妊娠期糖尿病的相关危险因素分析及其对母婴结局的影响
陈淑杰
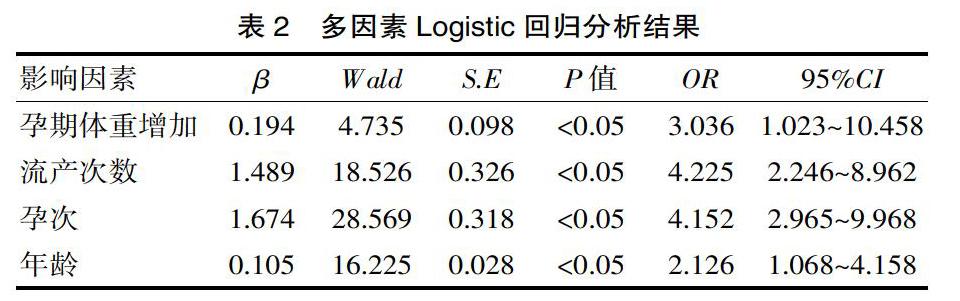
[摘要] 目的 分析妊娠期糖尿病的相关危险因素,同时探究其对母婴结局产生的影响。方法 选取2015年6月—2018年9月来该院诊治的120例妊娠期糖尿病产妇为研究对象,将其归为观察组,再选取同时期该院正常孕妇100例为对照组,对比两组产妇流产次数、孕次、产次、BMI(体重指数)等资料,探究妊娠期糖尿病的相关危险因素,同时探究其对母婴结局产生的影响。 结果 经多因素Logistic回归分析显示,妊娠期糖尿病的产科危险因素包括孕期体重增加、流产次数、孕次、年龄,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);与对照组对比,观察组妊娠高血压、剖宫产、产后出血、羊水过多、胎儿窘迫、早产儿、巨大儿发生率更高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。 结论 妊娠期糖尿病的危险因素多种多样,且会对母婴结局产生一定影响。
[关键词] 妊娠期糖尿病;危险因素;母婴结局;影响
[中图分类号] R714 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1672-4062(2019)05(b)-0023-03
[Abstract] Objective To analyze the risk factors of gestational diabetes mellitus and explore its influence on maternal and infant outcomes. Methods From June 2015 to September 2018, a total of 120 cases of gestational diabetes women diagnosed and treated in our hospital were selected as the research object, to be classified as observation group, then select our hospital from 100 cases of normal pregnant women at the same time as the control group. the maternal abortion frequency, pregnancy time, parity, BMI (body mass index) and other data were compared to explore the related risk factors of gestational diabetes, and to explore its impact in maternal and infant outcomes. Results Multivariate Logistic regression analysis showed that the obstetric risk factors of gestational diabetes included pregnancy weight gain, number of miscarriages, number of pregnancies and age, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Compared with the control group, the incidence of pregnancy hypertension, cesarean section, postpartum hemorrhage, hyperhydramnios, fetal distress, premature infants and macrosomia was higher in the observation group, with statistically significant differences (P<0.05). Conclusion The risk factors of gestational diabetes mellitus are varied and may affect maternal and infant outcomes.
[Key words] Gestational diabetes mellitus; Risk factors; Maternal and child outcomes; Impact
臨床上有研究显示,妊娠糖尿病的出现对母婴结局产生严重影响,可引发胎儿窘迫、巨大儿、妊娠期高血压以及流产等不良妊娠结局,严重情况下甚至会对患儿生命安全构成严重威胁[1-2]。该研究主要针对妊娠期糖尿病的相关危险因素进行探究,同时分析其对母婴结局产生的影响,现报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选取该院诊治的120例妊娠期糖尿病产妇为研究对象,将其归为观察组,纳入标准:①单胎妊娠;②确诊为妊娠期糖尿病;③自愿参与。排除标准:①中途退出;②产道异常;③合并克氏综合征、甲状腺功能减退以及甲状腺功能亢进等内分泌疾病;④人工授精;⑤吸烟;⑥有严重基础性疾病合并出现。产妇孕周32~41周,平均孕周(38.69±2.58)周。再选取同时期该院正常孕妇100例为对照组,孕周31~40周,平均孕周(38.05±2.46)周。研究通过伦理委员会的批准,对比两组基础资料,可比性显著,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。
1.2 方法
分析两组产妇流产次数、产次、孕次、年龄、孕前BMI(体重指数)、产前BMI、孕期体重增加情况等情况;对比两组产妇妊娠结局与新生儿结局。

