·L-1was used as positive control with S9 mix.The test was performed according to published guidelines[7-8].
CHL cells were seeded at 1×105cells in 5 mL of medium per 25 mL culture dish and incubated at 37℃overnight.CHL cells were then incubated for 24 h with medium containing Ace(10,20 and 40 mg·L-1)in the absence of S9 mix.In the presence of S9 mix,cells were incubated for 4 h in RPMI 1640 medium with 2%calf serum and with Ace 10,20 and 40 mg·L-1,separately.Cells were washed 3 times with normal saline and incubated with medium without Ace for 20 h.Concurrent positive and negative solvent controls were also set.Before the end of culture,colchicine was added to cells induced by S9 mix for 4 or 2 h.After incubation,the cultured cells were trypsinized and harvested.To make the chromosome slides,the harvested cells were separated by centrifugation at a speed of 1930×gfor 10 min.Then,they were resuspended and incubated in hypotonic potassium chloride solution(KCl 0.075 mol·L-1)for 30 min to separate the chromosomes and cells.Afterwards,2 mL of fixative containing methanol and glacial acetic acid(3∶1,V/V)was added and mixed gently to terminate the hypotonic reaction.The mixture was centrifuged at the speed of 1930×gfor 10 min,and the supernatant was discarded.After centrifugation,5 mL of fixative was added and mixed gently to fix the chromosomes.In the fixative,the samples were fixed and washed at least twice,and then dropped onto glass microscope slides that were flame-dried and Giemsa stain.Finally,the slides were examined in an oil immersion system by light microscopy(100×magnification).
At least 100 metaphases were observed per concentration.The number of chromosomes in each aberrant metaphase (including fissure,exchange,ring,break and polyploid)was counted and recorded.Fissure was not included in the total aberration rate.For statistical analysis of results,when the distortion rate was less than 5%or more than 10%,the tested compound was considered negative or positive respectively.
1.4 Bacterial reverse-mutation assay detected by Ames test
The potential mutagenicity was evaluated using previously employed strains[9-10]in the presence and absence of a metabolic activation system,according to the standard Ames protocol and the OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals[11].1%DMSO was used as a negative control.Dexon,MMS,sodiumazide,2-aminofluorene,1,8-dihydroxyanthraquinone were used as positive controls.Each strain had different effects on different mutagens used in diagnosis under the conditions with or without metabolic activation.Without S9 mix,TA97 and TA98 were positive in Dexon(50 μg per plate),MMS(2.0 μL per plate)induced TA100 and TA102 to be positive,and TA1535 was induced by sodiumazide(1.5 μg per plate).With S9 mix,2-aminofluorene(100 μg per plate)could induce TA97,TA98 and TA100 to be positive,while TA102 and TA1525 were positive in 1,8-dihydroxyanthraquinone(100 μg per plate)and CP(50 μg per plate)respectively.Ace was assayed at concentrations of 5,25,125 and 625 μg per plate in 0.5 mL phosphate buffer(0.2 mol·L-1,pH 7.4)per 0.5 mL S9 mix for without or with activation treatment.0.1 mL of the bacterial culture and 0.1 mL of the specimen or control were mixed and poured onto agar plates after addition of 2.5 mL of top agar at 45℃.Then,the plates were incubated for 48-72 h at 37℃.The results were evaluated in terms of the number of colonies.A two-fold or higher increase in the coloniy number over the negative control was taken to mean that the test compound was considered mutagenic.A lower increase in the number of colonies would indicate that the test was negative.
1.5 Statistical analysis
Data was analyzed by SPSS16.0 software.P<0.05 was considered statisticaely significant difference.The rate of chromosome aberration between the negative control and treatment groups was assessed by the χ2test.The number of bacterial reverse mutation colonies was expressed as the mean and standard deviation.Statistical difference from the control group was evaluated with independent samplet-test.
