基于状态观测器的多无人机编队跟踪控制
窦立谦,杨 闯,王丹丹,陈 涛,秦新立
Dou Liqian,Yang Chuang,Wang Dandan,Chen Tao,Qin Xinli
基于状态观测器的多无人机编队跟踪控制
窦立谦,杨 闯,王丹丹,陈 涛,秦新立
(天津大学电气自动化与信息工程学院,天津 300072)
针对一组欠驱动四旋翼无人机在编队飞行中仅有部分无人机可以直接获取领机状态信息的问题,提出了一种基于状态观测器的分布式有限时间编队跟踪控制策略.根据四旋翼无人机系统严格反馈的结构特点,将四旋翼无人机的动力学模型划分为位置子系统和姿态子系统,然后分别进行位置控制器和姿态控制器的设计.首先,考虑到在分布式的编队控制策略下,并非所有的无人机都能直接与领机进行通信并获取领机的状态信息.对每架四旋翼无人机分别设计分布式有限时间状态观测器估计自身与领机的相对状态信息,稳定性分析表明所设计的状态观测器的观测误差能够在有限时间内趋近于零;其次,在四旋翼无人机状态观测器观测结果的基础上设计了有限时间位置控制器,稳定性分析表明位置控制器能够在有限时间内实现对领机位置的稳定跟踪;然后根据位置环控制量解算出期望的姿态角,基于滑模控制方法设计了姿态控制器,稳定性分析表明各架无人机的姿态角能在有限时间内跟踪上期望的姿态角;最后,从仿真结果中能够看出所设计的状态观测器的观测误差能够在有限时间内趋近于零,即每架无人机的状态观测器能够在有限时间内观测到自身与领机的相对状态信息.从无人机飞行轨迹中能够看出各架无人机能够在有限时间内形成并保持期望的队形.
四旋翼无人机;编队跟踪控制;状态观测器;分布式;有限时间稳定
四旋翼无人机因其具有结构简单、机身质量轻、灵活性强而且能够垂直起降和定点悬停等优点,在环境监测、目标搜索、事故救援等领域得到广泛应用[1].多无人机编队通过多架无人机的协同飞行使系统的综合效能大大提高.随着任务日趋复杂,无人机数量逐渐增多,对编队控制提出更高的要求[2].无人机编队控制是多无人机协同控制的重要研究方向.无论在军事领域,还是在民用领域,多机编队都有巨大的应用前景,获得国内外学者广泛的关注.
四旋翼无人机是一个具有6自由度和4个控制输入的欠驱动系统,具有非线性、强耦合、多变量等特点,控制问题复杂.早期的编队控制主要采用集中式控制方法,其特点是精度高、便于控制,但要依赖于中央控制单元的计算能力和全局通信能力.
目前,应用比较成熟的多无人机编队控制方法主要有:leader-follower法[3]、基于行为法[4]和虚拟结构法[5].文献[6]提出了一种基于leader-follower法的编队控制算法.文献[7]研究了基于行为法的多无人机编队控制问题,但文中假设每架无人机之间可以相互通信以共享状态信息.文献[8]设计了一种小型四旋翼无人机群起飞后自主形成正多边形编队的分布式运动控制方法,在四旋翼无人机串级控制系统框架下,同时采用平均一致性算法和有领导一致性算法,但文中将四旋翼模型简化为一阶系统,控制误差较大.文献[9]设计了一种分布式协同控制算法,使用二阶四旋翼无人机模型,但是期望队形无法在有限时间内形成.
本文针对通信受限情况下,多机编队中领机参考状态不能被所有无人机直接获取的情况,设计了一种基于状态观测器的分布式有限时间编队控制策略.对每一架无人机设计状态观测器,可以在有限时间内观测自身与领机的状态差.利用状态观测器的观测值设计编队控制器实现有限时间内编队队形的形成与保持.通过稳定性分析来验证分布式有限时间控制器的有效性,并通过仿真来验证该控制策略的性能.
1 Quadrotor数学模型

