血栓弹力图在儿童脓毒症诊治中的临床疗效分析
刘斌 刘善利 崔伟华 赵令强 陈加峰
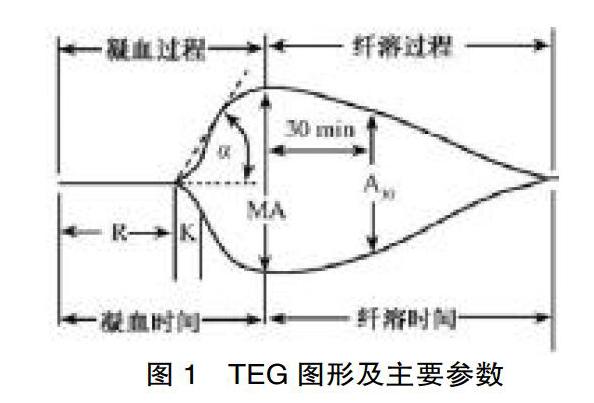

[摘要] 目的 分析血栓彈力图在儿童脓毒症诊治中的临床疗效。 方法 方便选取2017年6月—2018年6月期间该院收治的61例脓毒症患儿作为实验对象,依据结合显性DIC 评分结果将其分为试验1组(DIC评分≥5分,n=31)、试验2组(DIC评分<5分,n=30),同期选取30名健康体检者作为对照组,3组研究对象均开展常规凝血功能及TEG检测,对比分析3组研究对象的凝血功能指标、TEG指标及TEG指标诊断试验指标。 结果 凝血功能指标:对比试验2组和对照组,试验1组患儿的 PLT(86.25±42.56)×109/L降低,PT(17.54±3.72)s、APTT(40.25±7.42)s升高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);对比对照组,试验2组的PLT差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),PT、APTT、FBG升高(P<0.05)。TEG指标:对比对照组,试验1组患儿的R时间(7.45±1.62)min、K 时间(3.43±1.02)min升高,α角(3.41±1.02)°、MA值(54.58±6.43)mm及CI值(-2.56±1.93)降低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。对比对照组,试验2组患儿的K时间降低,α角、MA值及CI值升高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);TEG指标诊断试验指标的敏感度、特异度、阳性预测值及阴性预测值均较高。 结论 血栓弹力图可全面、准确地分析脓毒症患儿自身的凝血情况,同时与DIC评分具有明显的 相关性,血栓弹力图监测可对评价脓毒症患儿的严重程度、凝血状态, 血栓及出血的发生风险,进而指导临床展开治疗,临床借鉴价值高。
[关键词] 血栓弹力图;儿童脓毒症;诊治;临床疗效
[中图分类号] R720.597 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1674-0742(2019)05(c)-0021-03
[Abstract] Objective To analyze the clinical efficacy of thromboelastography in the diagnosis and treatment of children with sepsis. Methods 61 children with sepsis admitted to our hospital from June 2017 to June 2018 were convenient selected and enrolled in the study. According to the results of combined dominant DIC score, they were divided into test group 1 (DIC score ≥ 5 points, n= 31), test 2 group (DIC score <5 points, n=30), 30 healthy subjects were selected as the control group in the same period, and the three groups of subjects all performed routine coagulation function and TEG test, and compared the blood coagulation of the three groups. Functional indicators, TEG indicators and TEG indicators diagnostic test indicators were compared. Results Coagulation function index: in the comparison of test group 2 and the control group, the PLT (86.25±42.56)×109/L decreased, and the PT (17.54±3.72)s and APTT (40.25±7.42)s increased. Statistically significant (P<0.05); compared with the control group, there was no significant difference in PLT between the two groups(P>0.05), PT, APTT, FBG increased(P<0.05). TEG index: Compared with the control group, the R time(7.45±1.62) min, K time (3.43±1.02) min, and α angle (3.41±1.02)° were increased in the test group. The MA value (54.58±6.43) mm and the CI value (-2.56±1.93) decreased, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Compared with the control group, the K time of the two groups decreased, the angles of α, MA and CI increased, the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05); the sensitivity, specificity and positive prediction of the diagnostic indicators of TEG index value and the negative predictive value are higher. Conclusion The thromboelastogram can comprehensively and accurately analyze the coagulation status of children with sepsis and has a significant correlation with the DIC score. The thromboelastogram monitoring can evaluate the severity of the children with sepsis, coagulation status, and thrombosis. And the risk of bleeding, and then guide the clinical treatment, the clinical reference value is high.