2 RESULTS
2.1 Genotoxicity of acetylneroline valuated by ADMET,Derek,and Sara
The result of ADMET software prediction(Tab.1)showed that Ace in chromosomal aberrations was determined to be toxic with a high possibility 79%and MUT_m100 was seen as positive with a possibility of 59%.It suggested that Ace was suspected of inducing chromosomal aberrations and mutagenicity after rat liver microsomal activation inS.typhimuriumstrainTA100(Tab.1).The result of Derek and Sarah software prediction(Tab.1)showed that Ace was inactive and negative.It was listed as class 5 in ICH M7 Class.It suggested that the impurity was not genotoxic.
2.2 Chromosomal aberrations assay
The results of the chromosome aberration test were shown in Fig.2.The positive control values(CP or MMS)increased significantly in the assay with or without S-9 mix,indicating that the assay was valid.Under the metabolic activation system,the aberration rate of CP was apparently more than 10%and induced chromosome aberration.The aberration rate was between 5%and 10%at Ace 20 or 40 mg·L-1,and less than 5%at Ace 10 mg·L-1with S9 mix.Without any metabolic activation system,MMS also induced chromosome aberration because of the distortion rate over 20%.At Ace 40 mg·L-1,the aberration rate was less than 10%.The aberration rate was less than 5%at Ace 10 or 20 mg·L-1.To sum up,the assay results suggested that whether metabolic activation conditions existed or not the mutagenic potential of Ace had to be monitored at the high dose.
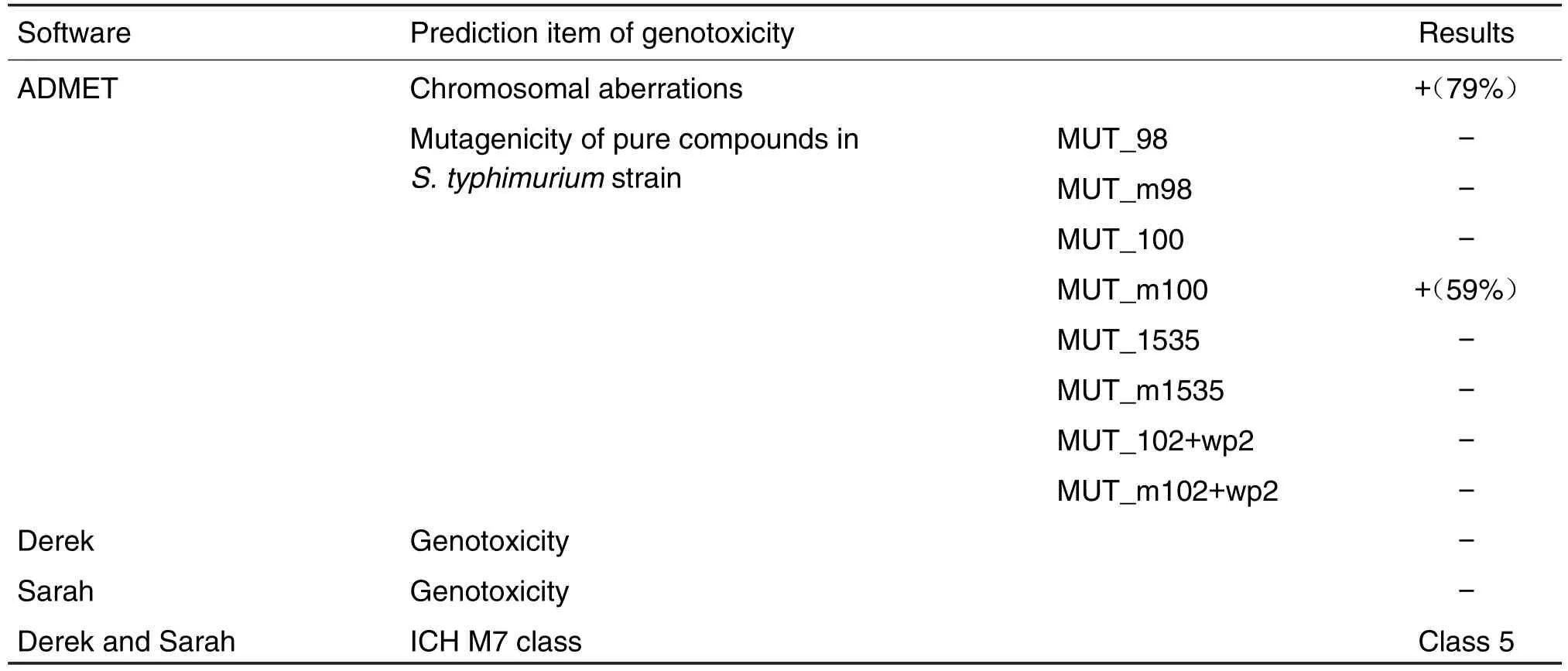
Tab.1 Genotoxicity of acetylneroline(Ace)valuated by ADMET,Derek,and Sarah.