图1 无人机结构和坐标系

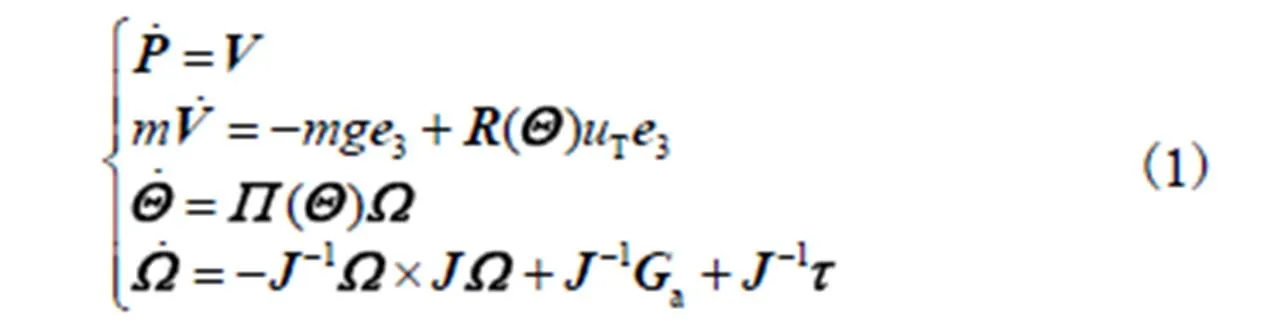



2 图论知识

3 编队控制目标
本文控制目标是为每一架无人机设计一种基于分布式有限时间状态观测器的编队跟踪控制器,使多架无人机形成并保持固定的编队队形飞行,具体为

4 有限时间编队控制器
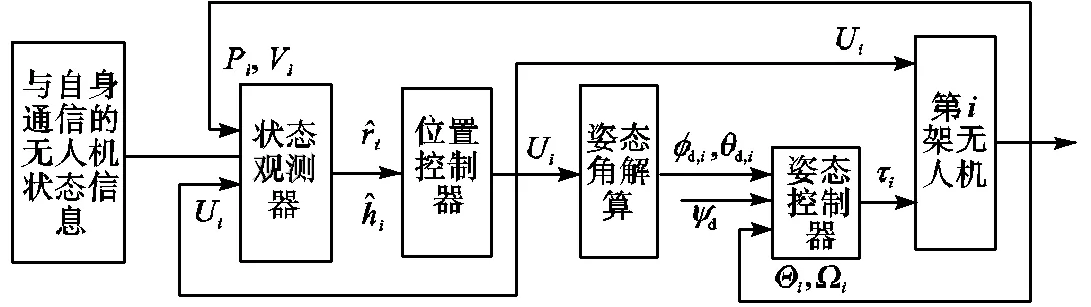
图2 第架四旋翼无人机控制结构
4.1 分布式有限时间观测器