Fig.2 Effect of acetylnerolin on chromosome aberration with(A)or without(B)S9 mix.CHL cells were incubated with Ace 10,20 and 40 mg·L-1for 4 h.1%DMSO was used as negative control.Methyl methane sulfonate(MMS)at 20 mL·L-1was used as positive control without metabolic activation and cyclophosphamide(CP)at 12 mg·L-1was used as positive control with metabolic activation.±s,n=3.*P<0.05,**P<0.01,compared with control group.
2.3 Effect of acetylnerolin on bacterial reversemutation assay
As results of Ames test(Tab.2 and Tab.3)showed,compared with negative controls,the number of revertant colonies showed an abnormal increase for all positive controls with or without S9 mix,thus providing the assay validation.In all the five strains without S9 mix(Tab.2),the number of revertant colonies in three positive controls(Dexon,MMS and Sodium azide)was more than twice that of the negative control groups and considered to lead to mutagenicity.However,the number of revertant colonies in Ace 5,25,125,and 625 μg per plate was not larger than in the negative control groups.Thus,it was considered that Ace did not induce mutation in the five strains without S9 mix.However,in all the five strains under the condition of S9 mix(Tab.3),the number of revertant colonies in the positive controls(2-AF,1,8-dihydroxyanthraqui-none,CP)was also obviously more than twice that of the negative control groups.Nevertheless,with Ace at 5,25,and 125 μg per plate,the number was close to that of the negative control groups.Moreover,some bacteriostatic effect was observed in Ace 625 μg per plate comparing with the negative control.Therefore,Ace was considered unable to mutate the five strains with S9 mix.To sum up,Ace lacked the ability of mutagenicity under the condition of metabolic activation or not.
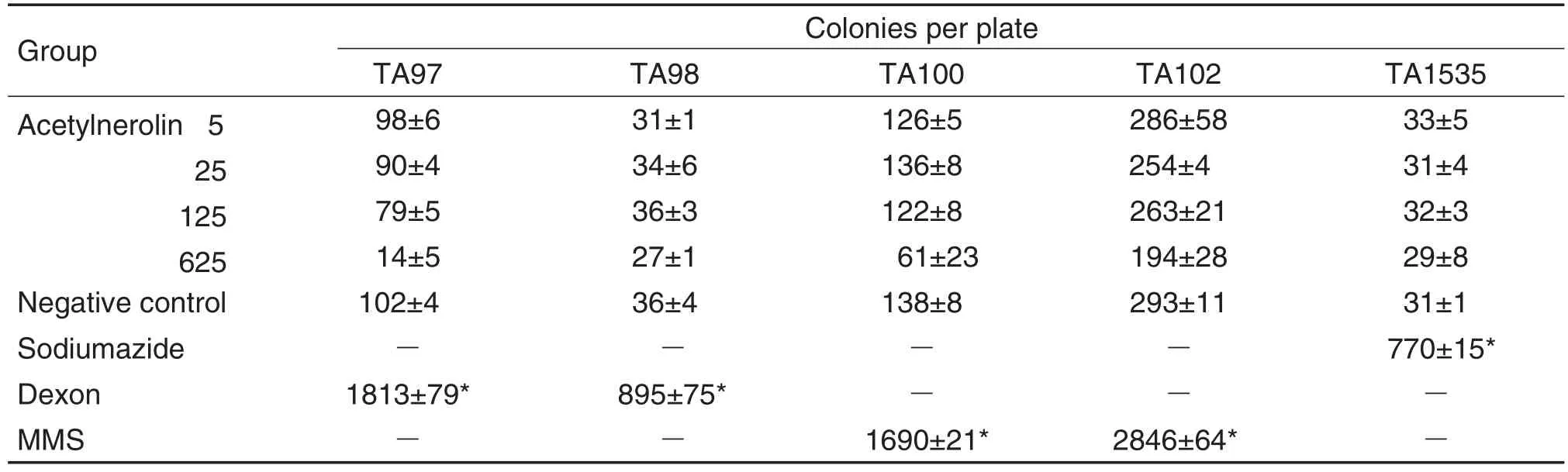
Tab.2 Results of bacterial reverse mutation(Ames)test without metabolic activation system(S9 mix).
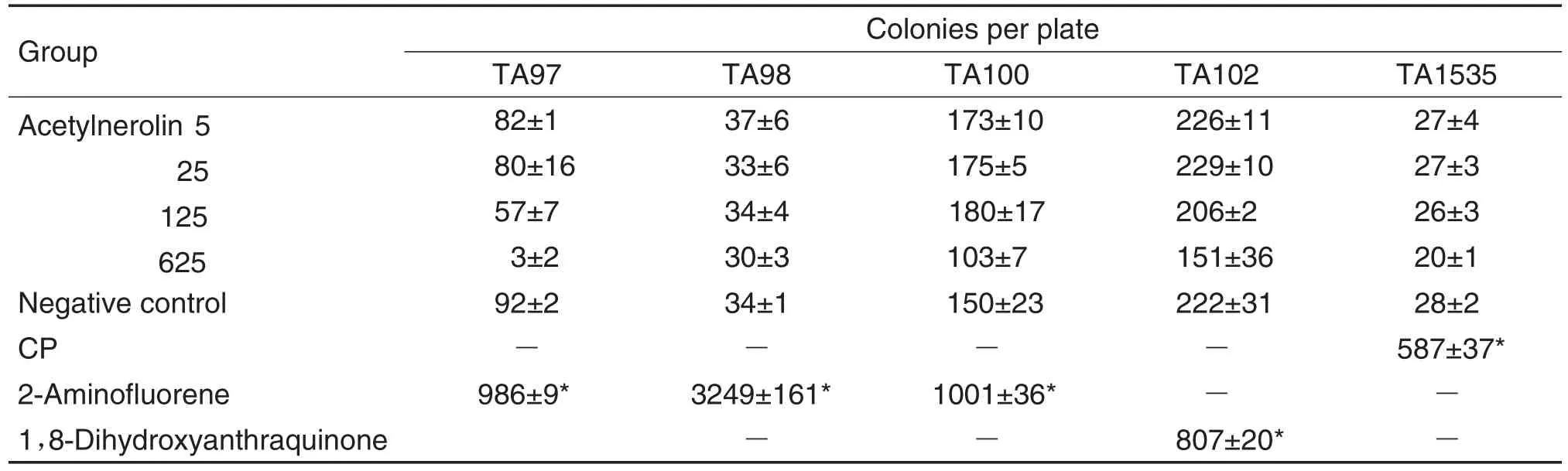
Tab.3 Results of Ames test with S9 mix
3 DlSCUSSlON
Drug impurities may not only affect the efficacy and stability of drugs,but also cause harm to patients health[12].In particular,GTIs can directly or indirectly damage cellular DNA and produce gene mutations(in vivogene mutations or mutagenesis)due to their potential carcinogenicity.Consequently,GTIs can cause adverse reactions in the course of drug use.Therefore,to ensure patients' safety,it is necessary to identify potential GTIs and set the limit for their presence in drugs.
A number of international and regional guidances instruct drug developers and regulatory agencies on how to evaluate and control impurities in drug substances and products.ICH Q3A,Q3B,and M7 provide clear rules and interpretations for the evaluation and control limits of impurities[5,13-14].The latest guidelines from the EMA and the FDA address the assessment and control of genotoxicity and carcinogenicity of impurities in drugs[3-4].The QSAR assessment model based on drug structure is one of the most widely used prediction methods that is recommended by the FDA and ICH M7 for the evaluation of GTIs[15].Chromosomes are the main genetic material of organisms.Substances with potential genotoxicity may induce chromosome structural aberrations after entering cells,which may harms human safety.Ames test shows that in the absence of histidine,only a few strains experience spontaneous reverse-mutation growth.In the presence of mutagenic substances,the bacteria will recover from the mutation involving nutritional deficiency to the original nutritional state,resulting in colony growth that is more than twice the normal value.This phenomenon is closely related to the mutagenicity and carcinogenicity of chemicals[16-17].Therefore,it is recommended that a chromosomal aberration,bacterial reverse mutation,or mouse lymphoma tests be used for verification when the prediction identifies a structure indicating genotoxicity.
In this study,we used three prediction software programs based on the QSAR model to predict the genotoxicity of various impurities found in NPX.The ADMET predictor,a QSAR model based on statistics developed by simulation plus,is widely used by the FDA,EMA,pharmaceutical companies,and academic institutions worldwide[18].Derek,developed by Lhasa UK,is based on knowledge rules,whereas Sarah is based on statistics[19-20].Although the results predicted by the Derek and Sarah indicated that Ace was not genotoxic,the ADMET prediction showed that the impurity had some of genotoxicity.To verify Ace′s toxicity,CHL cells were used for the chromosome aberration test.Ames test was also conducted to detect gene mutations.The chromosome aberration assay suggested that Ace was mutagenic because its aberrations rate was 7.00%and 7.67%at the dose of 40 μg per plate with and without S9 mix,respectively.However,there was no statistically significant increase in the number of reverting colonies at any concentrations in the Ames test.Through comprehensive analysis of the toxicity prediction results of Ace and the results ofin vitroexperiments,it was determined that Ace was capable of mutagenic chromosome aberration,and it should be controlled on the basis of the limit value of mutagenic toxic impurity for the safety of drug use.
For common impurities,the qualification limitis were less than 0.15%in the drug products[3-5].However,according to EMA guidelines for establishing a limit for GTIs,a limit value of TTC is 1.5 μg of GTIs per day,which is viewed as an acceptable risk for the most drugs,with the resulting risk of carcinogenesis less than one in a thou-sand in a lifetime.This approach is typically applied to mutagenic impurities present in pharmaceuticals used for a long-term treatment(more than 10 years)and where no carcinogenicity data is available for such drug(Classes 2 and 3)[3].According to the EMA and ICH M7 guidelines for the control of mutagenic toxic impurities[3,5],Ace is suspected of causing mutagenic aberrations in chromosomes.It is suggested that the amount of Ace in drugs be below 0.015%for individuals who will be receiving the drug for lifetime to ensure safety.In the course of research,the genotoxicity of naproxen impurities was evaluated,and the possibility of chromosomal aberrations was found in Ace.Therefore,the genotoxicity of Ace was confirmedin vitrotests to further control its content in naproxen.Our assessment and verification of Ace genotoxicity support the need to implement content limits of other impurities for which genotoxicity information is not available.For further exploration on chromosomal aberrations and changes in DNA structure caused by Ace,it is recommended that micronucleus test used to detect chromosome or mitotic organ damage can be applied to investigate chromosomal aberrationin vivo.