把模型(1)中的位置子系统写成


其中
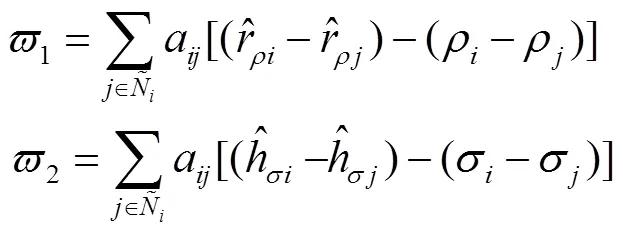

对时间求导得
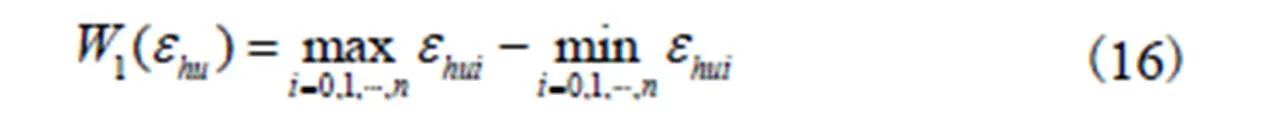




4.2 位置控制器
基于观测器的观测值,设计位置控制器的形式为


选择李雅普诺夫函数的形式为
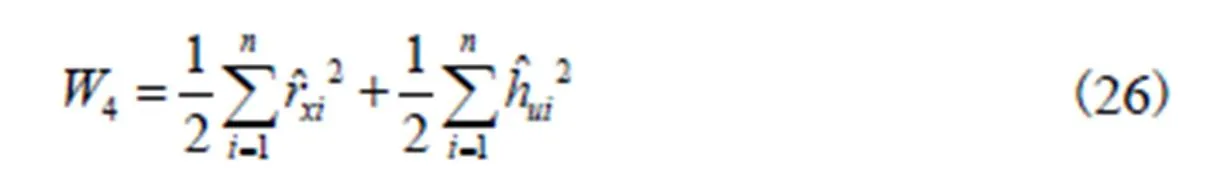


4.3 姿态控制器

期望偏航角为

旋翼提供的升力为

下面设计姿态跟踪控制器,定义姿态跟踪误差为

对其进行求导得

将模型(1)中的姿态子系统代入式(35)得

分两步证明系统(38)有限时间稳定,首先证明渐近稳定,选取李雅普诺夫函数的形式为




通过文献[15]中引理2.1可知系统(38)全局有限时间稳定.
5 系统仿真分析
为验证所提控制策略的正确性和有效性,以4架无人机组成编队并使编队中心沿着虚拟领机飞行进行仿真分析.图3给出了各无人机间的通信拓扑结构,其中0代表虚拟领机,1~4分别代表4架四旋翼从机.

图3 编队通信拓扑
无人机初始位置、速度及角速度参数如下:



图4 观测器状态值与每架无人机和领机速度差的差值曲线

图5 观测器状态值与每架无人机和领机位置差的差值曲线

图6 x-y平面及立体空间编队飞行轨迹
6 结 语
本文针对分布式下多架四旋翼无人机的编队控制问题,提出了一种基于状态观测器的分布式有限时间编队跟踪控制策略.分布式情况下,虚拟领机的状态信息只有部分从机可以直接获得.利用状态观测器来观测自身与领机的状态差,状态观测器能够在有限时间内估计出自身与领机的相对状态.根据观测器的观测结果设计的编队控制器,能够在有限时间内实现多架无人机形成并保持期望的队形.基于滑模方法设计的姿态控制器能够使无人机姿态在有限时间内跟踪上期望的姿态角.最后,仿真结果验证了所设计观测器的观测误差能够在有限时间内趋于零,所设计的控制器能够保证多架无人机快速形成并保持期望的编队队形.
[1] Kendoul F,Lara D,Fantoni I,et al. Nonlinear control for systems with bounded inputs:Real-time embedded control applied to UAVs[C]// IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. San Diego,CA,USA 2006:5888-5893.
[2] 宗 群,王丹丹,邵士凯,等. 多无人机协同编队飞行控制研究现状及发展[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报,2017,49(3):1-14. Zong Qun,Wang Dandan,Shao Shikai,et al. Research status and development of multi UAV coordinated formation flight control[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology,2017,49(3):1-14(in Chinese).
[3] Wang D,Zong Q,Tian B,et al. Neural network disturbance observer-based distributed finite-time formation tracking control for multiple unmanned helicopters[J]. ISA Transactions,2018,73:208-226.
[4] Turpin M,Michael N,Kumar V. Decentralized formation control with variable shapes for aerial robots[C]// IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Saint Paul,MN,USA,2012:23-30.
[5] Lalish E,Morgansen K A,Tsukamaki T. Formation tracking control using virtual structures and deconfliction[C]//IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. San Diego,CA,USA,2006:5699-5705.
[6] Gu Y,Seanor B,Campa G,et al. Design and flight testing evaluation of formation control laws[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology,2006,14(6):1105-1112.
[7] Kim S. Behavior-based decentralized control for multi-UAV formation flight[J]. Indian Journal of Genetics & Plant Breeding,2011,74(4):409-413.
[8] 邢关生,杜春燕,宗 群,等. 基于一致性的小型四旋翼机群自主编队分布式运动规划[J]. 控制与决策,2014,29(11):2081-2084.
Xing Guansheng,Du Chunyan,Zong Qun,et al. Consensus-based distributed motion planning for autonomous formation of miniature quadrotor groups[J]. Control and Decision,2014,29(11):2081-2084(in Chinese).
[9] Ghommam J,Luque-Vega L F,Castillo-Toledo B,et al. Three-dimensional distributed tracking control for multiple quadrotor helicopters[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute,2016,353(10):2344-2372.
[10] Zuo Z. Trajectory tracking control design with command-filtered compensation for a quadrotor[J]. IET Control Theory & Applications,2013,4(11):2343-2355.
[11] Andreasson M,Dimarogonas D V,Johansson K H. Undamped nonlinear consensus using integral Lyapunov functions[C]// IEEE American Control Conference. Montreal,QC,Canada,2012:6644-6649.
[12] Paden B E,Sastry S S. A calculus for computing Filippov’s differential inclusion with application to the variable structure control of robot manipulators[C]// IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. Athens,Greece,1987:578-582.
[13] Orlov Y. Finite time stability and robust control synthesis of uncertain switched systems[J]. SIAM Journal on Control & Optimization,2004,43(4):1253-1271.
[14] Khalil H K. Nonlinear Systems[M]. 3rd ed. Upper Saddle River,NJ:Prentice-Hall,Inc,2002.
[15] Du H,Zhu W,Wen G,et al. Finite-time formation control for a group of quadrotor aircraft[J]. Aerospace Science & Technology,2017,69:609-616.
State Observer-Based Formation Tracking Control for Multiple Quadrotors
Dou Liqian,Yang Chuang,Wang Dandan,Chen Tao,Qin Xinli
(School of Electrical and Information Engineering,Tianjin University,Tianjin 300072,China)
Abstract:A distributed finite-time formation tracking control strategy based on a state observer is proposed for a group of under-actuated quadrotors,where only a part of the quadrotors can directly obtain the state information of the leader quadrotor. According to the strict feedback architecture of the quadrotor system,the dynamic model of the quadrotor is divided into the position and attitude subsystems,from which the position and attitude controllers are designed,respectively. First,given that not all quadrotors can communicate with the leader and obtain its state information under the condition of using a distributed formation control strategy,the distributed finite-time state observer is designed for each quadrotor to estimate its relative state information and that of the leader quadrotor. The stability analysis shows that the error of the state observer can reach zero in finite time. Second,a finite-time position controller is designed based on the observed results of the state observer. The stability analysis shows that the position controller can achieve stable tracking of the position of the leader quadrotor in finite time. Based on this finding,the desired attitude angle can be calculated according to the values of the position controller,and the attitude controller can be designed using the sliding mode control method. The stability analysis shows that the desired attitude angle of each quadrotor can be tracked in finite time. Finally,the simulations results show that the error of the designed state observer can reach zero in finite time,indicating that the state observer of each quadrotor can obtain the relative state information between itself and the leader quadrotor in finite time. The flight trajectory of each quadrotor can be used to generate and maintain the desired formation in finite time.
quadrotor;formation tracking control;state observer;distributed;finite-time stable
TK448.21
A
0493-2137(2019)01-0090-08
2018-03-19;
2018-08-17.
窦立谦(1976— ),男,博士,副教授,douliqian@tju.edu.cn.
王丹丹,dandanwang0910@163.com.
国家自然科学基金资助项目(61873340,61773279).
the National Natural Science Foundation of China(No. 61873340,No. 61773279).
10.11784/tdxbz201803057
(责任编辑:孙立华)

